296. Best Meeting Point
Given an m x n binary grid grid where each 1 marks the home of one friend, return the minimal total travel distance.
The total travel distance is the sum of the distances between the houses of the friends and the meeting point.
The distance is calculated using Manhattan Distance, where distance(p1, p2) = |p2.x - p1.x| + |p2.y - p1.y|.
Example 1:
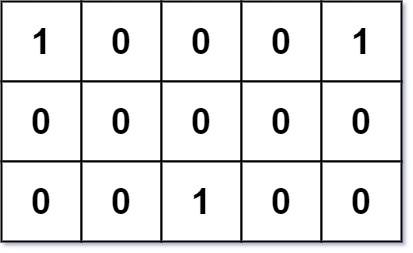
Input: grid = [[1,0,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,1,0,0]] Output: 6 Explanation: Given three friends living at (0,0), (0,4), and (2,2). The point (0,2) is an ideal meeting point, as the total travel distance of 2 + 2 + 2 = 6 is minimal. So return 6.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,1]] Output: 1
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 200grid[i][j]is either0or1.- There will be at least two friends in the
grid.
class Solution { /** 先看一维时有两个点A和B的情况, ______A_____P_______B_______ 那么我们可以发现,只要开会为位置P在[A, B]区间内,不管在哪,距离之和都是A和B之间的距离,如果P不在[A, B]之间,那么距离之和就会大于A和B之间的距离,那么我们现在再加两个点C和D: ______C_____A_____P_______B______D______ P点的最佳位置就是在[A, B]区间内,这样和四个点的距离之和为AB距离加上CD距离,在其他任意一点的距离都会大于这个距离。给位置排好序,然后用最后一个坐标减去第一个坐标,即CD距离,倒数第二个坐标减去第二个坐标,即AB距离,以此类推,直到最中间停止,那么一维的情况分析出来了,二维的情况就是两个一维相加即可 为了保证总长度最小,我们只要保证每条路径尽量不要重复就行了,比如1->2->3<-4这种一维的情况,如果起点是1,2和4,那2->3和1->2->3这两条路径就有重复了。为了尽量保证右边的点向左走,左边的点向右走,那我们就应该去这些点中间的点作为交点。由于是曼哈顿距离,我们可以分开计算横坐标和纵坐标,结果是一样的。所以我们算出各个横坐标到中点横坐标的距离,加上各个纵坐标到中点纵坐标的距离,就是结果了。 */ public int minTotalDistance(int[][] grid) { List<Integer> xs = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> ys = new ArrayList<>(); // 收集所有friends x 和 y list for(int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) { if(grid[i][j] == 1) { xs.add(i); ys.add(j); } } } Collections.sort(xs); Collections.sort(ys); return sum(xs) + sum(ys); } private int sum(List<Integer> list) { // 去中间点,或者偶数的时候中间两点任意一个,都可以得到最小距离 int mid = list.size() / 2; int result = 0; for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { result += Math.abs(list.get(i) - list.get(mid)); } return result; } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号