图算法(一)-MST最小生成树 1489, 1584
最小生成树(minimum spanning tree)的3种解法:
稀疏图:1>Prim PQ implementation O(ElogV) 2>Kruskal implementationm (ElogV)
稠密图:Prim Naive implementation O(V2)
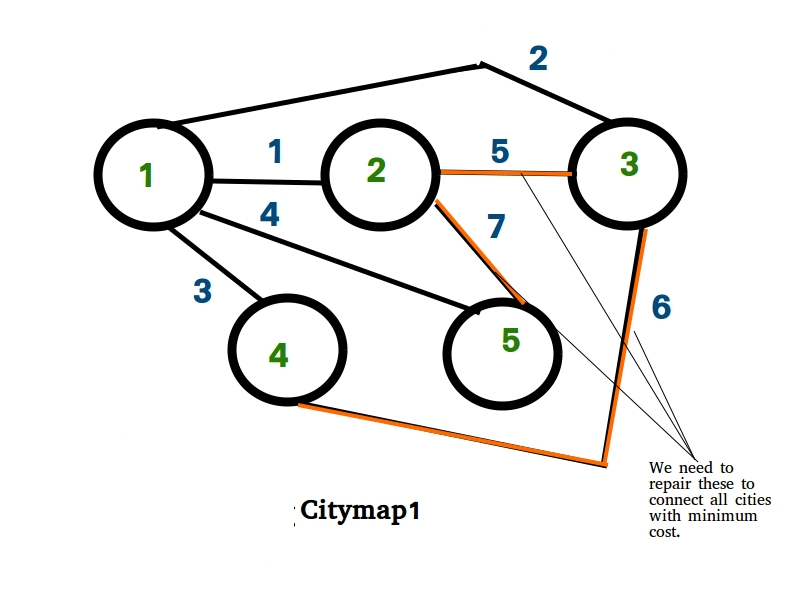
Minimum cost to connect all cities
It is sure that all the cities were connected before the roads were damaged.
Examples:
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important DSA concepts with the DSA Self Paced Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready. To complete your preparation from learning a language to DS Algo and many more, please refer Complete Interview Preparation Course.
In case you wish to attend live classes with experts, please refer DSA Live Classes for Working Professionals and Competitive Programming Live for Students.
Input : {{0, 1, 2, 3, 4},
{1, 0, 5, 0, 7},
{2, 5, 0, 6, 0},
{3, 0, 6, 0, 0},
{4, 7, 0, 0, 0}};
Output : 10
Prim PQ implementation
class Solution { record Edge(int pos, int val){} public int minimumCost(int n, int[][] connections) { //建图,为了方便从一个点访问其对应的边 List<Edge>[] graph = new List[n + 1]; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) graph[i] = new ArrayList(); for(int[] conn : connections) { int a = conn[0], b = conn[1], val = conn[2]; graph[a].add(new Edge(b, val)); graph[b].add(new Edge(a, val)); } //定义小顶堆用于存放边 PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> { return x.val - y.val; }); //define visited set int result = 0; Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet(); //将一个初始点放入集合 visited.add(1); //将其连接的边放入队列 for(Edge edge : graph[1]) pq.offer(edge); //如果队列不为空 while(!pq.isEmpty()){ //取出其中的最小边 Edge curr = pq.poll(); //如果对端端点已经访问过,那么跳过 if(visited.contains(curr.pos)) continue; //否则加入已访问集合 visited.add(curr.pos); result += curr.val; //将这个点周围的边加入队列 for(Edge edge : graph[curr.pos]){ pq.offer(edge); } //当所有点被访问之后,即可返回结果 if(visited.size() == n) return result; } return -1; } }
时间复杂度: O(ElogV)
Kruskal
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { public static void main (String[] args) { int result = mst(new int[][] {{0, 1, 1, 100, 0, 0}, {1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0}, {1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}, {100, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2}, {0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 2}, {0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0}}); System.out.println(result); } private static int mst(int[][] matrix){ List<Edge> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i=0;i<matrix.length-1;i++){ for(int j=i+1;j<matrix[0].length;j++){ if( matrix[i][j]!=0) list.add(new Edge(i,j,matrix[i][j])); } } Collections.sort(list,(x,y)->x.len-y.len); UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(matrix.length); int sum=0; int count=0; for(Edge edge:list){ if(uf.findParent(edge.x)!=uf.findParent(edge.y)) {//已经连通的不能再union uf.union(edge.x,edge.y); sum+=edge.len; count++; if(count==matrix.length-1) break;//当边数==顶点数-1 的时候,就已经全部连通了 } } return sum; } static class Edge{ int x;int y;int len; Edge(int x,int y,int len){ this.x=x; this.y=y; this.len=len; } } static class UnionFind{ int[] parent; UnionFind(int n){ parent = new int[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) parent[i]=i; } int findParent(int i){ if(parent[i]==i) return i; parent[i]=findParent(parent[i]); return parent[i]; } void union(int x,int y){ int px = findParent(x); int py = findParent(y); parent[px] = py; } } }
时间复杂度: O(ElogE)
Given a weighted undirected connected graph with n vertices numbered from 0 to n - 1, and an array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi, weighti] represents a bidirectional and weighted edge between nodes ai and bi. A minimum spanning tree (MST) is a subset of the graph's edges that connects all vertices without cycles and with the minimum possible total edge weight.
