2.Gradeclc.hpp
`#include
include
include
include
include
include
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class GradeCalc: public vector
public:
GradeCalc(const string &cname, int size);
void input(); // 录入成绩
void output() const; // 输出成绩
void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序)
int min() const; // 返回最低分
int max() const; // 返回最高分
float average() const; // 返回平均分
void info(); // 输出课程成绩信息
private:
void compute(); // 成绩统计
private:
string course_name; // 课程名
int n; // 课程人数
vector
vector
};
GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const string &cname, int size): course_name{cname}, n{size} {}
void GradeCalc::input() {
int grade;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> grade;
this->push_back(grade);
}
}
void GradeCalc::output() const {
for(auto ptr = this->begin(); ptr != this->end(); ++ptr)
cout << *ptr << " ";
cout << endl;
}
void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) {
if(ascending)
std::sort(this->begin(), this->end());
else
std::sort(this->begin(), this->end(), std::greater
}
int GradeCalc::min() const {
return *std::min_element(this->begin(), this->end());
}
int GradeCalc::max() const {
return *std::max_element(this->begin(), this->end());
}
float GradeCalc::average() const {
return std::accumulate(this->begin(), this->end(), 0) * 1.0 / n;
}
void GradeCalc::compute() {
for(int grade: *this) {
if(grade < 60)
counts.at(0)++;
else if(grade >= 60 && grade < 70)
counts.at(1)++;
else if(grade >= 70 && grade < 80)
counts.at(2)++;
else if(grade >= 80 && grade < 90)
counts.at(3)++;
else if(grade >= 90)
counts.at(4)++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i)
rates.at(i) = counts.at(i) * 1.0 / n;
}
void GradeCalc::info() {
cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << endl;
cout << "排序后成绩: \t";
sort(); output();
cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << endl;
cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << endl;
cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << endl;
compute(); // 统计各分数段人数、比例
vector<string> tmp{"[0, 60) ", "[60, 70)", "[70, 80)","[80, 90)", "[90, 100]"};
for(int i = tmp.size()-1; i >= 0; --i)
cout << tmp[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t"
<< std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i]*100 << "%" << endl;
}
task2.cpp
`#include "GradeCalc.hpp"
include
void test() {
int n;
cout << "输入班级人数: ";
cin >> n;
GradeCalc c1("OOP", n);
cout << "录入成绩: " << endl;;
c1.input();
cout << "输出成绩: " << endl;
c1.output();
cout << string(20, '*') + "课程成绩信息" + string(20, '*') << endl;
c1.info();
}
int main() {
test();
}
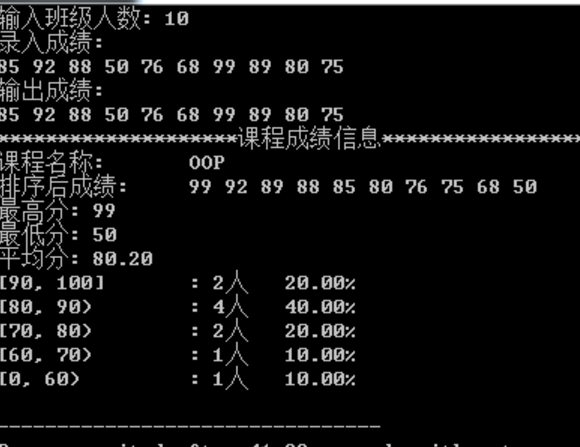
`
/头文件:
sort,max-element,min-element->algorithm(算法)
setprecision->iomanip(格式化io的功能)
accumulate,iota->numeric(数值操作函数)/
2/1:成绩存储在派生类GradeCalc中,(根据类的继承,可以推断其实就是存在动态一维数组,利用this指针存在vector容器当中)
通过this->begin(),this->end(),访问成绩
通过push-back(grade)存入成绩
2/2:
acccumulate是标准名称库中的求和函数,前三个参数分别是起始迭代器和结束迭代器,以及初始值,如line68中this->begin(),this->end(),0,实现从vector容器的第一个值迭代到最后实现求和。
首先需要了解到求和函数实际上是一个模板函数,其返回值和初始值类型保持一致,因此返回整形类型,但是平均值是double类型,因此需要1.0,如去掉那么将舍弃小数部分。
/sort(,,greater
2/3:有可能成绩有0.5的存在,那么数据类型就是double类型,那么可以用类模板完善
3.Gradecalc.hpp
`#include
include
include
include
include
include
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
class GradeCalc {
public:
