并查集(UnionFind) 系列 547,lintcode434,128,684,399,721,827,1631,1202
547. Number of Provinces
There are n cities. Some of them are connected, while some are not. If city a is connected directly with city b, and city b is connected directly with city c, then city a is connected indirectly with city c.
A province is a group of directly or indirectly connected cities and no other cities outside of the group.
You are given an n x n matrix isConnected where isConnected[i][j] = 1 if the ith city and the jth city are directly connected, and isConnected[i][j] = 0 otherwise.
Return the total number of provinces.
Example 1:
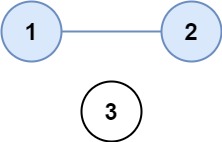
Input: isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]] Output: 2
Example 2:
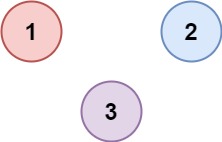
Input: isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]] Output: 3
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 200n == isConnected.lengthn == isConnected[i].lengthisConnected[i][j]is1or0.isConnected[i][i] == 1isConnected[i][j] == isConnected[j][i]
解法1: 并查集
class Solution { public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected) { //1.for loop len elements do unionfind UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(isConnected.length); for(int i=0;i<isConnected.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<isConnected.length;j++){ if(i!=j && isConnected[i][j]==1) { uf.union(i,j); } } } //2.count the parent[i]=i int count = 0; for(int i=0;i<isConnected.length;i++) if(uf.parent[i]==i) count++; return count; } //UnionFind implementation class UnionFind{ int[] parent; int[] rank; UnionFind(int n){ parent = new int[n]; rank = new int[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) parent[i]=i; } public int findParent(int x){ if(x==parent[x]) return x; parent[x] = findParent(parent[x]); return parent[x]; } public void union( int x,int y ){ int px = findParent(x); int py = findParent(y); if(px==py) return; if(rank[px]>rank[py]) parent[py]=px; else if(rank[px]<rank[py]) parent[px]=py; else{ parent[px]=py; rank[py]++; } } } }
解法二: dfs
class Solution { public int findCircleNum(int[][] isConnected) { //defind visited int len = isConnected.length; boolean[] visited = new boolean[len]; //for loop 0 ~ len-1 recursively find its connections int count = 0; for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ if(visited[i]) continue; count++; dfs(isConnected,i,visited); } return count; } private void dfs(int[][] isConnected,int i,boolean[] visited){ int len = isConnected.length; visited[i]=true; for(int j=0;j<len;j++){ if(isConnected[i][j]==1 && !visited[j] ) dfs(isConnected,j,visited); } } }
Given a n,m which means the row and column of the 2D matrix and an array of pair A( size k). Originally, the 2D matrix is all 0 which means there is only sea in the matrix. The list pair has k operator and each operator has two integer A[i].x, A[i].y means that you can change the grid matrix[A[i].x][A[i].y] from sea to island. Return how many island are there in the matrix after each operator.You need to return an array of size K.
0 is represented as the sea, 1 is represented as the island. If two 1 is adjacent, we consider them in the same island. We only consider up/down/left/right adjacent.
Example 1:
Input: n = 4, m = 5, A = [[1,1],[0,1],[3,3],[3,4]]
Output: [1,1,2,2]
Explanation:
0. 00000
00000
00000
00000
1. 00000
01000
00000
00000
2. 01000
01000
00000
00000
3. 01000
01000
00000
00010
4. 01000
01000
00000
00011Example 2:
Input: n = 3, m = 3, A = [[0,0],[0,1],[2,2],[2,1]]
Output: [1,1,2,2]/** * Definition for a point. * class Point { * int x; * int y; * Point() { x = 0; y = 0; } * Point(int a, int b) { x = a; y = b; } * } */ public class Solution { /** * @param n: An integer * @param m: An integer * @param operators: an array of point * @return: an integer array */ public List<Integer> numIslands2(int m, int n, Point[] operators) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList(); UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(m*n); int count=0; int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; if(operators==null) return result; for(Point p:operators){ //重复元素直接跳过 if(visited[p.x][p.y]) {//坑点1:重复元素记得跳过 result.add(count); continue; } count++; visited[p.x][p.y]=true; for(int[] dir:directions){ int nx = p.x+dir[0]; int ny = p.y+dir[1]; if( nx>=0 && ny>=0 && nx<m && ny<n ){ if(visited[nx][ny] && (uf.find(nx*n+ny)!=uf.find(p.x*n+p.y))){//坑点2:这里的列数是n,不是m, 因此是p.x*n+p.y ,另外当且仅当相邻点已经被访问过并且还没有连通的情况下才进行连通并count-- count--; uf.union(p.x*n+p.y,nx*n+ny); } } } result.add(count); } return result; } class UnionFind{ int[] parent; UnionFind(int n){ parent = new int[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) parent[i]=i; } int find(int x){ if(x==parent[x]) return x; parent[x] = find(parent[x]); return parent[x]; } void union(int x,int y){ int px = find(x); int py = find(y); if(px==py) return; parent[px]=py; } } }
