未分类题目
Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers.
If such an arrangement is impossible, it must rearrange it to the lowest possible order (i.e., sorted in ascending order).
The replacement must be in place and use only constant extra memory.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3] Output: [1,3,2]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,1] Output: [1,2,3]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,5] Output: [1,5,1]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000 <= nums[i] <= 100
解法:找到最后一个递增pair位置<A,B>交换他们的位置,然后将A位置后的序列进行排序
class Solution { public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) { int left=-1,right=-1; //找到最后一个递增pair boolean flag=false; for(int i=nums.length-2;i>=0 &&!flag;i--){ for(int j=nums.length-1;j>i;j--){ if(nums[j]>nums[i]){ left=i;right=j; flag=true; break; } } } if(left!=-1) { //交换位置left right int temp = nums[left]; nums[left]=nums[right]; nums[right]=temp; } //将left之后的数字重新排序 Arrays.sort(nums,left+1,nums.length); } }
Implement pow(x, n), which calculates x raised to the power n (i.e., xn).
Example 1:
Input: x = 2.00000, n = 10 Output: 1024.00000
Example 2:
Input: x = 2.10000, n = 3 Output: 9.26100
Example 3:
Input: x = 2.00000, n = -2 Output: 0.25000 Explanation: 2-2 = 1/22 = 1/4 = 0.25
Constraints:
-100.0 < x < 100.0-231 <= n <= 231-1-104 <= xn <= 104
class Solution { public double myPow(double x, int n) { long N=n; if(N<0){ x = 1/x; N=-N; } double curr_p=x; double result = 1; for(long i=N;i>0;i=i/2){ if(i%2==1) result*=curr_p; curr_p*=curr_p; } return result; } }
Give a binary string s, return the number of non-empty substrings that have the same number of 0's and 1's, and all the 0's and all the 1's in these substrings are grouped consecutively.
Substrings that occur multiple times are counted the number of times they occur.
Example 1:
Input: s = "00110011" Output: 6 Explanation: There are 6 substrings that have equal number of consecutive 1's and 0's: "0011", "01", "1100", "10", "0011", and "01". Notice that some of these substrings repeat and are counted the number of times they occur. Also, "00110011" is not a valid substring because all the 0's (and 1's) are not grouped together.
Example 2:
Input: s = "10101" Output: 4 Explanation: There are 4 substrings: "10", "01", "10", "01" that have equal number of consecutive 1's and 0's.
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 105s[i]is either'0'or'1'.

class Solution { public int countBinarySubstrings(String s) { int pre =0, curr=1; int count = 0; for(int i=1;i<s.length();i++){ if(s.charAt(i)==s.charAt(i-1)) curr++; else{ count+=Math.min(curr,pre); pre=curr; curr=1; } } count += Math.min(curr,pre); return count; } }
时间复杂度: O(N), 空间复杂度 :O(1)
There is a family tree rooted at 0 consisting of n nodes numbered 0 to n - 1. You are given a 0-indexed integer array parents, where parents[i] is the parent for node i. Since node 0 is the root, parents[0] == -1.
There are 105 genetic values, each represented by an integer in the inclusive range [1, 105]. You are given a 0-indexed integer array nums, where nums[i] is a distinct genetic value for node i.
Return an array ans of length n where ans[i] is the smallest genetic value that is missing from the subtree rooted at node i.
The subtree rooted at a node x contains node x and all of its descendant nodes.
Example 1:
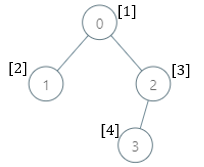
Input: parents = [-1,0,0,2], nums = [1,2,3,4] Output: [5,1,1,1] Explanation: The answer for each subtree is calculated as follows: - 0: The subtree contains nodes [0,1,2,3] with values [1,2,3,4]. 5 is the smallest missing value. - 1: The subtree contains only node 1 with value 2. 1 is the smallest missing value. - 2: The subtree contains nodes [2,3] with values [3,4]. 1 is the smallest missing value. - 3: The subtree contains only node 3 with value 4. 1 is the smallest missing value.
Example 2:
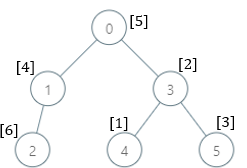
Input: parents = [-1,0,1,0,3,3], nums = [5,4,6,2,1,3] Output: [7,1,1,4,2,1] Explanation: The answer for each subtree is calculated as follows: - 0: The subtree contains nodes [0,1,2,3,4,5] with values [5,4,6,2,1,3]. 7 is the smallest missing value. - 1: The subtree contains nodes [1,2] with values [4,6]. 1 is the smallest missing value. - 2: The subtree contains only node 2 with value 6. 1 is the smallest missing value. - 3: The subtree contains nodes [3,4,5] with values [2,1,3]. 4 is the smallest missing value. - 4: The subtree contains only node 4 with value 1. 2 is the smallest missing value. - 5: The subtree contains only node 5 with value 3. 1 is the smallest missing value.
Example 3:
Input: parents = [-1,2,3,0,2,4,1], nums = [2,3,4,5,6,7,8] Output: [1,1,1,1,1,1,1] Explanation: The value 1 is missing from all the subtrees.
