greedy 881,1024,1326, 621, 1488, 3785
You are given an array people where people[i] is the weight of the ith person, and an infinite number of boats where each boat can carry a maximum weight of limit. Each boat carries at most two people at the same time, provided the sum of the weight of those people is at most limit.
Return the minimum number of boats to carry every given person.
Example 1:
Input: people = [1,2], limit = 3 Output: 1 Explanation: 1 boat (1, 2)
Example 2:
Input: people = [3,2,2,1], limit = 3 Output: 3 Explanation: 3 boats (1, 2), (2) and (3)
Example 3:
Input: people = [3,5,3,4], limit = 5 Output: 4 Explanation: 4 boats (3), (3), (4), (5)
Constraints:
1 <= people.length <= 5 * 1041 <= people[i] <= limit <= 3 * 104
最肥的人有可能一人占一条船,当然如果船的载量够大的话,可能还能挤上一个瘦子,那么最瘦的人是最可能挤上去的,所以策略就是胖子加瘦子的上船组合。那么这就是典型的贪婪算法的适用场景啊,首先要给所有人按体重排个序,从瘦子到胖子,这样我们才能快速的知道当前最重和最轻的人。
class Solution { public int numRescueBoats(int[] people, int limit) { Arrays.sort(people); int left = 0,right = people.length-1; int result = 0; while(left<=right){ if(people[right]+people[left]<=limit){ left++;right--; } else{ right--; } result++; } return result; } }
You are given a series of video clips from a sporting event that lasted time seconds. These video clips can be overlapping with each other and have varying lengths.
Each video clip is described by an array clips where clips[i] = [starti, endi] indicates that the ith clip started at starti and ended at endi.
We can cut these clips into segments freely.
- For example, a clip
[0, 7]can be cut into segments[0, 1] + [1, 3] + [3, 7].
Return the minimum number of clips needed so that we can cut the clips into segments that cover the entire sporting event [0, time]. If the task is impossible, return -1.
Example 1:
Input: clips = [[0,2],[4,6],[8,10],[1,9],[1,5],[5,9]], time = 10 Output: 3 Explanation: We take the clips [0,2], [8,10], [1,9]; a total of 3 clips. Then, we can reconstruct the sporting event as follows: We cut [1,9] into segments [1,2] + [2,8] + [8,9]. Now we have segments [0,2] + [2,8] + [8,10] which cover the sporting event [0, 10].
Example 2:
Input: clips = [[0,1],[1,2]], time = 5 Output: -1 Explanation: We cannot cover [0,5] with only [0,1] and [1,2].
Example 3:
Input: clips = [[0,1],[6,8],[0,2],[5,6],[0,4],[0,3],[6,7],[1,3],[4,7],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6],[3,4],[4,5],[5,7],[6,9]], time = 9 Output: 3 Explanation: We can take clips [0,4], [4,7], and [6,9].
Constraints:
1 <= clips.length <= 1000 <= starti <= endi <= 1001 <= time <= 100
class Solution { public int videoStitching(int[][] clips, int time) { //将所有片段进行排序 Arrays.sort(clips, (x,y)->{ if(x[0] != y[0]) return x[0] - y[0]; return x[1] - y[1]; }); //lastEnd 上一段结束时间, end下一段最长结束时间, count需要的clips数量, i当前clip int lastEnd=0, end=0, count=0, i=0; while(end < time){ //所有clip开始时间早于lastEnd的都可以合并,取最大的结束时间 while(i < clips.length && lastEnd >= clips[i][0]){ end = Math.max(end, clips[i++][1]); } //如果lastEnd == end 说明没有可以拼接的clip if(lastEnd == end) return -1; count++; lastEnd = end; } return count; } }
There is a one-dimensional garden on the x-axis. The garden starts at the point 0 and ends at the point n. (i.e The length of the garden is n).
There are n + 1 taps located at points [0, 1, ..., n] in the garden.
Given an integer n and an integer array ranges of length n + 1 where ranges[i] (0-indexed) means the i-th tap can water the area [i - ranges[i], i + ranges[i]] if it was open.
Return the minimum number of taps that should be open to water the whole garden, If the garden cannot be watered return -1.