128. Longest Consecutive Sequence
Given an unsorted array of integers nums, return the length of the longest consecutive elements sequence.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest consecutive elements sequence is [1, 2, 3, 4]. Therefore its length is 4.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1] Output: 9
Constraints:
0 <= nums.length <= 105-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
解法一:使用并查集记录元素下标,然后对每个元素进行两侧数字连接
class Solution { public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) { Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap(); UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(nums.length); for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ if(map.containsKey(nums[i])) continue; map.put(nums[i],i); if(map.get(nums[i]+1)!=null) uf.union(i,map.get(nums[i]+1)); if(map.get(nums[i]-1)!=null) uf.union(i,map.get(nums[i]-1)); } int max = 0; for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++) max = Math.max(max,uf.size[i]); return max; } class UnionFind{ int[] parent; int[] size; UnionFind(int n){ parent = new int[n]; size = new int[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { parent[i]=i; size[i]=1; } } int findParent(int i){ if(parent[i]==i) return i; parent[i] = findParent(parent[i]); return parent[i]; } void union(int x,int y){ int px = findParent(x); int py = findParent(y); if(px==py) return ; parent[px]=py; size[py]+=size[px]; } } }
解法二:使用hashset,保存所有元素,迭代数组元素从set移除两侧相邻元素直至找不到相邻
class Solution { public int longestConsecutive(int[] nums) { Set<Integer> set = new HashSet(); for(int num:nums) set.add(num); int max = 0; for(int num:nums){ if(!set.remove(num)) continue; //以当前元素开始向两侧查找相邻元素 int left = num-1; int right = num+1; while(set.remove(left)) left--; while(set.remove(right)) right++; //记录此次遍历的最大范围 max = Math.max(right-left-1,max); } return max; } }
684. Redundant Connection
In this problem, a tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles.
You are given a graph that started as a tree with n nodes labeled from 1 to n, with one additional edge added. The added edge has two different vertices chosen from 1 to n, and was not an edge that already existed. The graph is represented as an array edges of length n where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the graph.
Return an edge that can be removed so that the resulting graph is a tree of n nodes. If there are multiple answers, return the answer that occurs last in the input.
Example 1:
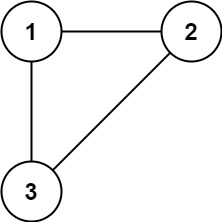
Input: edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]] Output: [2,3]
Example 2:
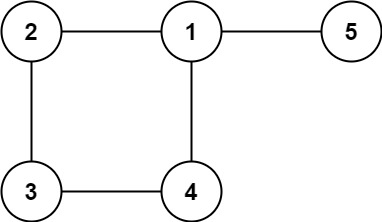
Input: edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,4],[1,5]] Output: [1,4]
Constraints:
n == edges.length3 <= n <= 1000edges[i].length == 21 <= ai < bi <= edges.lengthai != bi- There are no repeated edges.
- The given graph is connected.
class Solution { public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) { UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(edges.length); //逐条遍历edge,如果两个端点已经连接,那么这条边即为造成环的那条边;否则把他们union起来 for(int[] edge:edges){ if(uf.findParent(edge[0]-1)==uf.findParent(edge[1]-1)) return edge;//坑点,注意顶点时从1开始的,但是unionfind中是从0开始的 uf.union(edge[0]-1,edge[1]-1); } return null; } class UnionFind{ int[] parent; UnionFind(int n){ parent = new int[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) parent[i]=i; } int findParent( int x ){ if(parent[x]==x) return x; parent[x] = findParent(parent[x]); return parent[x]; } void union(int x,int y){ int px = findParent(x); int py = findParent(y); if(px==py) return; parent[px]=py; } } }
You are given an array of variable pairs equations and an array of real numbers values, where equations[i] = [Ai, Bi] and values[i] represent the equation Ai / Bi = values[i]. Each Ai or Bi is a string that represents a single variable.
