图算法(二)-最短路径
743. Network Delay Time
You are given a network of n nodes, labeled from 1 to n. You are also given times, a list of travel times as directed edges times[i] = (ui, vi, wi), where ui is the source node, vi is the target node, and wi is the time it takes for a signal to travel from source to target.
We will send a signal from a given node k. Return the time it takes for all the n nodes to receive the signal. If it is impossible for all the n nodes to receive the signal, return -1.
Example 1:

Input: times = [[2,1,1],[2,3,1],[3,4,1]], n = 4, k = 2 Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 1 Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: times = [[1,2,1]], n = 2, k = 2 Output: -1
Constraints:
1 <= k <= n <= 1001 <= times.length <= 6000times[i].length == 31 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi0 <= wi <= 100- All the pairs
(ui, vi)are unique. (i.e., no multiple edges.)
Dijkstra
class Solution { public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) { //1.define map to store the other vertics and distance Map<Integer,List<int[]>> map = new HashMap(); for(int[] time:times){ List<int[]> list = map.getOrDefault(time[0],new ArrayList()); list.add(new int[]{time[1],time[2]}); map.put(time[0],list); } //2.init distance int[] distance = new int[n+1]; //从起点到其他各点的距离 boolean[] visited = new boolean[n+1]; //标记是否已经访问过
//一开始将起始点到左右点的初始化为无穷大 Arrays.fill(distance,Integer.MAX_VALUE); //起始点到自己的距离为0 distance[k]=0; while(true){ int curr = -1;
//从所有点中找出距离最小 并且 未访问过的点 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(!visited[i]){ if(curr == -1 || distance[i] < distance[curr]) curr=i; } }
//如果没有找到,说明已经遍历完了 if(curr==-1) break;
//标记为true,避免重复访问 visited[curr]=true;
//遍历当前这个点的邻居节点,并更新距离 for(int[] other:map.getOrDefault(curr,Arrays.asList())){ if(distance[other[0]]>distance[curr]+other[1]) distance[other[0]] = distance[curr]+other[1];//relaxation } } int max = 0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) max = Math.max(max,distance[i]); return max==Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : max;//坑点,注意有可能压根不连通时要返回-1 } }
Dijkstra PQ 优化版
使用pq可以优化上面的获取离起点最短距离的点,这样不用遍历所有的distance去找出最小的
class Solution { public int networkDelayTime(int[][] times, int n, int k) { //1.define map to store the other vertics and distance Map<Integer,List<int[]>> map = new HashMap(); for(int[] time:times){ List<int[]> list = map.getOrDefault(time[0],new ArrayList()); list.add(new int[]{time[1],time[2]}); map.put(time[0],list); } //2.init distance int[] distance = new int[n+1]; Arrays.fill(distance,Integer.MAX_VALUE); PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((x,y)->x[1]-y[1]); //3.start from the source distance[k]=0; pq.offer(new int[]{k,0}); while(!pq.isEmpty()){ int[] curr = pq.poll(); for(int[] other:map.getOrDefault(curr[0],Arrays.asList())){ if(distance[other[0]]>distance[curr[0]]+other[1]) { distance[other[0]] = distance[curr[0]]+other[1];//relaxation pq.offer(new int[]{other[0],distance[other[0]]}); } } } int max = 0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) max = Math.max(max,distance[i]); return max==Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : max;//坑点,注意有可能压根不连通时要返回-1 } }
python version:
class Solution: def networkDelayTime(self, times: List[List[int]], n: int, k: int) -> int: #申请了n+1的空间,因为node是从1开始的,为什么第一个空位必须为0,因为最终要求取所有点中的最大路径长度返回 distance = [0] + [float("inf")] * n #将节点关系放入dict,便于后续快速查找 graph = defaultdict(list) for start, end, time in times: graph[start].append((end, time)) #起点距离自己距离为0 distance[k] = 0 #起点压栈 heap = [(0, k)] #开始遍历 while heap: time, node = heapq.heappop(heap) for other, timeCost in graph[node]: if time + timeCost < distance[other]: distance[other] = time + timeCost heapq.heappush(heap, (distance[other], other)) #取最大距离 mx = max(distance) #注意如果最大距离为无穷大说明有不连通的点,返回-1 return mx if mx < float("inf") else -1
787. Cheapest Flights Within K Stops
There are n cities connected by some number of flights. You are given an array flights where flights[i] = [fromi, toi, pricei] indicates that there is a flight from city fromi to city toi with cost pricei.
You are also given three integers src, dst, and k, return the cheapest price from src to dst with at most k stops. If there is no such route, return -1.
Example 1:

Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 1 Output: 200 Explanation: The graph is shown. The cheapest price from city0to city2with at most 1 stop costs 200, as marked red in the picture.
Example 2:

Input: n = 3, flights = [[0,1,100],[1,2,100],[0,2,500]], src = 0, dst = 2, k = 0 Output: 500 Explanation: The graph is shown. The cheapest price from city0to city2with at most 0 stop costs 500, as marked blue in the picture.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000 <= flights.length <= (n * (n - 1) / 2)flights[i].length == 30 <= fromi, toi < nfromi != toi1 <= pricei <= 104- There will not be any multiple flights between two cities.
