dfs + memo 1359,1547,2707,3250, 3276, 64
Given n orders, each order consist in pickup and delivery services.
Count all valid pickup/delivery possible sequences such that delivery(i) is always after of pickup(i).
Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 10^9 + 7.
Example 1:
Input: n = 1 Output: 1 Explanation: Unique order (P1, D1), Delivery 1 always is after of Pickup 1.
Example 2:
Input: n = 2 Output: 6 Explanation: All possible orders: (P1,P2,D1,D2), (P1,P2,D2,D1), (P1,D1,P2,D2), (P2,P1,D1,D2), (P2,P1,D2,D1) and (P2,D2,P1,D1). This is an invalid order (P1,D2,P2,D1) because Pickup 2 is after of Delivery 2.
Example 3:
Input: n = 3 Output: 90
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 500
第一步: 暴力dfs 时间复杂度为: O(2N)
class Solution { public int countOrders(int n) { return helper(n, n); } private int helper(int d, int p) { if(d < 0 || p < 0 || d < p) return 0; if(d == 0 && p == 0) return 1; int result = 0; if(d == p) {//所有pickup已经deliver,因此只能先pickup result += helper(d, p - 1) * p; } if(d > p) { // deliver > pickup,因此既可以继续deliver ,也可以pickup result += helper(d, p - 1) * p; //因为有p个可以deliver,因此有p种deliver的方法 result += helper(d - 1, p) * (d - p);//只有已经pickup的可以deliver,因此有d-p中deliver的方法 } return result; } }
第二步:考虑越界问题,将int改为long,并且增加取余
class Solution { private final int MOD = 1000000007; public int countOrders(int n) { return (int)helper(n, n); } private long helper(int d, int p) { if(d < 0 || p < 0 || d < p) return 0; if(d == 0 && p == 0) return 1; long result = 0; if(d == p) {//所有pickup已经deliver,因此只能先pickup result = (result + helper(d, p - 1) * p) % MOD; } if(d > p) { // deliver > pickup,因此既可以继续deliver ,也可以pickup result = (result + helper(d, p - 1) * p) % MOD; //因为有p个可以deliver,因此有p种deliver的方法 result = (result + helper(d - 1, p) * (d - p)) % MOD;//只有已经pickup的可以deliver,因此有d-p中deliver的方法 } return result; } }
第三步:增加memo避免重复计算, 时间复杂度为 O(N2), 空间复杂度为 O(N2).
class Solution { private final int MOD = 1000000007; public int countOrders(int n) { return (int)helper(n, n, new Long[n + 1][n + 1]); } private long helper(int d, int p, Long[][] mem) { if(d < 0 || p < 0 || d < p) return 0; if(d == 0 && p == 0) return 1; if(mem[d][p] != null) return mem[d][p]; long result = 0; if(d == p) {//所有pickup已经deliver,因此只能先pickup result = (result + helper(d, p - 1, mem) * p) % MOD; } if(d > p) { // deliver > pickup,因此既可以继续deliver ,也可以pickup result = (result + helper(d, p - 1, mem) * p) % MOD; //因为有p个可以deliver,因此有p种deliver的方法 result = (result + helper(d - 1, p, mem) * (d - p)) % MOD;//只有已经pickup的可以deliver,因此有d-p中deliver的方法 } mem[d][p] = result; return mem[d][p]; } }
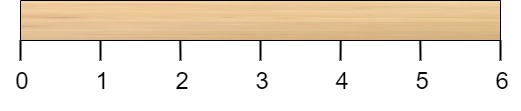
Given a wooden stick of length n units. The stick is labelled from 0 to n. For example, a stick of length 6 is labelled as follows:
Given an integer array cuts where cuts[i] denotes a position you should perform a cut at.
You should perform the cuts in order, you can change the order of the cuts as you wish.
The cost of one cut is the length of the stick to be cut, the total cost is the sum of costs of all cuts. When you cut a stick, it will be split into two smaller sticks (i.e. the sum of their lengths is the length of the stick before the cut). Please refer to the first example for a better explanation.
Return the minimum total cost of the cuts.
