实验4
task1
(1)

1 #pragma once 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <array> 4 #include <string> 5 class GradeCalc { 6 public: 7 GradeCalc(const std::string &cname); 8 void input(int n); // 录入n个成绩 9 void output() const; // 输出成绩 10 void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序) 11 int min() const; // 返回最低分(如成绩未录入,返回-1) 12 int max() const; // 返回最高分 (如成绩未录入,返回-1) 13 double average() const; // 返回平均分 (如成绩未录入,返回0.0) 14 void info(); // 输出课程成绩信息 15 private: 16 void compute(); // 成绩统计 17 private: 18 std::string course_name; // 课程名 19 std::vector<int> grades; // 课程成绩 20 std::array<int, 5> counts; // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80, 90), [90, 100] 21 std::array<double, 5> rates; // 保存各分数段人数占比 22 bool is_dirty; // 脏标记,记录是否成绩信息有变更 23 };

1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <array> 3 #include <cstdlib> 4 #include <iomanip> 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <numeric> 7 #include <string> 8 #include <vector> 9 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 10 GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const std::string &cname):course_name{cname},is_dirty{true} { 11 counts.fill(0); 12 rates.fill(0); 13 } 14 void GradeCalc::input(int n) { 15 if(n < 0) { 16 std::cerr << "无效输入! 人数不能为负数\n"; 17 std::exit(1); 18 } 19 20 grades.reserve(n); 21 int grade; 22 for(int i = 0; i < n;) { 23 std::cin >> grade; 24 if(grade < 0 || grade > 100) { 25 std::cerr << "无效输入! 分数须在[0,100]\n"; 26 continue; 27 } 28 29 grades.push_back(grade); 30 ++i; 31 } 32 is_dirty = true; // 设置脏标记:成绩信息有变更 33 } 34 void GradeCalc::output() const { 35 for(auto grade: grades) 36 std::cout << grade << ' '; 37 std::cout << std::endl; 38 } 39 40 void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) { 41 if(ascending) 42 std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end()); 43 else 44 std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end(), std::greater<int>()); 45 } 46 int GradeCalc::min() const { 47 if(grades.empty()) 48 return -1; 49 auto it = std::min_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); 50 return *it; 51 } 52 int GradeCalc::max() const { 53 if(grades.empty()) 54 return -1; 55 auto it = std::max_element(grades.begin(), grades.end()); 56 return *it; 57 } 58 double GradeCalc::average() const { 59 if(grades.empty()) 60 return 0.0; 61 double avg = std::accumulate(grades.begin(), grades.end(), 0.0)/grades.size(); 62 return avg; 63 } 64 void GradeCalc::info() { 65 if(is_dirty) 66 compute(); 67 std::cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << std::endl; 68 std::cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << 69 std::endl; 70 std::cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << std::endl; 71 std::cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << std::endl; 72 const std::array<std::string, 5> grade_range{"[0, 60) ", 73 "[60, 70)", 74 "[70, 80)", 75 "[80, 90)", 76 "[90, 100]"}; 77 78 for(int i = grade_range.size()-1; i >= 0; --i) 79 std::cout << grade_range[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t" 80 << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i]*100 << "%\n"; 81 } 82 void GradeCalc::compute() { 83 if(grades.empty()) 84 return; 85 counts.fill(0); 86 rates.fill(0.0); 87 // 统计各分数段人数 88 for(auto grade:grades) { 89 if(grade < 60) 90 ++counts[0]; // [0, 60) 91 else if (grade < 70) 92 ++counts[1]; // [60, 70) 93 else if (grade < 80) 94 ++counts[2]; // [70, 80) 95 else if (grade < 90) 96 ++counts[3]; // [80, 90) 97 else 98 ++counts[4]; // [90, 100] 99 } 100 // 统计各分数段比例 101 for(int i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i) 102 rates[i] = counts[i] * 1.0 / grades.size(); 103 104 is_dirty = false; // 更新脏标记 105 }