0 <= src, dst, k < nsrc != dst
BFS 这个解法会超时
class Solution { public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) { Map<Integer,List<int[]>> map = new HashMap(); for(int[] flight:flights){ List<int[]> list = map.getOrDefault(flight[0],new ArrayList()); list.add(new int[]{flight[1],flight[2]}); map.put(flight[0],list); } int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList(); queue.offer(new int[]{src,0}); //一层一层向外算 while(!queue.isEmpty() && k>=-1){ int size = queue.size(); k--; for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ int[] curr = queue.poll(); int node = curr[0]; int cost = curr[1]; if(node==dst) min = Math.min(min,cost); for(int[] flight:map.getOrDefault( node ,Arrays.asList())){ if(cost+flight[1]<min) queue.offer(new int[]{flight[0],cost+flight[1]});//如果遇到处理过的点cost已经比当前还小,那么直接跳过 } } } return min==Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : min; } }
类似dikjistra pq解法
class Solution { /** 分析: 1.应该采用最短路径解法 2.单纯最短路径无法解决,因为我们还需要控制stop的次数 思路: 1. 使用heap控制最短路径的优先被获取 -> 建立minheap,按照cost进行排序 2. 同时如果stop次数比之前最短路径少的,也要考虑 -> 创建step[],用于track每个节点的当前最少steps 坑点: steps更新不能在加入的时候就更新 */ public int findCheapestPrice(int n, int[][] flights, int src, int dst, int k) { // build graph 便于后续遍历使用 List<Node>[] graph = build(n, flights); // 建立minheap <city, steps, totalCost> PriorityQueue<int[]> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> { return x[2] - y[2]; }); // 建立step[],用于track每个节点的当前最少steps int[] steps = new int[n]; Arrays.fill(steps, Integer.MAX_VALUE); // 放入起始点,开始bfs heap.offer(new int[]{src, 0, 0}); steps[src] = 0; while(!heap.isEmpty()) { int[] curr = heap.poll(); int cCity = curr[0], cStep = curr[1], cCost = curr[2]; // 如果当前是终点,返回cost if(cCity == dst) return cCost; // 如果当前不是终点,但是已经没有步数可走,那么continue if(cStep > k) continue; // 如果当前点的步数没有比之前的更优,也没必要考虑 // 为啥? 因为我们是用pq来优先获取cost更小的,如果cost也大,步数也不优,那肯定不会最优 if(cStep > steps[cCity]) continue; // 更新当前点的step, 坑点steps更新不能在加入的时候就更新 steps[cCity] = cStep; // 加入其邻居节点 for(Node other : graph[cCity]) { heap.offer(new int[]{other.city, cStep + 1, cCost + other.cost}); } } return -1; } record Node(int city, int cost) {} private List<Node>[] build(int n, int[][] flights) { List<Node>[] graph = new List[n]; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) graph[i] = new ArrayList<>(); for(int[] flight : flights) { int start = flight[0], end = flight[1], cost = flight[2]; graph[start].add(new Node(end, cost)); } return graph; } }
505. The Maze II
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces (represented as 0) and walls (represented as 1). The ball can go through the empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the m x n maze, the ball's start position and the destination, where start = [startrow, startcol] and destination = [destinationrow, destinationcol], return the shortest distance for the ball to stop at the destination. If the ball cannot stop at destination, return -1.
The distance is the number of empty spaces traveled by the ball from the start position (excluded) to the destination (included).
You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls (see examples).
Example 1:
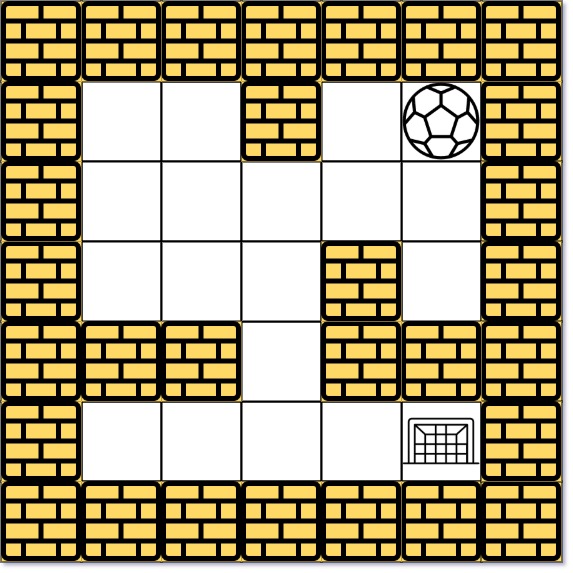
Input: maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [4,4] Output: 12 Explanation: One possible way is : left -> down -> left -> down -> right -> down -> right. The length of the path is 1 + 1 + 3 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 2 = 12.