GradeCalc(const string &cname, int size);
void input(); // 录入成绩
void output() const; // 输出成绩
void sort(bool ascending = false); // 排序 (默认降序)
int min() const; // 返回最低分
int max() const; // 返回最高分
float average() const; // 返回平均分
void info(); // 输出课程成绩信息
private:
void compute(); // 成绩统计
private:
string course_name; // 课程名
int n; // 课程人数
vector
vector
vector
};
GradeCalc::GradeCalc(const string &cname, int size): course_name{cname}, n{size} {}
void GradeCalc::input() {
int grade;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> grade;
grades.push_back(grade);
}
}
void GradeCalc::output() const {
for(int grade: grades)
cout << grade << " ";
cout << endl;
}
void GradeCalc::sort(bool ascending) {
if(ascending)
std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end());
else
std::sort(grades.begin(), grades.end(), std::greater
}
int GradeCalc::min() const {
return *std::min_element(grades.begin(), grades.end());
}
int GradeCalc::max() const {
return *std::max_element(grades.begin(), grades.end());
}
float GradeCalc::average() const {
return std::accumulate(grades.begin(), grades.end(), 0) * 1.0 / n;
}
void GradeCalc::compute() {
for(int grade: grades) {
if(grade < 60)
counts.at(0)++;
else if(grade >= 60 && grade < 70)
counts.at(1)++;
else if(grade >= 70 && grade < 80)
counts.at(2)++;
else if(grade >= 80 && grade < 90)
counts.at(3)++;
else if(grade >= 90)
counts.at(4)++;
}
for(int i = 0; i < rates.size(); ++i)
rates.at(i) = counts.at(i) *1.0 / n;
}
void GradeCalc::info() {
cout << "课程名称:\t" << course_name << endl;
cout << "排序后成绩: \t";
sort(); output();
cout << "最高分:\t" << max() << endl;
cout << "最低分:\t" << min() << endl;
cout << "平均分:\t" << std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << average() << endl;
compute(); // 统计各分数段人数、比例
vector<string> tmp{"[0, 60) ", "[60, 70)", "[70, 80)","[80, 90)", "[90, 100]"};
for(int i = tmp.size()-1; i >= 0; --i)
cout << tmp[i] << "\t: " << counts[i] << "人\t"
<< std::fixed << std::setprecision(2) << rates[i]*100 << "%" << endl;
} task3.cpp#include "GradeCalc.hpp"
include
void test() {
int n;
cout << "输入班级人数: ";
cin >> n;
GradeCalc c1("OOP", n);
cout << "录入成绩: " << endl;;
c1.input();
cout << "输出成绩: " << endl;
c1.output();
cout << string(20, '*') + "课程成绩信息" + string(20, '*') << endl;
c1.info();
}
int main() {
test();
}`
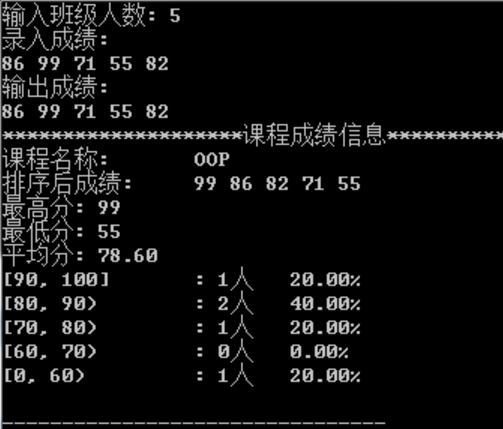
3/1:
存储在grades这个vector容器中
grades.begin(),grades.end()
grades.push-back(grade)
3/2:对于类的设计,类的继承和类的组合在某些面向对象的任务中相当于两条实现相同功能的途径,通过改变类的接口内部函数和数据成员的实现而不需要改变接口。
4/1
`#include
include
include
using namespace std;
void test1() {
string s1, s2;
cin >> s1 >> s2; // cin: 从输入流读取字符串, 碰到空白符(空格/回车/Tab)即结束
cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl;
}
void test2() {
string s1, s2;
getline(cin, s1); // getline(): 从输入流中提取字符串,直到遇到换行符
getline(cin, s2);
cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl;
}
void test3() {
string s1, s2;
getline(cin, s1, ' '); //从输入流中提取字符串,直到遇到指定分隔符
getline(cin, s2);
cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl;
cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl;
}
int main() {
cout << "测试1: 使用标准输入流对象cin输入字符串" << endl;
test1();
cout << endl;
cout << "测试2: 使用函数getline()输入字符串" << endl;
test2();
cout << endl;
cout << "测试3: 使用函数getline()输入字符串, 指定字符串分隔符" << endl;
test3();
}`
line35的作用对象是缓冲区---遇到换行符时清除前面所有的字符或清除输入流中所有的字符。关键字就是清除操作,避免前面的输入对有序的影响.