Example 1:
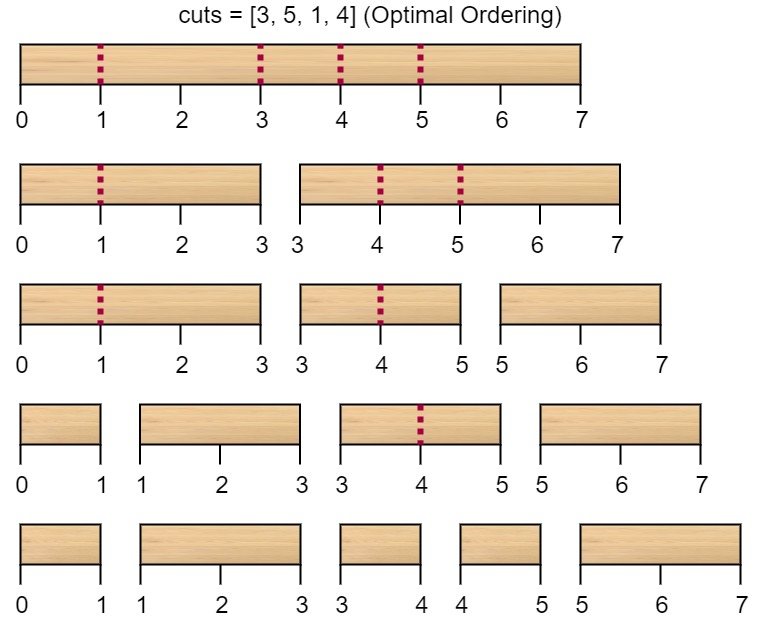
Input: n = 7, cuts = [1,3,4,5] Output: 16 Explanation: Using cuts order = [1, 3, 4, 5] as in the input leads to the following scenario:
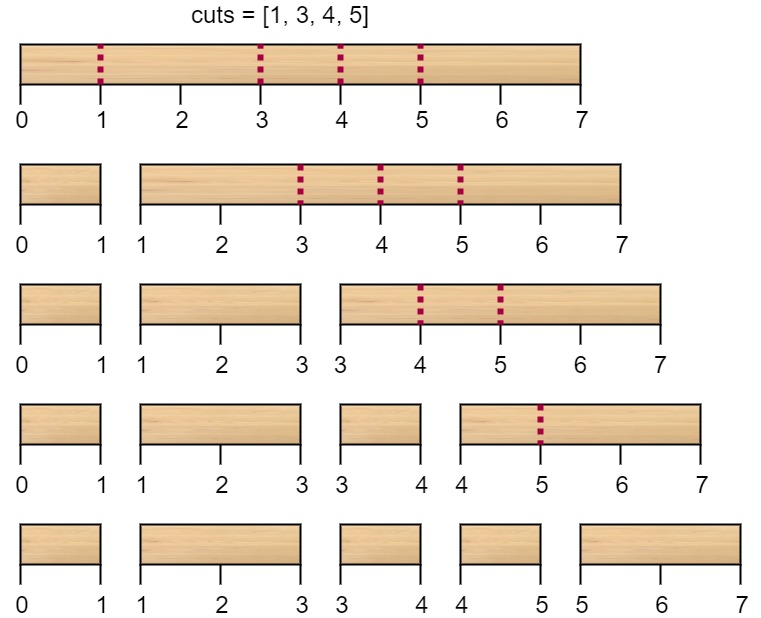
The first cut is done to a rod of length 7 so the cost is 7. The second cut is done to a rod of length 6 (i.e. the second part of the first cut), the third is done to a rod of length 4 and the last cut is to a rod of length 3. The total cost is 7 + 6 + 4 + 3 = 20. Rearranging the cuts to be [3, 5, 1, 4] for example will lead to a scenario with total cost = 16 (as shown in the example photo 7 + 4 + 3 + 2 = 16).
Example 2:
Input: n = 9, cuts = [5,6,1,4,2] Output: 22 Explanation: If you try the given cuts ordering the cost will be 25. There are much ordering with total cost <= 25, for example, the order [4, 6, 5, 2, 1] has total cost = 22 which is the minimum possible.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1061 <= cuts.length <= min(n - 1, 100)1 <= cuts[i] <= n - 1- All the integers in
cutsarray are distinct.
解法:尝试在每一个位置进行切分尝试
class Solution { public int minCost(int n, int[] cuts) { //排序 Arrays.sort(cuts); int[] newCuts = new int[cuts.length + 2]; //将头尾也加入 for(int i = 0; i < cuts.length; i++){ newCuts[i + 1] = cuts[i]; } newCuts[cuts.length + 1] = n; //执行dfs return cut(0, newCuts.length - 1, newCuts); } private int cut(int start, int end, int[] cuts) { //如果已经相邻则不需要继续切分 if(start >= end - 1) return 0; //默认切分cost为最大值 int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //尝试从每个非头尾位置进行切分 for(int i = start + 1; i < end; i++) { //取最小值 result = Math.min(result, cut(start, i, cuts) + cut(i, end, cuts) + cuts[end] - cuts[start]); } return result; } }
在暴力dfs的基础上增加memo
class Solution { public int minCost(int n, int[] cuts) { //排序 Arrays.sort(cuts); int[] newCuts = new int[cuts.length + 2]; //将头尾也加入 for(int i = 0; i < cuts.length; i++){ newCuts[i + 1] = cuts[i]; } newCuts[cuts.length + 1] = n; //增加memo int[][] memo = new int[newCuts.length][newCuts.length]; for(int[] arr : memo) Arrays.fill(arr, -1); //执行dfs return cut(0, newCuts.length - 1, newCuts, memo); } private int cut(int start, int end, int[] cuts, int[][] memo) { //如果已经相邻则不需要继续切分 if(start >= end - 1) return 0; //已经计算过的直接返回 if(memo[start][end] != -1) return memo[start][end]; //默认切分cost为最大值 int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //尝试从每个非头尾位置进行切分 for(int i = start + 1; i < end; i++) { //取最小值 result = Math.min(result, cut(start, i, cuts, memo) + cut(i, end, cuts, memo) + cuts[end] - cuts[start]); } memo[start][end] = result; return result; } }
You are given a 0-indexed string s and a dictionary of words dictionary. You have to break s into one or more non-overlapping substrings such that each substring is present in dictionary. There may be some extra characters in s which are not present in any of the substrings.