Example 2:
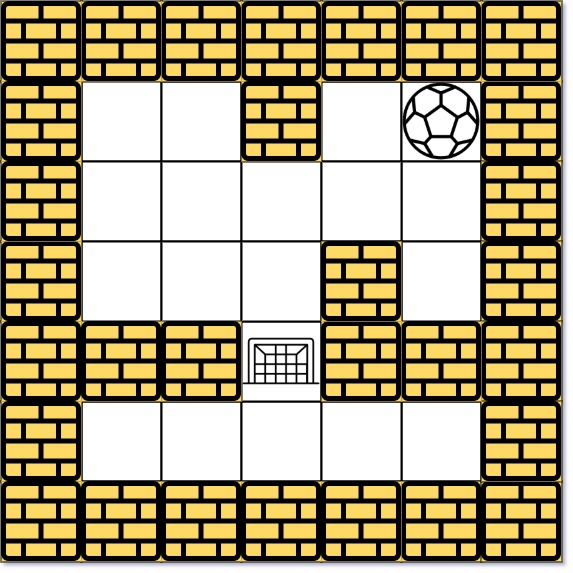
Input: maze = [[0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0],[1,1,0,1,1],[0,0,0,0,0]], start = [0,4], destination = [3,2] Output: -1 Explanation: There is no way for the ball to stop at the destination. Notice that you can pass through the destination but you cannot stop there.
Example 3:
Input: maze = [[0,0,0,0,0],[1,1,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1],[0,1,0,0,0]], start = [4,3], destination = [0,1] Output: -1
Constraints:
m == maze.lengthn == maze[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100maze[i][j]is0or1.start.length == 2destination.length == 20 <= startrow, destinationrow <= m0 <= startcol, destinationcol <= n- Both the ball and the destination exist in an empty space, and they will not be in the same position initially.
- The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces.
class Solution { class Node{ int x; int y; int distance; Node(int x,int y,int distance){ this.x=x; this.y=y; this.distance=distance; } } private int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; public int shortestDistance(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) { //define pq int m = maze.length,n=maze[0].length; //定义heap 用于存放当前到个点距离 PriorityQueue<Node> pq = new PriorityQueue<Node>((x,y)->x.distance-y.distance); //初始化到各点的距离为maxvalue int[][] distance =new int[maze.length][maze[0].length]; for(int i=0;i<m;i++) for(int j=0;j<n;j++) distance[i][j]=Integer.MAX_VALUE; //将start点放进去,距离为0 pq.offer(new Node(start[0],start[1],0)); distance[start[0]][start[1]] = 0; //从start点开始向四周遍历 while(!pq.isEmpty()){ Node node = pq.poll(); for(int[] direct:directions){ int x = node.x; int y = node.y; int step=0; while(x+direct[0]>=0 && x+direct[0]<m && y+direct[1]>=0 && y+direct[1]<n && maze[x+direct[0]][y+direct[1]]!=1){ x+=direct[0]; y+=direct[1]; step++; } //如果遇到可以relaxation的,加入队列,并更新distance if(distance[x][y]>node.distance+step){ pq.offer(new Node(x,y,distance[node.x][node.y]+step)); distance[x][y] = distance[node.x][node.y]+step; } } } //如果destination不是最大值,那么说明它被访问过,否则返回-1 return distance[destination[0]][destination[1]]==Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : distance[destination[0]][destination[1]]; } }
2203. Minimum Weighted Subgraph With the Required Paths
You are given an integer n denoting the number of nodes of a weighted directed graph. The nodes are numbered from 0 to n - 1.
You are also given a 2D integer array edges where edges[i] = [fromi, toi, weighti] denotes that there exists a directed edge from fromi to toi with weight weighti.
Lastly, you are given three distinct integers src1, src2, and dest denoting three distinct nodes of the graph.
Return the minimum weight of a subgraph of the graph such that it is possible to reach dest from both src1 and src2 via a set of edges of this subgraph. In case such a subgraph does not exist, return -1.
A subgraph is a graph whose vertices and edges are subsets of the original graph. The weight of a subgraph is the sum of weights of its constituent edges.
Example 1:
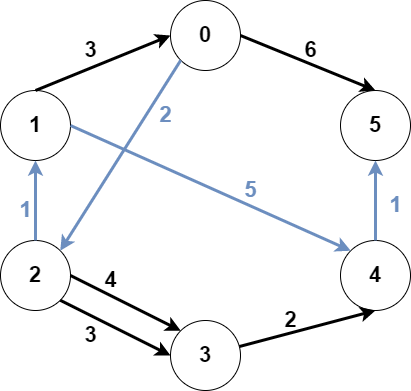
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,2,2],[0,5,6],[1,0,3],[1,4,5],[2,1,1],[2,3,3],[2,3,4],[3,4,2],[4,5,1]], src1 = 0, src2 = 1, dest = 5 Output: 9 Explanation: The above figure represents the input graph. The blue edges represent one of the subgraphs that yield the optimal answer. Note that the subgraph [[1,0,3],[0,5,6]] also yields the optimal answer. It is not possible to get a subgraph with less weight satisfying all the constraints.
