two pointer 31,15,408,243,244,245,11,443,723,2337,713
A permutation of an array of integers is an arrangement of its members into a sequence or linear order.
- For example, for
arr = [1,2,3], the following are considered permutations ofarr:[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[3,1,2],[2,3,1].
The next permutation of an array of integers is the next lexicographically greater permutation of its integer. More formally, if all the permutations of the array are sorted in one container according to their lexicographical order, then the next permutation of that array is the permutation that follows it in the sorted container. If such arrangement is not possible, the array must be rearranged as the lowest possible order (i.e., sorted in ascending order).
- For example, the next permutation of
arr = [1,2,3]is[1,3,2]. - Similarly, the next permutation of
arr = [2,3,1]is[3,1,2]. - While the next permutation of
arr = [3,2,1]is[1,2,3]because[3,2,1]does not have a lexicographical larger rearrangement.
Given an array of integers nums, find the next permutation of nums.
The replacement must be in place and use only constant extra memory.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: [1,3,2]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,1] Output: [1,2,3]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,5] Output: [1,5,1]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 100
分析:
case1: 1,3,2,5,4 从右向左找到第一个顺序对,i点 1,3,2,5,4 - - i 从i+1点向右找到大于nums[i]的最小值的位置 1,3,2,5,4 - - i j 交换i,j的位置 1,3,4,5,2 - - i j 对i之后的元素进行排序 1,3,4,2,5 case2: 4,3,2,1 没有找到逆序对,说明是permutation的最后一个,那么下一个就是permutation第一个
class Solution { public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) { if(nums.length==1) return ; //从右向左找第一个顺序对 int i = nums.length-2; while(i>=0){ if(nums[i+1]>nums[i]) break; i--; } //从当前i向右找到大于它的最小元素 int j=i+1; if(i>=0){ for(int k = i+1;k<nums.length;k++){ if(nums[i]<nums[k] && nums[k]<nums[j]) j=k; } } //交换位置 if(i>=0) swap(nums,i,j); //对于后续进行排序 Arrays.sort(nums,i+1,nums.length); } public void swap(int[] nums, int a, int b){ int temp = nums[a]; nums[a] = nums[b]; nums[b] = temp; } }
15. 3Sum
Given an integer array nums, return all the triplets [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] such that i != j, i != k, and j != k, and nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0.
Notice that the solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4] Output: [[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: nums = [0] Output: []
Constraints:
0 <= nums.length <= 3000-105 <= nums[i] <= 105
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) { Arrays.sort(nums); List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList(); for(int i=0;i<nums.length-2;i++){ if(i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1]) continue; int left = i+1,right = nums.length-1; while(left<right){ if(nums[left]+nums[right]+nums[i]>0) right--; else if(nums[left]+nums[right]+nums[i]<0) left++; else { result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[left],nums[right])); left++;right--; } while(left>i+1 && left<right && nums[left]==nums[left-1]) left++; while(right<nums.length-1 && left<right && nums[right]==nums[right+1]) right--; } } return result; } }
A string can be abbreviated by replacing any number of non-adjacent, non-empty substrings with their lengths. The lengths should not have leading zeros.
For example, a string such as "substitution" could be abbreviated as (but not limited to):
"s10n"("s ubstitutio n")"sub4u4"("sub stit u tion")"12"("substitution")"su3i1u2on"("su bst i t u ti on")"substitution"(no substrings replaced)
The following are not valid abbreviations:
"s55n"("s ubsti tutio n", the replaced substrings are adjacent)"s010n"(has leading zeros)"s0ubstitution"(replaces an empty substring)
Given a string word and an abbreviation abbr, return whether the string matches the given abbreviation.
A substring is a contiguous non-empty sequence of characters within a string.
Example 1:
Input: word = "internationalization", abbr = "i12iz4n"
Output: true
Explanation: The word "internationalization" can be abbreviated as "i12iz4n" ("i nternational iz atio n").
Example 2:
Input: word = "apple", abbr = "a2e" Output: false Explanation: The word "apple" cannot be abbreviated as "a2e".