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 4 void test() { 5 GradeCalc c1("OOP"); 6 std::cout << "录入成绩:\n"; 7 c1.input(5); 8 std::cout << "输出成绩:\n"; 9 c1.output(); 10 std::cout << "排序后成绩:\n"; 11 c1.sort(); c1.output(); 12 std::cout << "*************成绩统计信息*************\n"; 13 c1.info(); 14 } 15 16 int main() { 17 test(); 18 }
(2)运行结果
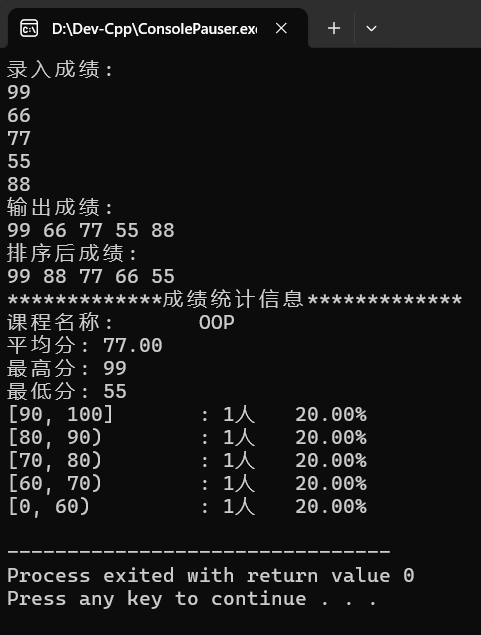
(3)回答问题
① std::string course_name;创建一个字符串course_name。
std::vector<int> grades;创建一个int类型的数组grades。
std::array<int, 5> counts;创建一个int类型且长度为5的数组counts,数组长度不可变
std::array<double, 5> rates;创建一个double类型且长度为5的数组rates,数组长度不可变
②不合法。因为Gradecalc类中未构造push_back函数。
③1)compute会被调用3次,is_dirty的作用是判断是否需要重新统计分数段人数和各分数段比例。
2)要调用位置。要先用update_grade函数修改数据,再调用compute函数。
④在sort函数中加。代码如下:
int j;
if(grades.size()%2==0)
j=grades.size()/2-1;
else
j=grades.size()/2;
std::cout<<"中位数:"<<grades[j]<<std::endl;
⑤不能去掉。当成绩被修改或重新录入时。
⑥1)没有影响。
2)去掉reserve(n)会导致vector在录入成绩过程中发生多次内存重分配和数据拷贝,降低性能。
task2
(1)