Find all the critical and pseudo-critical edges in the given graph's minimum spanning tree (MST). An MST edge whose deletion from the graph would cause the MST weight to increase is called a critical edge. On the other hand, a pseudo-critical edge is that which can appear in some MSTs but not all.
Note that you can return the indices of the edges in any order.
Example 1:
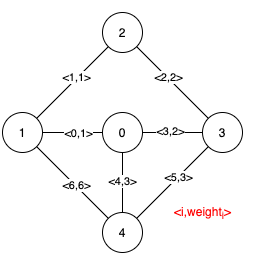
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,2],[0,3,2],[0,4,3],[3,4,3],[1,4,6]] Output: [[0,1],[2,3,4,5]] Explanation: The figure above describes the graph. The following figure shows all the possible MSTs:
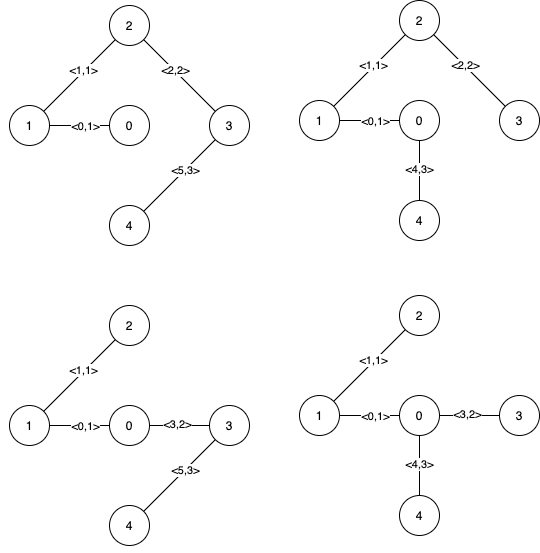
Notice that the two edges 0 and 1 appear in all MSTs, therefore they are critical edges, so we return them in the first list of the output. The edges 2, 3, 4, and 5 are only part of some MSTs, therefore they are considered pseudo-critical edges. We add them to the second list of the output.
Example 2:
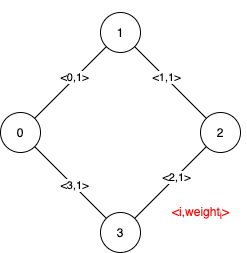
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,1],[0,3,1]] Output: [[],[0,1,2,3]] Explanation: We can observe that since all 4 edges have equal weight, choosing any 3 edges from the given 4 will yield an MST. Therefore all 4 edges are pseudo-critical.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 1001 <= edges.length <= min(200, n * (n - 1) / 2)edges[i].length == 30 <= ai < bi < n1 <= weighti <= 1000- All pairs
(ai, bi)are distinct.