Constraints:
1 <= word.length <= 20wordconsists of only lowercase English letters.1 <= abbr.length <= 10abbrconsists of lowercase English letters and digits.- All the integers in
abbrwill fit in a 32-bit integer.
class Solution { public boolean validWordAbbreviation(String word, String abbr) { int i=0,j=0; for(i=0;i<abbr.length();){ char c = abbr.charAt(i); //如果遇到数字,计算要跳过的数量直接跳过 if(Character.isDigit(c)){ int skip = 0; //数字以0开头,不合法,直接返回 if(c == '0') return false; // while(i < abbr.length() && Character.isDigit(abbr.charAt(i))){ skip = skip * 10 + (abbr.charAt(i) - '0'); i++; } j += skip; } //如果遇到字母,那么就跟原字符串比对 else{
//如果原串已经越界,或者与模版不匹配,返回false if(j >= word.length() || c != word.charAt(j)) return false; j++; i++; } } return j == word.length(); } }
Given an array of strings wordsDict and two different strings that already exist in the array word1 and word2, return the shortest distance between these two words in the list.
Example 1:
Input: wordsDict = ["practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"], word1 = "coding", word2 = "practice" Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: wordsDict = ["practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"], word1 = "makes", word2 = "coding" Output: 1
Constraints:
1 <= wordsDict.length <= 3 * 1041 <= wordsDict[i].length <= 10wordsDict[i]consists of lowercase English letters.word1andword2are inwordsDict.word1 != word2
解法: 定义两个变量分别为word1/word2的pos,用一个指针从左向右扫描,遇到对应的word1/word2时update其pos
时间复杂度: O(N)
class Solution { public int shortestDistance(String[] wordsDict, String word1, String word2) { int left =-1,right = -1,result=wordsDict.length; for(int i=0;i<wordsDict.length;i++){ if(word1.equals(wordsDict[i])){ left = i; } else if(word2.equals(wordsDict[i])){ right = i; } if(left>=0 && right>=0) result = Math.min(Math.abs(right-left), result); } return result; } }
Design a data structure that will be initialized with a string array, and then it should answer queries of the shortest distance between two different strings from the array.
Implement the WordDistance class:
WordDistance(String[] wordsDict)initializes the object with the strings arraywordsDict.int shortest(String word1, String word2)returns the shortest distance betweenword1andword2in the arraywordsDict.
Example 1:
Input
["WordDistance", "shortest", "shortest"]
[[["practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"]], ["coding", "practice"], ["makes", "coding"]]
Output
[null, 3, 1]
Explanation
WordDistance wordDistance = new WordDistance(["practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"]);
wordDistance.shortest("coding", "practice"); // return 3
wordDistance.shortest("makes", "coding"); // return 1
Constraints:
1 <= wordsDict.length <= 3 * 1041 <= wordsDict[i].length <= 10wordsDict[i]consists of lowercase English letters.word1andword2are inwordsDict.word1 != word2- At most
5000calls will be made toshortest.
解法:这题和上面一题实际是一样的,但是考虑到要多次调用shortest,每次调用会是O(N) ,这样不是太好。 因此我们可以使用map 将各word的位置以map形式存起来,这样就可以减少遍历
时间复杂度: O(K) ,k为word在数组中出现的次数
class WordDistance { HashMap<String,List<Integer>> map = new HashMap(); public WordDistance(String[] wordsDict) { for(int i=0;i<wordsDict.length;i++){ List<Integer> list = map.getOrDefault(wordsDict[i],new ArrayList()); list.add(i); map.put(wordsDict[i],list); } } public int shortest(String word1, String word2) { int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; List<Integer> list1 = map.get(word1); List<Integer> list2 = map.get(word2); int pos1 = 0; int pos2 = 0; while(pos1<list1.size() && pos2<list2.size()){ result = Math.min(Math.abs(list1.get(pos1)-list2.get(pos2)),result); if(list1.get(pos1)>list2.get(pos2)) pos2++; else pos1++; } return result; } }
Given an array of strings wordsDict and two strings that already exist in the array word1 and word2, return the shortest distance between these two words in the list.
Note that word1 and word2 may be the same. It is guaranteed that they represent two individual words in the list.