1 #pragma once 2 #include <vector> 3 #include <array> 4 #include <string> 5 class GradeCalc: private std::vector<int> { 6 public: 7 GradeCalc(const std::string &cname); 8 void input(int n); // 录入n个成绩 9 void output() const; // 输出成绩 10 void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序) 11 int min() const; // 返回最低分(如成绩未录入,返回-1) 12 int max() const; // 返回最高分 (如成绩未录入,返回-1) 13 double average() const; // 返回平均分 (如成绩未录入,返回0.0) 14 void info(); 15 // 输出课程成绩信息 16 private: 17 void compute(); 18 // 成绩统计 19 private: 20 std::string course_name; // 课程名 21 std::vector<int> grades; // 课程成绩 22 std::array<int, 5> counts; // 保存各分数段人数([0, 60), [60, 70), [70, 80), [80, 90), [90, 100] 23 std::array<double, 5> rates; // 保存各分数段人数占比 24 bool is_dirty; // 脏标记,记录是否成绩信息有变更 25 };
 Gradecalc.cpp
Gradecalc.cpp
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include "GradeCalc.hpp" 4 void test() { 5 GradeCalc c1("OOP"); 6 std::cout << "录入成绩:\n"; 7 c1.input(5); 8 std::cout << "输出成绩:\n"; 9 c1.output(); 10 std::cout << "排序后成绩:\n"; 11 c1.sort(); c1.output(); 12 std::cout << "*************成绩统计信息*************\n"; 13 c1.info(); 14 15 } 16 17 int main() { 18 test(); 19 }
(2)运行结果
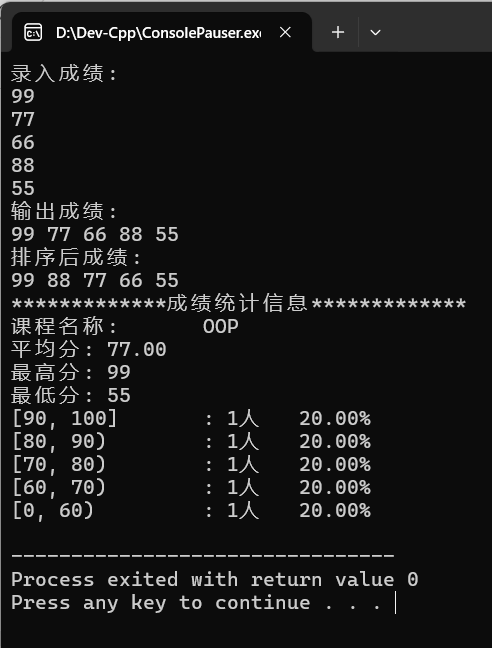
(3)回答问题
①class GradeCalc: private std::vector<int>{}
②不会。
不合法,因为私有继承不能在外部使用。
③组合方式只能通过明确的公有接口访问,而继承方式在类内部可以直接使用基类接口。
④组合方式更适合,因为有更好的封装性。
task3
(1)

1 #pragma once 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 5 enum class GraphType {circle, triangle, rectangle}; 6 7 // Graph类定义 8 class Graph { 9 public: 10 virtual void draw() {} 11 virtual ~Graph() = default; 12 }; 13 // Circle类声明 14 class Circle : public Graph { 15 public: 16 void draw(); 17 }; 18 // Triangle类声明 19 class Triangle : public Graph { 20 public: 21 void draw(); 22 }; 23 // Rectangle类声明 24 class Rectangle : public Graph { 25 public: 26 void draw(); 27 }; 28 // Canvas类声明 29 class Canvas { 30 public: 31 void add(const std::string& type); // 根据字符串添加图形 32 void paint() const; 33 ~Canvas(); 34 private: 35 std::vector<Graph*> graphs; 36 }; 37 // 使用统一接口绘制所有图形 38 // 手动释放资源 39 // 4. 工具函数 40 GraphType str_to_GraphType(const std::string& s); // 字符串转枚举类型 41 Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type); // 创建图形,返回堆对象指针

1 #include <algorithm> 2 #include <cctype> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <string> 5 #include "Graph.hpp" 6 // Circle类实现 7 void Circle::draw() 8 { std::cout << "draw a circle...\n"; } 9 // Triangle类实现 10 void Triangle::draw() { std::cout << "draw a triangle...\n"; } 11 // Rectangle类实现 12 void Rectangle::draw() { std::cout << "draw a rectangle...\n"; } 13 // Canvas类实现 14 void Canvas::add(const std::string& type) { 15 Graph* g = make_graph(type); 16 if (g) 17 graphs.push_back(g); 18 } 19 void Canvas::paint() const { 20 for (Graph* g : graphs) 21 g->draw(); 22 } 23 Canvas::~Canvas() { 24 for (Graph* g : graphs) 25 delete g; 26 } 27 // 工具函数实现 28 // 字符串 → 枚举转换 29 GraphType str_to_GraphType(const std::string& s) { 30 std::string t = s; 31 std::transform(s.begin(), s.end(), t.begin(), 32 [](unsigned char c) { return std::tolower(c);}); 33 if (t == "circle") 34 return GraphType::circle; 35 if (t == "triangle") 36 return GraphType::triangle; 37 if (t == "rectangle") 38 return GraphType::rectangle; 39 return GraphType::circle; // 缺省返回 40 } 41 // 创建图形,返回堆对象指针 42 Graph* make_graph(const std::string& type) { 43 switch (str_to_GraphType(type)) { 44 case GraphType::circle: return new Circle; 45 case GraphType::triangle: return new Triangle; 46 case GraphType::rectangle: return new Rectangle; 47 default: return nullptr; 48 } 49 }

