BFS 系列 127, 207, 210, 787, 788, 863, 317, 279, 1162, 773
A transformation sequence from word beginWord to word endWord using a dictionary wordList is a sequence of words beginWord -> s1 -> s2 -> ... -> sk such that:
- Every adjacent pair of words differs by a single letter.
- Every
sifor1 <= i <= kis inwordList. Note thatbeginWorddoes not need to be inwordList. sk == endWord
Given two words, beginWord and endWord, and a dictionary wordList, return the number of words in the shortest transformation sequence from beginWord to endWord, or 0 if no such sequence exists.
Example 1:
Input: beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log","cog"] Output: 5 Explanation: One shortest transformation sequence is "hit" -> "hot" -> "dot" -> "dog" -> cog", which is 5 words long.
Example 2:
Input: beginWord = "hit", endWord = "cog", wordList = ["hot","dot","dog","lot","log"] Output: 0 Explanation: The endWord "cog" is not in wordList, therefore there is no valid transformation sequence.
Constraints:
1 <= beginWord.length <= 10endWord.length == beginWord.length1 <= wordList.length <= 5000wordList[i].length == beginWord.lengthbeginWord,endWord, andwordList[i]consist of lowercase English letters.beginWord != endWord- All the words in
wordListare unique.
class Solution { public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) { Set<String> set = new HashSet(wordList); Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList(); queue.offer(beginWord); int level = 1; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); level++; for(int i=0;i<size;i++){//O(N) String s = queue.poll(); //遍历字符串每一位进行替换26个字母 for(int p = 0;p<s.length();p++){//O(L) //轮询26个字母 for(int ind=0;ind<26;ind++){//O(26) char c = (char)('a'+ind); String temp = s.substring(0,p)+c+s.substring(p+1);//O(L) if(set.contains(temp)){ //如果找到的就是endWord可以返回了 if(temp.equals(endWord)) return level; //Ω(1) think about it queue.offer(temp); //遍历过后要删掉 set.remove(temp); } } } } } return 0; } }
时间复杂度: O(N*L2*26) -> O(N*L2)
双向bfs解法:
class Solution { public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) { Set<String> set = new HashSet(wordList); Set<String> beginSet = new HashSet(); Set<String> endSet = new HashSet(); if(!set.contains(endWord)) return 0; beginSet.add(beginWord); endSet.add(endWord); int level = 1; while(!beginSet.isEmpty() && !endSet.isEmpty()){ Set<String> nextSet = new HashSet(); level++; for(String s:beginSet){ for(int p = 0;p<s.length();p++){ //轮询26个字母 for(int ind=0;ind<26;ind++){ char c = (char)('a'+ind); String temp = s.substring(0,p)+c+s.substring(p+1); if(endSet.contains(temp)) return level; if(set.contains(temp)){ nextSet.add(temp); set.remove(temp); } } } } if(beginSet.size()>endSet.size()){ beginSet=endSet; endSet=nextSet; } else beginSet=nextSet; } return 0; } }
时间复杂度:双向bfs的时间复杂度理论上应该是 单向bfs的开根号
207. Course Schedule
There are a total of numCourses courses you have to take, labeled from 0 to numCourses - 1. You are given an array prerequisites where prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that you must take course bi first if you want to take course ai.
- For example, the pair
[0, 1], indicates that to take course0you have to first take course1.
Return true if you can finish all courses. Otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]] Output: true Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0. So it is possible.
Example 2:
Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0],[0,1]] Output: false Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0, and to take course 0 you should also have finished course 1. So it is impossible.
Constraints:
1 <= numCourses <= 1050 <= prerequisites.length <= 5000prerequisites[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < numCourses- All the pairs prerequisites[i] are unique.
class Solution { public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] pre) { //1.put into map and calculate the degree Map<Integer,List<Integer>> map = new HashMap(); // graph int[] degrees = new int[numCourses];//degree for(int[] edge:pre){ int end = edge[0],start=edge[1]; degrees[end]++; //记录每个顶点的入度 List<Integer> list = map.getOrDefault(start,new ArrayList()); if(list.isEmpty()) map.put(start,list); list.add(end); } //2.put the start point into queue Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<degrees.length;i++) if(degrees[i]==0) queue.offer(i);//将入度为0的顶点放到队列 //3.bfs traversal int count = 0; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int num = queue.poll(); count++; List<Integer> list = map.get(num); if(list!=null){ for(int temp:list){ degrees[temp]--;//每遍历到该节点一次,将其入度减一 if(degrees[temp]==0) queue.offer(temp); //将入度为0的顶点放到队列 } } } return count==numCourses; } }
There are a total of numCourses courses you have to take, labeled from 0 to numCourses - 1. You are given an array prerequisites where prerequisites[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that you must take course bi first if you want to take course ai.