Example 1:
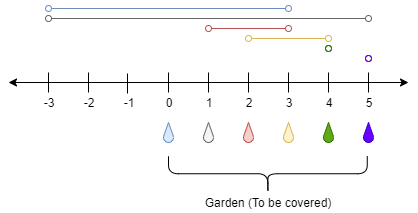
Input: n = 5, ranges = [3,4,1,1,0,0] Output: 1 Explanation: The tap at point 0 can cover the interval [-3,3] The tap at point 1 can cover the interval [-3,5] The tap at point 2 can cover the interval [1,3] The tap at point 3 can cover the interval [2,4] The tap at point 4 can cover the interval [4,4] The tap at point 5 can cover the interval [5,5] Opening Only the second tap will water the whole garden [0,5]
Example 2:
Input: n = 3, ranges = [0,0,0,0] Output: -1 Explanation: Even if you activate all the four taps you cannot water the whole garden.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 104ranges.length == n + 10 <= ranges[i] <= 100
class Solution { public int minTaps(int n, int[] ranges) { //按照覆盖范围生成intervals List<int[]> intervals = new ArrayList(); for(int i=0;i<ranges.length;i++){ int start = i - ranges[i], end = i + ranges[i]; intervals.add(new int[]{start, end}); } //下面即是interval合并,使用最少的interval //先sort Collections.sort(intervals, (x,y)->{ if(x[0] == y[0]) return x[1] - y[1]; return x[0] - y[0]; }); int count = 0; int end = 0;//下一段可以够到的最远位置 int preEnd=0;//上一段结束位置 int i=0; while(end<n){ //所有起始点能与preEnd相接的,统统合并,保留end可以到的最远距离 while(i <= n && preEnd >= intervals.get(i)[0]){//这个位置为啥是<= ? 因为range有n+1个 end = Math.max(end, intervals.get(i)[1]); i++; } //如果end==preEnd 说明没有可以接的上的,返回-1 if(preEnd == end) return -1; count++; preEnd = end; } return count; } }
Given a characters array tasks, representing the tasks a CPU needs to do, where each letter represents a different task. Tasks could be done in any order. Each task is done in one unit of time. For each unit of time, the CPU could complete either one task or just be idle.
However, there is a non-negative integer n that represents the cooldown period between two same tasks (the same letter in the array), that is that there must be at least n units of time between any two same tasks.
Return the least number of units of times that the CPU will take to finish all the given tasks.
Example 1:
Input: tasks = ["A","A","A","B","B","B"], n = 2 Output: 8 Explanation: A -> B -> idle -> A -> B -> idle -> A -> B There is at least 2 units of time between any two same tasks.
Example 2:
Input: tasks = ["A","A","A","B","B","B"], n = 0 Output: 6 Explanation: On this case any permutation of size 6 would work since n = 0. ["A","A","A","B","B","B"] ["A","B","A","B","A","B"] ["B","B","B","A","A","A"] ... And so on.
Example 3:
Input: tasks = ["A","A","A","A","A","A","B","C","D","E","F","G"], n = 2 Output: 16 Explanation: One possible solution is A -> B -> C -> A -> D -> E -> A -> F -> G -> A -> idle -> idle -> A -> idle -> idle -> A
Constraints:
1 <= task.length <= 104tasks[i]is upper-case English letter.- The integer
nis in the range[0, 100].
class Solution { public int leastInterval(char[] tasks, int n) { int[] count = new int[26]; int max = 0; //记录最大频次 for(char c : tasks){ count[c - 'A']++; max = Math.max(max, count[c - 'A']); } //计算最大频次的字母个数 int maxCount = 0; for(int num : count){ if(num == max) maxCount++; } /* 不够 AAABB A__A__A 不够 AAABBBC AB__AB__AB 足够 AAABBCDE A__A__A ABCABDAE */ /* max-1个间隔 * n+1个元素 + maxcount 为啥是max-1个间隔? 3个A中间会有两个间隔 A__A__A 为啥是n+1个元素? 间隔为n,那么一组元素就是n+1 A__ 为啥最后还 加 1? 如果最多频次元素多个的话,最后收尾的那些元素长度也需要加上,如: AAABBBC -> AB__AB__AB */ int result = (max - 1) * (n + 1) + maxCount; return Math.max(result, tasks.length); } }
There is an m x n cake that needs to be cut into 1 x 1 pieces.
You are given integers m, n, and two arrays:
horizontalCutof sizem - 1, wherehorizontalCut[i]represents the cost to cut along the horizontal linei.verticalCutof sizen - 1, whereverticalCut[j]represents the cost to cut along the vertical linej.
In one operation, you can choose any piece of cake that is not yet a 1 x 1 square and perform one of the following cuts:
- Cut along a horizontal line
iat a cost ofhorizontalCut[i]. - Cut along a vertical line
jat a cost ofverticalCut[j].
After the cut, the piece of cake is divided into two distinct pieces.
The cost of a cut depends only on the initial cost of the line and does not change.
Return the minimum total cost to cut the entire cake into 1 x 1 pieces.
