扫描线系列
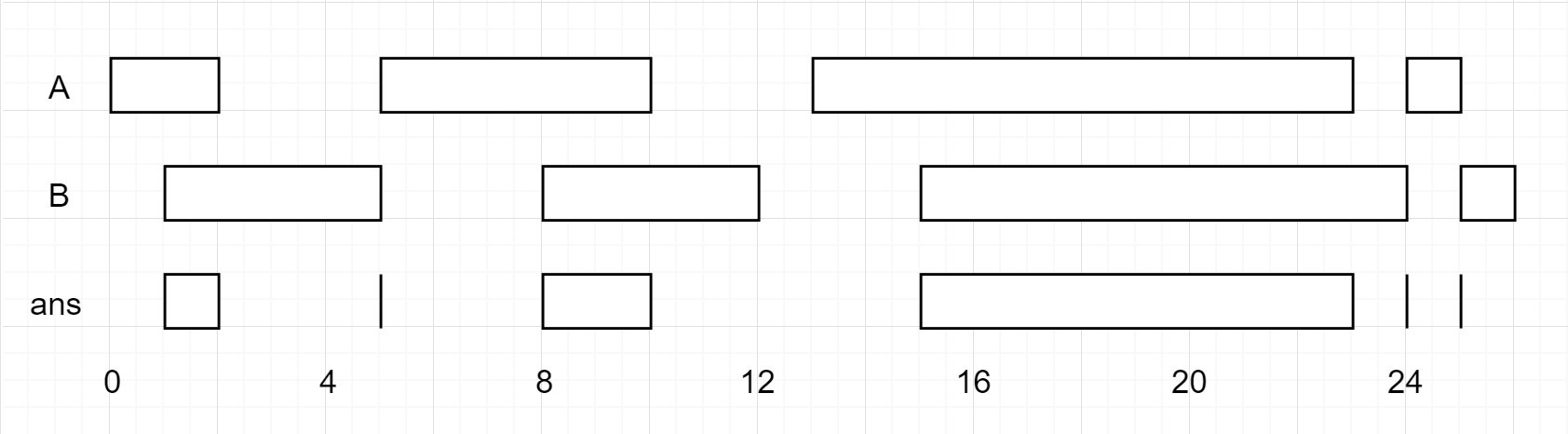
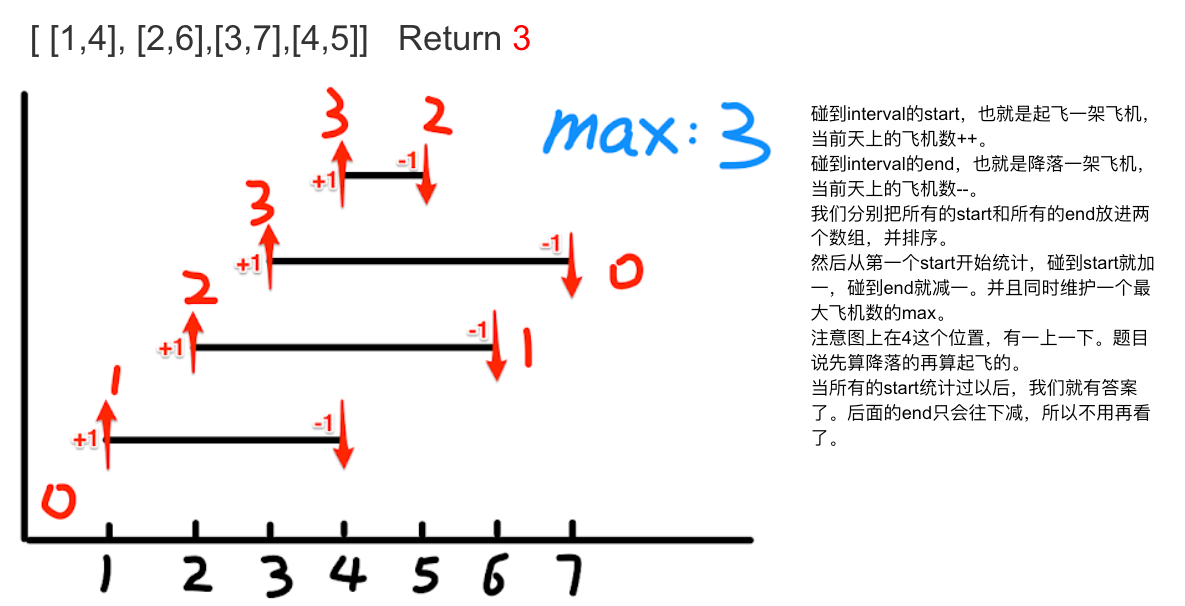
给出飞机的起飞和降落时间的列表,用序列 interval 表示. 请计算出天上同时最多有多少架飞机?
