(原)caffe中的conv
转载请注明出处:
https://www.cnblogs.com/darkknightzh/p/10486686.html
conv总体调用流程如下图所示:

说明:带o的为输出,如Wo代表输出宽度;带i的为输入,如Hi代表输入高度
1. 前向传播的计算ConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu
注:不考虑反向传播的计算过程…
前向传播时,分别调用base_conv_layer.cpp中的BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::forward_cpu_gemm和base_conv_layer.cpp中的BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::forward_cpu_bias
1 template <typename Dtype> 2 void ConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, 3 const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) 4 { 5 const Dtype* weight = this->blobs_[0]->cpu_data(); // weight参数 6 for (int i = 0; i < bottom.size(); ++i) { // 多少个输入。一般1个的比较常见吧 7 const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[i]->cpu_data(); // 第i个输入:NCHiWi 8 Dtype* top_data = top[i]->mutable_cpu_data(); // 第i个输出:NCHoWo 9 for (int n = 0; n < this->num_; ++n) { // batchsize 10 //forward_cpu_gemm输入为第n个channel的起始位置(C*Hi*Wi),及权重参数(No*Ni*Kh*Kw),输出为第n个channel的起始位置,(C*Ho*Wo) 11 this->forward_cpu_gemm(bottom_data + n * this->bottom_dim_, weight, top_data + n * this->top_dim_); 12 if (this->bias_term_) { // 含有bias 13 const Dtype* bias = this->blobs_[1]->cpu_data(); // bias参数 14 this->forward_cpu_bias(top_data + n * this->top_dim_, bias); // 计算增加bias后的输出 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 }
在forward之前,计算输出特征的尺寸函数为compute_output_shape
1 template <typename Dtype> 2 void ConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::compute_output_shape() { 3 const int* kernel_shape_data = this->kernel_shape_.cpu_data(); 4 const int* stride_data = this->stride_.cpu_data(); 5 const int* pad_data = this->pad_.cpu_data(); 6 const int* dilation_data = this->dilation_.cpu_data(); // 卷积核膨胀的宽高,默认为1;核膨胀,即在核中间加0 7 this->output_shape_.clear(); 8 for (int i = 0; i < this->num_spatial_axes_; ++i) { // HW总共维度,num_spatial_axes_=2 9 // i + 1 to skip channel axis 10 const int input_dim = this->input_shape(i + 1); //inline int input_shape(int i) {return (*bottom_shape_)[channel_axis_ + i];} 11 const int kernel_extent = dilation_data[i] * (kernel_shape_data[i] - 1) + 1; //得到膨胀之后的核的尺寸 12 const int output_dim = (input_dim + 2 * pad_data[i] - kernel_extent) / stride_data[i] + 1; //得到输出特征的尺寸 13 this->output_shape_.push_back(output_dim); // 输出特征宽高 14 } 15 }