- For example, the pair
[0, 1], indicates that to take course0you have to first take course1.
Return the ordering of courses you should take to finish all courses. If there are many valid answers, return any of them. If it is impossible to finish all courses, return an empty array.
Example 1:
Input: numCourses = 2, prerequisites = [[1,0]] Output: [0,1] Explanation: There are a total of 2 courses to take. To take course 1 you should have finished course 0. So the correct course order is [0,1].
Example 2:
Input: numCourses = 4, prerequisites = [[1,0],[2,0],[3,1],[3,2]] Output: [0,2,1,3] Explanation: There are a total of 4 courses to take. To take course 3 you should have finished both courses 1 and 2. Both courses 1 and 2 should be taken after you finished course 0. So one correct course order is [0,1,2,3]. Another correct ordering is [0,2,1,3].
Example 3:
Input: numCourses = 1, prerequisites = [] Output: [0]
Constraints:
1 <= numCourses <= 20000 <= prerequisites.length <= numCourses * (numCourses - 1)prerequisites[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < numCoursesai != bi- All the pairs
[ai, bi]are distinct.
class Solution { public int[] findOrder(int numCourses, int[][] pre) { int[] result = new int[numCourses]; //1.put into map and calculate the degree Map<Integer,List<Integer>> map = new HashMap(); // graph int[] degrees = new int[numCourses];//degree for(int[] edge:pre){ int end = edge[0],start=edge[1]; degrees[end]++; List<Integer> list = map.getOrDefault(start,new ArrayList()); if(list.isEmpty()) map.put(start,list); list.add(end); } //2.put the start point into queue Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<degrees.length;i++) if(degrees[i]==0) queue.offer(i); //3.bfs traversal int index = 0; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int num = queue.poll(); result[index++]=num; List<Integer> list = map.get(num); if(list!=null){ for(int temp:list){ degrees[temp]--; if(degrees[temp]==0) queue.offer(temp); } } } return index==numCourses ? result : new int[]{}; } }
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the ball's start position, the destination and the maze, determine whether the ball could stop at the destination.
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The start and destination coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
1.There is only one ball and one destination in the maze.
2.Both the ball and the destination exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
3.The given maze does not contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you could assume the border of the maze are all walls.
5.The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and both the width and height of the maze won't exceed 100.
Example 1:
Input:
map =
[
[0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0],
[1,1,0,1,1],
[0,0,0,0,0]
]
start = [0,4]
end = [3,2]
Output:
falseExample 2:
Input:
map =
[[0,0,1,0,0],
[0,0,0,0,0],
[0,0,0,1,0],
[1,1,0,1,1],
[0,0,0,0,0]
]
start = [0,4]
end = [4,4]
Output:
truepublic class Solution { public boolean hasPath(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) { int m = maze.length; int n = maze[0].length; boolean[][] visited = new boolean[m][n]; Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList(); queue.offer(start); int[][] directions = new int[][]{{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}}; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int[] temp = queue.poll(); //循环4个方向进行bfs for(int[] direct:directions){ int x = temp[0]+direct[0]; int y = temp[1]+direct[1]; while( x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && maze[x][y]==0 ){ x+=direct[0]; y+=direct[1]; } //退出循环的时候已经走到了墙或者外边界,所以这个地方要倒回来一步 x-=direct[0]; y-=direct[1]; if(!visited[x][y]) { queue.offer(new int[]{x,y}); visited[x][y]=true; if(x==destination[0] && y==destination[1]) return true; } } } return false; } }
There is a ball in a maze with empty spaces and walls. The ball can go through empty spaces by rolling up, down, left or right, but it won't stop rolling until hitting a wall. When the ball stops, it could choose the next direction.