Example 2:

Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1,1],[2,1,1]], src1 = 0, src2 = 1, dest = 2 Output: -1 Explanation: The above figure represents the input graph. It can be seen that there does not exist any path from node 1 to node 2, hence there are no subgraphs satisfying all the constraints.
Constraints:
3 <= n <= 1050 <= edges.length <= 105edges[i].length == 30 <= fromi, toi, src1, src2, dest <= n - 1fromi != toisrc1,src2, anddestare pairwise distinct.1 <= weight[i] <= 105
解法:题目本意是,要寻找一条path经过了 A/B两点,并且到dest的距离最短。
换一个思路想这个问题:其实就是寻找某个点,这个点到A/B/Dest的距离最短,那么我们可以分别求:
1.从A点出发到其他点的最短距离
2.从B点出发到其他点的最短距离
3.从dest点出发到其他点的最短距离(这个需要反向建图进行计算)
然后轮询所有的点,获得最短距离
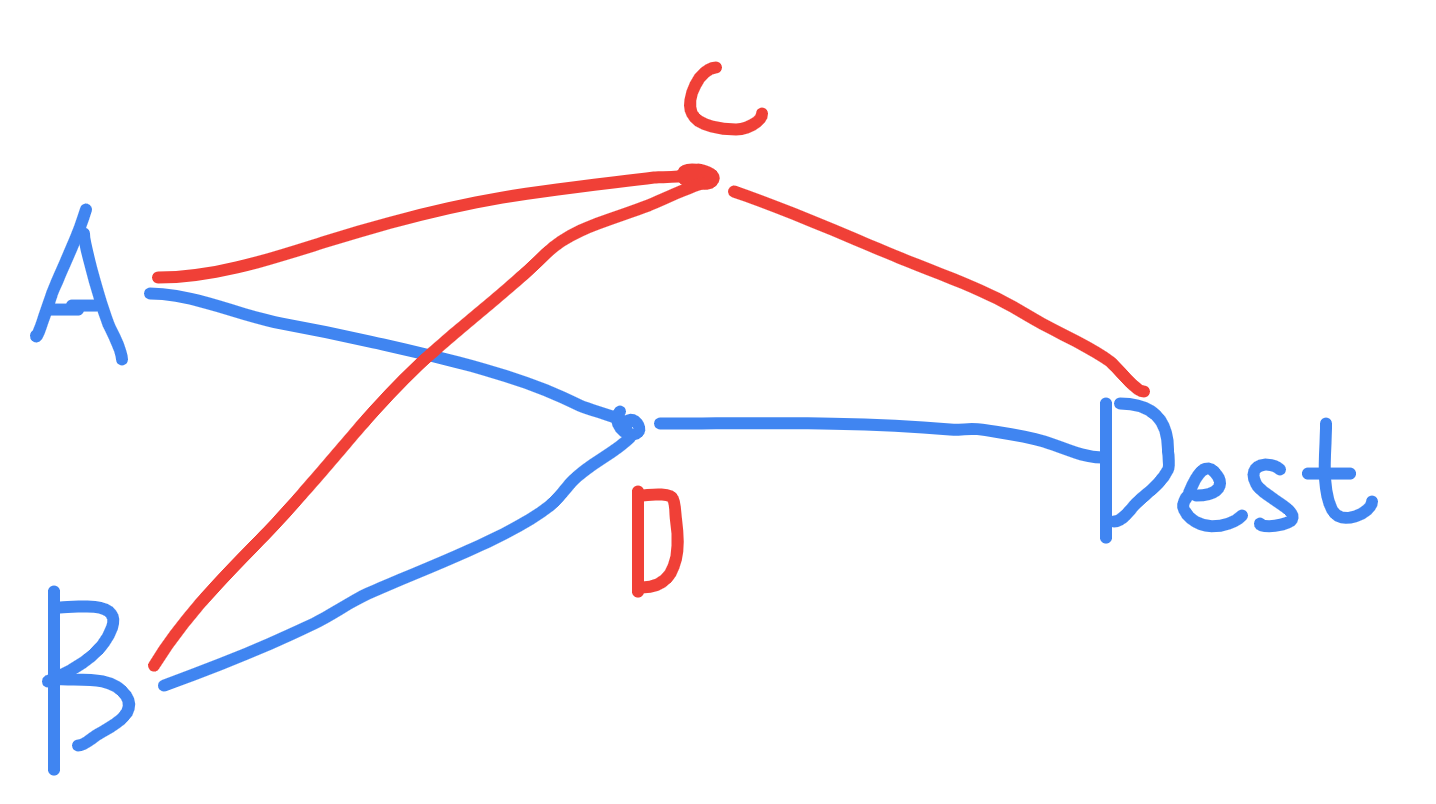
class Solution { public long minimumWeight(int n, int[][] edges, int src1, int src2, int dest) { //build graph List<int[]>[] graph = new List[n]; List<int[]>[] graph2 = new List[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { graph[i] = new ArrayList(); graph2[i] = new ArrayList(); } for(int[] edge:edges){ graph[edge[0]].add(new int[]{edge[1],edge[2]}); //正向建图 graph2[edge[1]].add(new int[]{edge[0],edge[2]});//反向建图 } //calculate shortestpath from src1,src2,dest long[] path1 = shortestPath(graph, src1); long[] path2 = shortestPath(graph, src2); long[] pathDest = shortestPath(graph2, dest); //for loop all the nodes to find the min sum of path to src1/src2/dest long min = Long.MAX_VALUE; for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ if(path1[i]!=Long.MAX_VALUE && path2[i]!=Long.MAX_VALUE && pathDest[i]!=Long.MAX_VALUE){ min = Math.min(path1[i]+path2[i]+pathDest[i],min); } } return min == Long.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : min; } private long[] shortestPath(List<int[]>[] graph, int start){ long[] path = new long[graph.length]; Arrays.fill(path, Long.MAX_VALUE); PriorityQueue<Pair> pq = new PriorityQueue<Pair>((x,y)->(int)(x.dis-y.dis)); pq.offer(new Pair(start,0l)); path[start] = 0l; while(!pq.isEmpty()){ Pair curr = pq.poll(); for(int[] pair:graph[curr.node]){ int end = pair[0],dis = pair[1]; if(path[curr.node]+dis<path[end]){ path[end] = path[curr.node]+dis; pq.offer(new Pair(end,path[curr.node]+dis)); } } } return path; } class Pair{ int node; long dis; Pair(int node,long dis){ this.node = node; this.dis = dis; } } }
You are given a 0-indexed 2D integer array grid of size m x n. Each cell has one of two values:
0represents an empty cell,1represents an obstacle that may be removed.
You can move up, down, left, or right from and to an empty cell.
Return the minimum number of obstacles to remove so you can move from the upper left corner (0, 0) to the lower right corner (m - 1, n - 1).
