单调栈(monotonic stack)系列 496,503,316,402,84,85,962,42,1776,321
496. Next Greater Element I
The next greater element of some element x in an array is the first greater element that is to the right of x in the same array.
You are given two distinct 0-indexed integer arrays nums1 and nums2, where nums1 is a subset of nums2.
For each 0 <= i < nums1.length, find the index j such that nums1[i] == nums2[j] and determine the next greater element of nums2[j] in nums2. If there is no next greater element, then the answer for this query is -1.
Return an array ans of length nums1.length such that ans[i] is the next greater element as described above.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [4,1,2], nums2 = [1,3,4,2] Output: [-1,3,-1] Explanation: The next greater element for each value of nums1 is as follows: - 4 is underlined in nums2 = [1,3,4,2]. There is no next greater element, so the answer is -1. - 1 is underlined in nums2 = [1,3,4,2]. The next greater element is 3. - 2 is underlined in nums2 = [1,3,4,2]. There is no next greater element, so the answer is -1.
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [2,4], nums2 = [1,2,3,4] Output: [3,-1] Explanation: The next greater element for each value of nums1 is as follows: - 2 is underlined in nums2 = [1,2,3,4]. The next greater element is 3. - 4 is underlined in nums2 = [1,2,3,4]. There is no next greater element, so the answer is -1.
Constraints:
1 <= nums1.length <= nums2.length <= 10000 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 104- All integers in
nums1andnums2are unique. - All the integers of
nums1also appear innums2.
解法:维护一个单调递减的栈,计算出nums2中所有元素的后续第一个大元素存在map中,然后只需要遍历nums1中元素填充即可
单调栈类题目循环过程中3个动作:1.维护单调栈 2.保存结果 3.放入新元素
class Solution { public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack(); Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap(); for(int i=nums2.length-1;i>=0;i--){ while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek()<nums2[i]){//维护单调栈 stack.pop(); } map.put( nums2[i],stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek() );//保存当前结果 stack.push(nums2[i]); //放入新元素 } int[] result = new int[nums1.length]; for(int i=0;i<nums1.length;i++) result[i]=map.get(nums1[i]); return result; } }
503. Next Greater Element II
Given a circular integer array nums (i.e., the next element of nums[nums.length - 1] is nums[0]), return the next greater number for every element in nums.
The next greater number of a number x is the first greater number to its traversing-order next in the array, which means you could search circularly to find its next greater number. If it doesn't exist, return -1 for this number.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,1] Output: [2,-1,2] Explanation: The first 1's next greater number is 2; The number 2 can't find next greater number. The second 1's next greater number needs to search circularly, which is also 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,3] Output: [2,3,4,-1,4]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
解法:这个题就是上一题的套娃题目,只是对于循环,我们需要扫描整个数组两遍
class Solution { public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack(); int[] result = new int[nums.length]; for(int i=nums.length*2-1;i>=0;i--){ while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek()<=nums[i%nums.length]){ stack.pop(); } result[i%nums.length] = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek(); stack.push(nums[i%nums.length]); } return result; } }
316. Remove Duplicate Letters
Given a string s, remove duplicate letters so that every letter appears once and only once. You must make sure your result is the smallest in lexicographical order among all possible results.
Example 1:
Input: s = "bcabc" Output: "abc"
Example 2:
Input: s = "cbacdcbc" Output: "acdb"
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 104sconsists of lowercase English letters.
关键点:
1. 单调栈
2. 存储每个元素最后一次出现的位置
3. 如果为了维护单调栈需要pop元素,先检查该元素是否还会再次出现?如果已经是最后一个位置,那么不要pop
4. 由于第三点,可能导致出现重复元素,因此需要加一个visited排重
class Solution { public String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) { //1.define a map , store last position of char int[] map = new int[26]; for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++) map[s.charAt(i)-'a']=i; //2.define a set to filter visited Set<Character> set = new HashSet(); //3.iterate Stack<Character> stack = new Stack(); for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){ char c = s.charAt(i);
// 判断是否已经有该元素 if(!set.contains(c)){
// pop之前要判定该元素是否已经是最后一个 while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek()>c && map[stack.peek()-'a']>i){ set.remove(stack.pop()); } stack.push(c); set.add(c); } } StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(""); for(char c:stack){ sb.append(c); } return sb.toString(); } }
402. Remove K Digits
Given string num representing a non-negative integer num, and an integer k, return the smallest possible integer after removing k digits from num.
Example 1:
Input: num = "1432219", k = 3 Output: "1219" Explanation: Remove the three digits 4, 3, and 2 to form the new number 1219 which is the smallest.
Example 2:
Input: num = "10200", k = 1 Output: "200" Explanation: Remove the leading 1 and the number is 200. Note that the output must not contain leading zeroes.