Given the ball's start position, the destination and the maze, find the shortest distance for the ball to stop at the destination. The distance is defined by the number of empty spaces traveled by the ball from the start position (excluded) to the destination (included). If the ball cannot stop at the destination, return -1.
The maze is represented by a binary 2D array. 1 means the wall and 0 means the empty space. You may assume that the borders of the maze are all walls. The start and destination coordinates are represented by row and column indexes.
1.There is only one ball and one destination in the maze.
2.Both the ball and the destination exist on an empty space, and they will not be at the same position initially.
3.The given maze does not contain border (like the red rectangle in the example pictures), but you could assume the border of the maze are all walls.
4.The maze contains at least 2 empty spaces, and both the width and height of the maze won't exceed 100.
Example 1:
Input:
(rowStart, colStart) = (0,4)
(rowDest, colDest)= (4,4)
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
Output: 12
Explanation:
(0,4)->(0,3)->(1,3)->(1,2)->(1,1)->(1,0)->(2,0)->(2,1)->(2,2)->(3,2)->(4,2)->(4,3)->(4,4)
Example 2:
Input:
(rowStart, colStart) = (0,4)
(rowDest, colDest)= (0,0)
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0
Output: 6
Explanation:
(0,4)->(0,3)->(1,3)->(1,2)->(1,1)->(1,0)->(0,0)
解法: 其实这个题就只是上一题的followup,需要改进的有两个点:
1.之前只需追踪是否访问过,这次需要判定是否为更短路径
2.之前只需走到终点即可返回,这次需要走遍所有路径,最终找到最短路径public class Solution { public int shortestDistance(int[][] maze, int[] start, int[] destination) { int m = maze.length; int n = maze[0].length; int[][] distance = new int[m][n]; for(int[] arr:distance) Arrays.fill(arr,Integer.MAX_VALUE); PriorityQueue<int[]> queue = new PriorityQueue<int[]>((x,y)->x[2]-y[2]); int[][] directions = new int[][]{{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}}; queue.offer(new int[]{start[0],start[1],0}); distance[start[0]][start[1]]=0;//起始点距离为0 while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int[] temp = queue.poll(); //循环4个方向进行bfs for(int[] direct:directions){ int x = temp[0]+direct[0]; int y = temp[1]+direct[1]; int step = temp[2]; int count = 0; while( x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && maze[x][y]==0 ){ x+=direct[0]; y+=direct[1]; count++; } //退出循环的时候已经走到了墙或者外边界,所以这个地方要倒回来一步 x-=direct[0]; y-=direct[1]; if(distance[x][y] > distance[temp[0]][temp[1]]+count ) { distance[x][y] = distance[temp[0]][temp[1]]+count; queue.offer(new int[]{x,y,temp[2]+count}); } } } return distance[destination[0]][destination[1]]==Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : distance[destination[0]][destination[1]]; } }
Given the root of a binary tree, the value of a target node target, and an integer k, return an array of the values of all nodes that have a distance k from the target node.
You can return the answer in any order.