Example 1:
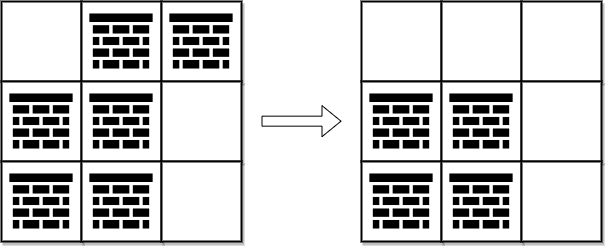
Input: grid = [[0,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]] Output: 2 Explanation: We can remove the obstacles at (0, 1) and (0, 2) to create a path from (0, 0) to (2, 2). It can be shown that we need to remove at least 2 obstacles, so we return 2. Note that there may be other ways to remove 2 obstacles to create a path.
Example 2:
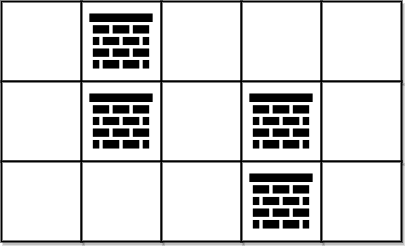
Input: grid = [[0,1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,1,0],[0,0,0,1,0]] Output: 0 Explanation: We can move from (0, 0) to (2, 4) without removing any obstacles, so we return 0.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1052 <= m * n <= 105grid[i][j]is either0or1.grid[0][0] == grid[m - 1][n - 1] == 0
class Solution { int m = 0, n = 0; int[][] directions = {{0,-1},{0,1},{-1,0},{1,0}}; public int minimumObstacles(int[][] grid) { m=grid.length; n=grid[0].length; int[] distance = new int[m*n]; Arrays.fill(distance, Integer.MAX_VALUE); PriorityQueue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((x,y)->{ return x.distance-y.distance; }); queue.offer(new Node(0,0,0)); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ Node curr = queue.poll(); for(int[] direction:directions){ int x = curr.x+direction[0],y=curr.y+direction[1]; if(x < 0 || x>=m || y<0 || y>=n) continue; if(curr.distance + grid[x][y] < distance[pos(x,y)]){ queue.offer(new Node(x,y,curr.distance + grid[x][y])); distance[pos(x,y)] = curr.distance + grid[x][y]; } } } return distance[pos(m-1,n-1)]; } private int pos(int x,int y){ return x*n+y; } class Node{ int x; int y; int distance; Node(int x,int y,int distance){ this.x = x; this.y = y; this.distance = distance; } } }
You are given an undirected weighted graph of n nodes (0-indexed), represented by an edge list where edges[i] = [a, b] is an undirected edge connecting the nodes a and b with a probability of success of traversing that edge succProb[i].
Given two nodes start and end, find the path with the maximum probability of success to go from start to end and return its success probability.
If there is no path from start to end, return 0. Your answer will be accepted if it differs from the correct answer by at most 1e-5.
Example 1:
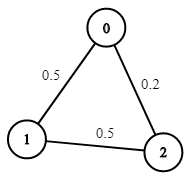
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.2], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.25000 Explanation: There are two paths from start to end, one having a probability of success = 0.2 and the other has 0.5 * 0.5 = 0.25.
