分治法(divide and conquer) 系列 215,912, 315,109, 106, 148, 50, 654, 427, 241, 493, 53
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the kth largest element in the array.
Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,2,1,5,6,4], k = 2 Output: 5
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6], k = 4 Output: 4
Constraints:
1 <= k <= nums.length <= 104-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
解法1: minheap解法
class Solution { public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) { //create a min heap PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((x,y)->x-y); for(int num:nums){ pq.offer(num); if(pq.size()>k) pq.poll(); } return pq.poll(); } }
时间复杂度: O(Nlog(K))
解法2: quickselect
这题思路不复杂,关键是边界条件的handle, 思考:为什么每轮partition用s和r交换,而不是s和l ? 另外一个注意点,第k大,我们要判定k-1,因为index从0开始
class Solution { public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) { return find(nums,k,0,nums.length-1); } private int find(int[] nums,int k,int s,int e){ int pivot = nums[s]; int l=s,r=e; while(true){ while(l<=e && nums[l]>=pivot ) l++;//一直向右直到碰到比pivot小的元素 while(r>=s && nums[r]<pivot ) r--;//一直向左,直到碰到比pivot等于或大于的元素 if(l>=r) break;//如果他们重合或已经交叉,那么可以退出 swap(nums,l,r);//如果没有重合,那么他们需要交换 } swap(nums,s,r);//s位置(pivot)是我们的划分基准值 if(r==k-1) return pivot; //为什么要跟k-1比较,因为第k大是从1开始数的 else if(r>k-1) return find(nums,k,s,r-1);// else return find(nums,k,r+1,e); } public void swap(int[] nums,int a,int b){ int temp = nums[a]; nums[a]=nums[b]; nums[b]=temp; } }
时间复杂度:average O(2N) ,worst O(N2)
O(N+N/2+N/4+...+1) =O(2N-1)=O(N)
Given an array of integers nums, sort the array in ascending order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [5,2,3,1] Output: [1,2,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,1,1,2,0,0] Output: [0,0,1,1,2,5]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 5 * 104-5 * 104 <= nums[i] <= 5 * 104
解法一:quick sort ,时间复杂度:O(nlogn), worst O(n2)
class Solution { public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) { quickSort(nums,0,nums.length-1); return nums; } private void quickSort(int[] nums,int start,int end){ if(start>=end) return; int pivot = nums[start]; int l = start,r=end; while(true){ while(l<=end && nums[l]<=pivot) l++; while(r>=start && nums[r]>pivot) r--; if(l>=r) break; swap(nums,l,r); } swap(nums,start,r); quickSort(nums,start,r-1); quickSort(nums,r+1,end); } private void swap(int[] nums,int a,int b){ int t = nums[a]; nums[a]=nums[b]; nums[b]=t; } }
解法二:mergesort 时间复杂度:O(nlogn)
class Solution { public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) { partition(nums,new int[nums.length],0,nums.length-1); return nums; } private void partition(int[] nums,int[] temp,int start,int end){ if(start>=end) return; int mid = start+(end-start)/2; partition(nums,temp,start,mid); partition(nums,temp,mid+1,end); merge(nums,temp,start,mid,mid+1,end); } private void merge(int[] nums,int[] temp,int lstart,int lend,int rstart,int rend){ int l = lstart,r=rstart; int ind = lstart; while(l<=lend && r<=rend ) { if(nums[l]<=nums[r]) temp[ind++]=nums[l++]; else temp[ind++]=nums[r++]; } while(l<=lend) temp[ind++]=nums[l++]; while(r<=rend) temp[ind++]=nums[r++]; for(int i=lstart;i<=rend;i++) nums[i]=temp[i]; } }
Given an array of integers. Find the Inversion Count in the array.
Inversion Count: For an array, inversion count indicates how far (or close) the array is from being sorted. If array is already sorted then the inversion count is 0. If an array is sorted in the reverse order then the inversion count is the maximum.
Formally, two elements a[i] and a[j] form an inversion if a[i] > a[j] and i < j.
Example 1:
Input: N = 5, arr[] = {2, 4, 1, 3, 5}
Output: 3
Explanation: The sequence 2, 4, 1, 3, 5
has three inversions (2, 1), (4, 1), (4, 3).
Example 2:
Input: N = 5
arr[] = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
Output: 0
Explanation: As the sequence is already
sorted so there is no inversion count.
Example 3:
Input: N = 3, arr[] = {10, 10, 10}
Output: 0
Explanation: As all the elements of array
are same, so there is no inversion count.
Your Task:
You don't need to read input or print anything. Your task is to complete the function inversionCount() which takes the array arr[] and the size of the array as inputs and returns the inversion count of the given array.
Expected Time Complexity: O(NLogN).
Expected Auxiliary Space: O(N).
