tree reconstruct 834
There is an undirected connected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1 and n - 1 edges.
You are given the integer n and the array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
Return an array answer of length n where answer[i] is the sum of the distances between the ith node in the tree and all other nodes.
Example 1:
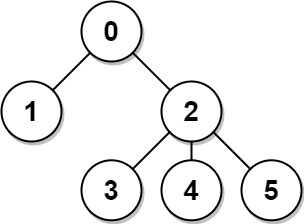
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[2,4],[2,5]] Output: [8,12,6,10,10,10] Explanation: The tree is shown above. We can see that dist(0,1) + dist(0,2) + dist(0,3) + dist(0,4) + dist(0,5) equals 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 8. Hence, answer[0] = 8, and so on.
Example 2:

Input: n = 1, edges = [] Output: [0]
Example 3:
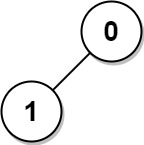
Input: n = 2, edges = [[1,0]] Output: [1,1]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 3 * 104edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != bi- The given input represents a valid tree.
class Solution { public int[] sumOfDistancesInTree(int n, int[][] edges) { //0.建图,这么做可以加速每个节点访问其子节点的速度 List<Integer>[] graph = new List[n]; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) graph[i] = new ArrayList(); for(int[] edge : edges) { int a = edge[0], b = edge[1]; graph[a].add(b); graph[b].add(a); } //将0作为root节点,计算所有子树的size //1.define a root node 0 //2.dfs calculate all the subtree size int[] size = new int[n]; subtreeSize(0, graph, -1, size); //计算root节点到所有节点的距离和 //3.dfs calculate the root node's distance to all the other nodes int[] result = new int[n]; result[0] = rootDistance(0, graph, -1, size); //最后递归根据父节点计算每个节点到其他点的距离和 //4.dfs calculate all the node's distance to the other nodes base on the formula calculateSubTree(0, graph, -1, size, result); return result; } //计算子书size private int subtreeSize(int curr, List<Integer>[] graph, int parent, int[] size){ int sum = 0; for(int child : graph[curr]){ if(child == parent) continue; sum += subtreeSize(child, graph, curr, size); } size[curr] = sum + 1; return size[curr]; } //计算子树距离和 private int rootDistance(int curr, List<Integer>[] graph, int parent, int[] size){ int result = 0; for(int child : graph[curr]){ if(child == parent) continue; //离所有child的距离,是child的所有距离和 + 1 + child的所有child个数(因为每增加一层,你离所有孙子的距离都得加一层) result += rootDistance(child, graph, curr, size) + size[child]; } return result; } //基于父节点计算子树距离和 private void calculateSubTree(int curr, List<Integer>[] graph, int parent, int[] size, int[] result){ if(parent != -1) result[curr] = result[parent] + graph.length - 2 * size[curr]; for(int child : graph[curr]){ if(child == parent) continue; calculateSubTree(child, graph, curr, size, result); } } }
n cities numbered from 0 to n - 1 and exactly n - 1 roads. The capital city is city 0. You are given a 2D integer array roads where roads[i] = [ai, bi] denotes that there exists a bidirectional road connecting cities ai and bi.There is a meeting for the representatives of each city. The meeting is in the capital city.
There is a car in each city. You are given an integer seats that indicates the number of seats in each car.
A representative can use the car in their city to travel or change the car and ride with another representative. The cost of traveling between two cities is one liter of fuel.
Return the minimum number of liters of fuel to reach the capital city.
Example 1:
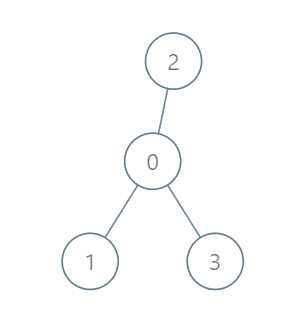
Input: roads = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]], seats = 5 Output: 3 Explanation: - Representative1 goes directly to the capital with 1 liter of fuel. - Representative2 goes directly to the capital with 1 liter of fuel. - Representative3 goes directly to the capital with 1 liter of fuel. It costs 3 liters of fuel at minimum. It can be proven that 3 is the minimum number of liters of fuel needed.
Example 2:
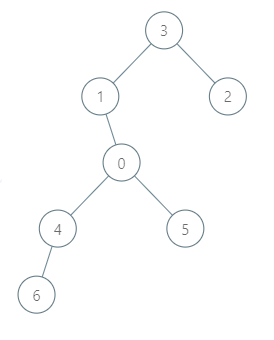
Input: roads = [[3,1],[3,2],[1,0],[0,4],[0,5],[4,6]], seats = 2 Output: 7 Explanation: - Representative2 goes directly to city 3 with 1 liter of fuel. - Representative2 and representative3 go together to city 1 with 1 liter of fuel. - Representative2 and representative3 go together to the capital with 1 liter of fuel. - Representative1 goes directly to the capital with 1 liter of fuel. - Representative5 goes directly to the capital with 1 liter of fuel. - Representative6 goes directly to city 4 with 1 liter of fuel. - Representative4 and representative6 go together to the capital with 1 liter of fuel. It costs 7 liters of fuel at minimum. It can be proven that 7 is the minimum number of liters of fuel needed.
Example 3:

Input: roads = [], seats = 1 Output: 0 Explanation: No representatives need to travel to the capital city.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 105roads.length == n - 1roads[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nai != biroadsrepresents a valid tree.1 <= seats <= 105
解法1: dfs
class Solution { long result = 0; long seats; public long minimumFuelCost(int[][] roads, int seats) { // 创建graph List<Integer>[] roadMap = buildMap(roads); this.seats = seats; //从capital出发计算与它直连的节点 for(int sub : roadMap[0]) { dfs(roadMap, sub, 0); } return result; } private List<Integer>[] buildMap(int[][] roads) { int len = roads.length + 1; List<Integer>[] roadMap = new List[len]; for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) roadMap[i] = new ArrayList<>(); for(int[] road : roads) { roadMap[road[0]].add(road[1]); roadMap[road[1]].add(road[0]); } return roadMap; } // 返回当前子树节点个数 private long dfs(List<Integer>[] roadMap, int curr, int parent) { // 默认只有root自己 long total = 1; // 遍历所有子节点 for(int other : roadMap[curr]) { if(other != parent) { total += dfs(roadMap, other, curr); } } // 计算当前节点去父节点需要多少油耗,加总到result result += Math.ceil((double) total / seats); return total; } }
解法2, bfs, 拨洋葱




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号