Spring BeanPostProcessor接口
[[Spring IOC 源码学习总笔记]]
BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor是 Spring 框架提供的一个扩展点接口,它允许开发者在 Spring 容器完成 Bean 的实例化、依赖注入之后,在初始化阶段的前后“拦截”并自定义 Bean 的逻辑。
package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>before</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
*
*这个是在 Bean 实例化并且填充属性之后调用, 但是 Bean 中一些生命周期方法如 InitializingBean 接口的
* afterPropertiesSet 方法、自定义的 init-method 方法等都尚未执行,在这些方法执行之前触发 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法。
*
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
/**
* Apply this {@code BeanPostProcessor} to the given new bean instance <i>after</i> any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet}
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* <p>In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding {@code bean instanceof FactoryBean} checks.
* <p>This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other {@code BeanPostProcessor} callbacks.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
*
* 在 InitializingBean 接口的 afterPropertiesSet 和自定义的 init-method 之后触发该方法。
*
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one;
* if {@code null}, no subsequent BeanPostProcessors will be invoked
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
容器注册 BeanPostProcessor 顺序的源码
在创建容器的过程中, 会将所有实现 BPP 接口的 bean 先实例化, 预注册/添加到 BeanFactory
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh 部分源码
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
// 容器刷新, 执行时, 需要锁住
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
/**
* 一, (ApplicationContex)预准备工作;
*/
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
/**
* 二, 获取一个新的 BeanFactory;
*/
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
/**
* 三,(BeanFactory)预准备工作;
*/
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
/**
* 四, beanFactory 已经准备好了, 给子类(Context)预留一个扩展点; (这里是空实现)
*/
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
/**
* 五, 调用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 和 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor;
*/
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
/**
* 六,注册 BeanPostProcessor (BPP)处理器;
* 1. 拿到所有实现 BeanPostProcessor 的 bean, 然后进行分类存起来
* 这有一个关键点, Spring 对 BeanDefinition 分成三种角色:
* 1. 用户定义的 Bean (ROLE_APPLICATION)
* 2. 较复杂的 (ROLE_SUPPORT) 较复杂的? (不重要, 不要每一个细节都扣...)
* 3. Spring 内置的(ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
* 2. 如果实现了 BeanPostProcessor 则会先(getBean)实例化这个bean
* 1. 这里先 (getBean)实例化, 实现 BPP接口的 bean
* 2. 这里按实现(PriorityOrdered)排序接口的、@Ordered注解的 等排序存起来. 实际调用的顺序 其实就是存起来的顺序
* 3. 另外 BeanPostProcessor 接口粗粒度太大了, Spring 还细分一些子接口:
* 1. SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 它提供了更高级的Bean实例化控制方法。主要作用在于允许对Bean的实例化过程进行更精细的控制和定制。
* 2. MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 在合并Bean定义(MergedBeanDefinition)之后但在实例化Bean之前,允许对合并后的Bean定义进行修改、调整或附加元数据。
* 3. DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor 它允许在Bean被销毁之前(例如,容器关闭或特定作用域的Bean销毁)执行一些操作。
* 等等以上也会存起来
* 4. 最终调用 BPP是在 {@link AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory)} 实例初始化其他Bean调用
*
*/
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
/**
* 七,初始化I18N国际化, 消息源;
*/
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
/**
* 八, 初始化 事件多播器;
*/
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
/**
* 九, 给子类(Context)留下一个扩展点
*/
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
/**
* 十,向多播器注册监听器;
*/
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
/**
* 十一,实例化剩下的所有单例bean
*/
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
....