Constraints:
1 ≤ N ≤ 5*105
1 ≤ arr[i] ≤ 1018
解法:这个题目解法很巧妙,实际我们只需要在mergesort的基础上增加1行代码就能搞定。
mergesort的merge过程中,如果右侧元素大于了左侧元素,那么此时产生了逆序对,并且该左侧元素之后的所有左侧元素都会跟该右侧元素产生逆序对(因为两边都是分别sort过的),
因此是count += lend-l+1; 而不是 count++;
class Solution { private static long count = 0; static long inversionCount(long arr[], long N) { int n = (int)N; partition(arr,new long[n],0,n-1); return count; } private static void partition(long arr[],long[] temp,int start,int end){ if(start>=end) return; int mid = start+(end-start)/2; partition(arr,temp,start,mid); partition(arr,temp,mid+1,end); merge(arr,temp,start,mid,mid+1,end); } private static void merge(long arr[],long[] temp,int lstart,int lend,int rstart,int rend){ int l = lstart,r=rstart,ind=lstart; while(l<=lend && r<=rend){ if(arr[l]<=arr[r]) temp[ind++]=arr[l++]; else {
//右边元素大于了左边元素,产生了逆序对 count += lend-l+1; temp[ind++]=arr[r++]; } } while(l<=lend) temp[ind++]=arr[l++]; while(r<=rend) temp[ind++]=arr[r++]; for(int i=lstart;i<=rend;i++) arr[i]=temp[i]; } }
You are given an integer array nums and you have to return a new counts array. The counts array has the property where counts[i] is the number of smaller elements to the right of nums[i].
Example 1:
Input: nums = [5,2,6,1] Output: [2,1,1,0] Explanation: To the right of 5 there are 2 smaller elements (2 and 1). To the right of 2 there is only 1 smaller element (1). To the right of 6 there is 1 smaller element (1). To the right of 1 there is 0 smaller element.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-1] Output: [0]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [-1,-1] Output: [0,0]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
解法:跟上一道题类似,mergesort的过程中通过计算逆序个数来得出结果, 时间复杂度: O(NlogN)
class Solution { class Node{ int val; int pos; Node(int val,int pos){ this.val = val; this.pos = pos; } } public List<Integer> countSmaller(int[] nums) { int[] result = new int[nums.length]; //将原数组存到node数组中,方便将其orignal index记录下来 Node[] nodes = new Node[nums.length]; for( int i=0;i<nums.length;i++ ) nodes[i] = new Node(nums[i],i); //进行mergesort的过程 mergeSort(nodes, result, 0, nums.length-1, new Node[nums.length]); //将最终结果数组放入list返回 List<Integer> list = new ArrayList(); for(int i=0;i<result.length;i++) list.add(result[i]); return list; } private void mergeSort(Node[] nums, int[] result, int start, int end, Node[] temparr){ if(start==end) return; //partition int mid = start+(end-start)/2; mergeSort(nums, result, start, mid, temparr); mergeSort(nums, result, mid+1, end, temparr); //merge two parts int l=start, r=mid+1, ind=start; int cnt = 0; while( l<=mid && r<=end ){ if(nums[l].val <= nums[r].val){ result[nums[l].pos]+=cnt; temparr[ind++]=nums[l++]; } else{ //遇到右边比左边小的,cnt++ cnt++; temparr[ind++]=nums[r++]; } } while( l<=mid ){ result[nums[l].pos]+=cnt;//填充左侧数组的时候,‘当前merge’中比它小的元素个数为cnt temparr[ind++]=nums[l++]; } while( r<=end ) temparr[ind++]=nums[r++]; //复制回原数组 for(int i=start;i<=end;i++) nums[i]=temparr[i]; } }
Given the head of a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example 1:
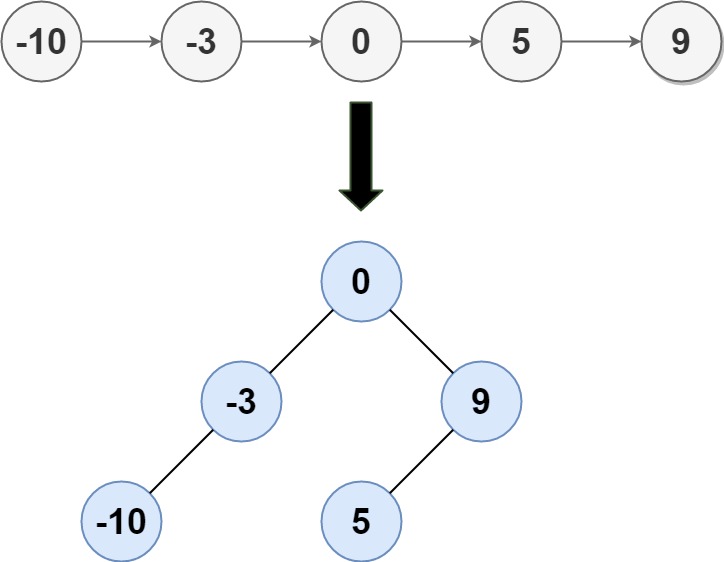
Input: head = [-10,-3,0,5,9] Output: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5] Explanation: One possible answer is [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the shown height balanced BST.
Example 2:
Input: head = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: head = [0] Output: [0]
Example 4:
Input: head = [1,3] Output: [3,1]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in
headis in the range[0, 2 * 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
解法一:比较粗暴,直接转数组,这样方便操作,然后直接从中间一刀一刀的切下去,中间点作为root,左右侧分别递归建立左右子树
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ /** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList(); while(head!=null) { list.add(head.val); head=head.next; } return divide(list,0,list.size()-1); } private TreeNode divide(List<Integer> list,int l,int r){ if(l>r) return null; int m = l+(r-l)/2; TreeNode root = new TreeNode(list.get(m)); root.left = divide(list,l,m-1); root.right = divide(list,m+1,r); return root; } }
时间复杂度:O(N), 空间复杂度O(N)
解法二:快慢指针
这个思路也很简单,就是利用快慢指针将链表一分为二,再分别进行deserialize
这题的关键点:递归在什么时候停下来?从head~tail 进行divide 是不包含tail这个节点的。
1.入口的tail是null
2.head == tail的时候,head这个点已经不需要计算了
class Solution { public TreeNode sortedListToBST(ListNode head) { return divide(head,null); } private TreeNode divide(ListNode head,ListNode tail){ if(head==tail) return null; ListNode s = head,f=head; while(f!=tail && f.next!=tail){ s=s.next; f=f.next.next; } TreeNode root = new TreeNode(s.val); root.left = divide(head,s); root.right = divide(s.next,tail); return root; } }
Given two integer arrays inorder and postorder where inorder is the inorder traversal of a binary tree and postorder is the postorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.