Constraints:
n == parents.length == nums.length2 <= n <= 1050 <= parents[i] <= n - 1fori != 0parents[0] == -1parentsrepresents a valid tree.1 <= nums[i] <= 105- Each
nums[i]is distinct.
// 思路:只需考虑Genetic Value 从1到root的那条单链
// 所有缺1的subtree,第一个缺失的正整数都是1
// 只有从1到root的这条单链,第一个缺失的正整数不是1
// 用一个HashSet存储已经遍历过的数字,miss初始设为1,while(set.contains(miss)){ miss++}
//
// 细节注意 if(j == pre) continue; // 处理过的节点不能再遍历,不然会超时
// 每个节点只遍历了一遍,所以复杂度是O(n)class Solution { public int[] smallestMissingValueSubtree(int[] parents, int[] nums) { Set<Integer> set = new HashSet();//用于存放访问过的节点 //把树建起来 Map<Integer,List<Integer>> map = new HashMap(); for(int i=0;i<parents.length;i++){ List<Integer> list = map.getOrDefault(parents[i],new ArrayList()); map.put(parents[i],list); list.add(i); } int[] result = new int[nums.length]; Arrays.fill(result,1); //找到值为1的那个点 int ind = findIn1(nums); //如果没找到值为1的,那么都是缺1,直接返回 if(ind==-1) return result; int missing = 1; int pre = -1; while(ind!=-1){ //把当前点的所有子节点加入到set当中 dfs(set,map,ind,nums,pre); //把当前点也加进去 set.add(nums[ind]); //missing++直至找到missing的那个 while(set.contains(missing)) missing++; result[ind]=missing; //保留当前遍历的节点, pre = ind; //节点移向父节点 ind = parents[ind]; } return result; } //dfs向下遍历该节点包含的所有子节点的值 private void dfs( Set<Integer> set, Map<Integer,List<Integer>> map, int pos,int[] nums,int pre){ //因为是从下往上,因此一条path,因此父节点遍历时 1这条path上的子节点已经遍历过了,因此就可以跳过,否则会超时 if(pos==pre) return; set.add(nums[pos]); List<Integer> list = map.get(pos); if(list!=null){ for(int i:list){ dfs(set,map,i,nums,pre); } } } //找到值为1的那个位置 private int findIn1( int[] nums ){ int ind=-1; for(int j=0;j<nums.length;j++){ if(nums[j]==1){ ind=j; break; } } return ind; } }
Given a binary string s, return the number of non-empty substrings that have the same number of 0's and 1's, and all the 0's and all the 1's in these substrings are grouped consecutively.
Substrings that occur multiple times are counted the number of times they occur.
Example 1:
Input: s = "00110011" Output: 6 Explanation: There are 6 substrings that have equal number of consecutive 1's and 0's: "0011", "01", "1100", "10", "0011", and "01". Notice that some of these substrings repeat and are counted the number of times they occur. Also, "00110011" is not a valid substring because all the 0's (and 1's) are not grouped together.
Example 2:
Input: s = "10101" Output: 4 Explanation: There are 4 substrings: "10", "01", "10", "01" that have equal number of consecutive 1's and 0's.
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 105s[i]is either'0'or'1'.
解法:
curr表示当前元素连续出现的次数 pre 表示other元素在当前元素之前连续出现的次数 然后我们在每次元素切换的时候,计算它之前元素可以形成的合法子串长度 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 curr 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 2 pre 0 0 2 2 2 2 2 2 count 0 2 2 2
class Solution { public int countBinarySubstrings(String s) { int curr =1,pre = 0,count = 0; for(int i=1;i<s.length();i++){ if(s.charAt(i-1) == s.charAt(i)){ curr++; } else{ count+=Math.min(curr,pre); pre = curr; curr=1; } } count+=Math.min(curr,pre); return count; } }
A valid encoding of an array of words is any reference string s and array of indices indices such that:
words.length == indices.length- The reference string
sends with the'#'character. - For each index
indices[i], the substring ofsstarting fromindices[i]and up to (but not including) the next'#'character is equal towords[i].
Given an array of words, return the length of the shortest reference string s possible of any valid encoding of words.
Example 1:
Input: words = ["time", "me", "bell"]
Output: 10
Explanation: A valid encoding would be s = "time#bell#" and indices = [0, 2, 5].
words[0] = "time", the substring of s starting from indices[0] = 0 to the next '#' is underlined in "time#bell#"
words[1] = "me", the substring of s starting from indices[1] = 2 to the next '#' is underlined in "time#bell#"
words[2] = "bell", the substring of s starting from indices[2] = 5 to the next '#' is underlined in "time#bell#"
Example 2:
Input: words = ["t"] Output: 2 Explanation: A valid encoding would be s = "t#" and indices = [0].
Constraints:
1 <= words.length <= 20001 <= words[i].length <= 7words[i]consists of only lowercase letters.
class Solution { public int minimumLengthEncoding(String[] words) { //将元素都放入set Set<String> set = new HashSet(Arrays.asList(words)); //遍历元素列表 for(String s:words){ //每个元素检查以其开头的所有子串(不包含它自己),如果存在相应子串那么可以移除 for(int i=1;i<s.length();i++){ set.remove(s.substring(i)); } } //最终结果即为生于的不可复用的元素长度和+元素个数(#) int result = 0; for(String s:set){ result += s.length()+1; } return result; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号