You are also given some queries, where queries[j] = [Cj, Dj] represents the jth query where you must find the answer for Cj / Dj = ?.
Return the answers to all queries. If a single answer cannot be determined, return -1.0.
Note: The input is always valid. You may assume that evaluating the queries will not result in division by zero and that there is no contradiction.
Example 1:
Input: equations = [["a","b"],["b","c"]], values = [2.0,3.0], queries = [["a","c"],["b","a"],["a","e"],["a","a"],["x","x"]] Output: [6.00000,0.50000,-1.00000,1.00000,-1.00000] Explanation: Given: a / b = 2.0, b / c = 3.0 queries are: a / c = ?, b / a = ?, a / e = ?, a / a = ?, x / x = ? return: [6.0, 0.5, -1.0, 1.0, -1.0 ]
Example 2:
Input: equations = [["a","b"],["b","c"],["bc","cd"]], values = [1.5,2.5,5.0], queries = [["a","c"],["c","b"],["bc","cd"],["cd","bc"]] Output: [3.75000,0.40000,5.00000,0.20000]
Example 3:
Input: equations = [["a","b"]], values = [0.5], queries = [["a","b"],["b","a"],["a","c"],["x","y"]] Output: [0.50000,2.00000,-1.00000,-1.00000]
Constraints:
1 <= equations.length <= 20equations[i].length == 21 <= Ai.length, Bi.length <= 5values.length == equations.length0.0 < values[i] <= 20.01 <= queries.length <= 20queries[i].length == 21 <= Cj.length, Dj.length <= 5Ai, Bi, Cj, Djconsist of lower case English letters and digits.
class Solution { public double[] calcEquation(List<List<String>> equations, double[] values, List<List<String>> queries) { UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(); for(int i=0;i<values.length;i++){ String divid1 = equations.get(i).get(0); String divid2 = equations.get(i).get(1); uf.union(divid1,divid2,values[i]); uf.print(); } double[] result = new double[queries.size()]; for(int i=0;i<queries.size();i++){ String divid1 = queries.get(i).get(0); String divid2 = queries.get(i).get(1); Pair parent1 = uf.findParent(divid1); Pair parent2 = uf.findParent(divid2); if(parent1==null || parent2==null || !parent1.parent.equals(parent2.parent)) //记得不仅仅是某个元素没出现时为-1,如果两个元素没有连通的时候也是-1 result[i]=-1; else result[i]= parent1.weight/parent2.weight; } return result; } class Pair{ String parent; double weight; Pair(String parent,double weight){ this.parent = parent; this.weight = weight; } } class UnionFind{ Map<String,Pair> map; UnionFind(){ map = new HashMap(); } Pair findParent(String str){ Pair pair = map.get(str); if(pair==null) return null; if(pair.parent.equals(str)) return pair; Pair gpair = findParent(pair.parent); pair.parent = gpair.parent; pair.weight = gpair.weight*pair.weight; return pair; } void union(String x,String y,double weight){ Pair parentX = findParent(x); Pair parentY = findParent(y); if(parentX==null && parentY==null){//如果X,Y均没有出现过,直接添加并且连通 parentX= new Pair(y,weight); parentY= new Pair(y,1.0); map.put(x,parentX); map.put(y,parentY); } else if(parentX==null){//如果X没出现过,将它挂到Y上 parentX= new Pair(y,weight); map.put(x,parentX); } else if(parentY==null){//如果Y没出现过,将它挂到X上 parentY = new Pair(x,1/weight); map.put(y,parentY); } else{//如果两个都出现过,那么当前我们拿到的时候他们的parent,此时要把他们的parent挂起来 map.put(parentX.parent, new Pair(parentY.parent, weight / parentX.weight * parentY.weight)); } } } }
721. Accounts Merge
Given a list of accounts where each element accounts[i] is a list of strings, where the first element accounts[i][0] is a name, and the rest of the elements are emails representing emails of the account.
Now, we would like to merge these accounts. Two accounts definitely belong to the same person if there is some common email to both accounts. Note that even if two accounts have the same name, they may belong to different people as people could have the same name. A person can have any number of accounts initially, but all of their accounts definitely have the same name.
After merging the accounts, return the accounts in the following format: the first element of each account is the name, and the rest of the elements are emails in sorted order. The accounts themselves can be returned in any order.
