DRF:源码剖析 - APIView
简介
继承了View,并重写了View中的方法(as_view()、dispatch()等),在原来View的基础上,有添加了新的功能
APIView基本使用
用法和View基本一样,但是有封装了新的功能,比如之前继承View,接收的 post 请求发送的 json数据只能存放在request.body中,取出来是字节串的形式,需要编码decode("utf-8"),现在使用了APIView之后,就可以直接获取到 json 数据,并解析,然后将解析后的数据存放入 request.data 中
# 视图函数 views.py
from rest_framework.views import APIView class LoginView(APIView): # parser_classes = [FormParser] def get(self, request): return render(request, 'login.html') def post(self, request): ret = request.data //可以解析json数据,并放入request.data中print(ret) return HttpResponse("Ok")
TemplateView基本使用
from django.views.generic import TemplateView class SurveyIndexView(TemplateView): template_name = "web/index.html" # 字段名不可变,可以渲染 html extra_context = { # 标题 "title": "欢迎使用问卷调查系统" } class SurveyDetailView(TemplateView): template_name = "web/detail.html" extra_context = { "title": "详情页" }
APIView源码剖析
简要解析:
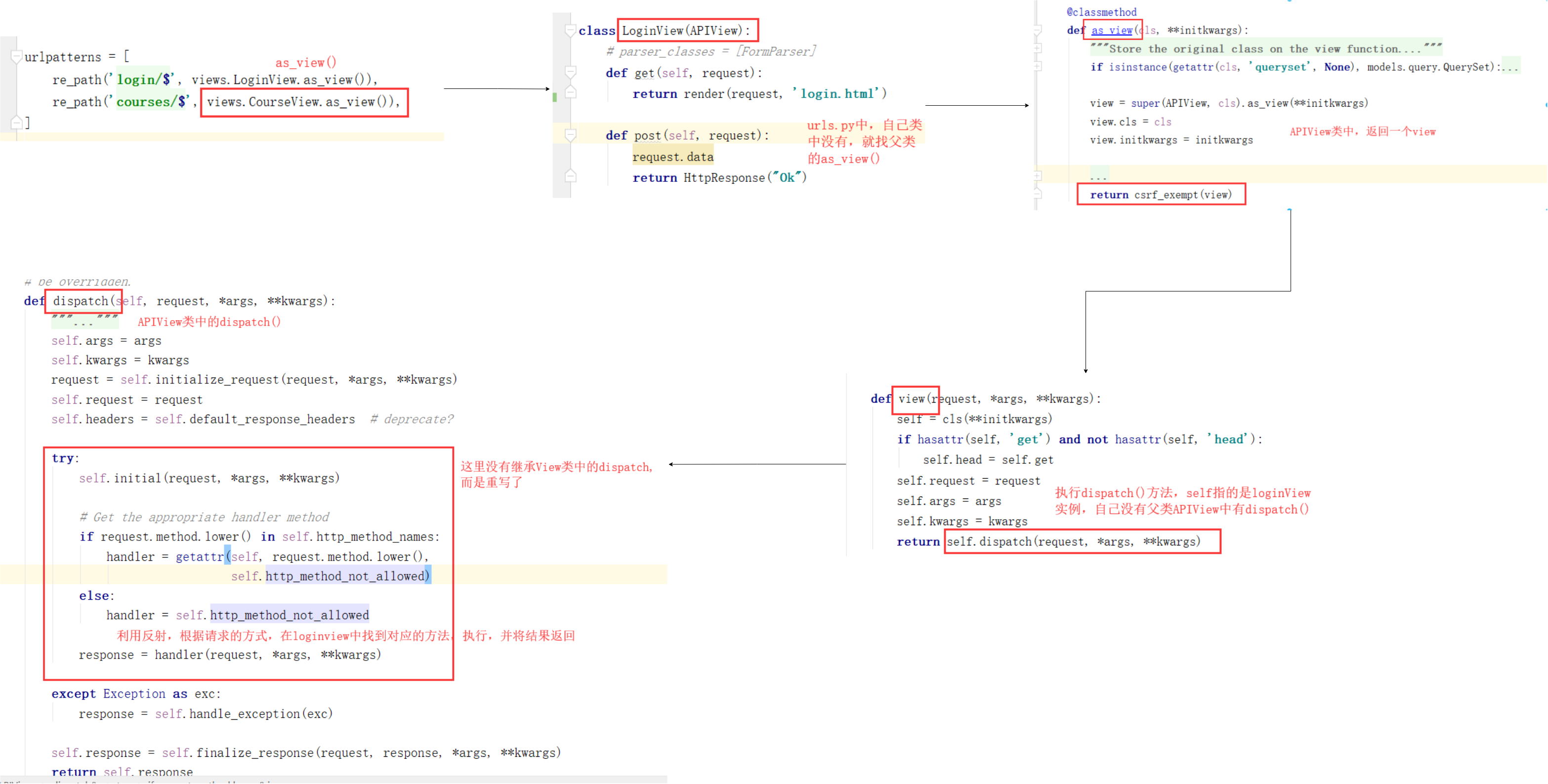
升级版:
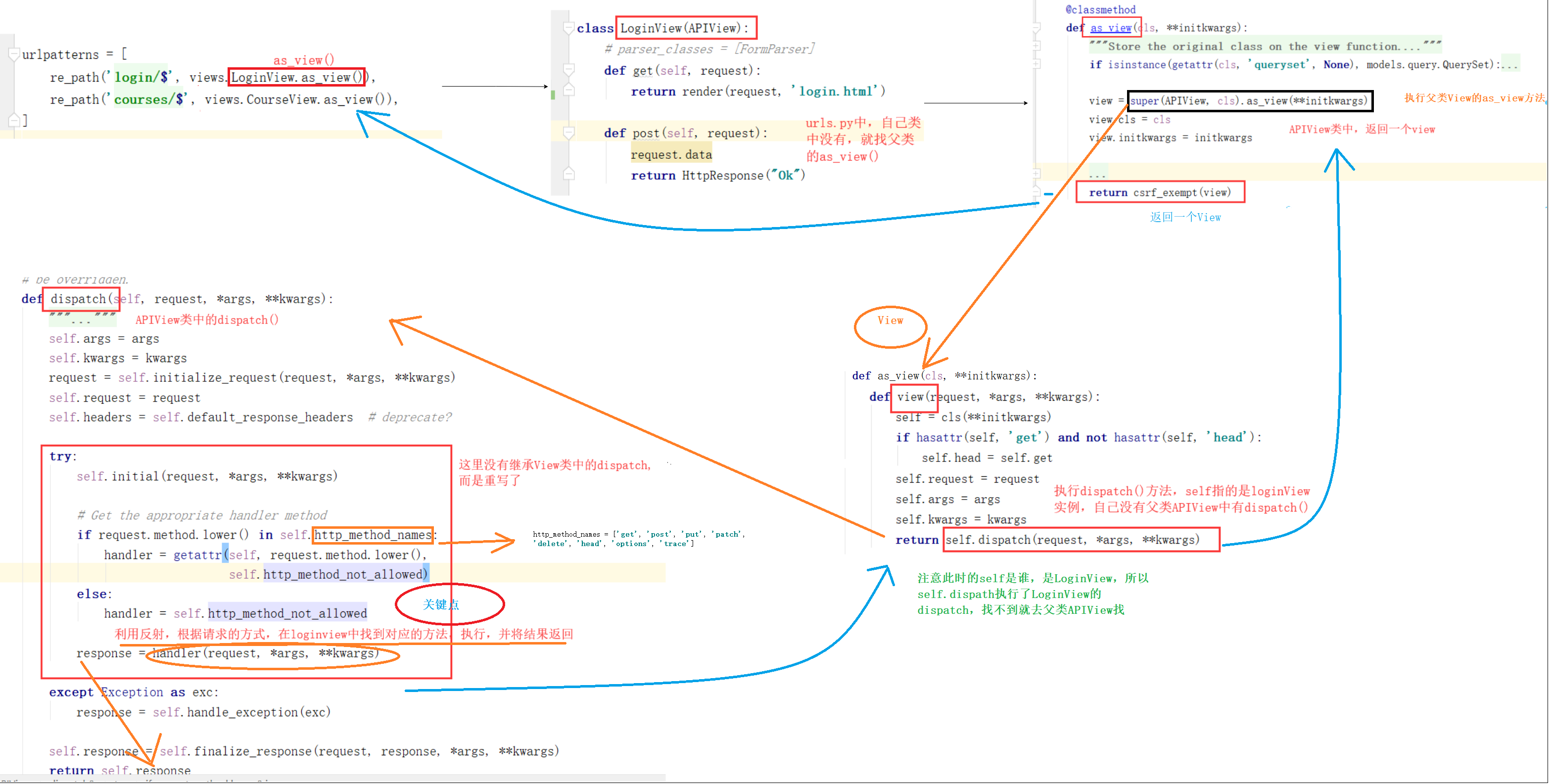
源码剖析相关知识回顾
一、cbv
