Spring注解版学习笔记——组件赋值,组件注入
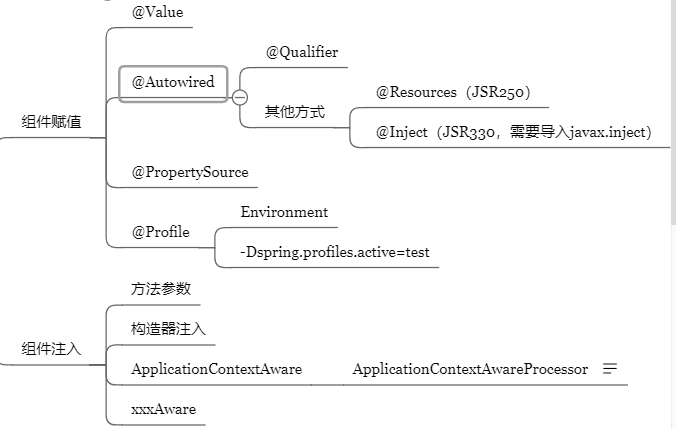
1、@Value
使用@Value赋值;
- 基本数值
- 可以写SpEL; #{}
- 可以写${};取出配置文件【properties】中的值(在运行环境变量里面的值)
1 public class Person { 2 3 4 @Value("张三") 5 private String name; 6 @Value("#{20-2}") 7 private Integer age; 8 9 @Value("${person.nickName}") 10 private String nickName; 11 12 /** 13 * 设置默认值 14 */ 15 @Value("${person.sex:man}") 16 private String sex; 17 18 /** 19 * 构造函数上使用 20 */ 21 public Person(@Value("${Person.area:jianhu}")String area){ 22 ... 23 } 24 }
2、@Autowired、@Resource、@Inject
@Autowired:自动注入:
- 默认优先按照类型去容器中找对应的组件:applicationContext.getBean(BookDao.class);找到就赋值
- 如果找到多个相同类型的组件,再将属性的名称作为组件的id去容器中查找 applicationContext.getBean("bookDao")
- @Qualifier("bookDao"):使用@Qualifier指定需要装配的组件的id,而不是使用属性名
- 自动装配默认一定要将属性赋值好,没有就会报错;可以使用@Autowired(required=false);
- @Primary:让Spring进行自动装配的时候,默认使用首选的bean;也可以继续使用@Qualifier指定需要装配的bean的名字
Spring还支持使用@Resource(JSR250)和@Inject(JSR330)[java规范的注解]
@Resource:
可以和@Autowired一样实现自动装配功能;默认是按照组件名称进行装配的;
没有能支持@Primary功能没有支持@Autowired(reqiured=false);
@Inject:
需要导入javax.inject的包,和Autowired的功能一样。没有required=false的功能;
@Autowired:Spring定义的; @Resource、@Inject都是java规范
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:解析完成自动装配功能; 可以看到 xxxBeanPostProcessor 一般是 BeanPostProcessor(Bean的后置处理器)的实现类