1 #include <string> 2 #include "Graph.hpp" 3 void test() { 4 Canvas canvas; 5 canvas.add("circle"); 6 canvas.add("triangle"); 7 canvas.add("rectangle"); 8 canvas.paint(); 9 } 10 int main() { 11 test(); 12 }
(2)运行结果
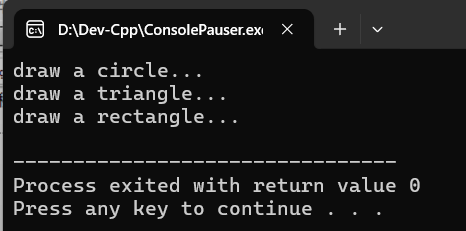
(3)回答问题
①组合: std::vector<Graph*> graphs;
存储和管理所有图形对象的指针。
继承:class Circle : public Graph {
class Triangle : public Graph{
class Rectangle : public Graph {
②1)失去多态性。
2)无法正确调用派生类的draw方法。
3)会导致内存泄漏。
③要在Graph.hpp中的enum中加入star枚举值,添加class Star:public Graph类声明。
在Graph.cpp中添加实现Star::draw();方法,在str_to_GraphType函数中添加字符串“Star”的判断,在make_graph函数中添加case分支。
④1)在Canvas::~Canvas()中通过delete逐个释放。
2)利:简单直接。弊:容易内存泄漏。
task4
(1)

1 #pragma once 2 #include <string> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include<memory> 6 7 class Toy{ 8 public: 9 Toy(const std::string& name,const std::string& type,float price); 10 virtual ~Toy()=default; 11 12 virtual void specialAbility() const=0; 13 virtual void interact()const; 14 15 void display()const; 16 void setBatteryLevel(int level); 17 void playSound(const std::string& sound)const; 18 19 std::string getName()const{return name_;} 20 std::string getType()const{return type_;} 21 float getPrice()const{return price_;} 22 int getBatteryLevel()const{return level_;} 23 24 protected: 25 std::string name_; 26 std::string type_; 27 float price_; 28 int level_; 29 bool is_electronic_; 30 }; 31 32 class TalkingRobot:public Toy{ 33 public: 34 TalkingRobot(const std::string& name,float price); 35 void specialAbility()const override; 36 void interact()const override; 37 38 private: 39 std::vector<std::string>phrases_; 40 }; 41 42 class GlowingBall:public Toy{ 43 public: 44 GlowingBall(const std::string& name,float price); 45 void specialAbility()const override; 46 void setLightColor(const std::string& color); 47 48 private: 49 std::string color_; 50 }; 51 52 class DancingGirl:public Toy{ 53 public: 54 DancingGirl(const std::string& name,float price); 55 void specialAbility()const override; 56 void interact()const override; 57 void setMove(const std::string& move); 58 59 private: 60 std::string move_; 61 };