Example 3:
Input: num = "10", k = 2 Output: "0" Explanation: Remove all the digits from the number and it is left with nothing which is 0.
Constraints:
1 <= k <= num.length <= 105numconsists of only digits.numdoes not have any leading zeros except for the zero itself.
解法:从前向后遍历,保持一个单调递增的栈,如果后面元素小于了前面元素,进行pop,知道k被用完为止
class Solution { public String removeKdigits(String num, int k) { Stack<Character> stack = new Stack(); if(num.length()==k) return "0"; for(char c:num.toCharArray()){ while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek()>c && k>0){ stack.pop(); k--; } stack.push(c); } StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer(""); boolean flag = false; int ind=0; for(char c:stack){ if(ind>=stack.size()-k) break;//第一坑,如果原始num是单调递增的话,k还没被用过或没用完,如果k没用过,这里要从num末尾k个删除 ind++; if(c=='0'&&!flag) continue;//第二坑,记得要把开头的0清理掉 if(c!='0') flag = true; s.append(c); } return s.length()==0 ? "0" : s.toString();//第三坑,如果删空了,要返回"0"的 } }
84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Given an array of integers heights representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, return the area of the largest rectangle in the histogram.
Example 1:
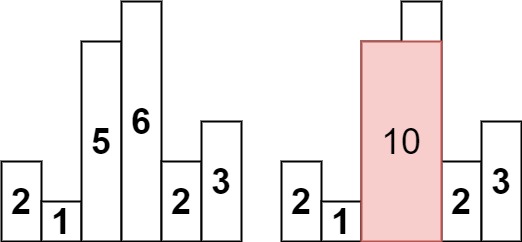
Input: heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3] Output: 10 Explanation: The above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1. The largest rectangle is shown in the red area, which has an area = 10 units.
Example 2:
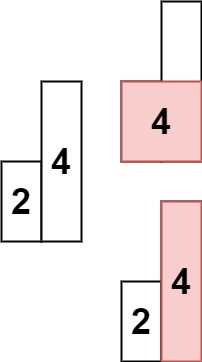
Input: heights = [2,4] Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= heights.length <= 1050 <= heights[i] <= 104
class Solution { public int largestRectangleArea(int[] h) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack(); int sum = 0; for(int i=0;i<h.length;i++){
//keep一个单调递增的栈 while(!stack.isEmpty() && h[i]<h[stack.peek()] ){ int preH = h[stack.pop()]; int width = i - (stack.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack.peek() + 1); //关键点:计算宽度 sum = Math.max(preH * width,sum);//记录结果 } stack.push(i);//注意栈中我们保存的是元素位置而不是元素本身 } while(!stack.isEmpty()){//需要将最后一段递增序列进行处理 int preH = h[stack.pop()]; int width = h.length - (stack.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack.peek() + 1); sum = Math.max(preH * width,sum); } return sum; } }
85. Maximal Rectangle
Given a rows x cols binary matrix filled with 0's and 1's, find the largest rectangle containing only 1's and return its area.
Example 1:

Input: matrix = [["1","0","1","0","0"],["1","0","1","1","1"],["1","1","1","1","1"],["1","0","0","1","0"]] Output: 6 Explanation: The maximal rectangle is shown in the above picture.
Example 2:
Input: matrix = [] Output: 0
Example 3:
Input: matrix = [["0"]] Output: 0
Example 4:
Input: matrix = [["1"]] Output: 1
Example 5:
Input: matrix = [["0","0"]] Output: 0
Constraints:
rows == matrix.lengthcols == matrix[i].length0 <= row, cols <= 200matrix[i][j]is'0'or'1'.
解法:我们可以把以每一行以及它以上的数据作为一个直方图,这样就把问题转化为了上一道题,进行直方图最大面积计算,遍历所有行,计算最大的直方图面积
class Solution { public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) { int m = matrix.length; if(m==0) return 0; int n = matrix[0].length; int[][] result = new int[m][n]; //把每一行及其上方数据看作一个直方图 for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ for(int j=0;j<n;j++){ if(i==0) result[i][j] = matrix[i][j]-'0'; else result[i][j] = matrix[i][j]=='0' ? 0 : result[i-1][j]+1; } } //对矩阵中每一行进行直方图最大面积计算 int max = 0; for(int i=0;i<m;i++){ max = Math.max(max,histogram(result[i])); } return max; } public int histogram(int[] arr){ int sum = 0; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack(); for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ while(!stack.isEmpty() && arr[stack.peek()]>arr[i]){ int preH = arr[stack.pop()]; int width = i- (stack.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack.peek()+1); sum = Math.max(sum,preH*width); } stack.push(i); } while(!stack.isEmpty()){ int preH = arr[stack.pop()]; int width = arr.length- (stack.isEmpty() ? 0 : stack.peek()+1); sum = Math.max(sum,preH*width); } return sum; } }
时间复杂度: 直方图生成O(m+n) + 最大面积判定m行,n个列直方图判定O(m*n) --> 最终结果:O(mn)
962. Maximum Width Ramp
A ramp in an integer array nums is a pair (i, j) for which i < j and nums[i] <= nums[j]. The width of such a ramp is j - i.