Return the minimum number of extra characters left over if you break up s optimally.
Example 1:
Input: s = "leetscode", dictionary = ["leet","code","leetcode"] Output: 1 Explanation: We can break s in two substrings: "leet" from index 0 to 3 and "code" from index 5 to 8. There is only 1 unused character (at index 4), so we return 1.
Example 2:
Input: s = "sayhelloworld", dictionary = ["hello","world"] Output: 3 Explanation: We can break s in two substrings: "hello" from index 3 to 7 and "world" from index 8 to 12. The characters at indices 0, 1, 2 are not used in any substring and thus are considered as extra characters. Hence, we return 3.
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 501 <= dictionary.length <= 501 <= dictionary[i].length <= 50dictionary[i]andsconsists of only lowercase English lettersdictionarycontains distinct words
这个dfs解法会超时
class Solution: def minExtraChar(self, s: str, dictionary: List[str]) -> int: slen = len(s) #计算从curr开始的字符串 def dfs(curr: int): #如果是末尾,那么返回0 if curr == slen: return 0 #设置结果为一个大值 result = 1000000 #从curr开始向后切分 for i in range(curr, slen): ts = s[curr: i + 1] #如果切分的子串在dict中,那么extra cost为0,最终结果为i+1后面的cost if ts in dictionary: result = min(result, dfs(i + 1)) #如果切分的子串不在dict中,那么extra cost为0,最终结果为i+1后面的cost + 当前子串长度 else: result = min(result, dfs(i + 1) + i + 1 - curr) return result return dfs(0)
增加momoization
class Solution: def minExtraChar(self, s: str, dictionary: List[str]) -> int: slen = len(s) mem = [-1] * slen #计算从curr开始的字符串 def dfs(curr: int): #如果是末尾,那么返回0 if curr == slen: return 0 if mem[curr] != -1: return mem[curr] #设置结果为一个大值 result = 1000000 #从curr开始向后切分 for i in range(curr, slen): ts = s[curr: i + 1] #如果切分的子串在dict中,那么extra cost为0,最终结果为i+1后面的cost if ts in dictionary: result = min(result, dfs(i + 1)) #如果切分的子串不在dict中,那么extra cost为0,最终结果为i+1后面的cost + 当前子串长度 else: result = min(result, dfs(i + 1) + i + 1 - curr) mem[curr] = result return result return dfs(0)
3250. Find the Count of Monotonic Pairs I
You are given an array of positive integers nums of length n.
We call a pair of non-negative integer arrays (arr1, arr2) monotonic if:
- The lengths of both arrays are
n. arr1is monotonically non-decreasing, in other words,arr1[0] <= arr1[1] <= ... <= arr1[n - 1].arr2is monotonically non-increasing, in other words,arr2[0] >= arr2[1] >= ... >= arr2[n - 1].arr1[i] + arr2[i] == nums[i]for all0 <= i <= n - 1.
Return the count of monotonic pairs.