1 #include"Toy.hpp" 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstdlib> 4 Toy::Toy(const std::string& name, const std::string& type, float price) 5 : name_(name), type_(type), price_(price),level_(100), is_electronic_(true) {} 6 7 void Toy::interact() const { 8 std::cout << name_ << " is being interacted with!" << std::endl; 9 } 10 11 void Toy::display() const { 12 std::cout << "Name: " << name_ 13 << " | Type: " << type_ 14 << " | Price: $" << price_ 15 << " | Battery: " << level_ << "%" << std::endl; 16 } 17 void Toy::setBatteryLevel(int level) { 18 level_ = level; 19 std::cout << name_ << " battery level set to " << level << "%" << std::endl; 20 } 21 void Toy::playSound(const std::string& sound) const { 22 std::cout << name_ << " plays: \"" << sound << "\"" << std::endl; 23 } 24 TalkingRobot::TalkingRobot(const std::string& name, float price) 25 : Toy(name, "Talking Robot", price) { 26 phrases_ = {"Hello!", "I love you!", "Time for hug!", "You're my best friend!"}; 27 } 28 void TalkingRobot::specialAbility() const { 29 std::cout << name_ << " says: \"" << phrases_[rand() % phrases_.size()] << "\"" << std::endl; 30 } 31 void TalkingRobot::interact() const { 32 std::cout << name_ << " gives you a warm hug and says: "; 33 specialAbility(); 34 } 35 GlowingBall::GlowingBall(const std::string& name, float price) 36 : Toy(name, "Glowing Unicorn", price), color_("rainbow") {} 37 38 void GlowingBall::specialAbility() const { 39 std::cout << name_ << " glows with beautiful " <<color_ << " colors!" << std::endl; 40 } 41 42 void GlowingBall::setLightColor(const std::string& color) { 43 color_ = color; 44 std::cout << name_ << " light color changed to " << color << std::endl; 45 } 46 47 48 DancingGirl::DancingGirl(const std::string& name, float price) 49 : Toy(name, "Dancing Panda", price), move_("disco") {} 50 51 void DancingGirl::specialAbility() const { 52 std::cout << name_ << " dances in " << move_ << " mode!" << std::endl; 53 } 54 55 void DancingGirl::interact() const { 56 std::cout << name_ << " starts moving to the beat: "; 57 specialAbility(); 58 } 59 60 void DancingGirl::setMove(const std::string& move) { 61 move_ = move; 62 std::cout << name_ << " dance move set to " << move << std::endl; 63 }

1 #pragma once 2 #include"Toy.hpp" 3 #include<vector> 4 #include<memory> 5 6 class ToyFactory{ 7 public: 8 ToyFactory(); 9 10 void addToy(std::unique_ptr<Toy> toy); 11 void displayAllToys()const; 12 void demonstrateAllAbility()const; 13 void selectToyName(const std::string& name)const; 14 15 void createTalkingRobot(const std::string &name,float price); 16 void createGlowingBall(const std::string &name,float price); 17 void createDancingGirl(const std::string &name,float price); 18 19 private: 20 std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Toy>> toys_; 21 };

1 #include "ToyFactory.hpp" 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include<memory> 4 5 ToyFactory::ToyFactory() = default; 6 7 void ToyFactory::addToy(std::unique_ptr<Toy> toy) { 8 toys_.push_back(std::move(toy)); 9 std::cout << "Toy added to factory!" << std::endl; 10 } 11 12 void ToyFactory::displayAllToys() const { 13 std::cout << "\n=== All Toys in Factory ===" << std::endl; 14 for (const auto& toy : toys_) { 15 toy->display(); 16 } 17 } 18 19 void ToyFactory::demonstrateAllAbility() const { 20 std::cout << "\n=== Demonstrating All Special Abilities ===" << std::endl; 21 for (const auto& toy : toys_) { 22 std::cout << ">>> "; 23 toy->specialAbility(); 24 } 25 } 26 27 void ToyFactory::selectToyName(const std::string& name) const { 28 auto it = std::find_if(toys_.begin(), toys_.end(), 29 [&](const std::unique_ptr<Toy>&toy) { return toy->getName() == name; }); 30 31 if (it != toys_.end()) { 32 std::cout << "Found toy: "; 33 (*it)->display(); 34 std::cout << "Special ability: "; 35 (*it)->specialAbility(); 36 } else { 37 std::cout << "Toy '" << name << "' not found!" << std::endl; 38 } 39 } 40 41 void ToyFactory::createTalkingRobot(const std::string& name, float price) { 42 toys_.push_back(std::unique_ptr<Toy>(new TalkingRobot(name,price))); 43 std::cout<<"Toy added to factory!"<<std::endl; 44 } 45 46 void ToyFactory::createGlowingBall(const std::string &name, float price) { 47 toys_.push_back(std::unique_ptr<Toy>(new GlowingBall(name,price))); 48 std::cout<<"Toy added to factory!"<<std::endl; 49 } 50 51 void ToyFactory::createDancingGirl(const std::string& name, float price) { 52 toys_.push_back(std::unique_ptr<Toy>(new DancingGirl(name,price))); 53 std::cout<<"Toy added to factory!"<<std::endl; 54 }