Given an integer array nums, return the maximum width of a ramp in nums. If there is no ramp in nums, return 0.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [6,0,8,2,1,5] Output: 4 Explanation: The maximum width ramp is achieved at (i, j) = (1, 5): nums[1] = 0 and nums[5] = 5.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [9,8,1,0,1,9,4,0,4,1] Output: 7 Explanation: The maximum width ramp is achieved at (i, j) = (2, 9): nums[2] = 1 and nums[9] = 1.
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 5 * 1040 <= nums[i] <= 5 * 104
解法1:
class Solution { public int maxWidthRamp(int[] nums) { List<Integer> stack = new ArrayList(); int result = 0; for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ //维护一个单调递减的栈 //如果出现非递减的情况,则从stack中二分查找第一个小于等于该元素的位置 if( !stack.isEmpty() && nums[stack.get(stack.size()-1)]<=nums[i] ){ int l=0,r=stack.size(); while(l<r){ int mid = l+(r-l)/2; if(nums[stack.get(mid)]<=nums[i]) r = mid; else l = mid+1; } result = Math.max(result,i-stack.get(l)); } else stack.add(i); } return result; } }
时间复杂度:O(NlogN)
解法2:
class Solution { public int maxWidthRamp(int[] nums) { //建立单调递减栈 Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack(); for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ if(stack.isEmpty() || nums[i]<nums[stack.peek()]) stack.push(i); } //从后向前遍历,与栈顶元素比对,如果大于栈定元素,那么可以记录当前距离,pop继续跟之前的比较 int max = 0; for(int i=nums.length-1;i>=0;i--){ while(!stack.isEmpty() && nums[stack.peek()]<=nums[i] ){ max = Math.max(max,i-stack.pop()); } } return max; } }
时间复杂度:O(N)
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it can trap after raining.
Example 1:

Input: height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] Output: 6 Explanation: The above elevation map (black section) is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
Example 2:
Input: height = [4,2,0,3,2,5] Output: 9
Constraints:
n == height.length1 <= n <= 2 * 1040 <= height[i] <= 105
class Solution { public int trap(int[] height) { //维护单调递减的栈 Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack(); int sum = 0; for(int i=0;i<height.length;i++){ //如果比栈顶元素高,说明形成了凹槽可以储水 while(!stack.isEmpty() && height[stack.peek()]<height[i]){ int pre = stack.pop();//这个实际就是当前凹槽的底部 if(stack.isEmpty()) break;//如果左挡板没有,那么不能储水 int h = Math.min(height[stack.peek()],height[i])-height[pre];//左右挡板高度取小减去底部高度,即为当前计算储水高度 int w = i-stack.peek()-1; sum+= h*w; } stack.push(i); } return sum; } }
1776. Car Fleet II
There are n cars traveling at different speeds in the same direction along a one-lane road. You are given an array cars of length n, where cars[i] = [positioni, speedi] represents:
positioniis the distance between theithcar and the beginning of the road in meters. It is guaranteed thatpositioni < positioni+1.speediis the initial speed of theithcar in meters per second.
For simplicity, cars can be considered as points moving along the number line. Two cars collide when they occupy the same position. Once a car collides with another car, they unite and form a single car fleet. The cars in the formed fleet will have the same position and the same speed, which is the initial speed of the slowest car in the fleet.
Return an array answer, where answer[i] is the time, in seconds, at which the ith car collides with the next car, or -1 if the car does not collide with the next car. Answers within 10-5 of the actual answers are accepted.
Example 1:
Input: cars = [[1,2],[2,1],[4,3],[7,2]] Output: [1.00000,-1.00000,3.00000,-1.00000] Explanation: After exactly one second, the first car will collide with the second car, and form a car fleet with speed 1 m/s. After exactly 3 seconds, the third car will collide with the fourth car, and form a car fleet with speed 2 m/s.