Example 1:

Input: inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3] Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Example 2:
Input: inorder = [-1], postorder = [-1] Output: [-1]
Constraints:
1 <= inorder.length <= 3000postorder.length == inorder.length-3000 <= inorder[i], postorder[i] <= 3000inorderandpostorderconsist of unique values.- Each value of
postorderalso appears ininorder. inorderis guaranteed to be the inorder traversal of the tree.postorderis guaranteed to be the postorder traversal of the tree.
解法:
其实这个题关键是要吃透tree的3中traversal,本题的关键点:
1.postorder的最右侧节点一定是root.
2.有了root,通过root可以找到该点在inorder中的位置,那么该位置的左侧即为root的左子树,该位置的右侧即为root的右子树.
3.那么接下来就可以递归调用分别去反序列化左右子树了,可以根据inorder中左右子树的节点个数来确定postorder中左右子树的切分点
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) { return des(inorder,postorder,0,inorder.length-1,0,postorder.length-1); } private TreeNode des(int[] in, int[] post,int ins,int ine,int ps,int pe){ int rootind = findInd(in,post[pe]); TreeNode root = new TreeNode(post[pe]); if(ins<rootind) root.left = des(in,post,ins,rootind-1,ps,ps+(rootind-ins-1)); if(rootind<ine) root.right =des(in,post,rootind+1,ine,pe-(ine-rootind),pe-1); return root; } private int findInd(int[] arr,int val){ for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){ if(arr[i]==val) return i; } return -1; } }
时间复杂度:O(n2) ,如果使用map来存储inorder的元素,可以加速find 将时间复杂度降到O(n)
Given two integer arrays preorder and inorder where preorder is the preorder traversal of a binary tree and inorder is the inorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.
Example 1:

Input: preorder = [3,9,20,15,7], inorder = [9,3,15,20,7] Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Example 2:
Input: preorder = [-1], inorder = [-1] Output: [-1]
Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 3000inorder.length == preorder.length-3000 <= preorder[i], inorder[i] <= 3000preorderandinorderconsist of unique values.- Each value of
inorderalso appears inpreorder. preorderis guaranteed to be the preorder traversal of the tree.inorderis guaranteed to be the inorder traversal of the tree.
解法:这题就是上一题的套娃,上一题是从postorder最后一个元素为root开始, 这题是从preorder第一个元素为root开始,其他都一样
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) { return build(preorder,inorder,0,preorder.length-1,0,inorder.length-1); } private TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int[] inorder,int prestart,int preend,int instart,int inend){ int rootind = find(inorder,preorder[prestart]); TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[prestart]); int leftend = prestart+1+(rootind-instart-1); if(rootind>instart) root.left = build(preorder,inorder,prestart+1,leftend,instart,rootind-1); if(rootind<inend) root.right = build(preorder,inorder,leftend+1,inend,rootind+1,inend); return root; } private int find(int[] arr,int val){ for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) if(arr[i]==val) return i; return -1; } }
Given the head of a linked list, return the list after sorting it in ascending order.
Example 1:
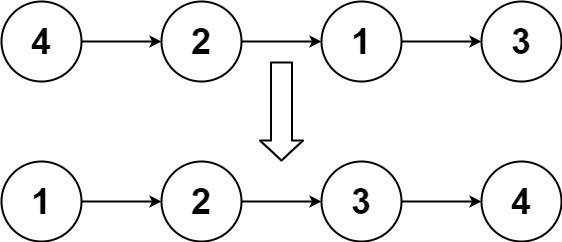
Input: head = [4,2,1,3] Output: [1,2,3,4]
Example 2:

Input: head = [-1,5,3,4,0] Output: [-1,0,3,4,5]
Example 3:
Input: head = [] Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 5 * 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
注意点:快慢指针切分后,第二段的起始位置(慢指针的next)一定记得提前保留下来,否则在第一段处理后会被置空
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */ class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if(head==null) return null; return helper(head,null); } private ListNode helper( ListNode head,ListNode tail ){ if(head==tail) { if(head!=null) head.next=null; return head; } //快慢指针 ListNode s = head,f=head; while(f!=tail && f.next!=tail){ s=s.next; f=f.next.next; } ListNode first = head; ListNode second = s.next;//这个第二段的起始位置一定要提前保存,否则前一段执行过程中s.next会被拆除 first = helper(first,s); second = helper(second,tail); return merge(first,second); } private ListNode merge(ListNode first,ListNode second){ ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); ListNode curr = dummy; while( first!=null && second!=null ){ if(first.val<=second.val){ curr.next = first; first=first.next; } else{ curr.next=second; second=second.next; } curr = curr.next; } if(first!=null) curr.next=first; if(second!=null) curr.next=second; return dummy.next; } }
时间复杂度: O(NlogN)
下面是同样的思路,但对区间排序处理的时候,head~tail,tail是不包含的,这么写看起来更清晰,不容易出错
class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if(head==null) return null; return partition(head,null); } private ListNode partition(ListNode head,ListNode tail){ if(head.next==tail) {//递归结束条件 head.next=null;//这个地方是为了防止形成链表环 return head; } //找中点 ListNode slow = head,fast=head; while(fast!=tail && fast.next!=tail){ fast=fast.next; slow=slow.next; if(fast!=tail) fast=fast.next; } //分别做partition ListNode left = partition(head, slow); ListNode right = partition(slow,tail); return merge(left,right); } private ListNode merge(ListNode first,ListNode second){ ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); ListNode curr = dummy; while( first!=null && second!=null ){ if(first.val<=second.val){ curr.next = first; first=first.next; } else{ curr.next=second; second=second.next; } curr = curr.next; } if(first!=null) curr.next=first; if(second!=null) curr.next=second; return dummy.next; } }
