weighted job schedule 1235
1235. Maximum Profit in Job Scheduling
Hard
We have n jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from startTime[i] to endTime[i], obtaining a profit of profit[i].
You're given the startTime, endTime and profit arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
If you choose a job that ends at time X you will be able to start another job that starts at time X.
Example 1:
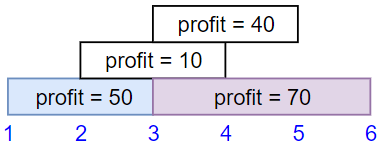
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70] Output: 120 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first and fourth job. Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
Example 2:
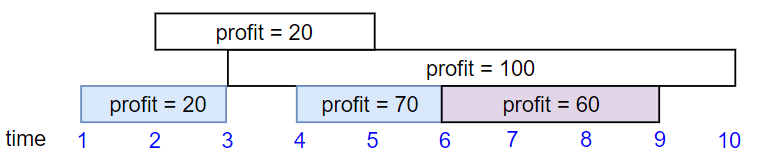
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60] Output: 150 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job. Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
Example 3:
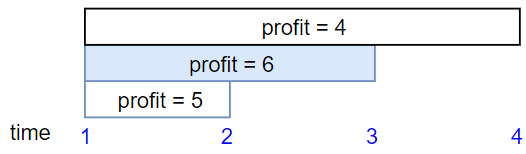
Input: startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4] Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 1041 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 1091 <= profit[i] <= 104
解法1:
class Solution { /** 举例: [1,3,50] [2,4,10] [3,5,40] [3,6,70] [1,6,80] 按照结束时间逐个遍历 [1,3,50] 截止3,可以产生50profit,[<3,50>] [2,4,10] 截止4,根据开始时间2,搜索2之前可以产生的profit为0,加上本次profit为10(0+10),而截至上次3已经可以产生50profit,因此 treemap:[<3,50>,<4,50>] [3,5,40] 截止5,根据开始时间3,搜索3之前可以产生的profit为50,加上本地profit为40(50+40),而截至上次4可以产生50profit,因此 treemap:[<3,50>,<4,50>,<5,90>] [3,6,70] 截止6,根据开始时间3,搜索3之前可以产生的profit为50,加上本地profit为70(50+70),而截至上次5可以产生90profit,因此 treemap:[<3,50>,<4,50>,<5,90>,<6,120>] [1,6,80] 截止6,根据开始时间1,搜索1之前可以产生的profit为0,加上本地profit为80(0+80),而截至上次6可以产生90profit,因此 treemap:[<3,50>,<4,50>,<5,90>,<6,120>] */ record Job(int start, int end, int profit){} public int jobScheduling(int[] startTime, int[] endTime, int[] profit) { Job[] jobs = new Job[startTime.length]; for(int i = 0; i < startTime.length; i++) { jobs[i] = new Job(startTime[i], endTime[i], profit[i]); } //按照结束时间进行排序 Arrays.sort(jobs,(x, y) -> x.end - y.end); // <endtime, profit> TreeMap<Integer, Integer> treemap = new TreeMap<>(); treemap.put(0, 0); for(Job job: jobs) { //job.start前能达到的profit + 当前profit int currProfit = treemap.floorEntry(job.start).getValue() + job.profit; //取出最近时间的profit int lastProfit = treemap.lastEntry().getValue(); //两个profit 取大值,即为当前时间点可以产生的最大profit int maxProfit = Math.max(currProfit, lastProfit); treemap.put(job.end, maxProfit); } //取出最近时间的profit即为结果 return treemap.lastEntry().getValue(); } }
解法2: 使用heap
class Solution { public int jobScheduling(int[] startTime, int[] endTime, int[] profit) { List<int[]> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0; i < startTime.length; i++) { list.add(new int[]{startTime[i], endTime[i], profit[i]}); } //将任务按照开始时间排序 Collections.sort(list, (x, y) -> x[0] - y[0]); //创建一个堆,用于存放截止某些之间的最大profit PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> x[0] - y[0]); int preProfit = 0; for(int[] tuple : list) { int start = tuple[0], end = tuple[1], value = tuple[2]; //如果小于当前start,那么只需要保留截止start之前的最大profit即可 while(!pq.isEmpty() && pq.peek()[0] <= start) { preProfit = Math.max(preProfit, pq.poll()[1]); } //将当前value + starttime之前的最大profit, 放入heap pq.offer(new int[]{end, value + preProfit}); } //轮询heap,找出最大profit int result = 0; while(!pq.isEmpty()) { result = Math.max(result, pq.poll()[1]); } return result; } }
Follow up 1: 将实现max profit的joblist 打印出来
class Solution { public int jobScheduling(int[] startTime, int[] endTime, int[] profit) { Job[] jobs = new Job[startTime.length]; for(int i = 0; i < startTime.length; i++) { jobs[i] = new Job(startTime[i], endTime[i], profit[i]); } Arrays.sort(jobs, (x, y) -> x.end - y.end); TreeMap<Integer, MaxProfit> treemap = new TreeMap<>(); treemap.put(0, new MaxProfit(0,new ArrayList())); for(Job job : jobs) { MaxProfit max = treemap.floorEntry(job.start).getValue(); int maxProfit = max.profit + job.profit; MaxProfit last = treemap.lastEntry().getValue();
//如果当前job会产生更大profit,要在之前job中添加当前job 进入list if(maxProfit > last.profit) { MaxProfit curr = new MaxProfit(maxProfit, new ArrayList(max.list)); curr.list.add(job); treemap.put(job.end, curr); }
//如果上一个的job能产生更大profit,直接复制list过来 else{ MaxProfit curr = new MaxProfit(last.profit, new ArrayList(last.list)); treemap.put(job.end, curr); } } MaxProfit result = treemap.lastEntry().getValue(); for(Job j : result.list) { System.out.println(j); } return result.profit; } } class MaxProfit { MaxProfit(int profit, List<Job> list) { this.profit = profit; this.list = list; } int profit; List<Job> list; } class Job{ int start; int end; int profit; Job(int start, int end, int profit) { this.start = start; this.end = end; this.profit = profit; } @Override public String toString() { return this.start + ":" + this.end + ":" + this.profit; } }
Follow up 2: 将max profit




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号