Example 1:
Input: accounts = [["John","johnsmith@mail.com","john_newyork@mail.com"],["John","johnsmith@mail.com","john00@mail.com"],["Mary","mary@mail.com"],["John","johnnybravo@mail.com"]] Output: [["John","john00@mail.com","john_newyork@mail.com","johnsmith@mail.com"],["Mary","mary@mail.com"],["John","johnnybravo@mail.com"]] Explanation: The first and second John's are the same person as they have the common email "johnsmith@mail.com". The third John and Mary are different people as none of their email addresses are used by other accounts. We could return these lists in any order, for example the answer [['Mary', 'mary@mail.com'], ['John', 'johnnybravo@mail.com'], ['John', 'john00@mail.com', 'john_newyork@mail.com', 'johnsmith@mail.com']] would still be accepted.
Example 2:
Input: accounts = [["Gabe","Gabe0@m.co","Gabe3@m.co","Gabe1@m.co"],["Kevin","Kevin3@m.co","Kevin5@m.co","Kevin0@m.co"],["Ethan","Ethan5@m.co","Ethan4@m.co","Ethan0@m.co"],["Hanzo","Hanzo3@m.co","Hanzo1@m.co","Hanzo0@m.co"],["Fern","Fern5@m.co","Fern1@m.co","Fern0@m.co"]] Output: [["Ethan","Ethan0@m.co","Ethan4@m.co","Ethan5@m.co"],["Gabe","Gabe0@m.co","Gabe1@m.co","Gabe3@m.co"],["Hanzo","Hanzo0@m.co","Hanzo1@m.co","Hanzo3@m.co"],["Kevin","Kevin0@m.co","Kevin3@m.co","Kevin5@m.co"],["Fern","Fern0@m.co","Fern1@m.co","Fern5@m.co"]]
Constraints:
1 <= accounts.length <= 10002 <= accounts[i].length <= 101 <= accounts[i][j] <= 30accounts[i][0]consists of English letters.accounts[i][j] (for j > 0)is a valid email.
class Solution { public List<List<String>> accountsMerge(List<List<String>> accounts) { //unionfind 将同一个account下的email都连通起来 UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(); Map<String,String> emailName = new HashMap();//这个map用来映射email-name的关系 for(List<String> list:accounts){ String name = list.get(0); for(int i=1;i<list.size();i++){ emailName.put(list.get(i),name); if(i>1) uf.union(list.get(1),list.get(i)); } } //将连通过的email以parent进行groupby放入map中 groupmap存储的是<parent,<emailList>> Map<String,List<String>> groupmap = new HashMap(); for(String email:emailName.keySet()){ String parentEmail = uf.findParent(email); List<String> list = groupmap.getOrDefault(parentEmail,new ArrayList()); list.add(email); groupmap.put(parentEmail,list); } //将groupmap中的结果 1.进行排序 2.从emailName中取出accountName放在首位 3.加入最终结果list List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList(); for(String email:groupmap.keySet()){ List<String> list = groupmap.get(email); Collections.sort(list); list.add(0,emailName.get(email)); result.add(list); } return result; } } class UnionFind{ private Map<String,String> map; UnionFind(){ map = new HashMap(); } public String findParent(String curr){ String parent = map.get(curr); if(parent==null){ map.put(curr,curr); } else{ if(parent.equals(curr)) return curr; map.put(curr,findParent(parent)); } return map.get(curr); } public void union(String s1,String s2){ String parent1 = findParent(s1); String parent2 = findParent(s2); map.put(parent1,parent2); } }
You are given an n x n binary matrix grid. You are allowed to change at most one 0 to be 1.
Return the size of the largest island in grid after applying this operation.
An island is a 4-directionally connected group of 1s.
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[1,0],[0,1]] Output: 3 Explanation: Change one 0 to 1 and connect two 1s, then we get an island with area = 3.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,1],[1,0]] Output: 4 Explanation: Change the 0 to 1 and make the island bigger, only one island with area = 4.
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,1],[1,1]] Output: 4 Explanation: Can't change any 0 to 1, only one island with area = 4.