Example 1:
Input: wordsDict = ["practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"], word1 = "makes", word2 = "coding" Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: wordsDict = ["practice", "makes", "perfect", "coding", "makes"], word1 = "makes", word2 = "makes" Output: 3
Constraints:
1 <= wordsDict.length <= 1051 <= wordsDict[i].length <= 10wordsDict[i]consists of lowercase English letters.word1andword2are inwordsDict.
class Solution { public int shortestWordDistance(String[] wordsDict, String word1, String word2) { int right =Integer.MAX_VALUE,left = -right,result=wordsDict.length; for(int i=0;i<wordsDict.length;i++){ if(word1.equals(wordsDict[i])){ if(word1.equals(word2)){//如果两个word是一样的,那么我们将right left = right; } right = i; } else if(word2.equals(wordsDict[i])){ left = i; } if(left>=0 && right>=0) result = Math.min(Math.abs(right-left), result); } return result; } }
You are given an integer array height of length n. There are n vertical lines drawn such that the two endpoints of the ith line are (i, 0) and (i, height[i]).
Find two lines that together with the x-axis form a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Return the maximum amount of water a container can store.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
Example 1:
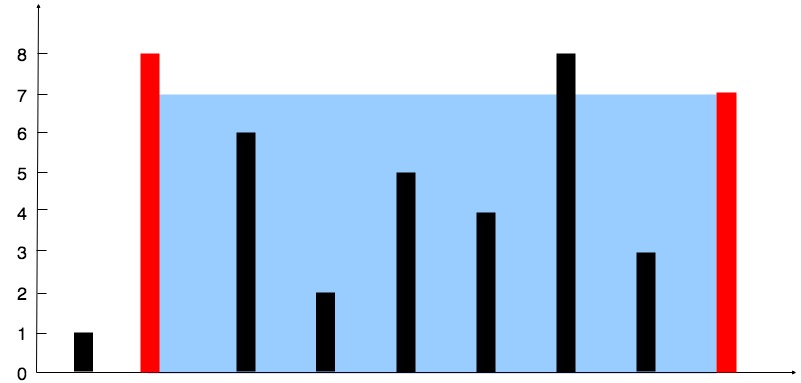
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7] Output: 49 Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 2:
Input: height = [1,1] Output: 1
Constraints:
n == height.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= height[i] <= 104
解法:从两端的夹板向内收敛,如果左侧夹板低于右侧夹板,那么我们将左侧夹板进行移动,为什么?因为如果我们移动右侧夹板(大的那个)只会使得面积更小。 反之亦然。
class Solution { public int maxArea(int[] height) { int left = 0,right = height.length-1; int result = 0; while(left<right){ result = Math.max(result, (right-left) * Math.min(height[left],height[right])); if(height[left]<height[right]) left++; else right--; } return result; } }
Given an array of characters chars, compress it using the following algorithm:
Begin with an empty string s. For each group of consecutive repeating characters in chars:
- If the group's length is
1, append the character tos. - Otherwise, append the character followed by the group's length.
The compressed string s should not be returned separately, but instead, be stored in the input character array chars. Note that group lengths that are 10 or longer will be split into multiple characters in chars.
After you are done modifying the input array, return the new length of the array.
You must write an algorithm that uses only constant extra space.
Example 1:
Input: chars = ["a","a","b","b","c","c","c"] Output: Return 6, and the first 6 characters of the input array should be: ["a","2","b","2","c","3"] Explanation: The groups are "aa", "bb", and "ccc". This compresses to "a2b2c3".
Example 2:
Input: chars = ["a"] Output: Return 1, and the first character of the input array should be: ["a"] Explanation: The only group is "a", which remains uncompressed since it's a single character.
Example 3:
Input: chars = ["a","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b","b"] Output: Return 4, and the first 4 characters of the input array should be: ["a","b","1","2"]. Explanation: The groups are "a" and "bbbbbbbbbbbb". This compresses to "ab12".