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode: # def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): # self.val = val # self.next = next class Solution: def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]: def partition(head, tail): #如果head指向tail,tail永远不包含,所以返回head if head.next == tail: head.next = None return head #找到中间点,切分成两半 slow, fast = head, head while fast != tail and fast.next != tail: slow = slow.next fast = fast.next.next #两边分别partition first = partition(head, slow) second = partition(slow, tail) #merge list pre = ListNode(0) curr = pre while first != None and second != None: if first.val <= second.val: curr.next = first first = first.next else: curr.next = second second = second.next curr = curr.next while first != None: curr.next = first first = first.next curr = curr.next while second != None: curr.next = second second = second.next curr = curr.next return pre.next #edge case, 如果head为null,直接返回 if head == None: return None return partition(head, None)
Implement pow(x, n), which calculates x raised to the power n (i.e., xn).
Example 1:
Input: x = 2.00000, n = 10 Output: 1024.00000
Example 2:
Input: x = 2.10000, n = 3 Output: 9.26100
Example 3:
Input: x = 2.00000, n = -2 Output: 0.25000 Explanation: 2-2 = 1/22 = 1/4 = 0.25
Constraints:
-100.0 < x < 100.0-231 <= n <= 231-1-104 <= xn <= 104
class Solution { public double myPow(double x, int n) { //n==0 或者 x==1时 if(n==0) return 1; if(x==0 || x==1) return x; //如果n为负数时, long num = n;//坑点:这个地方要用long,因为-2147483648 取反会溢出 if(num<0) { x=1/x; num=-num; } return pow(x,num); } private double pow(double x, long n){ //递归终止条件 if(n==1) return x; //切两半 double half = pow(x,n/2); //如果指数为偶数,直接返回两个half的乘积 if(n%2==0) return half*half; //如果指数为奇数,需要再多乘一个x return half*half*x; } }
class Solution: def myPow(self, x: float, k: int) -> float: def helper(x, n): if n == 0: return 1 if n == 1: return x half = helper(x, n // 2) if n % 2 == 1: return half * half * x return half * half if k >= 0: return helper(x, k) return 1 / helper(x, -k)
654. Maximum Binary Tree
nums with no duplicates. A maximum binary tree can be built recursively from nums using the following algorithm:- Create a root node whose value is the maximum value in
nums. - Recursively build the left subtree on the subarray prefix to the left of the maximum value.
- Recursively build the right subtree on the subarray suffix to the right of the maximum value.
Return the maximum binary tree built from nums.
Example 1:

Input: nums = [3,2,1,6,0,5]
Output: [6,3,5,null,2,0,null,null,1]
Explanation: The recursive calls are as follow:
- The largest value in [3,2,1,6,0,5] is 6. Left prefix is [3,2,1] and right suffix is [0,5].
- The largest value in [3,2,1] is 3. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [2,1].
- Empty array, so no child.
- The largest value in [2,1] is 2. Left prefix is [] and right suffix is [1].
- Empty array, so no child.
- Only one element, so child is a node with value 1.
- The largest value in [0,5] is 5. Left prefix is [0] and right suffix is [].
- Only one element, so child is a node with value 0.
- Empty array, so no child.
Example 2:

Input: nums = [3,2,1] Output: [3,null,2,null,1]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 10000 <= nums[i] <= 1000- All integers in
numsare unique.
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) { return construct(nums,0,nums.length-1); } private TreeNode construct(int[] nums,int start,int end){ if(start>end) return null; int maxPos = start; for(int i=start;i<=end;i++){ if(nums[maxPos]<nums[i]) maxPos=i; } TreeNode curr = new TreeNode(nums[maxPos]); curr.left = construct(nums,start,maxPos-1); curr.right = construct(nums,maxPos+1,end); return curr; } }
解法二:单调栈
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack(); for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ TreeNode node = new TreeNode(nums[i]); TreeNode left = null; //出栈挂左节点 while(!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek().val<nums[i]){ left = stack.pop(); } if(left!=null) node.left = left; //入栈挂右节点 if(!stack.isEmpty()) stack.peek().right=node; stack.push(node); } for(TreeNode node:stack){ return node; } return null; } }
Given a n * n matrix grid of 0's and 1's only. We want to represent the grid with a Quad-Tree.
Return the root of the Quad-Tree representing the grid.
Notice that you can assign the value of a node to True or False when isLeaf is False, and both are accepted in the answer.