2. forward_cpu_gemm
该函数首先判断是否为1*1的卷积,如果不是,则调用conv_im2col_cpu函数,将输入ChiWi变换成(C*Kh*Kw)*Ho*Wo的临时矩阵col_buffer_。
之后调用caffe_cpu_gemm,每次计算一部分输出,如果group_为1,则一次计算完:output(Co*(Ho*Wo))=1* weights(Co*(Ci*Kh*Kw))* col_buff((Ci*Kh*Kw)*(Ho*Wo)) + 0* output
1 template <typename Dtype> 2 void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::forward_cpu_gemm(const Dtype* input, 3 const Dtype* weights, Dtype* output, bool skip_im2col) { //bool skip_im2col = false 4 const Dtype* col_buff = input; 5 if (!is_1x1_) { // 不是1*1卷积 6 if (!skip_im2col) 7 { 8 // 调用base_conv_layer.hpp中的im2col_cpu,将输入CiHiWi变换成(Ci*Kh*Kw)*Ho*Wo的临时变量 9 // 由于调用本函数的函数ConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu中调用batchsize次本函数,因而本函数内部不包含batchsize 10 conv_im2col_cpu(input, col_buffer_.mutable_cpu_data()); 11 } 12 col_buff = col_buffer_.cpu_data(); 13 } 14 for (int g = 0; g < group_; ++g) { // group_默认为1 15 caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, conv_out_channels_ / group_, // Co 16 conv_out_spatial_dim_, kernel_dim_, // Ho*Wo // 卷积核的Ci*Kh*Kw 17 (Dtype)1., weights + weight_offset_ * g, col_buff + col_offset_ * g, 18 (Dtype)0., output + output_offset_ * g); 19 } 20 }
3. conv_im2col_cpu
该函数为内联函数,对im2col_cpu进行了封装,方便调用,如下:
1 inline void conv_im2col_cpu(const Dtype* data, Dtype* col_buff) { 2 if (!force_nd_im2col_ && num_spatial_axes_ == 2) { 3 im2col_cpu(data, conv_in_channels_, 4 conv_input_shape_.cpu_data()[1], conv_input_shape_.cpu_data()[2], 5 kernel_shape_.cpu_data()[0], kernel_shape_.cpu_data()[1], 6 pad_.cpu_data()[0], pad_.cpu_data()[1], 7 stride_.cpu_data()[0], stride_.cpu_data()[1], 8 dilation_.cpu_data()[0], dilation_.cpu_data()[1], col_buff); 9 } 10 else { 11 im2col_nd_cpu(data, num_spatial_axes_, conv_input_shape_.cpu_data(), 12 col_buffer_shape_.data(), kernel_shape_.cpu_data(), 13 pad_.cpu_data(), stride_.cpu_data(), dilation_.cpu_data(), col_buff); 14 } 15 }
