index only scan是否回表?VS mysql 的回表实现
PG—index_only_scan
结论
- 执行计划 Index Only Scan 并不是表示不回表
- 先检查vm文件,如果没有做过vacuum没有vm文件,可能会更慢
- 因为索引是按顺序存储的,只需访问一个索引块就可以得到min(),max(),所以效率很高
postgres=# explain (analyze,buffers,costs off) select a from t1 where b = 5;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Scan using i1 on t1 (actual time=0.066..0.068 rows=1 loops=1)
Index Cond: (b = 5)
Buffers: shared hit=1 read=3
Planning Time: 0.773 ms
Execution Time: 0.128 ms
(5 rows)
从执行计划就可以看到,使用了索引,但是postgresql仍然需要访问表获取列a的值。我们还可以创建一个索引,包含我们需要的所有列:但是仍然有一个Heap Fetches:1
postgres=# create index i2 on t1(b,a);
CREATE INDEX
postgres=# explain (analyze,buffers,costs off) select a from t1 where b = 5;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Only Scan using i2 on t1 (actual time=0.346..0.353 rows=1 loops=1)
Index Cond: (b = 5)
Heap Fetches: 1
Buffers: shared hit=1 read=3
Planning Time: 0.402 ms
Execution Time: 0.401 ms
(6 rows)
这个表有个free space map文件,但是还没有visibility map文件。没有visibility map,postgresql就不知道是否所有的行对当前事务都是可见的,因此需要去访问表获取数据。当创建了visibility map之后:Heap Fetches:0
说明没有从表获取数据,真正做到了仅索引扫描
postgres=# vacuum t1;
VACUUM
postgres=# explain (analyze,buffers,costs off) select a from t1 where b = 5;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Only Scan using i2 on t1 (actual time=0.044..0.045 rows=1 loops=1)
Index Cond: (b = 5)
Heap Fetches: 0
Buffers: shared hit=4
Planning Time: 0.230 ms
Execution Time: 0.102 ms
(6 rows)
查看行的物理位置,以及block中的行是否对事务可见
postgres=# select ctid,* from t1 where b=5;
ctid | a | b | c
-------+---+---+---
(0,5) | 5 | 5 | 5
(1 row)
可以看到,行位于block 0,且是第五行。我们来看看block中的行是否对所有事务都可见:
postgres=# create extension pg_visibility;
CREATE EXTENSION
postgres=# select pg_visibility_map('t1'::regclass, 0);
pg_visibility_map
-------------------
(t,f)
(1 row)
mysql—回表
例子1
先索引扫描,再通过ID去取索引中未能提供的数据,即为回表。
mysql> create table T(
id int primary key,
k int not null,
name varchar(16),
index (k))engine=InnoDB;
如果语句是 select * from T where ID=500,即主键查询方式,则只需要搜索 ID 这棵 B+ 树;
mysql> select * from T where ID=500;
+-----+---+-------+
| id | k | name |
+-----+---+-------+
| 500 | 5 | name5 |
+-----+---+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
如果语句是 select * from T where k=5,即普通索引查询方式,则需要先搜索 k 索引树,得到 ID 的值为 500,再到 ID 索引树搜索一次。这个过程称为回表。
mysql> select * from T where k=5;
+-----+---+-------+
| id | k | name |
+-----+---+-------+
| 500 | 5 | name5 |
+-----+---+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
也就是说,基于非主键索引的查询需要多扫描一棵索引树。因此,我们在应用中应该尽量使用主键查询
例子2(直观)
-
建表:
id为PK,聚集索引,叶子节点存储行记录;name为KEY,普通索引,叶子节点存储PK值,即id;
t(id PK, name KEY, sex, flag); -
表中有四条记录:
1, shenjian, m, A
3, zhangsan, m, A
5, lisi, m, A
9, wangwu, f, B
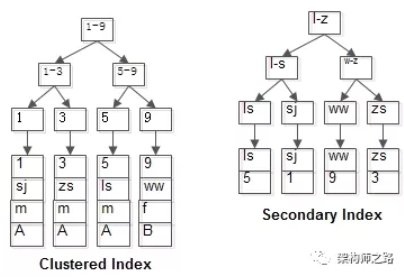
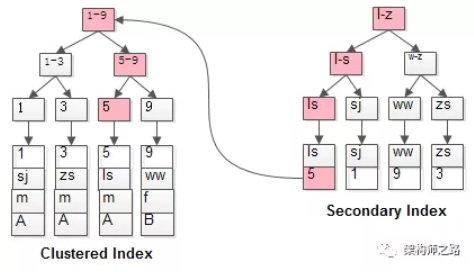
- 普通索引的查询过程通常情况下,需要扫码两遍索引树。
select * from t where name=‘lisi’;
select id,name from user where name=‘shenjian’;
能够命中name索引,索引叶子节点存储了主键id,通过name的索引树即可获取id和name,无需回表,符合索引覆盖,效率较高。
select id,name,sex from user where name=‘shenjian’;
能够命中name索引,索引叶子节点存储了主键id,但sex字段必须回表查询才能获取到需要再次通过id值扫码聚集索引获取sex字段,效率会降低。
- 重新建联合索引
create table user (
id int primary key,
name varchar(20),
sex varchar(5),
index(name, sex)
)engine=innodb;
就都能够命中索引覆盖,无需回表了。
优化思路
- count(index)
- 取多值的SQL,将单列索引升级为联合索引
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/abclife/p/13906623.html
https://blog.csdn.net/csdn_kou/article/details/87622921
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_36114091/article/details/113337533?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2~default~baidujs_baidulandingword~default-0.base&spm=1001.2101.3001.4242
本文来自博客园,作者:{dyy},转载请注明原文链接:{https://www.cnblogs.com/ddlearning/}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号