Flask:ai 语音(小机器人)
引言
人工智能是利用技术来实现与小机器人对话,主要涉及语音的处理,将文字和语音相互转化
这里的语音和文字之间的相互转化采用的是 百度 ai 技术
小机器人示例对话采用的是 图灵机器人 技术
语音相关介绍
一、语音合成介绍
1、登录百度AI 然后创建应用,随便给应用起个名字,
2、将下面应用的三个值最后传入代码中
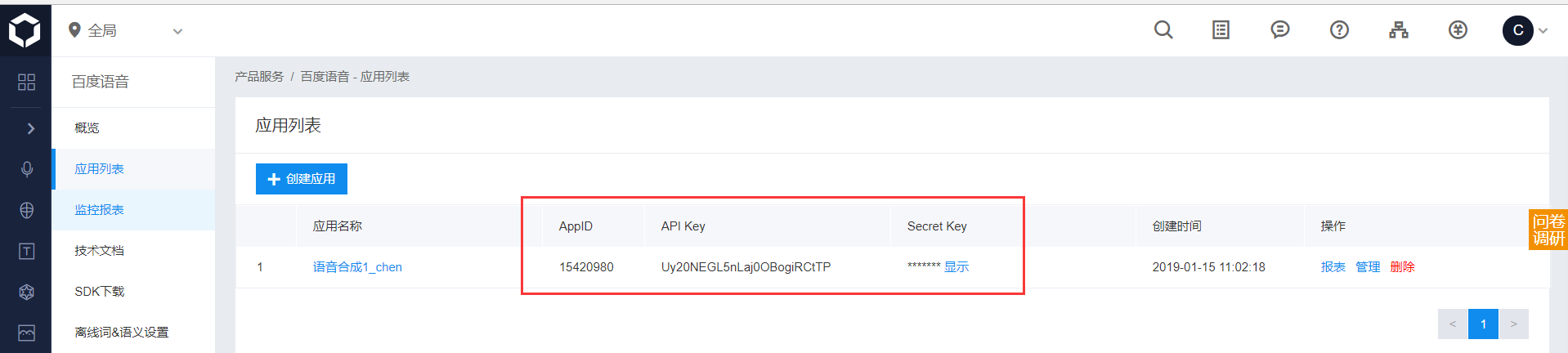
3、查看左边技术文档,根据要求选择 pythonsdk
具体的参数都在文档中有解释
4、小示例展示
from aip import AipSpeech # 引入百度的语音aip APP_ID ='15420980' API_KEY = 'Uy20NEGL5nLaj0OBogiRCtTP' SECRET_KEY = 'ZdzhQlCNTgYYsvXsUKvDxFXNd1TDlUnu ' # 设置三个键 client = AipSpeech(APP_ID,API_KEY,SECRET_KEY) # 床架客户端 result = client.synthesis('北京天气怎么样?','zh',1,{ 'vol':5, 'spd':4, 'pit':7, 'per':4 }) print(result) if not isinstance(result, dict): # 生成语音文件并写入 with open('audio.mp3', 'wb') as f: f.write(result)
二、语音识别介绍
1、同语音合成一样需要建立一个应用,当然这里可以继续使用上面创建的应用的 key
2、文档要看语音识别的 python sdk
3、语音识别,百度AI 现在是只能识别 .pcm 格式的,因此给定的音频文件需要进行转换
这里需要借助 ffmpeg 软件,将其解压后,bin文件添加到系统环境变量中,就可以直接使用 ffmpeg 命令
ffmpeg -y -i 22.pm3 -acodec pcm_s16le -f s16le -ac 1 -ar 16000 22.pcm
4、小示例展示
import os from aip import AipSpeech APP_ID = '15420980' API_KEY = 'Uy20NEGL5nLaj0OBogiRCtTP' SECRET_KEY = 'ZdzhQlCNTgYYsvXsUKvDxFXNd1TDlUnu ' client = AipSpeech(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY) # 读取文件 def get_file_content(filePath): os.system(f"ffmpeg -y -i {filePath} -acodec pcm_s16le -f s16le -ac 1 -ar 16000 {filePath}.pcm") # 改变音频格式 with open(f"{filePath}.pcm", 'rb') as fp: return fp.read() # 识别本地文件 res = client.asr(get_file_content('tq.mp3'), 'pcm', 16000, { 'dev_pid': 1536, }) print(res) print(res.get('result')[0]) # {'corpus_no': '6646705983405283123', 'err_msg': 'success.', 'err_no': 0, 'result': ['今天天气怎么样'], 'sn': '869088824281547556832'} # 今天天气怎么样
三、自定义简单小对话(结合 1 2 )
需求:将前面的两者进行封装到函数中,完成一个简单的小对话
import os import time from aip import AipSpeech, AipNlp # AipNIp 进行文字模糊匹配 """ 你的 APPID AK SK """ APP_ID = '15420336' API_KEY = 'VwSGcqqwsCl282LGKnFwHDIA' SECRET_KEY = 'h4oL6Y9yRuvmD0oSdQGQZchNcix4TF5P' nlp = AipNlp(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY) # 也需要建立客户端 client = AipSpeech(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY) # 读取文件 def get_file_content(filePath): os.system(f"ffmpeg -y -i {filePath} -acodec pcm_s16le -f s16le -ac 1 -ar 16000 {filePath}.pcm") # 更改文件格式 with open(f"{filePath}.pcm", 'rb') as fp: return fp.read() def audio2text(filepath): # 识别本地文件 res = client.asr(get_file_content(filepath), 'pcm', 16000, { 'dev_pid': 1536, }) print(res.get("result")[0]) return res.get("result")[0] def text2audio(text): filename = f"{time.time()}.mp3" result = client.synthesis(text, 'zh', 1, { 'vol': 5, "spd": 3, "pit": 7, "per": 4 }) # 识别正确返回语音二进制 错误则返回dict 参照下面错误码 if not isinstance(result, dict): with open(filename, 'wb') as f: f.write(result) return filename text = audio2text("wyn2.wma") # 给定音频文件 if nlp.simnet("你叫什么名字", text).get("score") >= 0.68: # 进行模糊匹配 text = "我的名字叫银角大王8" else: text = "我不知道你在说什么" # 返回内容 filename = text2audio(text) os.system(filename) # windows系统给定文件名,利用system可以直接打开文件并播放
总结:
1、用到了文字的模糊匹配也是百度 aip 提供的
四、图灵机器人介绍
前面介绍了自定义的简单小对话,但是自己定义会非常的麻烦,数据量也较少,这里采用图灵机器人中的提供的接口,来实现智能对话,通过给图灵机器人发送文字消息,然后对方返回答案的文字
使用:
1、在图灵机器人官网注册账号