Constraints:
1 <= chars.length <= 2000chars[i]is a lowercase English letter, uppercase English letter, digit, or symbol.
class Solution { public int compress(char[] chars) { int i=0,j=0; StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(""); for(i=0;i<chars.length;i++){ if(chars[i]!=chars[j]){ sb.append(chars[j]); if(i-j>1) sb.append(i-j); j=i; } } sb.append(chars[j]); if(i-j>1) sb.append(i-j); for(int k=0;k<sb.length();k++){ chars[k]=sb.charAt(k); } return sb.length(); } }
This question is about implementing a basic elimination algorithm for Candy Crush.
Given an m x n integer array board representing the grid of candy where board[i][j] represents the type of candy. A value of board[i][j] == 0 represents that the cell is empty.
The given board represents the state of the game following the player's move. Now, you need to restore the board to a stable state by crushing candies according to the following rules:
- If three or more candies of the same type are adjacent vertically or horizontally, crush them all at the same time - these positions become empty.
- After crushing all candies simultaneously, if an empty space on the board has candies on top of itself, then these candies will drop until they hit a candy or bottom at the same time. No new candies will drop outside the top boundary.
- After the above steps, there may exist more candies that can be crushed. If so, you need to repeat the above steps.
- If there does not exist more candies that can be crushed (i.e., the board is stable), then return the current board.
You need to perform the above rules until the board becomes stable, then return the stable board.
Example 1:
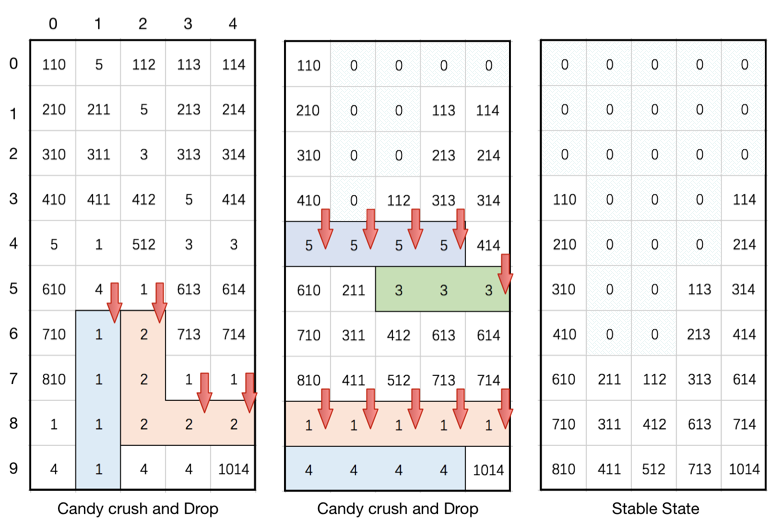
Input: board = [[110,5,112,113,114],[210,211,5,213,214],[310,311,3,313,314],[410,411,412,5,414],[5,1,512,3,3],[610,4,1,613,614],[710,1,2,713,714],[810,1,2,1,1],[1,1,2,2,2],[4,1,4,4,1014]] Output: [[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[110,0,0,0,114],[210,0,0,0,214],[310,0,0,113,314],[410,0,0,213,414],[610,211,112,313,614],[710,311,412,613,714],[810,411,512,713,1014]]
Example 2:
Input: board = [[1,3,5,5,2],[3,4,3,3,1],[3,2,4,5,2],[2,4,4,5,5],[1,4,4,1,1]] Output: [[1,3,0,0,0],[3,4,0,5,2],[3,2,0,3,1],[2,4,0,5,2],[1,4,3,1,1]]
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length3 <= m, n <= 501 <= board[i][j] <= 2000
class Solution { public int[][] candyCrush(int[][] board) { while(mark(board)) crush(board); return board; } private boolean mark(int[][] board){ boolean flag = false; for(int i=0;i<board.length;i++){ for(int j=1;j<board[0].length-1;j++){ if( Math.abs(board[i][j]) == Math.abs(board[i][j-1]) && Math.abs(board[i][j]) == Math.abs(board[i][j+1]) && board[i][j]!=0 ){ board[i][j-1] = board[i][j] = board[i][j+1] = Math.abs(board[i][j])*-1; flag = true; } } } for(int j=0;j<board[0].length;j++){ for(int i=1;i<board.length-1;i++){ if( Math.abs(board[i][j]) == Math.abs(board[i-1][j]) && Math.abs(board[i][j]) == Math.abs(board[i+1][j]) && board[i][j]!=0 ){ board[i-1][j] = board[i][j] = board[i+1][j] = Math.abs(board[i][j])*-1; flag = true; } } } return flag; } private void crush(int[][] board){ for(int col=0;col<board[0].length;col++){ int i = board.length-1, j = board.length-1; while(j>=0){ if(board[j][col]>0){ board[i--][col] = board[j][col]; } j--; } while(i>=0){ board[i--][col]=0; } } } }
You are given two strings start and target, both of length n. Each string consists only of the characters 'L', 'R', and '_' where:
- The characters
'L'and'R'represent pieces, where a piece'L'can move to the left only if there is a blank space directly to its left, and a piece'R'can move to the right only if there is a blank space directly to its right. - The character
'_'represents a blank space that can be occupied by any of the'L'or'R'pieces.
