最长公共子序列
Longest common subarray in the given two arrays
Given two arrays A[] and B[] of N and M integers respectively, the task is to find the maximum length of equal subarray or the longest common subarray between the two given array.
Examples:
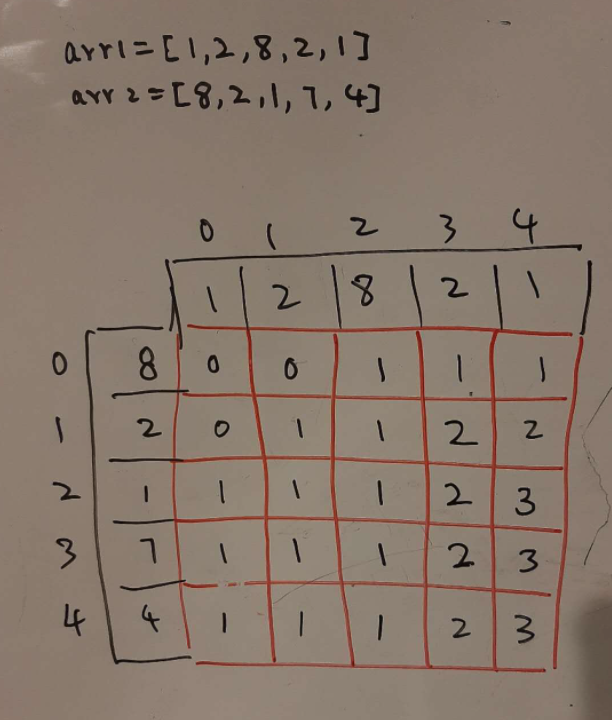
Input: A[] = {1, 2, 8, 2, 1}, B[] = {8, 2, 1, 4, 7}
Output: 3
Explanation:
The subarray that is common to both arrays are {8, 2, 1} and the length of the subarray is 3.
Input: A[] = {1, 2, 3, 2, 1}, B[] = {8, 7, 6, 4, 7}
Output: 0
Explanation:
There is no such subarrays which are equal in the array A[] and B[].
public class LongestCommonSubArray { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(lcs(new int[]{1,2,8,2,1,5},new int[]{4})); } private static int lcs(int[] num1,int[] num2){ int[][] mem = new int[num1.length+1][num2.length+1]; int max = 0; for(int i=1;i<=num1.length;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=num2.length;j++){ if(num1[i-1]==num2[j-1]){ mem[i][j]=mem[i-1][j-1]+1; max = Math.max(max,mem[i][j]); } } } return max; } }
Given two strings text1 and text2, return the length of their longest common subsequence. If there is no common subsequence, return 0.
A subsequence of a string is a new string generated from the original string with some characters (can be none) deleted without changing the relative order of the remaining characters.
- For example,
"ace"is a subsequence of"abcde".
A common subsequence of two strings is a subsequence that is common to both strings.
Example 1:
Input: text1 = "abcde", text2 = "ace" Output: 3 Explanation: The longest common subsequence is "ace" and its length is 3.
Example 2:
Input: text1 = "abc", text2 = "abc" Output: 3 Explanation: The longest common subsequence is "abc" and its length is 3.
Example 3:
Input: text1 = "abc", text2 = "def" Output: 0 Explanation: There is no such common subsequence, so the result is 0.
Constraints:
1 <= text1.length, text2.length <= 1000text1andtext2consist of only lowercase English characters.
解法一:递归暴力解
class Solution { public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) { return recursive(text1,0,text2,0); }
//计算ind1 ind2 到末尾的lcs private int recursive(String text1, int ind1, String text2, int ind2){ if(ind1==text1.length() || ind2==text2.length()) return 0; if(text1.charAt(ind1)==text2.charAt(ind2)){//如果当前位置相等,那么直接算各自下一个位置的情况 return recursive(text1,ind1+1,text2,ind2+1)+1; } else //如果当前位置不等,那么尝试第一个或者第二个指针右移 return Math.max(recursive(text1,ind1+1,text2,ind2),recursive(text1,ind1,text2,ind2+1)); } }
解法二:上面暴力解有很多的重复计算,在上面暴力解法基础上增加memoization
class Solution { public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) { Integer[][] mem = new Integer[text1.length()+1][text2.length()+1]; return recursive(text1,0,text2,0,mem); } private int recursive(String text1, int ind1, String text2, int ind2,Integer[][] mem){ if(mem[ind1][ind2]!=null) return mem[ind1][ind2]; if(ind1==text1.length() || ind2==text2.length()) return 0; if(text1.charAt(ind1)==text2.charAt(ind2)){ mem[ind1][ind2]=recursive(text1,ind1+1,text2,ind2+1,mem)+1; } else mem[ind1][ind2]=Math.max(recursive(text1,ind1+1,text2,ind2,mem),recursive(text1,ind1,text2,ind2+1,mem)); return mem[ind1][ind2]; } }
解法三:dp
class Solution { public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) { int[][] mem = new int[text1.length()+1][text2.length()+1]; for(int i=1;i<=text1.length();i++){ for(int j=1;j<=text2.length();j++){ if(text1.charAt(i-1)==text2.charAt(j-1)){ mem[i][j]=mem[i-1][j-1]+1; } else{ mem[i][j] = Math.max(mem[i][j-1],mem[i-1][j]); } } } return mem[text1.length()][text2.length()]; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号