class based view的使用,
django.views import View class LoginView(View): def get(self, request): pass
其源码解析:

二、@classmethod & @classonlymethod
1、@classmethod

类方法也是装饰器,在加载的时候就执行了,
既可以用实例对象调用,也可以用类直接调用,最好是用类直接调用
2、@classonlymethod
使用的时候需要引用:
from django.utils.decorators import classonlymethod
(1)用实例对象调用会报错
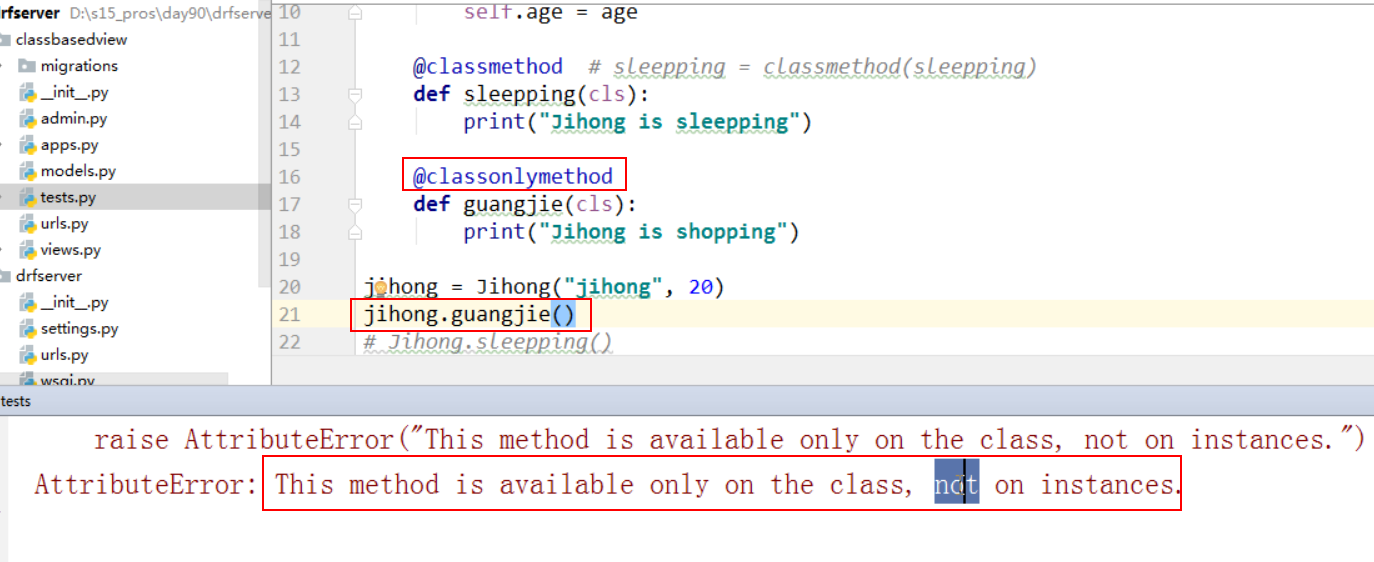
(2)需要用类名直接调用

三、反射(getattr, hasattr, setattr)
1、类的实例对象存储在 __dict__()方法中,
以下为 实例对象 和 类名 分别调用类中的__dict__() 得到的结果

2、hasattr() 可以判断实例对象中是否有该属性或方法

1) 有为true 没有为false