Example 2:
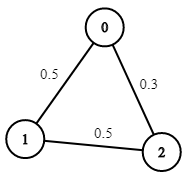
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[0,2]], succProb = [0.5,0.5,0.3], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.30000
Example 3:
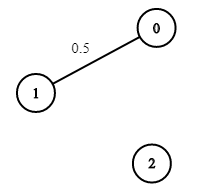
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1]], succProb = [0.5], start = 0, end = 2 Output: 0.00000 Explanation: There is no path between 0 and 2.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10^40 <= start, end < nstart != end0 <= a, b < na != b0 <= succProb.length == edges.length <= 2*10^40 <= succProb[i] <= 1- There is at most one edge between every two nodes.
class Solution { public double maxProbability(int n, int[][] edges, double[] succProb, int start, int end) { //build graph List<Pair>[] graph = new List[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) graph[i] = new ArrayList(); for(int i=0;i<edges.length;i++){ int left = edges[i][0], right=edges[i][1]; graph[left].add(new Pair(right,succProb[i])); graph[right].add(new Pair(left,succProb[i])); } //define heap, distance PriorityQueue<Pair> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((x,y)->{ return Double.compare(y.pro,x.pro); }); double[] probs = new double[n]; //traversal pq.offer(new Pair(start, 1.0)); probs[start]=1.0; while(!pq.isEmpty()){ Pair curr = pq.poll(); if(curr.node == end) return curr.pro; for(Pair pair:graph[curr.node]){ if(probs[pair.node] < curr.pro*pair.pro){ pq.offer(new Pair(pair.node, curr.pro*pair.pro)); probs[pair.node]=curr.pro*pair.pro; } } } return 0.0; } class Pair{ int node; double pro; Pair(int node, double pro){ this.node = node; this.pro = pro; } } }
Given an m x n integer matrix grid, return the maximum score of a path starting at (0, 0) and ending at (m - 1, n - 1) moving in the 4 cardinal directions.
The score of a path is the minimum value in that path.
- For example, the score of the path
8 → 4 → 5 → 9is4.
Example 1:
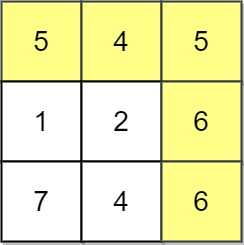
Input: grid = [[5,4,5],[1,2,6],[7,4,6]] Output: 4 Explanation: The path with the maximum score is highlighted in yellow.
Example 2:
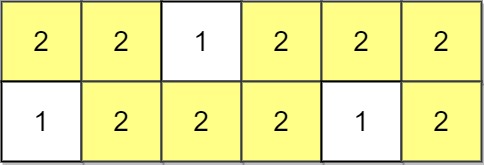
Input: grid = [[2,2,1,2,2,2],[1,2,2,2,1,2]] Output: 2
Example 3:
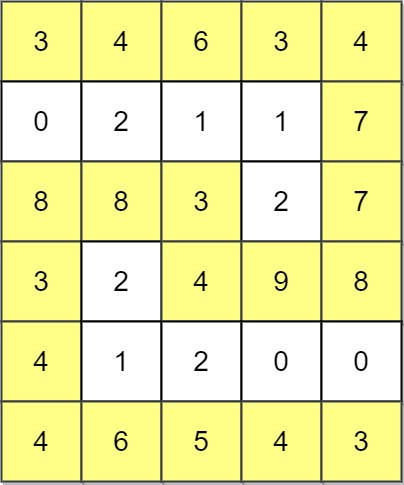
Input: grid = [[3,4,6,3,4],[0,2,1,1,7],[8,8,3,2,7],[3,2,4,9,8],[4,1,2,0,0],[4,6,5,4,3]] Output: 3
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 109
class Solution { /* 如何证明 bfs + heap 的做法是对的? */ private int M, N; record Pos(int x, int y){} private int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}; public int maximumMinimumPath(int[][] grid) { M = grid.length; N = grid[0].length; //define pq PriorityQueue<Pos> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b)->{ return grid[b.x][b.y] - grid[a.x][a.y]; }); Set<Pos> visited = new HashSet(); //put the 0,0 into the pq Pos start = new Pos(0, 0); pq.offer(start); visited.add(start); //start bfs int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; while(!pq.isEmpty()) { Pos curr = pq.poll(); result = Math.min(grid[curr.x][curr.y], result); if(curr.x == M - 1 && curr.y == N - 1) return result; for(int[] direct : directions) { int x = curr.x + direct[0], y = curr.y + direct[1]; Pos next = new Pos(x, y); if(x < 0 || x >= M || y < 0 || y >= N || visited.contains(next)) continue; visited.add(next); pq.offer(next); } } return 0; } }
2662. Minimum Cost of a Path With Special Roads
You are given an array start where start = [startX, startY] represents your initial position (startX, startY) in a 2D space. You are also given the array target where target = [targetX, targetY] represents your target position (targetX, targetY).