A Quad-Tree is a tree data structure in which each internal node has exactly four children. Besides, each node has two attributes:
val: True if the node represents a grid of 1's or False if the node represents a grid of 0's.isLeaf: True if the node is leaf node on the tree or False if the node has the four children.
class Node {
public boolean val;
public boolean isLeaf;
public Node topLeft;
public Node topRight;
public Node bottomLeft;
public Node bottomRight;
}
We can construct a Quad-Tree from a two-dimensional area using the following steps:
- If the current grid has the same value (i.e all
1'sor all0's) setisLeafTrue and setvalto the value of the grid and set the four children to Null and stop. - If the current grid has different values, set
isLeafto False and setvalto any value and divide the current grid into four sub-grids as shown in the photo. - Recurse for each of the children with the proper sub-grid.
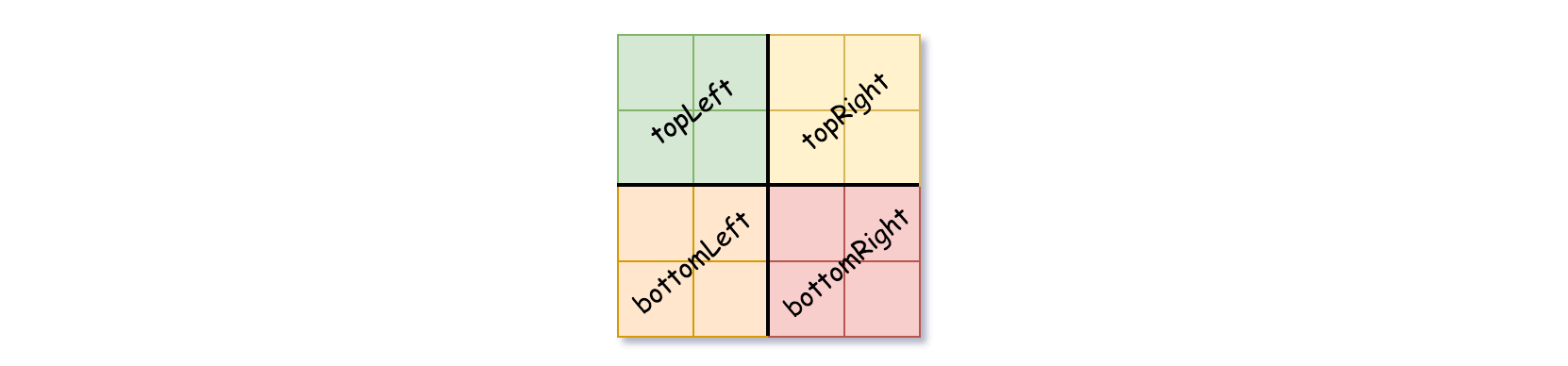
If you want to know more about the Quad-Tree, you can refer to the wiki.
Quad-Tree format:
The output represents the serialized format of a Quad-Tree using level order traversal, where null signifies a path terminator where no node exists below.
It is very similar to the serialization of the binary tree. The only difference is that the node is represented as a list [isLeaf, val].
If the value of isLeaf or val is True we represent it as 1 in the list [isLeaf, val] and if the value of isLeaf or val is False we represent it as 0.
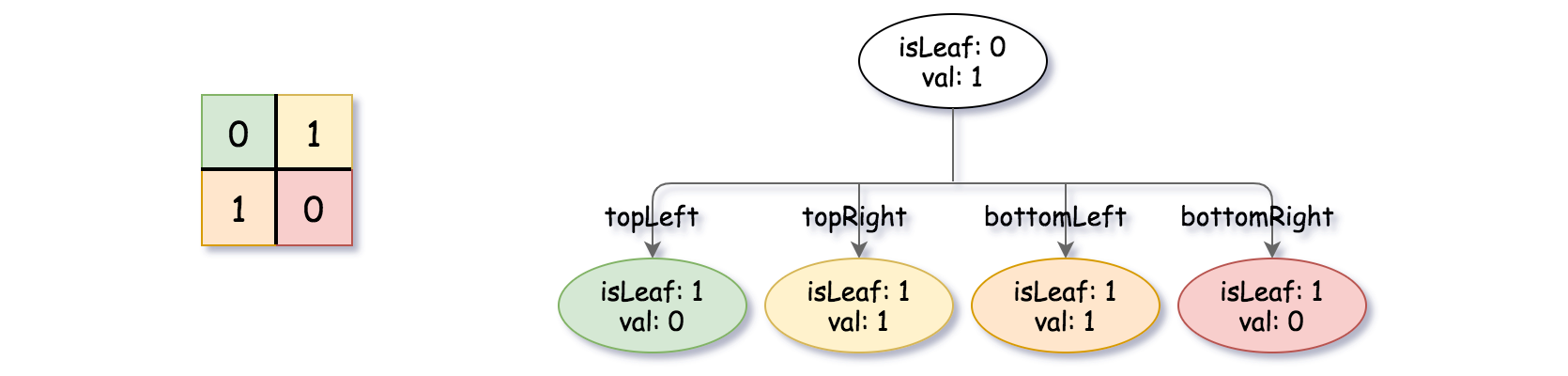
Example 1:
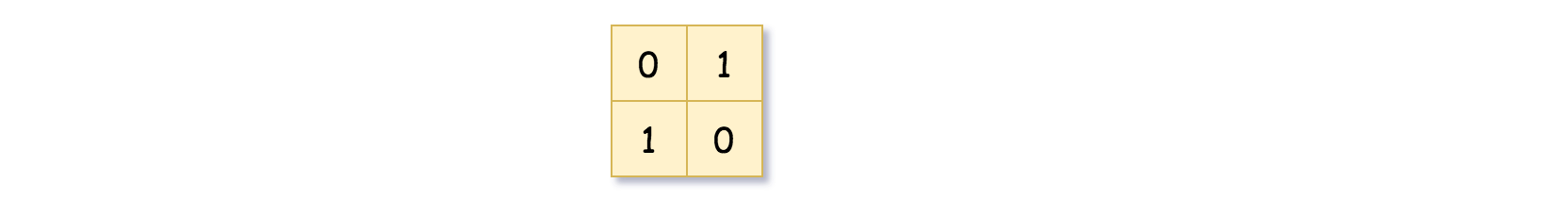
Input: grid = [[0,1],[1,0]] Output: [[0,1],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1],[1,0]] Explanation: The explanation of this example is shown below: Notice that 0 represnts False and 1 represents True in the photo representing the Quad-Tree.