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(int n, int[][] edges) { //1.将数组下标位置加入edges int[][] nEdges = new int[edges.length][4]; for(int i=0;i<edges.length;i++) nEdges[i] = new int[]{edges[i][0],edges[i][1],edges[i][2],i}; Arrays.sort(nEdges,(x,y)->x[2]-y[2]); //初次计算mst int min = mst(n,nEdges,-1,-1); //逐条edge移除后,检查新mst是否大于原始mst List<Integer> critical = new ArrayList(); List<Integer> pseudo = new ArrayList(); for(int i=0;i<edges.length;i++){ int curr = mst(n,nEdges,i,-1); //如果去除此边会mst会变大,说明是critical if(min<curr || curr==-1 ) critical.add(i); else{ //如果mst中强制增加这条边mst没有变大,说明是pseudo 此处关键点,如何判定是pseudo的边 if(min==mst(n,nEdges,-1,i)) pseudo.add(i); } } //3.return result; return Arrays.asList(critical,pseudo); } private int mst(int n, int[][] edges,int exclude,int include){ int count = 0,sum=0; UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n); if(include>=0) {//如果强制加入的边不为空,先加入强制的边 int i = 0; for(i=0;i<edges.length;i++) if(edges[i][3]==include) break; uf.union(edges[i][0],edges[i][1]); sum+=edges[i][2]; count++; } for( int i=0;i<edges.length;i++ ){ int[] edge = edges[i]; if(edge[3]==exclude) continue;//滤除要过滤的边 if(uf.findParent(edge[0])!=uf.findParent(edge[1])){ uf.union(edge[0],edge[1]); sum+=edge[2]; count++; if(count==n-1) return sum; } } return count==n-1 ? sum : -1; } class UnionFind{ int[] parent; UnionFind(int n){ parent = new int[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) parent[i]=i; } void union(int x,int y){ parent[findParent(x)] = parent[findParent(y)]; } int findParent(int x){ if(x==parent[x]) return x; parent[x]= findParent(parent[x]); return parent[x]; } } }
You are given an array points representing integer coordinates of some points on a 2D-plane, where points[i] = [xi, yi].
The cost of connecting two points [xi, yi] and [xj, yj] is the manhattan distance between them: |xi - xj| + |yi - yj|, where |val| denotes the absolute value of val.
Return the minimum cost to make all points connected. All points are connected if there is exactly one simple path between any two points.
Example 1:
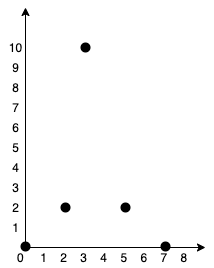
Input: points = [[0,0],[2,2],[3,10],[5,2],[7,0]] Output: 20 Explanation:

We can connect the points as shown above to get the minimum cost of 20. Notice that there is a unique path between every pair of points.
Example 2:
Input: points = [[3,12],[-2,5],[-4,1]] Output: 18
Constraints:
1 <= points.length <= 1000-106 <= xi, yi <= 106- All pairs
(xi, yi)are distinct.
解法: kruskal
关键点在于 如何构建unionfind和端点,这里我们巧妙使用数组下标作为这些点的标识
class Solution { record Edge(int x, int y, int distance){} public int minCostConnectPoints(int[][] points) { //特殊情况处理 if(points.length == 1) return 0; //建立小顶堆 PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> x.distance - y.distance); //将所有点互连,计算edge距离并加入heap for(int i = 0; i < points.length; i++){ for(int j = i + 1; j < points.length; j++){ int dis = Math.abs(points[i][0] - points[j][0]) + Math.abs(points[i][1] - points[j][1]); Edge edge = new Edge(i, j, dis); pq.offer(edge); } } UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(points.length); int result = 0, count = 0; //从小到大逐条边进行遍历,进行union操作 while(!pq.isEmpty()){ Edge curr = pq.poll(); if(uf.findParent(curr.x) == uf.findParent(curr.y)) continue; uf.union(curr.x, curr.y); result += curr.distance; count++; if(count == points.length - 1) return result; } return -1; } } class UnionFind{ int[] parent; UnionFind(int n){ parent = new int[n]; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) parent[i] = i; } int findParent(int x){ if(x == parent[x]) return x; parent[x] = findParent(parent[x]); return parent[x]; } void union(int x, int y){ int px = findParent(x); int py = findParent(y); if(px == py) return; parent[px] = py; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号