The cost of going from a position (x1, y1) to any other position in the space (x2, y2) is |x2 - x1| + |y2 - y1|.
There are also some special roads. You are given a 2D array specialRoads where specialRoads[i] = [x1i, y1i, x2i, y2i, costi] indicates that the ith special road can take you from (x1i, y1i) to (x2i, y2i) with a cost equal to costi. You can use each special road any number of times.
Return the minimum cost required to go from (startX, startY) to (targetX, targetY).
Example 1:
Input: start = [1,1], target = [4,5], specialRoads = [[1,2,3,3,2],[3,4,4,5,1]] Output: 5 Explanation: The optimal path from (1,1) to (4,5) is the following: - (1,1) -> (1,2). This move has a cost of |1 - 1| + |2 - 1| = 1. - (1,2) -> (3,3). This move uses the first special edge, the cost is 2. - (3,3) -> (3,4). This move has a cost of |3 - 3| + |4 - 3| = 1. - (3,4) -> (4,5). This move uses the second special edge, the cost is 1. So the total cost is 1 + 2 + 1 + 1 = 5. It can be shown that we cannot achieve a smaller total cost than 5.
Example 2:
Input: start = [3,2], target = [5,7], specialRoads = [[3,2,3,4,4],[3,3,5,5,5],[3,4,5,6,6]] Output: 7 Explanation: It is optimal to not use any special edges and go directly from the starting to the ending position with a cost |5 - 3| + |7 - 2| = 7.
Constraints:
start.length == target.length == 21 <= startX <= targetX <= 1051 <= startY <= targetY <= 1051 <= specialRoads.length <= 200specialRoads[i].length == 5startX <= x1i, x2i <= targetXstartY <= y1i, y2i <= targetY1 <= costi <= 105
class Solution { record Pos(int x, int y) {} record Pair(Pos pos, int len) {} public int minimumCost(int[] start, int[] end, int[][] specialRoads) { //set将用于收集图涉及的所有点 Set<Pos> set = new HashSet(); //记录所有的捷径 Map<Pos, Map<Pos, Integer>> specRoad = new HashMap(); build(specialRoads, specRoad, set); Pos sPos = new Pos(start[0], start[1]); Pos ePos = new Pos(end[0], end[1]); set.add(sPos); set.add(ePos); PriorityQueue<Pair> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> x.len - y.len); //定义起点到所有点的最短距离,默认设置为最大值 Map<Pos, Integer> distance = new HashMap(); for(Pos temp : set) { if(temp == sPos) { distance.put(sPos, 0); } else{ distance.put(temp, Integer.MAX_VALUE); } } //将起点自己放入队列 pq.offer(new Pair(sPos, 0)); while(!pq.isEmpty()) { //取出距离start最近的点 Pair currPair = pq.poll(); if(currPair.pos.x == ePos.x && currPair.pos.y == ePos.y) return currPair.len; Pos curr = currPair.pos; //遍历它周围的点 for(Pos other : set) { //如果是自己掠过 if(other == curr) continue; //计算当前点到邻居的距离 int len = getDis(curr, other); //如果有捷径的话,更新为捷径距离 if(specRoad.containsKey(curr) && specRoad.get(curr).containsKey(other)) { len = Math.min(len, specRoad.get(curr).get(other)); } //如果从 起点到当前点的距离+当前点到邻居的距离小于 起点到邻居的距离,那么将其压入队列 if(currPair.len + len < distance.get(other)){ pq.offer(new Pair(other, currPair.len + len)); distance.put(other, currPair.len + len); } } } return -1; } //将捷径的路压入map便于后续查找 private void build(int[][] specialRoads, Map<Pos, Map<Pos, Integer>> graph, Set<Pos> set) { for(int[] road : specialRoads) { Pos start = new Pos(road[0], road[1]); Pos end = new Pos(road[2], road[3]); setDis(graph, start, end, road[4]); set.add(start); set.add(end); } } private void setDis(Map<Pos, Map<Pos, Integer>> graph, Pos start, Pos end, int len) { //如果捷径的距离比曼哈顿距离还远,那就不算捷径 if(getDis(start, end) <= len) return; Map<Pos, Integer> startMap = graph.getOrDefault(start, new HashMap()); startMap.put(end, len); graph.put(start, startMap); } //求取曼哈顿距离 private int getDis(Pos start, Pos end) { return Math.abs(start.x - end.x) + Math.abs(start.y - end.y); } }
n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The graph consists of m edges represented by a 2D array edges, where edges[i] = [ai, bi, wi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi with weight wi.Consider all the shortest paths from node 0 to node n - 1 in the graph. You need to find a boolean array answer where answer[i] is true if the edge edges[i] is part of at least one shortest path. Otherwise, answer[i] is false.
Return the array answer.
Note that the graph may not be connected.