如果删除,多次输入时,上次输入会留下一个换行符,在test2中,s1直接提取\n,即得空字符串
cin的结束符是空格,回车,tab
getline可以指定换行符,默认是换行符.
4/2:
`#include
include
include
include
using namespace std;
void output(const vector
for(auto &s: v)
cout << s << endl;
}
void test() {
int n;
while(cout << "Enter n: ", cin >> n) {
vector
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
string s;
cin >> s;
v1.push_back(s);
}
cout << "output v1: " << endl;
output(v1);
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
cout << "测试: 使用cin多组输入字符串" << endl;
test();
}`

4/3
`#include
include
include
include
using namespace std;
void output(const vector
for(auto &s: v)
cout << s << endl;
}
void test() {
int n;
while(cout << "Enter n: ", cin >> n) {
cin.ignore(numeric_limits
vector<string> v2;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
string s;
getline(cin, s);
v2.push_back(s);
}
cout << "output v2: " << endl;
output(v2);
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
cout << "测试: 使用函数getline()多组输入字符串" << endl;
test();
}`

4/2:同上,由于getline的结束符是换行符,多次输入时上次的输入流中残余的换行符会影响后一次的读取。
`#pragma once
include
using namespace std;
template
class GameResourceManager {
public:
GameResourceManager(T x) :resource{x} {}
T get() {
return resource;
}
T update(T x) {
if (resource+x < 0)
resource = 0;
else resource += x;
return resource;
}
private:
T resource;
}; 6.info.hpp#pragma once
include
include
include
using namespace std;
class info {
public:
info(string name, string x, string c, int y): nickname(name), contact(x), city(c), n(y) {}
void display() {
cout << left<< setw(15) << "昵称:";
cout << nickname<<endl;
cout << left<< setw(15) << "联系方式:";
cout << contact<<endl;
cout << left<< setw(15) << "所在城市:";
cout << city<<endl;
cout << left << setw(15) << "预定人数:";
cout << n<<endl;
}
private:
string nickname;
string contact;
string city;
int n;
};
info.cpp
include"info.hpp"
include
include
include "info.hpp"
include
include
include
using std::vector;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;}
info.cppint main() {
const int capacity = 100;
vector
string s1, s2, s3;
int m, count = 0;
char c;
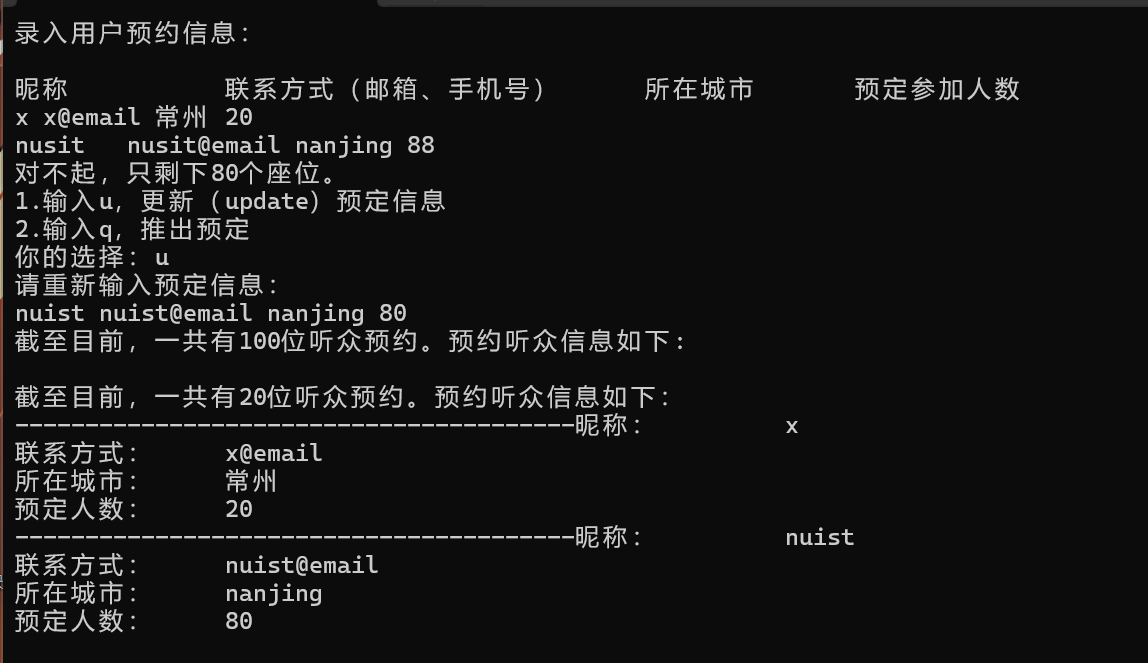
cout << "录入用户预约信息:" << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << left << setw(15) << "昵称" << setw(30) << "联系方式(邮箱、手机号)" << setw(15) << "所在城市" << setw(12) << "预定参加人数" << endl;
while (cin >> s1 >> s2 >> s3 >> m)
{
if (count + m > capacity)
{
cout << "对不起,只剩下" << capacity - count << "个座位。" << endl;
cout << "1.输入u,更新(update)预定信息" << endl;
cout << "2.输入q,推出预定" << endl;
cout << "你的选择:";
cin >> c;
if (c == 'u') {