2、创建一个小机器人,每个小机器人都有一个自己的 apikey 需要在代码中进行设置,然后对小机器人做一些简单的设置
示例:
import requests args = { "reqType": 0, "perception": { "inputText": { "text": "附近的酒店" } }, "userInfo": { "apiKey": "f0b694a1abd64fffb8ad062c1de1de35", "userId": "22" # userid 主要是用来确定身份,可以联系用户的上下文进行回答,一个apikey只能有一个userid } } url = 'http://openapi.tuling123.com/openapi/api/v2' res = requests.post(url, json=args)
print(res.content) # 内容 text = res.json().get("results")[0].get('values').get("text") print(text)
总结:
1、url ,只能发post 请求,这里使用 requests 模块发送
2、apikey,就是创建的小机器人的 apikey
3、userid 主要是用来确定身份,可以联系用户的上下文进行回答,一个apikey只能有一个userid
五、与图灵小机器人简单小对话(结合 3 4)
这里说的内容还是通过传递音频文件,得到答案
import os import time from aip import AipSpeech, AipNlp """ 你的 APPID AK SK """ APP_ID = '15420336' API_KEY = 'VwSGcqqwsCl282LGKnFwHDIA' SECRET_KEY = 'h4oL6Y9yRuvmD0oSdQGQZchNcix4TF5P' nlp = AipNlp(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY) client = AipSpeech(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY) # 读取文件 def get_file_content(filePath): os.system(f"ffmpeg -y -i {filePath} -acodec pcm_s16le -f s16le -ac 1 -ar 16000 {filePath}.pcm") with open(f"{filePath}.pcm", 'rb') as fp: return fp.read() def audio2text(filepath): # 识别本地文件 res = client.asr(get_file_content(filepath), 'pcm', 16000, { 'dev_pid': 1536, }) print(res.get("result")[0]) return res.get("result")[0] def text2audio(text): filename = f"{time.time()}.mp3" result = client.synthesis(text, 'zh', 1, { 'vol': 5, "spd": 3, "pit": 7, "per": 4 }) # 识别正确返回语音二进制 错误则返回dict 参照下面错误码 if not isinstance(result, dict): with open(filename, 'wb') as f: f.write(result) return filename def to_tuling(text): import requests args = { "reqType": 0, "perception": { "inputText": { "text": text } }, "userInfo": { "apiKey": "f0b694a1abd64fffb8ad062c1de1de35", "userId": "22" } } url = 'http://openapi.tuling123.com/openapi/api/v2' res = requests.post(url, json=args) print(res.content) # 语音对话返回的内容 text = res.json().get("results")[0].get('values').get("text") print(text) return text # res = nlp.simnet("你叫什么名字","你的名字是什么") # print(res) # 分值 text = audio2text("wyn.wma") # 自说的话是通过音频文件传入的 if nlp.simnet("你叫什么名字", text).get("score") >= 0.68: text = "我的名字叫银角大王8" else: text = to_tuling(text) # 不再是不知道说什么,而是根据图灵来回答 filename = text2audio(text) os.system(filename)
web端小机器人智能对话实例
需求:
在web端录制自己说话的音频,然后发送给后端;后端接收问题后,返回答案
(1)前端代码:
templates / index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <audio src="" controls autoplay id="player"></audio> <p> <button onclick="start_reco()" style="background-color: yellow">录制语音指令</button> </p> <p> <button onclick="stop_reco_audio()" style="background-color: blue">发送语音指令</button> </p> </body> <script type="text/javascript" src="/static/jQuery3.1.1.