2)字典本身没有 .name取值,实际上是调用了 __getitem__方法,封装了这种 .name 取值的方式
3、setattr() 可以添加属性
以下两种方式都可以添加属性
4、getattr() 也可以通过这种方式取属性值
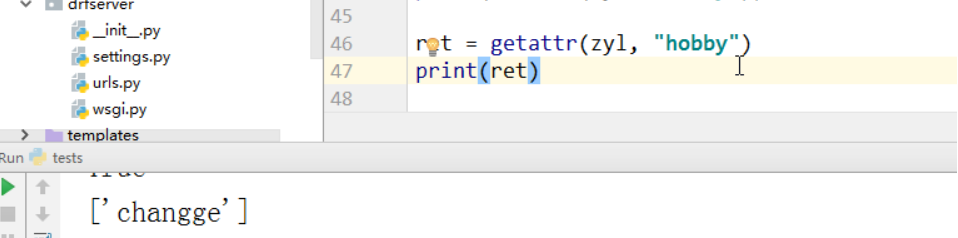
注意:取方法如果自己没有,就去父类中找
四、self 定位,始终指向调用者
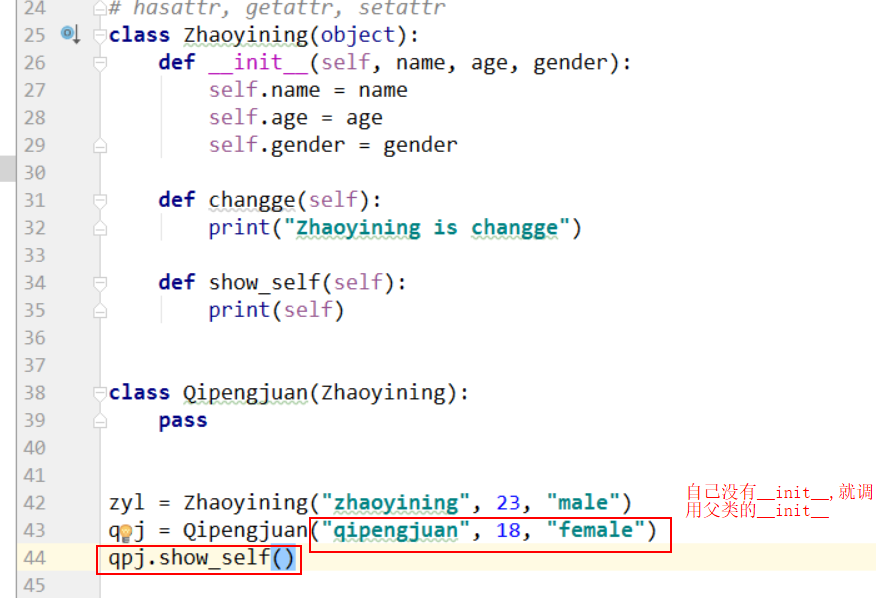
show_self,指的是 qpj 的show_self, 谁调用就指向谁, 始终指向调用者。
五、http请求协议
沟通双方约定俗成的规范,解析数据规则
form enctype (urlencode formdata)
六、javascript中的序列化成json类型
JSON.stringity("......") 序列化
JSON.parse("......") 反序列化



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号