关键在第六步: 注册所有的 BeanPostProcessor, 调用栈:
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#registerBeanPostProcessors
org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#registerBeanPostProcessors(org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext)
/**
* in short:
* 1. 拿到所有实现 BeanPostProcessor 的 bean, 然后进行分类存起来
* 这有一个关键点, Spring 对 BeanDefinition 分成三种角色:
* 1. 用户定义的 Bean (ROLE_APPLICATION)
* 2. 较复杂的 (ROLE_SUPPORT) 较复杂的? 通常是一个外部配置
* 3. Spring 内置的(ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
* 2. 如果实现了 BeanPostProcessor 则会实例化这个bean, 但注意这里只是注册,并不会调用BeanPostProcessor的相关方法
*
* 另外 BeanPostProcessor 粗粒度太大, Spring 还细分一些子接口:
* - SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 它提供了更高级的Bean实例化控制方法。主要作用在于允许对Bean的实例化过程进行更精细的控制和定制。
* - MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 在合并Bean定义(MergedBeanDefinition)之后但在实例化Bean之前,允许对合并后的Bean定义进行修改、调整或附加元数据。
* - DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor 它允许在Bean被销毁之前(例如,容器关闭或特定作用域的Bean销毁)执行一些操作。
*/
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// WARNING: Although it may appear that the body of this method can be easily
// refactored to avoid the use of multiple loops and multiple lists, the use
// of multiple lists and multiple passes over the names of processors is
// intentional. We must ensure that we honor the contracts for PriorityOrdered
// and Ordered processors. Specifically, we must NOT cause processors to be
// instantiated (via getBean() invocations) or registered in the ApplicationContext
// in the wrong order.
//
// Before submitting a pull request (PR) to change this method, please review the
// list of all declined PRs involving changes to PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate
// to ensure that your proposal does not result in a breaking change:
// https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues?q=PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate+is%3Aclosed+label%3A%22status%3A+declined%22
/**
* 拿到所有实现 BeanPostProcessor 的 bean名称
*/
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
/**
* 计算 BeanPostProcessor(BPP) 的总数, +1 是什么操作?
* 原因是: 下一行,又加了一个 BeanPostProcessorChecker
*/
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
// BeanPostProcessorChecker 这个BeanPostProcessor, 没啥实际作用, 就是记录了一些日志;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(
new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, postProcessorNames, beanProcessorTargetCount));
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
/**
* 对 BeanPostProcessor 进行分类存起来, 再调用
* 比如
* 1. priorityOrderedPostProcessors //有实现(PriorityOrdered)排序接口的
* 2. internalPostProcessors Spring内部的bean, 见: Spring将bean分为三种角色
* 3. @Ordered 注解的
* 4. nonOrderedPostProcessorNames //没有noneOrder的
*/
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
/**
* 注意, 若 bean 还实现了 PriorityOrdered 接口, 也去去实例化它;
*/
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
/**
* 注册所有常规BeanPostProcessors
* 这里 getBean 实例化bean !;
*/
// Now, register all regular(常规) BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
/**
* 最后, 注册所有 内置 BeanPostProcessor
*/
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
//最后再重新放一次, 让它在最后
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
调用 BeanFactory的addBeanPostProcessor方法, 最终会存放的会存放到 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#beanPostProcessors 的List 集合中
org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#registerBeanPostProcessors(org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, java.util.List<? extends org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor>)
private static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<? extends BeanPostProcessor> postProcessors) {
if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory abstractBeanFactory) {
// Bulk addition is more efficient against our CopyOnWriteArrayList there
abstractBeanFactory.addBeanPostProcessors(postProcessors);
}
else {
for (BeanPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor);
}
}
}
所以, 可以理解存放顺序就是调用顺序, 逻辑是: 1. 先调用实现 org.springframework.core.PriorityOrdered 接口的 2. 在调用实现 org.springframework.core.Ordered 接口的
容器调用 BeanPostProcessor 过程的源码
在第十一步: 实例化剩下的所有单例bean
实例化bean 过程偏长, 与主题无关, 暂略, 这里只看调用的 BPP 的主要逻辑, 调用栈
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#finishBeanFactoryInitialization
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#preInstantiateSingletons
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean 部分源码
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
/**
* 1. 真正在jvm层面实例化对象;
*/
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
..............