cout << "请重新输入预定信息:" << endl;
continue;
}
else if (c == 'q')
break;
}
else if (count + m == capacity)
{
info c(s1, s2, s3, m);
audience_list.push_back(c);
cout << "截至目前,一共有" << capacity << "位听众预约。预约听众信息如下:" << endl;
break;
}
else
count += m;
info c(s1, s2, s3, m);
audience_list.push_back(c);//存储
}
cout << endl;
cout << "截至目前,一共有" << count << "位听众预约。预约听众信息如下:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < audience_list.size(); ++i) {
cout << string(40, '-');
audience_list[i].display();
}
}`

7.
date.h
pragma once
class Date {
private:
int year;
int month;
int day;
int totalDays;
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day);
int getYear()const { return year; }
int getMonth()const { return month; }
int getDay()const { return day; }
int getMaxDay()const;
bool isLeapYear()const {
return year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0;
}
void show() const;
int distance(const Date& date)const {
return totalDays - date.totalDays;
}
};
account.h
pragma once
include"date.h"
include"accumulator.h"
include
using namespace std;
class Account {
private:
string id;
double balance;
static double total;
protected:
Account(const Date& date, const string &id);
void record(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc);
void error(const string& msg) const;
public:const string& getId() { return id; }
double getBalance()const { return balance; }
static double getTotal() { return total; }
void show()const;
};
class SavingsAccount:public Account {
private:
Accumulator acc;
double rate;
public:
SavingsAccount(const Date& date, const string& id, double rate);
double getRate() const { return rate; }
void deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc);
void withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc);
void settle(const Date& date);
};
class CreditAccount :public Account {
private:
Accumulator acc;
double credit;
double rate;
double fee;
double getDebt()const {
double balance = getBalance();
return(balance < 0 ? balance : 0);
}
public:CreditAccount(const Date& date, const string& id, double credit, double rate, double fee);
double getCredit()const { return credit; }
double getRate()const { return rate; }
double getFee() const { return fee; }
double getAvailableCredit()const {
if (getBalance() < 0)return credit + getBalance();
else return credit;
}
void deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc);
void withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc);
void settle(const Date& date);
void show()const;
};
task7.cpp
include "account.h"
include