Example 1:
Input: m = 3, n = 2, horizontalCut = [1,3], verticalCut = [5]
Output: 13
Explanation:
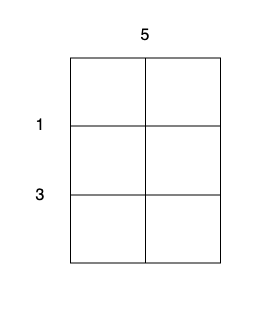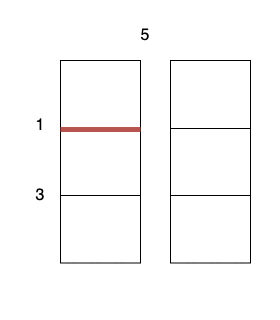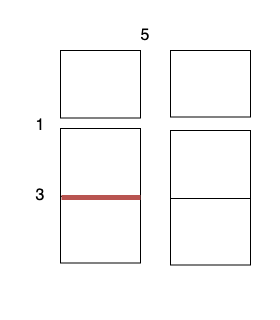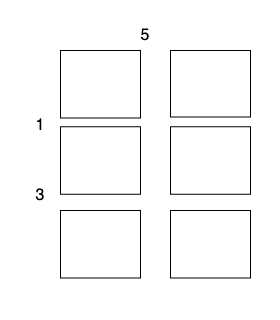
- Perform a cut on the vertical line 0 with cost 5, current total cost is 5.
- Perform a cut on the horizontal line 0 on
3 x 1subgrid with cost 1. - Perform a cut on the horizontal line 0 on
3 x 1subgrid with cost 1. - Perform a cut on the horizontal line 1 on
2 x 1subgrid with cost 3. - Perform a cut on the horizontal line 1 on
2 x 1subgrid with cost 3.
The total cost is 5 + 1 + 1 + 3 + 3 = 13.
Example 2:
Input: m = 2, n = 2, horizontalCut = [7], verticalCut = [4]
Output: 15
Explanation:
- Perform a cut on the horizontal line 0 with cost 7.
- Perform a cut on the vertical line 0 on
1 x 2subgrid with cost 4. - Perform a cut on the vertical line 0 on
1 x 2subgrid with cost 4.
The total cost is 7 + 4 + 4 = 15.
Constraints:
1 <= m, n <= 105horizontalCut.length == m - 1verticalCut.length == n - 11 <= horizontalCut[i], verticalCut[i] <= 103
class Solution { /** 思路:贪心算法, cost最高的应该先切分 */ public long minimumCost(int m, int n, int[] hCut, int[] vCut) { Arrays.sort(hCut); Arrays.sort(vCut); // 从最贵的开始切 int i = m - 2, j = n - 2; long result = 0; while(i >= 0 || j >= 0) { if(i >= 0 && j >= 0) { if(hCut[i] > vCut[j]) { // 当前切分cost:cost * 块数 result += (long)hCut[i] * (n - j - 1); i--; } else { result += (long)vCut[j] * (m - i - 1); j--; } } else if(i >= 0) { result += (long)hCut[i] * (n - j - 1); i--; } else { result += (long)vCut[j] * (m - i - 1); j--; } } return result; } }
代码简化:
class Solution { /** 思路:贪心算法, cost最高的应该先切分 */ public long minimumCost(int m, int n, int[] hCut, int[] vCut) { Arrays.sort(hCut); Arrays.sort(vCut); // 从最贵的开始切 int i = m - 2, j = n - 2; long result = 0; while(i >= 0 || j >= 0) { if(j < 0 || (i >= 0 && hCut[i] > vCut[j])) { // 当前切分cost:cost * 块数 result += (long)hCut[i] * (n - j - 1); i--; } else { result += (long)vCut[j] * (m - i - 1); j--; } } return result; } }
nth lake, the nth lake becomes full of water. If it rains over a lake that is full of water, there will be a flood. Your goal is to avoid floods in any lake.Given an integer array rains where:
rains[i] > 0means there will be rains over therains[i]lake.rains[i] == 0means there are no rains this day and you can choose one lake this day and dry it.
Return an array ans where:
ans.length == rains.lengthans[i] == -1ifrains[i] > 0.ans[i]is the lake you choose to dry in theithday ifrains[i] == 0.
If there are multiple valid answers return any of them. If it is impossible to avoid flood return an empty array.
Notice that if you chose to dry a full lake, it becomes empty, but if you chose to dry an empty lake, nothing changes.
Example 1:
Input: rains = [1,2,3,4] Output: [-1,-1,-1,-1] Explanation: After the first day full lakes are [1] After the second day full lakes are [1,2] After the third day full lakes are [1,2,3] After the fourth day full lakes are [1,2,3,4] There's no day to dry any lake and there is no flood in any lake.
Example 2:
Input: rains = [1,2,0,0,2,1] Output: [-1,-1,2,1,-1,-1] Explanation: After the first day full lakes are [1] After the second day full lakes are [1,2] After the third day, we dry lake 2. Full lakes are [1] After the fourth day, we dry lake 1. There is no full lakes. After the fifth day, full lakes are [2]. After the sixth day, full lakes are [1,2]. It is easy that this scenario is flood-free. [-1,-1,1,2,-1,-1] is another acceptable scenario.