Example 2:
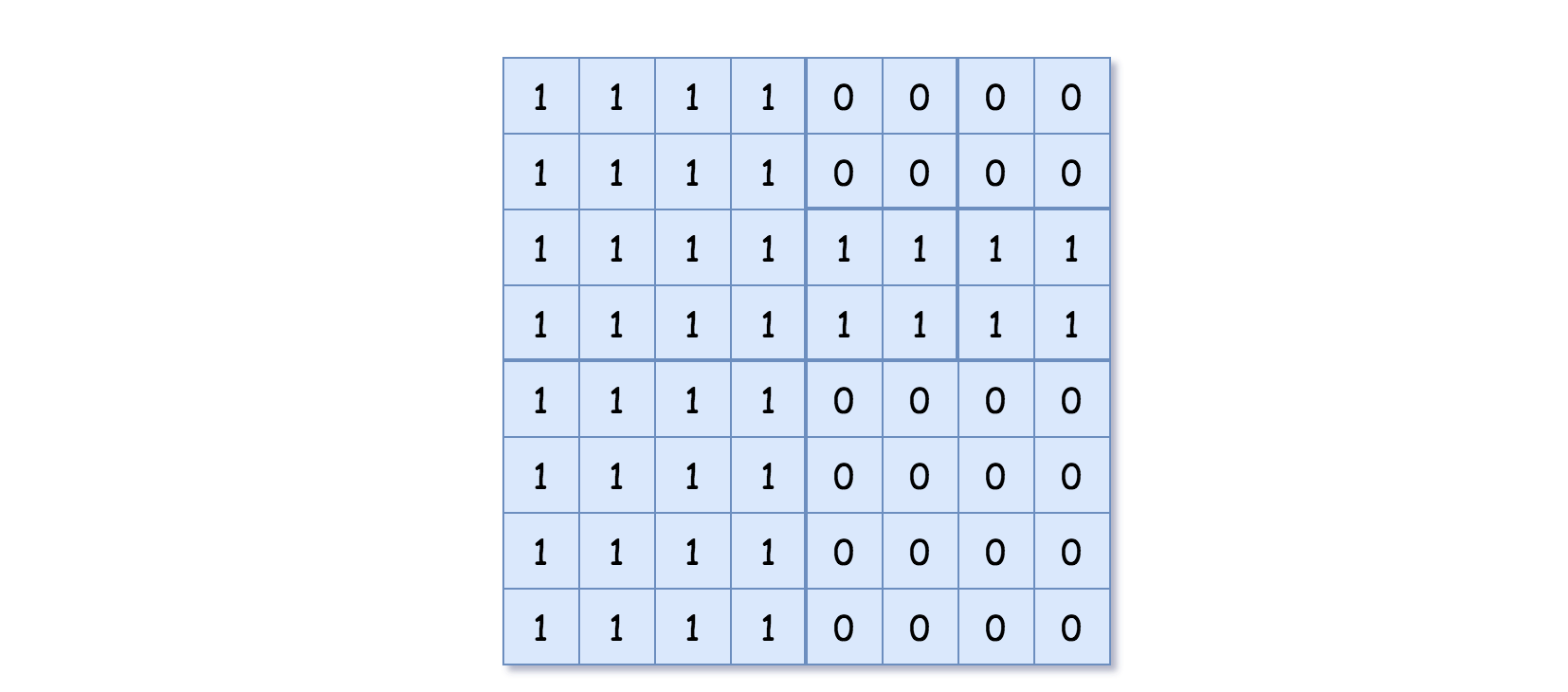
Input: grid = [[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0],[1,1,1,1,0,0,0,0]] Output: [[0,1],[1,1],[0,1],[1,1],[1,0],null,null,null,null,[1,0],[1,0],[1,1],[1,1]] Explanation: All values in the grid are not the same. We divide the grid into four sub-grids. The topLeft, bottomLeft and bottomRight each has the same value. The topRight have different values so we divide it into 4 sub-grids where each has the same value. Explanation is shown in the photo below:
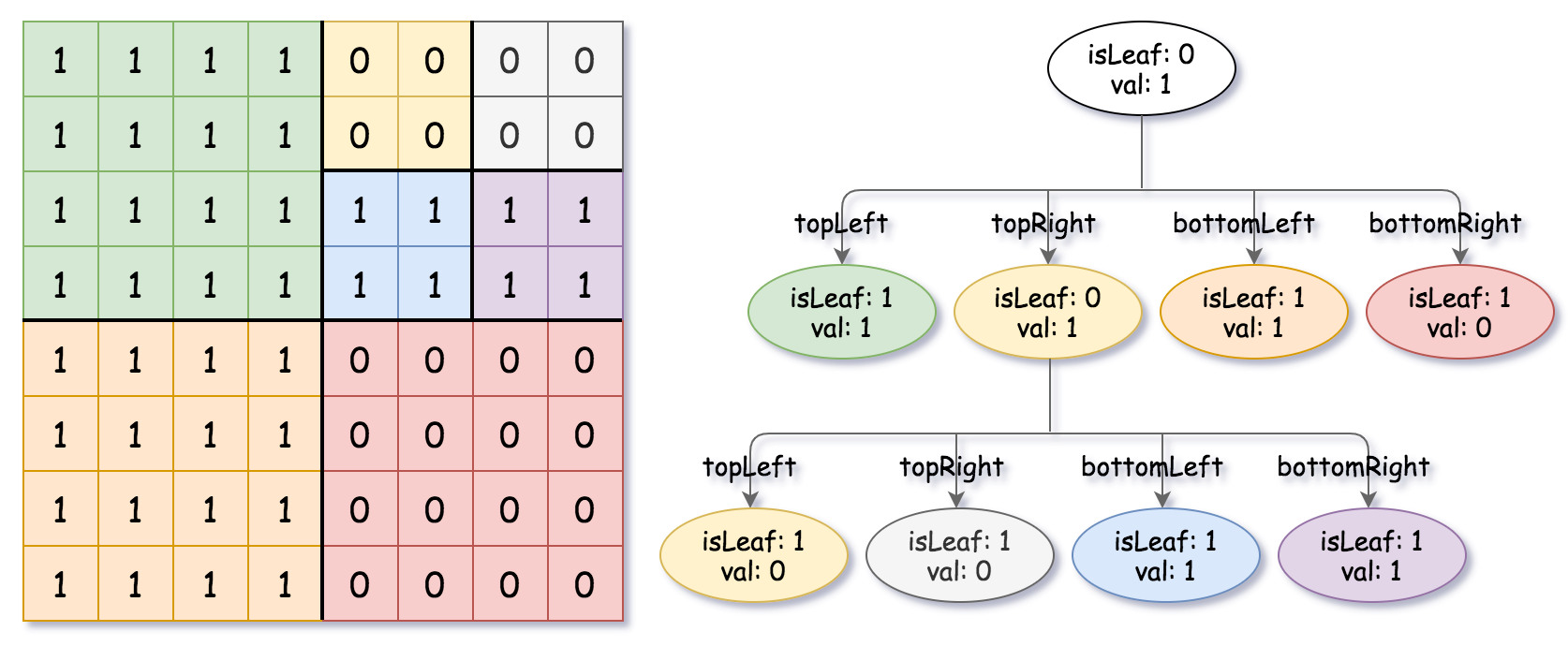
Constraints:
n == grid.length == grid[i].lengthn == 2xwhere0 <= x <= 6
时间复杂度: O(N)
/* // Definition for a QuadTree node. class Node { public boolean val; public boolean isLeaf; public Node topLeft; public Node topRight; public Node bottomLeft; public Node bottomRight; public Node() { this.val = false; this.isLeaf = false; this.topLeft = null; this.topRight = null; this.bottomLeft = null; this.bottomRight = null; } public Node(boolean val, boolean isLeaf) { this.val = val; this.isLeaf = isLeaf; this.topLeft = null; this.topRight = null; this.bottomLeft = null; this.bottomRight = null; } public Node(boolean val, boolean isLeaf, Node topLeft, Node topRight, Node bottomLeft, Node bottomRight) { this.val = val; this.isLeaf = isLeaf; this.topLeft = topLeft; this.topRight = topRight; this.bottomLeft = bottomLeft; this.bottomRight = bottomRight; } }; */ class Solution { public Node construct(int[][] grid) { return build(grid, 0, grid.length-1, 