Example 1:
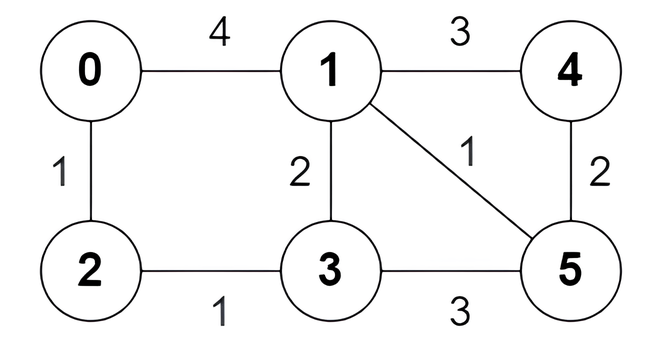
Input: n = 6, edges = [[0,1,4],[0,2,1],[1,3,2],[1,4,3],[1,5,1],[2,3,1],[3,5,3],[4,5,2]]
Output: [true,true,true,false,true,true,true,false]
Explanation:
The following are all the shortest paths between nodes 0 and 5:
- The path
0 -> 1 -> 5: The sum of weights is4 + 1 = 5. - The path
0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 5: The sum of weights is1 + 1 + 3 = 5. - The path
0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 1 -> 5: The sum of weights is1 + 1 + 2 + 1 = 5.
Example 2:
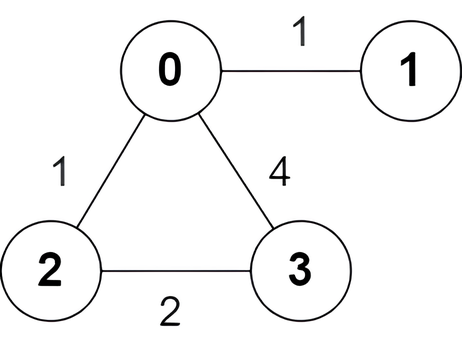
Input: n = 4, edges = [[2,0,1],[0,1,1],[0,3,4],[3,2,2]]
Output: [true,false,false,true]
Explanation:
There is one shortest path between nodes 0 and 3, which is the path 0 -> 2 -> 3 with the sum of weights 1 + 2 = 3.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 5 * 104m == edges.length1 <= m <= min(5 * 104, n * (n - 1) / 2)0 <= ai, bi < nai != bi1 <= wi <= 105- There are no repeated edges.
class Solution { /** 解题关键点: 1.dijkstra求最短路径,关键:要遍历完所有最优解,而不是只找1个最优解 2.过程中将path记录下来 3.巧妙的地方,在建图的时候,将原始edge的下标也计入graph中,这样可以方便的path track */ public boolean[] findAnswer(int n, int[][] edges) { // build graph List<Node>[] graph = new List[n]; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) graph[i] = new ArrayList(); for(int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) { int start = edges[i][0], end = edges[i][1], cost = edges[i][2]; graph[start].add(new Node(end, cost, i)); //注意 下标i也记在了图中 graph[end].add(new Node(start, cost, i)); } // result 初始化结果数组 boolean[] result = new boolean[edges.length]; // dijkstra 最短路径搜索 int[] distance = new int[n]; Arrays.fill(distance, Integer.MAX_VALUE); PriorityQueue<Dnode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> x.cost - y.cost); queue.offer(new Dnode(0, 0, new ArrayList())); while(!queue.isEmpty()) { Dnode curr = queue.poll(); // 如果当前不是到curr节点的最短路径,直接跳过 if(curr.cost > distance[curr.pos]) continue; distance[curr.pos] = curr.cost; for(Node other : graph[curr.pos]) { List<Integer> temp = new ArrayList(curr.path); temp.add(other.ind); queue.offer(new Dnode(other.pos, other.cost + curr.cost, temp)); } if(curr.pos == n - 1) { //找到了最短路径 for(int index : curr.path) { result[index] = true; } } } return result; } record Node(int pos, int cost, int ind){} //图节点 record Dnode(int pos, int cost, List<Integer> path) {} //最短路径heap中节点 }
class Solution: ''' 关键点: 1.djestra的过程中记录path,path的记录的关键:建图的时候,将edge的index也挂在图中 2.找到最短路径后,不结束,继续将所有最优解拿到 ''' def findAnswer(self, n: int, edges: List[List[int]]) -> List[bool]: # 建图 graph = defaultdict(list) for i, (u, v, w) in enumerate(edges): graph[u].append((v, w, i)) #注意将edges的下标:i也挂进去了,便于后面记录path graph[v].append((u, w, i)) # 初始化ans ans = [False for _ in edges] # 初始化distance distances = [math.inf for _ in range(n)] #start 入queue q = [(0, 0, [])] while q != []: dis, u, paths = heapq.heappop(q) # 如果cost大于最优值,跳过 if dis > distances[u]: continue # 更新最优值 distances[u] = dis # 遍历所有neighbor节点 for v, w, e in graph[u]: heapq.heappush(q, (dis+w, v, paths + [e])) # 如果到达终点,那么标记当前path中所有edge为true # 这里没有结束 if u == n-1: for e in paths: ans[e] = True return ans



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号