Return true if it is possible to obtain the string target by moving the pieces of the string start any number of times. Otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
Input: start = "_L__R__R_", target = "L______RR" Output: true Explanation: We can obtain the string target from start by doing the following moves: - Move the first piece one step to the left, start becomes equal to "L___R__R_". - Move the last piece one step to the right, start becomes equal to "L___R___R". - Move the second piece three steps to the right, start becomes equal to "L______RR". Since it is possible to get the string target from start, we return true.
Example 2:
Input: start = "R_L_", target = "__LR" Output: false Explanation: The 'R' piece in the string start can move one step to the right to obtain "_RL_". After that, no pieces can move anymore, so it is impossible to obtain the string target from start.
Example 3:
Input: start = "_R", target = "R_" Output: false Explanation: The piece in the string start can move only to the right, so it is impossible to obtain the string target from start.
Constraints:
n == start.length == target.length1 <= n <= 105startandtargetconsist of the characters'L','R', and'_'.
class Solution { /* start 满足target的充分条件是: 1.除去_后剩余的LR字符串应该是相同的 2.L在start中位置对应在target中L的相同或者靠右位置 3.R在start中位置对应在target中R的相同或者靠左位置 */ public boolean canChange(String start, String target) { //无论怎么移动,所有L和R的相对位置不会改变,因为他们只能移动到空位 //直接用双指针模拟同时走两个字符串 int i = 0, j = 0; while (i < start.length() || j < target.length()) { //移动到第一个不是_的位置 while (i < start.length() && start.charAt(i) == '_') i++; while (j < target.length() && target.charAt(j) == '_') j++; //如果其中一个指针已经到结尾,判断二者是否同时都到尾了 if (i >= start.length() || j >= target.length()) return i == start.length() && j == target.length(); //如果不匹配,return false if (start.charAt(i) != target.charAt(j)) return false; //L在start中位置对应在target中L的相同或者靠右位置 if (start.charAt(i) == 'R' && i > j) return false; //R在start中位置对应在target中R的相同或者靠左位置 if (start.charAt(i) == 'L' && i < j) return false; i++; j++; } return true; } }
713. Subarray Product Less Than K
Given an array of integers nums and an integer k, return the number of contiguous subarrays where the product of all the elements in the subarray is strictly less than k.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [10,5,2,6], k = 100 Output: 8 Explanation: The 8 subarrays that have product less than 100 are: [10], [5], [2], [6], [10, 5], [5, 2], [2, 6], [5, 2, 6] Note that [10, 5, 2] is not included as the product of 100 is not strictly less than k.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3], k = 0 Output: 0
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 1041 <= nums[i] <= 10000 <= k <= 106
class Solution { public int numSubarrayProductLessThanK(int[] nums, int k) { if(k==0) return 0; int result = 1; int i=0,count = 0; //j指针逐步向右移动 for(int j=0;j<nums.length;j++){ result*=nums[j]; //如果不满足条件了,左侧元素滑出窗口 while(result>=k && i<j){ result/=nums[i++]; } //判定当前满足条件的话将结果加总到最终count if(result<k) count+=j-i+1; //技巧:每次都是以右边界来计算有效个数 } return count; } }
review: 31,233




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号