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
/**
* 2.填充Bean属性
*/
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
/**
* 3.初始化Bean对象
* 1.先调用这三个 BeanNameAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware
* 这三个是在创建BeanFactory 时忽略的三个 Aware 接口
* 2. 调用所有 BeanPostProcessors#postProcessBeforeInitialization (作用: 在Bean初始化之前调用)
* 3. 调用 init-method 方法
* 4. 调用所有 BeanPostProcessors#postProcessAfterInitialization (作用: 在Bean初始化之后调用)
*/
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException bce && beanName.equals(bce.getBeanName())) {
throw bce;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
.... 省略部分源码
return exposedObject;
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#initializeBean(java.lang.String, java.lang.Object, org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition)
/**
* Initialize the given bean instance, applying factory callbacks
* as well as init methods and bean post processors.
* <p>Called from {@link #createBean} for traditionally defined beans,
* and from {@link #initializeBean} for existing bean instances.
* @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
* @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
* @param mbd the bean definition that the bean was created with
* (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance)
* @return the initialized bean instance (potentially wrapped)
* @see BeanNameAware
* @see BeanClassLoaderAware
* @see BeanFactoryAware
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
* @see #invokeInitMethods
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
/**
* 先调用这三个 BeanNameAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware
* 这三个是在创建BeanFactory 时忽略的三个 Aware 接口
* { @link org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory() }
*
*/
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
/**
* 调用所有 BeanPostProcessors#postProcessBeforeInitialization
* (作用 在Bean初始化之前调用)
* 比如 Spring 中Aware属性的设置, 是通过这种方式扩展的
* - org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationContextAwareProcessor
* 对应调用 ApplicationContextAware, EnvironmentAware, ApplicationEventPublisherAware 等Aware方法
*
*/
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
/**
* 调用 init-method 方法
*/
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
/**
* 调用所有 BeanPostProcessors#postProcessAfterInitialization
* (作用 在Bean初始化之后调用)
*
* - AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class
* org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator 对应的类有根据情况有三个可能
* InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class,
* AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class,
* AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class
*
* 如果需要代理, 这里会真正的对原始 bean 进行代理 进行代理的创建 createProxy
*
*/
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
调时机是: 实例 Bean对象 -> 填充Bean的属性 -> 调完Aware接口的注入 -> 调用(BPP) 的Before方法 -> 调用 init-method -> 调用(BPP) 的After方法 ; 也符合大家所知的bean生命周期
且都使用了 applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization 和 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法的返回值作为 wrappedBean 返回出去.
所以:
接口中的两个方法都要将传入的 bean 返回,而不能返回 null,如果返回的是 null 那么我们通过getBean() 方法将得不到目标对象。
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
@Deprecated(since = "6.1")
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
@Deprecated(since = "6.1")
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
BeanPostProcessor 的子接口
另外 BeanPostProcessor 粗粒度太大, Spring 还细分一些子接口:
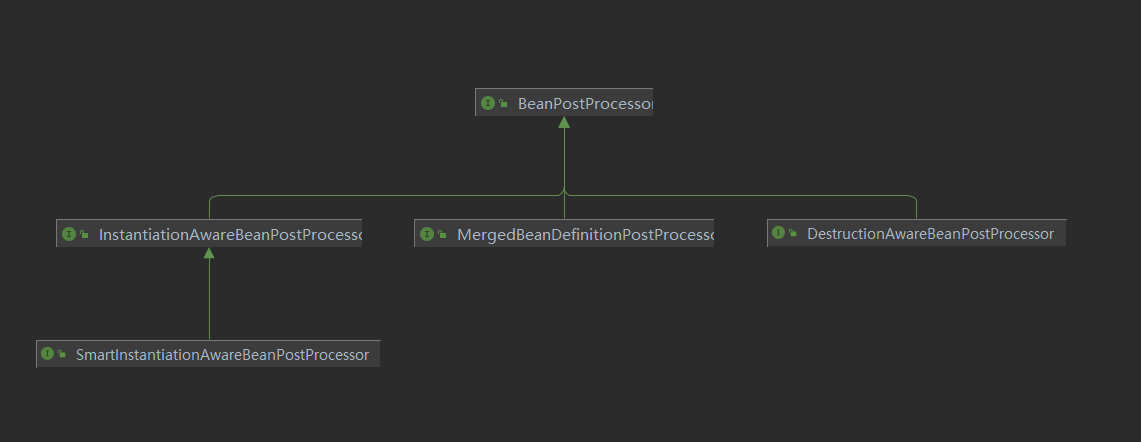
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
@Autowired、@Inject 等就是根据这个回调来实现最终注入依赖的属性的。
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
// BeanPostProcessor 接口方法
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
// BeanPostProcessor 接口方法
default boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return true;
}
/**
* Post-process the given property values before the factory applies them
* to the given bean.