1 public interface BeanPostProcessor { 2 3 /** 4 * Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean 5 * initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet} 6 * or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values. 7 * The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original. 8 * <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is. 9 * @param bean the new bean instance 10 * @param beanName the name of the bean 11 * @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one; 12 * if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked 13 * @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors 14 * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet 15 */ 16 @Nullable 17 default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 18 return bean; 19 } 20 21 /** 22 * Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean 23 * initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet} 24 * or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values. 25 * The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original. 26 * <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean 27 * instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The 28 * post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created 29 * objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks. 30 * <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a 31 * {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method, 32 * in contrast to all other {@code BeanPostProcessor} callbacks. 33 * <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is. 34 * @param bean the new bean instance 35 * @param beanName the name of the bean 36 * @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one; 37 * if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked 38 * @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors 39 * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet 40 * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean 41 */ 42 @Nullable 43 default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { 44 return bean; 45 } 46 47 }
@Autowired:构造器,参数,方法,属性;都是从容器中获取参数组件的值
- [标注在方法位置]:@Bean+方法参数;参数从容器中获取;默认不写@Autowired效果是一样的;都能自动装配
- [标在构造器上]:如果组件只有一个有参构造器,这个有参构造器的@Autowired可以省略,参数位置的组件还是可以自动从容器中获取
- 放在参数位置
3、@PropertySource
使用@PropertySource读取外部配置文件中的k/v保存到运行的环境变量中;加载完外部的配置文件以后使用${}取出配置文件的值
1 @PropertySource(value={"classpath:/person.properties"}) 2 @Configuration 3 public class MainConfigOfPropertyValues { 4 5 @Bean 6 public Person person(){ 7 return new Person(); 8 } 9 10 }
@PropertySource 默认无法加载yml文件
如果需要实现加载yml文件,参考: https://juejin.im/post/5c4aea2e51882522c03ea475
4、@Profile
Profile:Spring为我们提供的可以根据当前环境,动态的激活和切换一系列组件的功能;
@Profile:指定组件在哪个环境的情况下才能被注册到容器中,不指定,任何环境下都能注册这个组件
- 加了环境标识的bean,只有这个环境被激活的时候才能注册到容器中。默认是default环境
- 写在配置类上,只有是指定的环境的时候,整个配置类里面的所有配置才能开始生效
- 没有标注环境标识的bean在,任何环境下都是加载的;

1 @PropertySource("classpath:/dbconfig.properties") 2 @Configuration 3 public class MainConfigOfProfile implements EmbeddedValueResolverAware{ 4 5 @Value("${db.user}") 6 private String user; 7 8 private StringValueResolver valueResolver; 9 10 private String driverClass; 11 12 13 @Bean 14 public Yellow yellow(){ 15 return new Yellow(); 16 } 17 18 @Profile("test") 19 @Bean("testDataSource") 20 public DataSource dataSourceTest(@Value("${db.password}")String pwd) throws Exception{ 21 ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); 22 dataSource.setUser(user); 23 dataSource.setPassword(pwd); 24 dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"); 25 dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass); 26 return dataSource; 27 } 28 29 30 @Profile("dev") 31 @Bean("devDataSource") 32 public DataSource dataSourceDev(@Value("${db.password}")String pwd) throws Exception{ 33 ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); 34 dataSource.setUser(user); 35 dataSource.setPassword(pwd); 36 dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_crud"); 37 dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass); 38 return dataSource; 39 } 40 41 @Profile("prod") 42 @Bean("prodDataSource") 43 public DataSource dataSourceProd(@Value("${db.password}")String pwd) throws Exception{ 44 ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource(); 45 dataSource.setUser(user); 46 dataSource.setPassword(pwd); 47 dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/scw_0515"); 48 49 dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass); 50 return dataSource; 51 } 52 53 @Override 54 public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver) { 55 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 56 this.valueResolver = resolver; 57 driverClass = valueResolver.resolveStringValue("${db.driverClass}"); 58 } 59 60 }
如何指定对应环境:
- 使用命令行动态参数: 在虚拟机参数位置加载 -Dspring.profiles.active=test
- 代码的方式激活某种环境;

1 @Test 2 public void test01(){ 3 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = 4 new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); 5 //1、创建一个applicationContext 6 //2、设置需要激活的环境 7 applicationContext.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("dev"); 8 //3、注册主配置类 9 applicationContext.register(MainConfigOfProfile.class); 10 //4、启动刷新容器 11 applicationContext.refresh(); 12 13 14 String[] namesForType = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(DataSource.class); 15 for (String string : namesForType) { 16 System.out.println(string); 17 } 18 19 Yellow bean = applicationContext.getBean(Yellow.class); 20 System.out.println(bean); 21 applicationContext.close(); 22 }