4. im2col_cpu
该函数用于将图像转换成卷积所需的列格式。a中黑色实线方框中为特征(或像素),虚线中为边界填充的0,红色虚线框为3*3的卷积核大小。如对于a所示的7*9输入图像(为方便b中的显示,因而a中值为1—63),四个边界各填充一个0后,通过该函数,得到的col格式如b所示,其中红色虚线为a中的位置对应的列格式的像素。b中…代表依次递增的5个特征。可以认为b中矩阵为一个kernel_h*kernel_w*output_h*output_w的行向量,也可以认为是一个(kernel_h*kernel_w)*(output_h*output_w)的2维的矩阵(每一行的长度为output_h*output_w)。通过这种方式得到的col格式数据,与卷积核可通过矩阵相乘,提高运算速度。
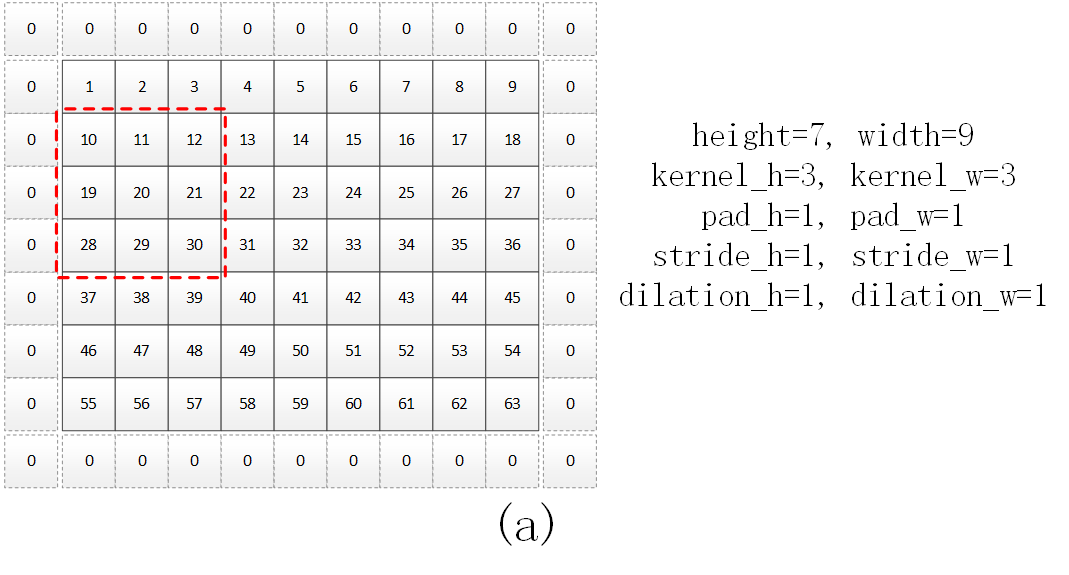
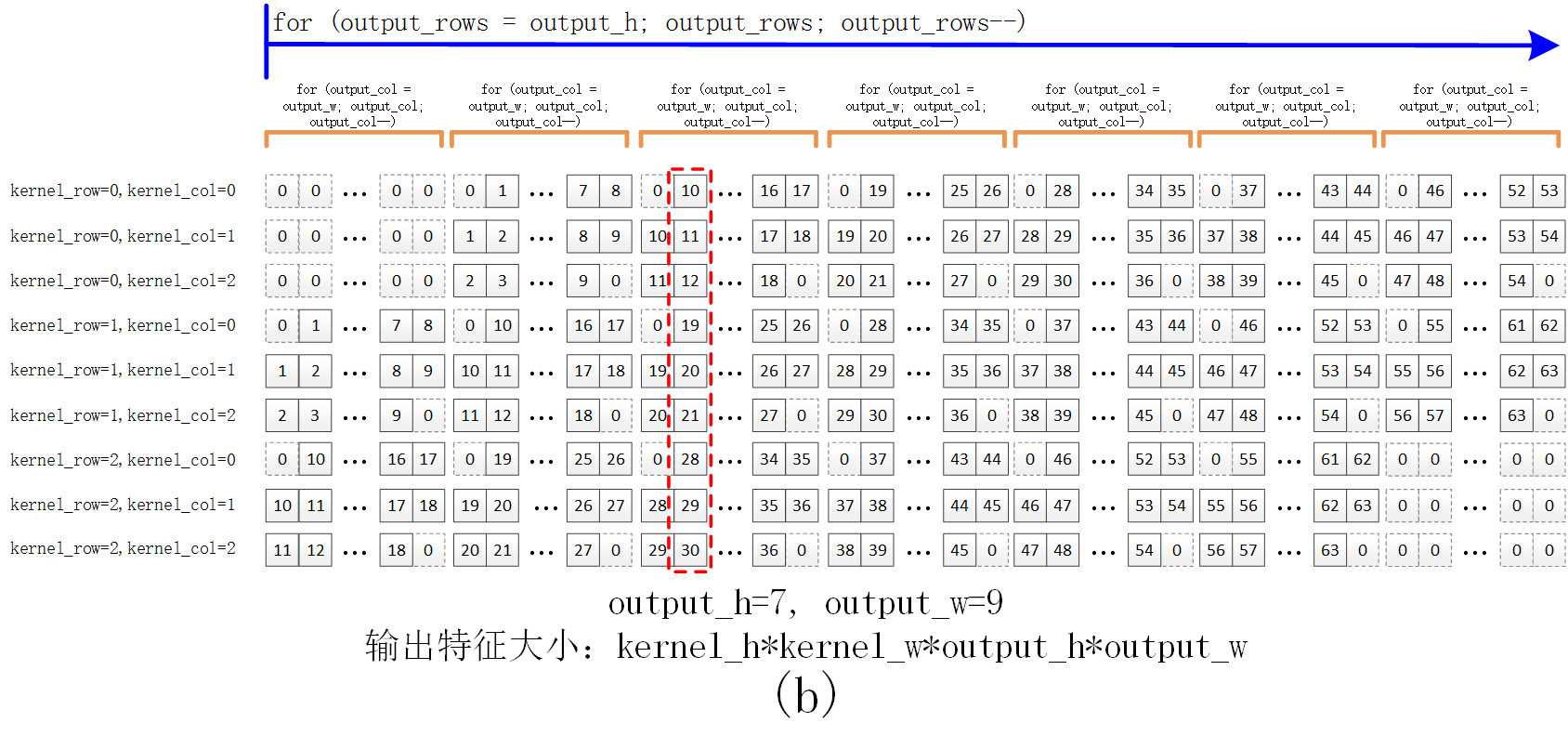
该函数代码如下。其中output_rows的for循环对应b中的蓝色箭头范围,output_col的for循环对应b中的橙色半框范围。
1 template <typename Dtype> 2 void im2col_cpu(const Dtype* data_im, const int channels, // channels为输入特征个数 3 const int height, const int width, const int kernel_h, const int kernel_w, 4 const int pad_h, const int pad_w, // 特征边界填充的宽高 5 const int stride_h, const int stride_w, // 间隔的宽高 6 const int dilation_h, const int dilation_w, // 卷积核膨胀的宽高,默认为1;核膨胀,即在核中间加0 // https://blog.csdn.net/wangyuxi__/article/details/83003357 7 Dtype* data_col) { // 为(kernel_h*kernel_w)*(output_h*output_w)的缓冲区。每一行为滑动窗口的某个位置对应的所有特征 8 const int output_h = (height + 2 * pad_h - (dilation_h * (kernel_h - 1) + 1)) / stride_h + 1; // 输出特征宽高 9 const int output_w = (width + 2 * pad_w - (dilation_w * (kernel_w - 1) + 1)) / stride_w + 1; 10 const int channel_size = height * width; // 输入特征的每个通道的总特征数 11 for (int channel = channels; channel--; data_im += channel_size) // 每次循环完毕,输入特征偏移一个通道 12 { 13 for (int kernel_row = 0; kernel_row < kernel_h; kernel_row++) 14 { 15 for (int kernel_col = 0; kernel_col < kernel_w; kernel_col++) 16 { 17 int input_row = -pad_h + kernel_row * dilation_h; // 每次核在特征上的起始行坐标 18 for (int output_rows = output_h; output_rows; output_rows--) // 遍历输入特征每行 19 { 20 if (!is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(input_row, height)) // a<0 或者 a>=b,即当前行超出输入边界 21 { 22 for (int output_cols = output_w; output_cols; output_cols--) // 每列填0 23 { 24 *(data_col++) = 0; 25 } 26 } 27 else { // 当前行在输入边界内 28 int input_col = -pad_w + kernel_col * dilation_w; // 每次核在特征上的起始列坐标 29 for (int output_col = output_w; output_col; output_col--) // 遍历输入特征每列 30 { 31 if (is_a_ge_zero_and_a_lt_b(input_col, width)) // 当前列在输入边界内 32 { 33 *(data_col++) = data_im[input_row * width + input_col]; // 将输入特征赋值给data_col 34 } 35 else // 当前列超出输入边界 36 { 37 *(data_col++) = 0; 38 } 39 input_col += stride_w; // 输入特征位置增加stride_w 40 } 41 } 42 input_row += stride_h; // 输入特征位置增加stride_h 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 }
5. BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::forward_cpu_bias
该函数为output =1*bias(C*1)* bias_multiplier_(1*(H*W))+ 1*output。其中C为输出特征的通道数No,H为特征高Ho,W为特征宽Wo,最终得到某个batch中CoHoWo的特征。
1 template <typename Dtype> 2 void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::forward_cpu_bias(Dtype* output, 3 const Dtype* bias) { 4 caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, num_output_, //输出特征维度No 5 out_spatial_dim_, 1, (Dtype)1., bias, bias_multiplier_.cpu_data(), // Wo*Ho 6 (Dtype)1., output); 7 }
bias_multiplier_为1*(Wo*Ho)的向量,在void BaseConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::Reshape中将其所有的值均设置为1:
1 out_spatial_dim_ = top[0]->count(first_spatial_axis); // Wo*Ho 2 if (bias_term_) { 3 vector<int> bias_multiplier_shape(1, out_spatial_dim_); 4 bias_multiplier_.Reshape(bias_multiplier_shape); 5 caffe_set(bias_multiplier_.count(), Dtype(1), // bias_multiplier_为1*(Wo*Ho)的向量,所有元素值为1 6 bias_multiplier_.mutable_cpu_data()); 7 }
6. caffe_cpu_gemm
该函数调用cblas_sgemm,实现矩阵相乘:
1 template<> 2 void caffe_cpu_gemm<float>(const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransA, 3 const CBLAS_TRANSPOSE TransB, const int M, const int N, const int K, 4 const float alpha, const float* A, const float* B, const float beta, 5 float* C) { 6 int lda = (TransA == CblasNoTrans) ? K : M; 7 int ldb = (TransB == CblasNoTrans) ? N : K; 8 cblas_sgemm(CblasRowMajor, TransA, TransB, M, N, K, alpha, A, lda, B, 9 ldb, beta, C, N); 10 }
cblas_sgemm具体见:http://www.cnblogs.com/darkknightzh/p/5553336.html
posted on 2019-03-06 22:48 darkknightzh 阅读(1820) 评论(0) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号