0, grid[0].length-1); } private Node build(int[][] grid, int up, int down, int left, int right){ //如果已经是单个元素,那么必定是leaf,直接返回 if(up == down) return new Node( grid[up][left]==1, true); //分别对4个象限进行dfs Node upLeft = build(grid, up, up+(down-up)/2, left, left+(right-left)/2 ); Node upRight = build(grid, up, up+(down-up)/2, left+(right-left)/2+1, right); Node downLeft = build(grid, up+(down-up)/2+1, down, left, left+(right-left)/2); Node downRight = build(grid, up+(down-up)/2+1, down, left+(right-left)/2+1, right); //如果4个象限val相同,而且均为leaf,那么当前可以直接返回leaf if(upLeft.val==upRight.val && upRight.val==downLeft.val && downLeft.val==downRight.val && upLeft.isLeaf && upRight.isLeaf && downLeft.isLeaf && downRight.isLeaf) return new Node(grid[up][left]==1, true); //否则,返回子树 else return new Node(grid[up][left]==1, false, upLeft, upRight, downLeft, downRight); } }
Given a string expression of numbers and operators, return all possible results from computing all the different possible ways to group numbers and operators. You may return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
Input: expression = "2-1-1" Output: [0,2] Explanation: ((2-1)-1) = 0 (2-(1-1)) = 2
Example 2:
Input: expression = "2*3-4*5" Output: [-34,-14,-10,-10,10] Explanation: (2*(3-(4*5))) = -34 ((2*3)-(4*5)) = -14 ((2*(3-4))*5) = -10 (2*((3-4)*5)) = -10 (((2*3)-4)*5) = 10
Constraints:
1 <= expression.length <= 20expressionconsists of digits and the operator'+','-', and'*'.- All the integer values in the input expression are in the range
[0, 99].