Example 2:
Input: cars = [[3,4],[5,4],[6,3],[9,1]] Output: [2.00000,1.00000,1.50000,-1.00000]
Constraints:
1 <= cars.length <= 1051 <= positioni, speedi <= 106positioni < positioni+1
class Solution { public double[] getCollisionTimes(int[][] cars) { //define stack to store the speed, increase Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack(); double[] result = new double[cars.length]; Arrays.fill(result,-1.0); for(int i=cars.length-1;i>=0;i--){ while( !stack.isEmpty() ){ int lastCar = stack.peek(); // 1.当前车的速度大于前面车的速度 2.1 前面的车不会与再前面追尾 或者 2.2 在 前面车与前面的前面车追尾之前,先跟前面的车相撞 if(cars[lastCar][1] < cars[i][1] && ( result[lastCar]==-1 || getTime(i,lastCar,cars)<result[lastCar] ) ) { result[i]=getTime(i,lastCar,cars); break; } //否则pop out stack.pop(); } stack.push(i); } return result; } private double getTime(int i,int last,int[][] cars){ return (cars[last][0]-cars[i][0])*1.0/(cars[i][1]-cars[last][1]); } }
You are given two integer arrays nums1 and nums2 of lengths m and n respectively. nums1 and nums2 represent the digits of two numbers. You are also given an integer k.
Create the maximum number of length k <= m + n from digits of the two numbers. The relative order of the digits from the same array must be preserved.
Return an array of the k digits representing the answer.
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [3,4,6,5], nums2 = [9,1,2,5,8,3], k = 5 Output: [9,8,6,5,3]
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [6,7], nums2 = [6,0,4], k = 5 Output: [6,7,6,0,4]
Example 3:
Input: nums1 = [3,9], nums2 = [8,9], k = 3 Output: [9,8,9]
Constraints:
m == nums1.lengthn == nums2.length1 <= m, n <= 5000 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 91 <= k <= m + n
解法: 单调栈 + 未排序数组merge
class Solution { public int[] maxNumber(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k) { int[] max = new int[k]; Arrays.fill(max,-1); for(int i=0;i<=k;i++){ if(i<=nums1.length && k-i<=nums2.length) max = getMaxResult(max,getMaxNumber(nums1,nums2,i,k-i)); } return max; } private int[] getMaxNumber(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int k1,int k2){ int[] result = merge(getMax(nums1,nums1.length-k1),getMax(nums2,nums2.length-k2)); return result; }
//如何merge两个未排序的数组,得到最大数组 private int[] merge(List<Integer> nums1, List<Integer> nums2) { int k = nums1.size()+nums2.size(); int[] ans = new int[k]; for (int i = 0, j = 0, r = 0; r < k; ++r) ans[r] = greater(nums1, i, nums2, j) ? nums1.get(i++) : nums2.get(j++); return ans; } public boolean greater(List<Integer> nums1, int i, List<Integer> nums2, int j) { while (i < nums1.size() && j < nums2.size() && nums1.get(i) == nums2.get(j)) { i++; j++; } return j == nums2.size() || (i < nums1.size() && nums1.get(i) > nums2.get(j)); }
//使用单调栈得到移除k个元素后的最大数组 private List<Integer> getMax(int[] nums,int k){ List<Integer> list = new ArrayList(); for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ while(!list.isEmpty() && list.get(list.size()-1)<nums[i] && k>0){ list.remove(list.size()-1); k--; } list.add(nums[i]); } while(k>0){ list.remove(list.size()-1); k--; } return list; } private int[] getMaxResult(int[] nums1,int[] nums2){ for(int i=0;i<nums1.length;i++){ if(nums1[i]>nums2[i]) return nums1; else if(nums1[i]<nums2[i]) return nums2; } return nums1; } }
You are given an integer array nums with distinct elements.
A nums[l...r] of nums is called a bowl if:
- The subarray has length at least 3. That is,
r - l + 1 >= 3. - The minimum of its two ends is strictly greater than the maximum of all elements in between. That is,
min(nums[l], nums[r]) > max(nums[l + 1], ..., nums[r - 1]).
Return the number of bowl subarrays in nums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,5,3,1,4]
Output: 2
Explanation:
The bowl subarrays are [3, 1, 4] and [5, 3, 1, 4].
[3, 1, 4]is a bowl becausemin(3, 4) = 3 > max(1) = 1.[5, 3, 1, 4]is a bowl becausemin(5, 4) = 4 > max(3, 1) = 3.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,1,2,3,4]
Output: 3
Explanation:
The bowl subarrays are [5, 1, 2], [5, 1, 2, 3] and [5, 1, 2, 3, 4].
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1000000000,999999999,999999998]
Output: 0
Explanation:
No subarray is a bowl.
Constraints:
3 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 109numsconsists of distinct elements.
class Solution: def bowlSubarrays(self, nums: List[int]) -> int: stack = [] result = 0 # 找 L < R 的情况 for i in range(0, len(nums)): while stack and nums[stack[-1]] < nums[i]: if abs(stack.pop() - i) > 1: result += 1 stack.append(i) stack.clear() # 反过来找 L > R 的情况 for i in range(len(nums) - 1, -1, -1): while stack and nums[stack[-1]] < nums[i]: if abs(stack.pop() - i) > 1: result += 1 stack.append(i) return result



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号