Example 3:
Input: rains = [1,2,0,1,2] Output: [] Explanation: After the second day, full lakes are [1,2]. We have to dry one lake in the third day. After that, it will rain over lakes [1,2]. It's easy to prove that no matter which lake you choose to dry in the 3rd day, the other one will flood.
Constraints:
1 <= rains.length <= 1050 <= rains[i] <= 109
class Solution: def avoidFlood(self, rains: List[int]) -> List[int]: # 记录lake下雨的日期 lake_rain_day = {} # 记录不下雨的日期,可以用来抽干lake dry_days = SortedList() # 结果集合初始化,只要是大于0的湖泊就可以 ans = [100000000] * len(rains) for i in range(len(rains)): # 如果没下雨,那么将日期记录到list if rains[i] == 0: dry_days.add(i) # 如果下雨了,那么要看这个lake是否已经有水,有的话要找之前没下雨的一天提前抽干 else: # 下雨了,所以当天肯定不能dry,所以-1 ans[i] = -1 # 如果下过雨,那么需要dry if rains[i] in lake_rain_day: # 找到rains[i]这个lake下雨那天(lake_rain_day[rains[i]])后可以抽干的那天 dry_day_ind = dry_days.bisect(lake_rain_day[rains[i]]) #如果找不到就发洪水了 if dry_day_ind == len(dry_days): return [] # 找到那天,用于抽干rains[i]lake ans[dry_days[dry_day_ind]] = rains[i] # 移除这天,因为被用过了 dry_days.discard(dry_days[dry_day_ind]) # 记录lake下雨日期 lake_rain_day[rains[i]] = i return ans
 Companies
CompaniesYou are given two integer arrays, nums and forbidden, each of length n.
You may perform the following operation any number of times (including zero):
- Choose two distinct indices
iandj, and swapnums[i]withnums[j].
Return the minimum number of swaps required such that, for every index i, the value of nums[i] is not equal to forbidden[i]. If no amount of swaps can ensure that every index avoids its forbidden value, return -1.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3], forbidden = [3,2,1]
Output: 1
Explanation:
One optimal set of swaps:
- Select indices
i = 0andj = 1innumsand swap them, resulting innums = [2, 1, 3]. - After this swap, for every index
i,nums[i]is not equal toforbidden[i].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [4,6,6,5], forbidden = [4,6,5,5]
Output: 2
Explanation:
One optimal set of swaps:- Select indices
i = 0andj = 2innumsand swap them, resulting innums = [6, 6, 4, 5]. - Select indices
i = 1andj = 3innumsand swap them, resulting innums = [6, 5, 4, 6]. - After these swaps, for every index
i,nums[i]is not equal toforbidden[i].
Example 3:
Input: nums = [7,7], forbidden = [8,7]
Output: -1
Explanation:
It is not possible to makenums[i] different from forbidden[i] for all indices.Example 4:
Input: nums = [1,2], forbidden = [2,1]
Output: 0
Explanation:
No swaps are required because nums[i] is already different from forbidden[i] for all indices, so the answer is 0.
Constraints:
1 <= n == nums.length == forbidden.length <= 1051 <= nums[i], forbidden[i] <= 109
class Solution: def minSwaps(self, nums: List[int], forbidden: List[int]) -> int: sameMap = {} # 相同元素频次统计 countMap = {} # 所有元素频次统计 countMax = 0 # 最多元素频次 n = len(nums) sum_same, max_same = 0, 0 # 所有相同元素个数, 最多相同元素频次 for i in range(n): countMap[nums[i]] = countMap.get(nums[i], 0) + 1 countMap[forbidden[i]] = countMap.get(forbidden[i], 0) + 1 countMax = max(countMax, countMap[nums[i]], countMap[forbidden[i]]) if nums[i] == forbidden[i]: sameMap[nums[i]] = sameMap.get(nums[i], 0) + 1 sum_same += 1 max_same = max(max_same, sameMap[nums[i]]) # 不可能的场景, 如果某个元素个数超过了一半 if countMax > n: return -1 # 最多相同的元素大于一半,需要交换max_same次 # 最多相同的元素小于等于一半,需要交换(sum_same+1)/2次 # 二者取最大 return max(max_same, (sum_same + 1) // 2) ''' 不可能的场景, 如果某个元素个数超过了nums+forbidden总数,那么不可能找到满足的 1,1,1,4,7 1,1,1,4,6 最多相同的元素小于等于一半,需要交换(sum_same+1)/2次 1,1,2,3,4 1,1,2,3,4 最多相同的元素大于一半,需要交换max_same次 1,1,1,3,4,5 1,1,1,3,4,6 '''




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号