* <p>The default implementation returns the given {@code pvs} as-is.
*
* 将给定的属性值应用到指定的bean之前进行回调
* 可以用来检查和修改属性,最终返回的PropertyValues会应用到bean中
* `@Autowired、@Resource` 在Spring中 就是根据这个回调来实现最终注入依赖的属性的
*
* @param pvs the property values that the factory is about to apply (never {@code null})
* @param bean the bean instance created, but whose properties have not yet been set
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the actual property values to apply to the given bean (can be the passed-in
* PropertyValues instance), or {@code null} to skip property population
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @since 5.1
*/
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return pvs;
}
}
那么 postProcessProperties 在哪里调用呢?
相关源码
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean 填充Bean属性方法
/**
* Populate the bean instance in the given BeanWrapper with the property values
* from the bean definition.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param bw the BeanWrapper with bean instance
*/
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
// 验证一下入参
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
if (bw.getWrappedClass().isRecord()) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to a record");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for records since they are immutable.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
/**
* 如果是AOP, pointcut, advice相关的, synthetic 会配置为 true
*/
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
if (!bp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
/**
* 包含一个或多个{@link PropertyValue}对象的Holder,通常针对特定目标bean的一次更新
* 可以理解为: 该bean所有属性的描述
*/
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
/**
* 获取自动注入的方式
*/
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
/**
* 该分支处理通过 名称或者类型 注入的属性
* (有注解才会走这个分支)
*/
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
/**
* 通过名称注入
*/
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
/**
* 通过类型注入
*/
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
/**
* <!> 回调所有 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties 方法
* 比如, `@Autowired` 的处理对应实现类: {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}
* (作用是: 在工厂将属性值应用到给定bean之前,对它们进行处理)
*
*/
if (hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
// <!> 回调InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties 方法
for (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessorCache().instantiationAware) {
PropertyValues pvsToUse = bp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
....
<!> 回调InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties 方法
后面注入在: org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// 注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor & SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 它提供了更高级的Bean实例化控制方法。主要作用在于允许对Bean的实例化过程进行更精细的控制和定制。
public interface SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
//用来返回目标对象的类型(比如代理对象通过raw class获取proxy type 用于类型匹配)
@Nullable
default Class<?> predictBeanType(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
//这里提供一个拓展点用来解析获取用来实例化的构造器(比如未通过bean定义构造器以及参数的情况下,会根据这个回调来确定构造器)
@Nullable
default Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return null;
}
//获取要提前暴露的bean的引用,用来支持单例对象的循环引用(一般是bean自身,如果是代理对象则需要取用代理引用)
default Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
相关源码
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBean(java.lang.String, org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition, java.lang.Object[])
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating instance of bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
/**
* 1. 解析到 BeanDefinition 的 Class
*/
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
/**
* 2. 创建BeanDefinition 复制一份 RootBeanDefinition
*/
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
// Prepare method overrides.