Example 1:
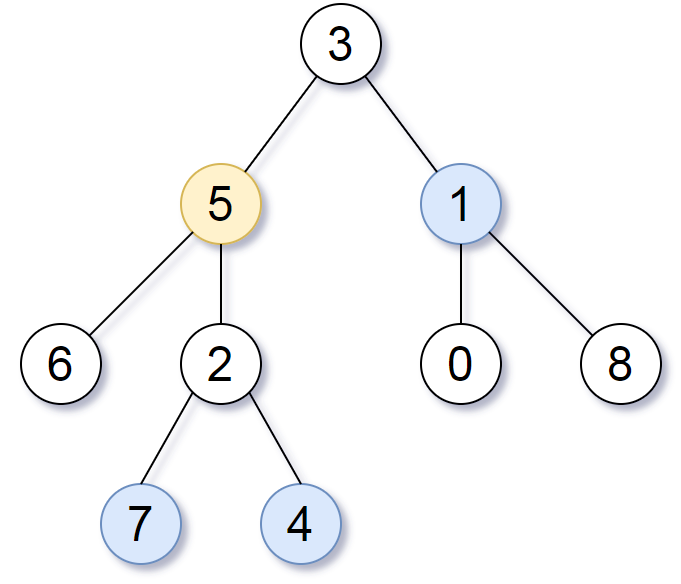
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, k = 2 Output: [7,4,1] Explanation: The nodes that are a distance 2 from the target node (with value 5) have values 7, 4, and 1.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1], target = 1, k = 3 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 500]. 0 <= Node.val <= 500- All the values
Node.valare unique. targetis the value of one of the nodes in the tree.0 <= k <= 1000
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ class Solution { public List<Integer> distanceK(TreeNode root, TreeNode target, int k) { //树遍历建图 Map<TreeNode,List<TreeNode>> graph = new HashMap(); traversal(root,graph); //从目标节点开始做bfs,step==k的加入result Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList(); queue.offer(target); Set<TreeNode> visited = new HashSet(); visited.add(target); int step = 0; List<Integer> result = new ArrayList(); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ TreeNode curr = queue.poll(); if(step==k) result.add(curr.val); for(TreeNode t:graph.getOrDefault(curr,Arrays.asList())){ if(visited.contains(t)) continue; visited.add(t); queue.offer(t); } } step++; if(step>k) return result;//如果step已经大于k,那么不需要再继续遍历 } return result; } //树遍历建图 private void traversal(TreeNode root,Map<TreeNode,List<TreeNode>> graph){ if(root==null) return; List<TreeNode> list; if(root.left!=null){ list = graph.getOrDefault(root,new ArrayList()); list.add(root.left); graph.put(root,list); list = graph.getOrDefault(root.left,new ArrayList()); list.add(root); graph.put(root.left,list); } if(root.right!=null){ list = graph.getOrDefault(root,new ArrayList()); list.add(root.right); graph.put(root,list); list = graph.getOrDefault(root.right,new ArrayList()); list.add(root); graph.put(root.right,list); } traversal(root.left,graph); traversal(root.right,graph); } }
317. Shortest Distance from All Buildings
You are given an m x n grid grid of values 0, 1, or 2, where:
- each
0marks an empty land that you can pass by freely, - each
1marks a building that you cannot pass through, and - each
2marks an obstacle that you cannot pass through.
You want to build a house on an empty land that reaches all buildings in the shortest total travel distance. You can only move up, down, left, and right.
Return the shortest travel distance for such a house. If it is not possible to build such a house according to the above rules, return -1.
The total travel distance is the sum of the distances between the houses of the friends and the meeting point.
The distance is calculated using Manhattan Distance, where distance(p1, p2) = |p2.x - p1.x| + |p2.y - p1.y|.
Example 1:
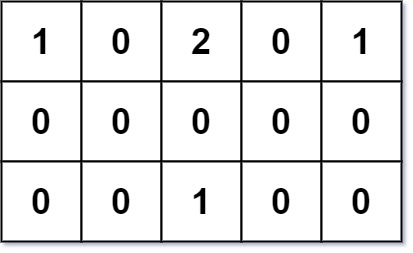
Input: grid = [[1,0,2,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,1,0,0]] Output: 7 Explanation: Given three buildings at (0,0), (0,4), (2,2), and an obstacle at (0,2). The point (1,2) is an ideal empty land to build a house, as the total travel distance of 3+3+1=7 is minimal. So return 7.
Example 2:
Input: grid = [[1,0]] Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1]] Output: -1
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 50grid[i][j]is either0,1, or2.- There will be at least one building in the
grid.