using namespace std;
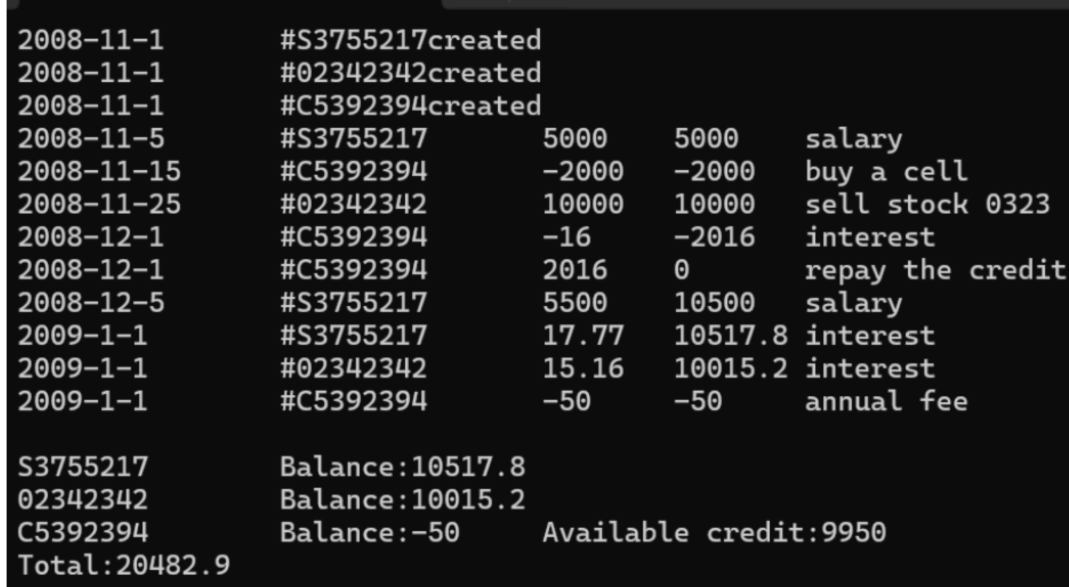
int main() {
Date date(2008, 11, 1);
SavingsAccount sa1(date, "S3755217", 0.015);
SavingsAccount sa2(date, "02342342", 0.015);
CreditAccount ca(date, "C5392394", 10000, 0.0005, 50);
sa1.deposit(Date(2008, 11, 5), 5000, "Salary");
ca.withdraw(Date(2008, 11, 15), 2000, "buy a cell");
sa2.deposit(Date(2008, 11, 25), 10000, "sell stock 0323");
ca.settle(Date(2008, 12, 1));
ca.deposit(Date(2008, 12,1), 2016, "repay the credit");
sa1.deposit(Date(2008, 12, 5), 5500, "salary");
sa1.settle(Date(2009, 1, 1));
sa2.settle(Date(2009, 1, 1));
ca.settle(Date(2009, 1, 1));
cout << endl;
sa1.show(); cout << endl;
sa2.show(); cout << endl;
ca.show(); cout << endl;
cout << "Total: " << Account::getTotal() << endl;
return 0;
}
accumulator.h
pragma once
include"date.h"
include"accumulator.h"
include
using namespace std;
class Account {
private:
string id;
double balance;
static double total;
protected:
Account(const Date& date, const string &id);
void record(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc);
void error(const string& msg) const;
public:const string& getId() { return id; }
double getBalance()const { return balance; }
static double getTotal() { return total; }
void show()const;
};
class SavingsAccount:public Account {
private:
Accumulator acc;
double rate;
public:
SavingsAccount(const Date& date, const string& id, double rate);
double getRate() const { return rate; }
void deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc);
void withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc);
void settle(const Date& date);
};
class CreditAccount :public Account {
private:
Accumulator acc;
double credit;
double rate;
double fee;
double getDebt()const {
double balance = getBalance();
return(balance < 0 ? balance : 0);
}
public:CreditAccount(const Date& date, const string& id, double credit, double rate, double fee);
double getCredit()const { return credit; }
double getRate()const { return rate; }
double getFee() const { return fee; }
double getAvailableCredit()const {
if (getBalance() < 0)return credit + getBalance();
else return credit;
}
void deposit(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc);
void withdraw(const Date& date, double amount, const string& desc);
void settle(const Date& date);
void show()const;
};
派生类通过继承的方式无需重复定义基类中的成员,对于接口,如若功能相同,则可以直接调用,如若功能需要增加,可以在作用域标识符引用的基础上增加新的功能。eg:CredieAccount.show
由于每一个类对应的指针类型不同,因此不能用循环对于不同的类杂糅在一块进行操作,只能单独处理,因此可以引入虚基类的概念。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号