try {
/**
* 3. 准备和验证 lookup-method 和 replace-method;
*/
mbdToUse.prepareMethodOverrides();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(),
beanName, "Validation of method overrides failed", ex);
}
try {
/**
* <!>给 BeanPostProcessors 一个返回代理实例的机会;
* 注意, 这里的逻辑:
* 如果其 BeanPostProcessors的子接口返回不为null, 则直接使用这个bean实例返回了, 不走 doCreateBean流程了
* (注意的注意! 如果有用户自定义的拦截创建, 甚至优先Spring的AOP代理创建)
*/
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbdToUse.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"BeanPostProcessor before instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#resolveBeforeInstantiation
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
// 如果是合成的(mbd是AOP的时候,为true)并且实现 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 接口
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
// 使用 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口 生成的 bean 返回
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
if (bean != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor 它允许在Bean被销毁之前(例如,容器关闭或特定作用域的Bean销毁)执行一些操作。
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor
public interface DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
//这里实现销毁对象的逻辑
void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
//判断是否需要处理这个对象的销毁
default boolean requiresDestruction(Object bean) {
return true;
}
}
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 算是整个 BeanPostProcessor 家族中比较另类的一个接口了,它虽然是 BeanPostProcessor,但是却可以处理 BeanDefinition。
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 介入的时机就是 Bean 创建成功之后,Bean 中各个属性填充之前。
相关源码
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
/**
* 1. 真正在jvm层面实例化对象;
*
*/
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
/**
* 获取 BeanWrapper中的原始 Bean 实例
*/
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
/**
* 获取Bean Class类型
*/
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
/**
* <!> 实例化完了, 处理 MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor 的接口回调
*/
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.markAsPostProcessed();
}
}
// Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
/**
* 填充属性
*/
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
.....
处理 init-method, @PostConstruct, @PreDestroy 的实现
对应其子类 org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
注意: 这里只是查询到封装为元信息保存到 BeanDefinition, 还不会调用
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#findLifecycleMetadata(org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition, java.lang.Class<?>)
/**
* 1. 查找相应的注解方法信息, 封装为 LifecycleMetadata 元数据(使用集合存起来包含: initMethods 列表,destroyMethods列表...)
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#buildLifecycleMetadata(java.lang.Class)}
* 2. 再将这些 LifecycleMetadata 元数据, 注册(修改)到 BeanDefinition 中
* {@link LifecycleMetadata#checkInitDestroyMethods(RootBeanDefinition)}
* beanDefinition.registerExternallyManagedInitMethod(methodIdentifier);
* beanDefinition.registerExternallyManagedDestroyMethod(methodIdentifier);
*/
private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanClass) {
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(beanClass);
metadata.checkInitDestroyMethods(beanDefinition);
return metadata;
}
处理 @Autowired 的实现
对应子类 org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
注意: 这里只是查询到封装为元信息保存到 BeanDefinition, 还不会调用
雷同的逻辑
org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#findInjectionMetadata
private InjectionMetadata findInjectionMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> beanType, RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
// 查找 注解方法信息, 封装为元数据对象
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, beanType, null);
// 注册(修改)到 BeanDefinition 中
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
return metadata;
}
其他常见的
以下是几个常见的BeanPostProcessor实现及其主要作用:
-
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor: 用于实现 EnvironmentAware/EmbeddedValueResolverAware/ResourceLoaderAware/MessageSourceAware/ApplicationContextAware 接口(注意只限定以上Aware接口的属性注入, 其他Aware不是由它注入)的bean注入属性。
-
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: (它的父类就是 InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor ) 解析常见的注解,如@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy,并在初始化前后执行相应的方法。用于支持JSR-250规范的注解。
-
BeanValidationPostProcessor: 集成Bean Validation API,对标注了@Valid注解的属性进行验证。用于支持JSR-303规范的注解。
-
AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor: 处理异步方法的注解,如@Async。在bean初始化后,为标注了@Async注解的方法创建代理,以支持异步调用。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号