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500grid[i][j]is either0or1.
class Solution { public int largestIsland(int[][] grid) { int m=grid.length,n=grid[0].length; UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(m*n); int max = 0; //bfs遍历val=1的点,将相连的union起来 for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ for(int j=0;j<n;j++){ if(grid[i][j]==1){ bfs(grid,i,j,uf); max = Math.max(max,uf.size[i*n+j]); } } } //逐个判定剩余的val=0的点,判定它的四周能与几个岛相连,然后把连接的岛面积加起来 取max for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ for(int j=0;j<n;j++){ if(grid[i][j]==0){ Set<Integer> set = new HashSet(); for(int[] direct:directions){ int xx = i+direct[0]; int yy = j+direct[1]; if(xx<0 || xx>=grid.length || yy<0 || yy>=grid[0].length || grid[xx][yy]==0) continue; set.add(uf.findParent(xx*n+yy)); } int sum = 1; for(int p:set) sum+=uf.size[p]; max = Math.max(max,sum); } } } return max; } private int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; //bfs union相连的岛 private void bfs(int[][] grid,int x,int y,UnionFind uf){ Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList(); queue.offer(new int[]{x,y}); grid[x][y]='2'; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int[] curr = queue.poll(); for(int[] direct:directions){ int xx = curr[0]+direct[0]; int yy = curr[1]+direct[1]; if(xx<0 || xx>=grid.length || yy<0 || yy>=grid[0].length || grid[xx][yy]!=1) continue; grid[xx][yy]=2; uf.union(xx*grid[0].length+yy,curr[0]*grid[0].length+curr[1]); queue.offer(new int[]{xx,yy}); } } } class UnionFind{ int[] parent; int[] size; UnionFind(int len){ parent = new int[len]; size = new int[len]; for(int i=0;i<len;i++) {parent[i]=i;size[i]=1;} } int findParent(int x){ if(parent[x]==x) return x; parent[x] = findParent(parent[x]); return parent[x]; } void union(int x,int y){ int px = findParent(x); int py = findParent(y); parent[px] = py; size[py] +=size[px]; } } }
You are a hiker preparing for an upcoming hike. You are given heights, a 2D array of size rows x columns, where heights[row][col] represents the height of cell (row, col). You are situated in the top-left cell, (0, 0), and you hope to travel to the bottom-right cell, (rows-1, columns-1) (i.e., 0-indexed). You can move up, down, left, or right, and you wish to find a route that requires the minimum effort.
A route's effort is the maximum absolute difference in heights between two consecutive cells of the route.
Return the minimum effort required to travel from the top-left cell to the bottom-right cell.
Example 1:
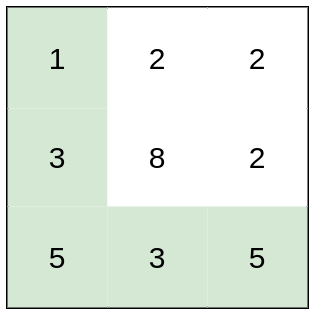
Input: heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]] Output: 2 Explanation: The route of [1,3,5,3,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 2 in consecutive cells. This is better than the route of [1,2,2,2,5], where the maximum absolute difference is 3.
Example 2:
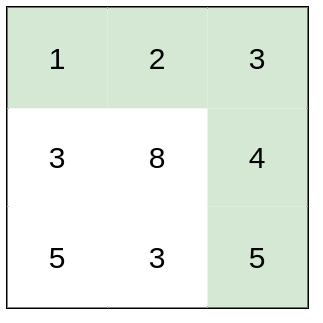
Input: heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]] Output: 1 Explanation: The route of [1,2,3,4,5] has a maximum absolute difference of 1 in consecutive cells, which is better than route [1,3,5,3,5].
Example 3:
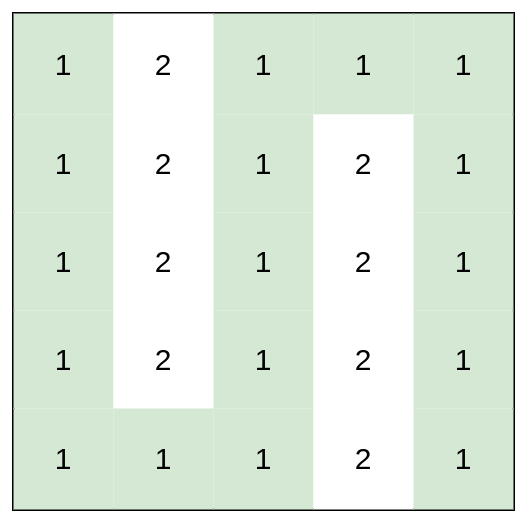
Input: heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]] Output: 0 Explanation: This route does not require any effort.