class Solution { public int shortestDistance(int[][] grid) { int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //清算building的数量 int bulCount=0; for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++) for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++) if(grid[i][j]==1) bulCount++; //逐个空地计算到所有building的距离和 for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){ if(grid[i][j]==0) min = Math.min(min,bfs(grid,i,j,bulCount)); } } return min==Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : min; } private int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; private int bfs(int[][] grid,int x,int y,int bulCount){ boolean[][] visited = new boolean[grid.length][grid[0].length]; Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList(); queue.offer(new int[]{x,y}); visited[x][y]=true; int level = 0; int count = 0; int traversalBulCount=0; while(!queue.isEmpty() && traversalBulCount<bulCount){ level++; int size = queue.size(); for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ int[] curr = queue.poll(); for(int[] direct:directions){ int xx = curr[0]+direct[0]; int yy = curr[1]+direct[1]; if(xx>=0 && xx<grid.length && yy>=0 && yy<grid[0].length && grid[xx][yy]!=2 && !visited[xx][yy]){ if(grid[xx][yy]==1){ count+=level; traversalBulCount++; } else if(grid[xx][yy]==0){ queue.offer(new int[]{xx,yy}); } visited[xx][yy]=true; } } } } //如果这个位置不能去到所有的house,那么刚刚访问过的空地也都无法去到house,可以直接标记为2,下次无需进行bfs判定 if(traversalBulCount!=bulCount ){ for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){ if(visited[i][j]&&grid[i][j]==0) grid[i][j]=2; } } return Integer.MAX_VALUE; } return count; } }
时间复杂度: 从所有的空地出发(O(M*N)), 每个空地探索所有的buildingO(M*N) --> O(M2*N2)
Given an integer n, return the least number of perfect square numbers that sum to n.
A perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 1, 4, 9, and 16 are perfect squares while 3 and 11 are not.
Example 1:
Input: n = 12 Output: 3 Explanation: 12 = 4 + 4 + 4.
Example 2:
Input: n = 13 Output: 2 Explanation: 13 = 4 + 9.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 104
class Solution { public int numSquares(int n) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();
// 找出所有平方数,放入list for(int i=1;i*i<=n;i++) list.add(i*i); int level = 1;
Set<Integer> visit = new HashSet(); visit.add(n); while(!visit.isEmpty()){ Set<Integer> temp = new HashSet(); for(Integer num:visit){ for(Integer square:list){ if(num-square==0) return level; else if(num-square<0) break; else temp.add(num-square); } visit = temp; } level++; } return level; } }
Given an n x n grid containing only values 0 and 1, where 0 represents water and 1 represents land, find a water cell such that its distance to the nearest land cell is maximized, and return the distance. If no land or water exists in the grid, return -1.
The distance used in this problem is the Manhattan distance: the distance between two cells (x0, y0) and (x1, y1) is |x0 - x1| + |y0 - y1|.
Example 1:

Input: grid = [[1,0,1],[0,0,0],[1,0,1]] Output: 2 Explanation: The cell (1, 1) is as far as possible from all the land with distance 2.
Example 2:

Input: grid = [[1,0,0],[0,0,0],[0,0,0]] Output: 4 Explanation: The cell (2, 2) is as far as possible from all the land with distance 4.
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 100grid[i][j]is0or1
class Solution { public int maxDistance(int[][] grid) { //将所有的land扔到队列中 Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList(); for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){ for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){ if(grid[i][j]==1) queue.offer(new int[]{i,j}); } } //如果没有land或者都是land直接return -1 if(queue.size()==0||queue.size()==grid.length*grid[0].length) return -1; //开始进行bfs int[][] directions = {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}}; int step = 0; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); step++; for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ int[] pos = queue.poll(); int x = pos[0],y=pos[1]; for(int[] direction:directions){ if(x+direction[0]>=0 && x+direction[0]<grid.length && y+direction[1]>=0 && y+direction[1]<grid[0].length && grid[x+direction[0]][y+direction[1]]==0){ queue.offer(new int[]{x+direction[0],y+direction[1]}); grid[x+direction[0]][y+direction[1]]=1; } } } } return step-1; } }
1293. Shortest Path in a Grid with Obstacles Elimination
You are given an m x n integer matrix grid where each cell is either 0 (empty) or 1 (obstacle). You can move up, down, left, or right from and to an empty cell in one step.
Return the minimum number of steps to walk from the upper left corner (0, 0) to the lower right corner (m - 1, n - 1) given that you can eliminate at most k obstacles. If it is not possible to find such walk return -1.
Example 1:

Input: grid = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,0],[0,1,1],[0,0,0]], k = 1 Output: 6 Explanation: The shortest path without eliminating any obstacle is 10. The shortest path with one obstacle elimination at position (3,2) is 6. Such path is (0,0) -> (0,1) -> (0,2) -> (1,2) -> (2,2) -> (3,2) -> (4,2).