Since the answer may be very large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,3,2]
Output: 4
Explanation:
The good pairs are:
([0, 1, 1], [2, 2, 1])([0, 1, 2], [2, 2, 0])([0, 2, 2], [2, 1, 0])([1, 2, 2], [1, 1, 0])
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,5,5,5]
Output: 126
Constraints:
1 <= n == nums.length <= 20001 <= nums[i] <= 50
解法1: 暴力解
class Solution { int result = 0; public int countOfPairs(int[] nums) { helper(nums, 0, new int[nums.length], new int[nums.length]); return result; } private void helper(int[] nums, int curr, int[] arr1, int[] arr2) { if(curr == nums.length) { result++; return; } for(int i = 0; i <= nums[curr]; i++) { if(curr > 0 && arr1[curr - 1] > i) continue; if(curr > 0 && arr2[curr - 1] < nums[curr] - i) continue; arr1[curr] = i; arr2[curr] = nums[curr] - i; helper(nums, curr + 1, arr1, arr2); } } }
解法2: 加memo
class Solution { private static final int MOD = 1000000007; public int countOfPairs(int[] nums) { // 初始化 memo Long[][][] memo = new Long[nums.length][51][51]; return (int)helper(nums, 0, 0, 0, memo); } private long helper(int[] nums, int curr, int pre1, int pre2, Long[][][] memo) { if(curr == nums.length) return 1; // 如果已经计算过,直接返回 if(memo[curr][pre1][pre2] != null) return memo[curr][pre1][pre2]; long result = 0; for(int i = 0; i <= nums[curr]; i++) { // 如果不是第一个数字,要做arr1->increasing 和 arr2->decreasing 校验 if(curr > 0 && pre1 > i) continue; if(curr > 0 && pre2 < nums[curr] - i) continue; // 累加当前结果 result += helper(nums, curr + 1, i, nums[curr] - i, memo); } // 注意不要超过MOD if(result > MOD) result = result % MOD; memo[curr][pre1][pre2] = result; return result; } }
You are given a 2D matrix grid consisting of positive integers.
You have to select one or more cells from the matrix such that the following conditions are satisfied:
- No two selected cells are in the same row of the matrix.
- The values in the set of selected cells are unique.
Your score will be the sum of the values of the selected cells.
Return the maximum score you can achieve.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,3,2],[1,1,1]]
Output: 8
Explanation:
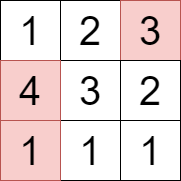
We can select the cells with values 1, 3, and 4 that are colored above.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[8,7,6],[8,3,2]]
Output: 15
Explanation:
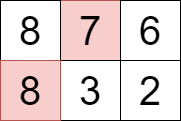
We can select the cells with values 7 and 8 that are colored above.
Constraints:
1 <= grid.length, grid[i].length <= 101 <= grid[i][j] <= 100
dfs
class Solution { public int maxScore(List<List<Integer>> grid) { return helper(grid, 0, new HashSet()); } private int helper(List<List<Integer>> grid, int x, Set<Integer> vals) { int m = grid.size(), n = grid.get(0).size(); if(x >= m) return 0; int max = 0; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int val = grid.get(x).get(i); if(vals.contains(val)) { max = Math.max(helper(grid, x + 1, vals), max); continue; } vals.add(val); max = Math.max(helper(grid, x + 1, vals) + val, max); vals.remove(val); } return max; } }
class Solution { public int maxScore(List<List<Integer>> grid) { // put element into set Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>(); for(int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { for(int j = 0; j < grid.get(i).size(); j++) { int num = grid.get(i).get(j); List<Integer> list = map.getOrDefault(num, new ArrayList()); list.add(i); map.put(num, list); } } // list List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(int num : map.keySet()) { list.add(num); } Collections.sort(list, (x, y) -> y - x); // helper return helper(map, list, 0, 0); } private int helper(Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map, List<Integer> list, int curr, int mask) { if(curr == list.size()) return 0; int num = list.get(curr); int result = 0; for(int row : map.get(num)) { if(((1<<row)&mask) == 0) { result = Math.max(helper(map, list, curr + 1, ((1<<row))|mask) + num, result); } else { result = Math.max(helper(map, list, curr + 1, mask), result); } } return result; } }
class Solution { public int maxScore(List<List<Integer>> grid) { // put element into set Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>(); for(int i = 0; i < grid.size(); i++) { for(int j = 0; j < grid.get(i).size(); j++) { int num = grid.get(i).get(j); List<Integer> list = map.getOrDefault(num, new ArrayList()); list.add(i); map.put(num, list); } } // list List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(int num : map.keySet()) { list.add(num); } Collections.sort(list, (x, y) -> y - x); // helper int maskVal = 1<<grid.size(); Integer[][] memo = new Integer[list.size()][maskVal]; return helper(map, list, 0, 0, memo); } private int helper(Map<Integer, List<Integer>> map, List<Integer> list, int curr, int mask, Integer[][] memo) { if(curr == list.size()) return 0; if(memo[curr][mask] != null) return memo[curr][mask]; int num = list.get(curr); int result = 0; for(int row : map.get(num)) { if(((1<<row)&mask) == 0) { result = Math.max(helper(map, list, curr + 1, ((1<<row))|mask, memo) + num, result); } else { result = Math.max(helper(map, list, curr + 1, mask, memo), result); } } memo[curr][mask] = result; return result; } }
https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-path-sum/




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号