Constraints:
rows == heights.lengthcolumns == heights[i].length1 <= rows, columns <= 1001 <= heights[i][j] <= 106
class Solution { public int minimumEffortPath(int[][] heights) { int m = heights.length; int n = heights[0].length; List<int[]> edges = new ArrayList();
//将矩阵中点的关系,转化为边,每个点都向右➡️和下⬇️生成edge for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ for(int j=0;j<n;j++){ int curr = i*n+j; if(j!=n-1){ int right = i*n+j+1; int rh = Math.abs(heights[i][j]-heights[i][j+1]); edges.add(new int[]{curr,right,rh}); } if(i!=m-1){ int down = (i+1)*n+j; int dh = Math.abs(heights[i][j]-heights[i+1][j]); edges.add(new int[]{curr,down,dh}); } } }
//对edge按照两点高度差进行排序 Collections.sort(edges,(x,y)->x[2]-y[2]); UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(m*n); int source = 0,dest = (m-1)*n+n-1;
//逐条边取出,直至起始点相连 for(int[] edge:edges){ uf.union(edge[0],edge[1]); if(uf.find(source)==uf.find(dest)) return edge[2]; } return 0; } } class UnionFind{ int[] parent; UnionFind(int n){ parent = new int[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { parent[i]=i; } } int find(int x){ if(x!=parent[x]) parent[x]=find(parent[x]); return parent[x]; } void union(int x,int y){ int px = find(x); int py = find(y); if(px!=py) parent[px] = py; } }
You are given a string s, and an array of pairs of indices in the string pairs where pairs[i] = [a, b] indicates 2 indices(0-indexed) of the string.
You can swap the characters at any pair of indices in the given pairs any number of times.
Return the lexicographically smallest string that s can be changed to after using the swaps.
Example 1:
Input: s = "dcab", pairs = [[0,3],[1,2]] Output: "bacd" Explaination: Swap s[0] and s[3], s = "bcad" Swap s[1] and s[2], s = "bacd"
Example 2:
Input: s = "dcab", pairs = [[0,3],[1,2],[0,2]] Output: "abcd" Explaination: Swap s[0] and s[3], s = "bcad" Swap s[0] and s[2], s = "acbd" Swap s[1] and s[2], s = "abcd"
Example 3:
Input: s = "cba", pairs = [[0,1],[1,2]] Output: "abc" Explaination: Swap s[0] and s[1], s = "bca" Swap s[1] and s[2], s = "bac" Swap s[0] and s[1], s = "abc"
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 10^50 <= pairs.length <= 10^50 <= pairs[i][0], pairs[i][1] < s.lengthsonly contains lower case English letters.
class Solution { /** 思路:给定这样3个pair:[0,2],[1,5],[2,5]。 0,1,2,5 这4个元素的位置可以随意变换 所以我们可以使用连通图,将所有节点分为不同的group,同一个group中的元素可以按照字母顺序进行填充 */ public String smallestStringWithSwaps(String s, List<List<Integer>> pairs) { UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(s.length()); // 遍历所有元素,建立连通图 for (List<Integer> edge : pairs) { int source = edge.get(0); int destination = edge.get(1); // Perform the union of end points uf.union(source, destination); } // 遍历所有元素,建立从group parent -> 元素list的map, 将各group分list存放 Map<Integer, List<Integer>> rootToComponent = new HashMap<>(); // Group the vertices that are in the same component for (int vertex = 0; vertex < s.length(); vertex++) { int root = uf.find(vertex); // Add the vertices corresponding to the component root rootToComponent.putIfAbsent(root, new ArrayList<>()); rootToComponent.get(root).add(vertex); } // 用于存放结果字符串 char[] smallestString = new char[s.length()]; // 遍历所有的group for (List<Integer> indices : rootToComponent.values()) { // 建立一个sorted list存放 该组元素按照字母sort后的顺序 List<Integer> sorted = new ArrayList<>(indices); Collections.sort(sorted, (x, y) -> { return s.charAt(x) - s.charAt(y); }); // 填充该组的元素到result, for (int index = 0; index < indices.size(); index++) { smallestString[indices.get(index)] = s.charAt(sorted.get(index)); } } return new String(smallestString); } } class UnionFind { private int[] root; // Initialize the array root and rank // Each vertex is representative of itself with rank 1 public UnionFind(int size) { root = new int[size]; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { root[i] = i; } } // Get the root of a vertex public int find(int x) { if (x == root[x]) { return x; } return root[x] = find(root[x]); } // Perform the union of two components public void union(int x, int y) { int rootX = find(x); int rootY = find(y); root[rootY] = rootX; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号