class Solution { public List<Integer> diffWaysToCompute(String expression) { return dfs(expression); } private List<Integer> dfs(String expression){ //定义当前表达式返回集合 List<Integer> result = new ArrayList(); for(int i=0; i<expression.length(); i++){ char c = expression.charAt(i); //如果遇到运算符,则分别对运算符左右两侧进行dfs if( c=='+' || c=='-' || c=='*'){ List<Integer> pre = dfs(expression.substring(0,i)); List<Integer> post = dfs(expression.substring(i+1)); //将左右两侧子表达式的运算结果进行配对 for(int preItem:pre){ for(int postItem:post){ if(c=='+') result.add(preItem + postItem); else if(c=='-') result.add(preItem - postItem); else if(c=='*') result.add(preItem * postItem); } } } } //如果result是空的说明当前是个纯数字无表达式 if(result.isEmpty()) result.add(Integer.valueOf(expression)); return result; } }
在上面基础上增加memoization
class Solution { public List<Integer> diffWaysToCompute(String expression) { Map<String,List<Integer>> mem = new HashMap(); return dfs(expression, mem); } private List<Integer> dfs(String expression, Map<String,List<Integer>> mem){ if(mem.containsKey(expression)) return mem.get(expression); List<Integer> result = new ArrayList(); for(int i=0; i<expression.length(); i++){ char c = expression.charAt(i); if( c=='+' || c=='-' || c=='*'){ List<Integer> pre = dfs(expression.substring(0,i), mem); List<Integer> post = dfs(expression.substring(i+1), mem); for(int preItem:pre){ for(int postItem:post){ if(c=='+') result.add(preItem + postItem); else if(c=='-') result.add(preItem - postItem); else if(c=='*') result.add(preItem * postItem); } } } } if(result.isEmpty()) result.add(Integer.valueOf(expression)); return result; } }
Given an integer array nums, return the number of reverse pairs in the array.
A reverse pair is a pair (i, j) where 0 <= i < j < nums.length and nums[i] > 2 * nums[j].
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,2,3,1] Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,4,3,5,1] Output: 3
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 5 * 104-231 <= nums[i] <= 231 - 1
class Solution { public int reversePairs(int[] nums) { //在mergesort的过程中进行判定 mergeSort(nums, 0, nums.length-1, new int[nums.length]); return count; } private int count = 0; private void mergeSort(int[] nums, int start, int end, int[] temp){ if(start>=end) return; //partition,左右两侧分别进行mergesort int mid = start+(end-start)/2; mergeSort(nums, start, mid, temp); mergeSort(nums, mid+1, end, temp); //merge之前进行reverse pair的计算 int left = start, right=mid+1; while(left <= mid && right<=end){ if(nums[left] > nums[right]*2l){ //坑点,这个位置乘2之后要转为long,否则越界判定出现错误 count+=mid-left+1; right++; } else{ left++; } } //左右两半进行merge left = start; right=mid+1; int ind=left; while( left<=mid && right<=end ){ if(nums[left] <= nums[right]) temp[ind++] = nums[left++]; else temp[ind++] = nums[right++]; } while(left <= mid) temp[ind++] = nums[left++]; while(right <= end) temp[ind++] = nums[right++]; for(int i=start; i<=end; i++) nums[i] = temp[i]; } }
Given an integer array nums, find the
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4] Output: 6 Explanation: The subarray [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum 6.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1] Output: 1 Explanation: The subarray [1] has the largest sum 1.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [5,4,-1,7,8] Output: 23 Explanation: The subarray [5,4,-1,7,8] has the largest sum 23.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
Follow up: If you have figured out the O(n) solution, try coding another solution using the divide and conquer approach, which is more subtle.
1. 解法一: kadane
2. 解法二: divide and conquer
class Solution { public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) { return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1); } private int helper(int[] nums, int start, int end) { if(start > end) return Integer.MIN_VALUE; // 找中点 int mid = start + (end - start) / 2; // 从中间向左遍历,找到最大值 int leftSum = 0, leftMax = 0; for(int i = mid - 1; i >= 0; i--) { leftSum += nums[i]; leftMax = Math.max(leftSum, leftMax); } // 从中间向右遍历,找到最大值 int rightSum = 0, rightMax = 0; for(int i = mid + 1; i <= end; i++) { rightSum += nums[i]; rightMax = Math.max(rightSum, rightMax); } // 那么算出了包括中点的情况下的最大值 int midResult = leftMax + rightMax + nums[mid]; // return max(midmax, leftmax, rightmax); return Math.max( Math.max( helper(nums, start, mid - 1), //左侧自己的最大值 helper(nums, mid + 1, end) //右侧自己的最大值 ), midResult ); } }
待补充题目:
4.
53. https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-subarray/discuss/405559/Easy-Understand-Java-Solutions-with-Explanations-(B-F-Divide-And-Conquer-DP)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号