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include"ToyFactory.hpp" 3 void testToySystem() { 4 ToyFactory factory; 5 6 std::cout << "=== Creating Electronic Plush Toys ===" << std::endl; 7 8 // 创建各种玩具 9 factory.createTalkingRobot("Robot1", 129.99); 10 factory.createGlowingBall("ball1", 19.99); 11 factory.createDancingGirl("girl1", 34.99); 12 factory.createTalkingRobot("Robot2", 159.99); 13 14 // 显示所有玩具信息 15 factory.displayAllToys(); 16 17 // 演示所有特异功能 18 factory.demonstrateAllAbility(); 19 20 // 交互测试 21 std::cout << "\n=== Interaction Test ===" << std::endl; 22 factory.selectToyName("Robot1"); 23 factory.selectToyName("ball1"); 24 25 // 测试不存在的玩具 26 factory.selectToyName("Unknown Toy"); 27 } 28 29 int main() { 30 testToySystem(); 31 return 0; 32 }
(2)运行结果
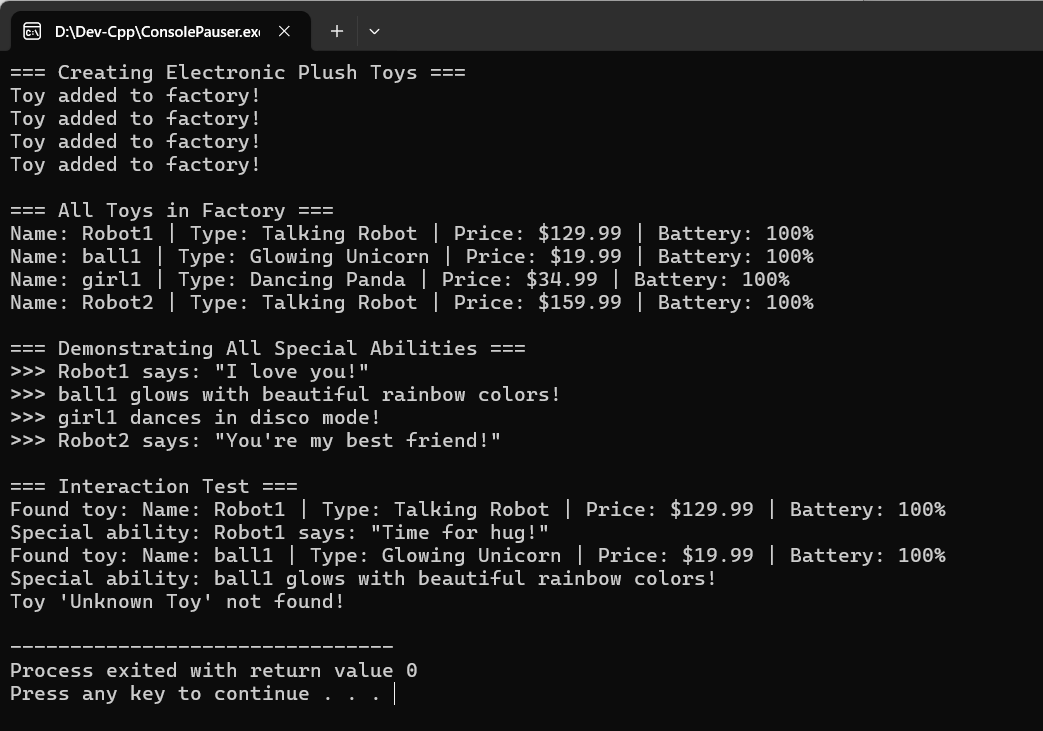





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号