Example 2:

Input: grid = [[0,1,1],[1,1,1],[1,0,0]], k = 1 Output: -1 Explanation: We need to eliminate at least two obstacles to find such a walk.
Constraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 401 <= k <= m * ngrid[i][j]is either0or1.grid[0][0] == grid[m - 1][n - 1] == 0
解法1:
class Solution { //step:已经走的步数 k:剩余的子弹 record Node(int x, int y, int step, int k){} public int shortestPath(int[][] grid, int k) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; //3维状态,加了一维子弹数目,剩余子弹数目不同时可以重复经过一个点 boolean[][][] visited = new boolean[m][n][k+1]; Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList(); //初始节点入队列 queue.offer(new Node(0, 0, 0, k)); visited[0][0][k] = true; int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ Node curr = queue.poll(); //到达右下角的话 返回步数 if(curr.x == m -1 && curr.y == n - 1) return curr.step; //四个方向 for(int[] direct : directions){ int i = curr.x + direct[0]; int j = curr.y + direct[1]; //越界 if(i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n) continue; //下次剩余子弹数 int nextK = curr.k - grid[i][j]; //如果子弹数<0,那么说明不能继续走了 if(nextK < 0) continue; //下面继续走 if(visited[i][j][nextK]) continue; visited[i][j][nextK] = true; queue.offer(new Node(i, j, curr.step + 1, nextK)); } } return -1; } }
解法2:
class Solution { //step:已经走的步数 k:剩余的子弹 record Node(int x, int y, int step, int k){} public int shortestPath(int[][] grid, int k) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; //3维状态,加了一维子弹数目,剩余子弹数目不同时可以重复经过一个点 int[][] visited = new int[m][n]; for(int[] arr : visited) Arrays.fill(arr, -1); Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList(); //初始节点入队列 queue.offer(new Node(0, 0, 0, k)); visited[0][0] = k; int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ Node curr = queue.poll(); //到达右下角的话 返回步数 if(curr.x == m -1 && curr.y == n - 1) return curr.step; //四个方向 for(int[] direct : directions){ int i = curr.x + direct[0]; int j = curr.y + direct[1]; //越界 if(i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n) continue; //下次剩余子弹数 int nextK = curr.k - grid[i][j]; //如果子弹数比之前还小,那么说明没必要继续走了,因为步数相同(因为是bfs)的情况下,子弹还少,再走也不可能比之前更优 if(nextK <= visited[i][j]) continue; //下面继续走 visited[i][j] = nextK; queue.offer(new Node(i, j, curr.step + 1, nextK)); } } return -1; } }
解法3: A*
class Solution { /* A* 解法,新增了一个estimate步数,即每次都是优先取estimate最佳的点 max: m+n-2 表示到达终点的预估最大步数(不考虑障碍物的情况下) 使用了heap来保证每次优先取estimate最佳的点 */ //step:已经走的步数 k:剩余的子弹 record Node(int x, int y, int step, int k, int est){} public int shortestPath(int[][] grid, int k) { int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length, max = m + n - 2; //3维状态,加了一维子弹数目,剩余子弹数目不同时可以重复经过一个点 int[][] visited = new int[m][n]; for(int[] arr : visited) Arrays.fill(arr, -1); Queue<Node> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b)->a.est - b.est); //初始节点入队列 queue.offer(new Node(0, 0, 0, k, max)); visited[0][0] = k; int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}; while(!queue.isEmpty()){ Node curr = queue.poll(); //到达右下角的话 返回步数 if(curr.x == m -1 && curr.y == n - 1) return curr.step; //四个方向 for(int[] direct : directions){ int i = curr.x + direct[0]; int j = curr.y + direct[1]; //越界 if(i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n) continue; //下次剩余子弹数 int nextK = curr.k - grid[i][j]; //如果子弹数比之前还小,那么说明没必要继续走了,因为步数相同(因为是bfs)的情况下,子弹还少,再走也不可能比之前更优 if(nextK <= visited[i][j]) continue; //下面继续走 visited[i][j] = nextK; queue.offer(new Node(i, j, curr.step + 1, nextK, max - i - j + curr.step + 1)); } } return -1; } }
On an 2 x 3 board, there are five tiles labeled from 1 to 5, and an empty square represented by 0. A move consists of choosing 0 and a 4-directionally adjacent number and swapping it.