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="/static/Recorder.js"></script> # 该js主要是用来录制音频文件的 <script type="text/javascript"> var reco = null; var audio_context = new AudioContext(); navigator.getUserMedia = (navigator.getUserMedia || navigator.webkitGetUserMedia || navigator.mozGetUserMedia || navigator.msGetUserMedia); navigator.getUserMedia({audio: true}, create_stream, function (err) { console.log(err) }); function create_stream(user_media) { var stream_input = audio_context.createMediaStreamSource(user_media); reco = new Recorder(stream_input); } function start_reco() { reco.record(); } function stop_reco_audio() { reco.stop(); send_audio(); reco.clear(); } function send_audio() { reco.exportWAV(function (wav_file) { var formdata = new FormData(); formdata.append("record", wav_file); console.log(formdata); $.ajax({ url: "http://192.168.13.67:9527/ai", type: 'post', processData: false, contentType: false, data: formdata, dataType: 'json', success: function (data) { console.log(data); document.getElementById("player").src = "http://192.168.13.67:9527/get_audio/" + data.filename } }); }) } </script> </html>
(2)后端代码
app.py
from flask import Flask,render_template,request,jsonify,send_file from uuid import uuid4 import baidu_ai # 引入写好的语音相关的代码 app = Flask(__name__) @app.route("/") def index(): return render_template("index.html") @app.route("/ai",methods=["POST"]) def ai(): # 1、保存录音文件(接收前台发送的录制好的音频数据) audio = request.files.get("record") filename = f"{uuid4()}.wav" audio.save(filename) # 2、将录音文件转成文字(将录音文件格式转换为PCM发送给百度进行语音识别) q_text = baidu_ai.audio2text(filename) # 3、将识别的问题交给图灵或自主处理获取答案 print(1111) a_text = baidu_ai.to_tuling(q_text) print(222, a_text) # 4、将答案发送给百度语音合成,合成音频文件 a_file = baidu_ai.text2audio(a_text) # 返回的音频文件的名字 # 5、将音频文件发送给前端播放 # 将名字发给前端,前端再发送请求,然后前端再发送请求,后端将文件send_file给前端 return jsonify({"filename":a_file}) # 将音频文件名发送给前端 @app.route("/get_audio/<filename>") def getaudio(filename): return send_file(filename) if __name__ == '__main__': app.run("0.0.0.0",9527,debug=True)
baidu_ai.py (引用文件)
import os import time from aip import AipSpeech, AipNlp APP_ID = '15420980' API_KEY = 'Uy20NEGL5nLaj0OBogiRCtTP' SECRET_KEY = 'ZdzhQlCNTgYYsvXsUKvDxFXNd1TDlUnu' nlp = AipNlp(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY) client = AipSpeech(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY) # 读取文件 def get_file_content(filePath): os.system(f"ffmpeg -y -i {filePath} -acodec pcm_s16le -f s16le -ac 1 -ar 16000 {filePath}.pcm") with open(f"{filePath}.pcm", 'rb') as fp: return fp.read() def audio2text(filepath): # 识别本地文件 res = client.asr(get_file_content(filepath), 'pcm', 16000, { 'dev_pid': 1536, }) print(res.get("result")[0]) return res.get("result")[0] def text2audio(text): filename = f"{time.time()}.mp3" result = client.synthesis(text, 'zh', 1, { 'vol': 5, "spd": 3, "pit": 7, "per": 4 }) # 识别正确返回语音二进制 错误则返回dict 参照下面错误码 if not isinstance(result, dict): with open(filename, 'wb') as f: f.write(result) return filename def to_tuling(text): import requests args = { "reqType": 0, "perception": { "inputText": { "text": text } }, "userInfo": { "apiKey": "f0b694a1abd64fffb8ad062c1de1de35", "userId": "22" } } url = "http://openapi.tuling123.com/openapi/api/v2" res = requests.post(url, json=args) text = res.json().get("results")[0].get("values").get("text") print("图灵答案", text) return text



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号