The state of the board is solved if and only if the board is [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]].
Given the puzzle board board, return the least number of moves required so that the state of the board is solved. If it is impossible for the state of the board to be solved, return -1.
Example 1:
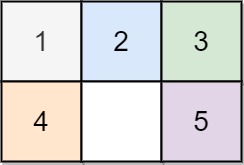
Input: board = [[1,2,3],[4,0,5]] Output: 1 Explanation: Swap the 0 and the 5 in one move.
Example 2:
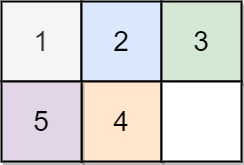
Input: board = [[1,2,3],[5,4,0]] Output: -1 Explanation: No number of moves will make the board solved.
Example 3:
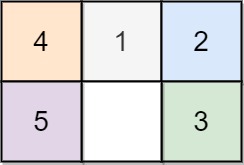
Input: board = [[4,1,2],[5,0,3]] Output: 5 Explanation: 5 is the smallest number of moves that solves the board. An example path: After move 0: [[4,1,2],[5,0,3]] After move 1: [[4,1,2],[0,5,3]] After move 2: [[0,1,2],[4,5,3]] After move 3: [[1,0,2],[4,5,3]] After move 4: [[1,2,0],[4,5,3]] After move 5: [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]]
Constraints:
board.length == 2board[i].length == 30 <= board[i][j] <= 5- Each value
board[i][j]is unique.
class Solution { public int slidingPuzzle(int[][] board) { // define queue Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(); Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>(); String origin = ""; for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { origin += board[i][j]; } } visited.add(origin); queue.offer(origin); // bfs int step = 0; while(!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) { String curr = queue.poll(); if(curr.equals("123450")) return step; for(String other : others(curr)) { if(visited.add(other)) { queue.offer(other); } } } step++; } // return -1; } // 找到0的位置,然后将0与周围数字进行交换 private List<String> others(String arr) { int x = 0, y = 0; for(int i = 0; i < arr.length(); i++) { if(arr.charAt(i) == '0') { x = i / 3; y = i % 3; } } int ori = x * 3 + y; List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(int[] direct : directions) { int xx = x + direct[0], yy = y + direct[1]; if(xx >= 0 && xx < 2 && yy >= 0 && yy < 3) { char[] temp = arr.toCharArray(); int pos = xx * 3 + yy; swap(temp, ori, pos); list.add(new String(temp)); } } return list; } private void swap(char[] temp, int ori, int pos) { char c = temp[ori]; temp[ori] = temp[pos]; temp[pos] = c; } int[][] directions = new int[][]{{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}}; }
简化了遍历各个方向:
class Solution { public int slidingPuzzle(int[][] board) { // define queue Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(); Set<String> visited = new HashSet<>(); String origin = ""; for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { origin += board[i][j]; } } visited.add(origin); queue.offer(origin); // bfs int step = 0; while(!queue.isEmpty()) { int size = queue.size(); for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) { String curr = queue.poll(); if(curr.equals("123450")) return step; for(String other : others(curr)) { if(visited.add(other)) { queue.offer(other); } } } step++; } // return -1; } // 找到0的位置,然后将0与周围数字进行交换 private List<String> others(String str) { char[] arr = str.toCharArray(); int zeroPos = 0; for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { if(arr[i] == '0') { zeroPos = i; break; } } List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); for(int other : directions[zeroPos]) { list.add(swap(str, zeroPos, other)); } return list; } private String swap(String temp, int a, int b) { StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer(temp); s.setCharAt(a, temp.charAt(b)); s.setCharAt(b, temp.charAt(a)); return s.toString(); } /** 根据0所在不同位置,可以交换的情况 */ private final int[][] directions = { { 1, 3 }, { 0, 2, 4 }, { 1, 5 }, { 0, 4 }, { 3, 5, 1 }, { 4, 2 }, }; } /** [123] [405] [123] [123] [103] [450] [045] [425] */



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号