如果多架飞机降落和起飞在同一时刻,我们认为降落有优先权。
样例 1:
输入: [(1, 10), (2, 3), (5, 8), (4, 7)]
输出: 3
解释:
第一架飞机在1时刻起飞, 10时刻降落.
第二架飞机在2时刻起飞, 3时刻降落.
第三架飞机在5时刻起飞, 8时刻降落.
第四架飞机在4时刻起飞, 7时刻降落.
在5时刻到6时刻之间, 天空中有三架飞机.样例 2:
输入: [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4)]
输出: 1
解释: 降落优先于起飞.
解法:
![]()
![]()
/** * Definition of Interval: * public classs Interval { * int start, end; * Interval(int start, int end) { * this.start = start; * this.end = end; * } * } */ public class Solution { /** * @param airplanes: An interval array * @return: Count of airplanes are in the sky. */ public int countOfAirplanes(List<Interval> airplanes) { List<int[]> list = new ArrayList(); for(Interval pair:airplanes){ list.add(new int[]{pair.start,1});//起飞的时候+1 list.add(new int[]{pair.end,-1});//降落的时候-1 } Collections.sort(list,(x,y)->{ //此处确保降落(-1)排在起飞(1)之前 if(x[0]==y[0]) return x[1]-y[1]; return x[0]-y[0]; }); int count=0,max = 0; for(int[] pair:list){ count += pair[1]; max = Math.max(max,count); } return max; } }
[LeetCode] 252. Meeting Rooms 会议室
Given an array of meeting time intervals consisting of start and end times [[s1,e1],[s2,e2],...] (si < ei), determine if a person could attend all meetings.
Example 1:
Input: [[0,30],[5,10],[15,20]]
Output: false
Example 2:
Input: [[7,10],[2,4]] Output: true
/** * Definition of Interval: * public classs Interval { * int start, end; * Interval(int start, int end) { * this.start = start; * this.end = end; * } * } */ public class Solution { /** * @param intervals: an array of meeting time intervals * @return: if a person could attend all meetings */ public boolean canAttendMeetings(List<Interval> intervals) { // Write your code here Collections.sort(intervals,(x,y)->{ if(x.start==y.start) return x.end-y.end; return x.start-y.start; }); for(int i=1;i<intervals.size();i++){ Interval pre = intervals.get(i-1); Interval curr = intervals.get(i); if(curr.start<pre.end) return false; } return true; } }
[[s1,e1],[s2,e2],...] (si < ei), find the minimum number of conference rooms required.Input: intervals = [(0,30),(5,10),(15,20)]
Output: 2
Explanation:
We need two meeting rooms
room1: (0,30)
room2: (5,10),(15,20)Example2
Input: intervals = [(2,7)]
Output: 1
Explanation:
Only need one meeting room 第一种解法:数飞机
/** * Definition of Interval: * public classs Interval { * int start, end; * Interval(int start, int end) { * this.start = start; * this.end = end; * } * } */ public class Solution { /** * @param intervals: an array of meeting time intervals * @return: the minimum number of conference rooms required */ public int minMeetingRooms(List<Interval> intervals) { List<int[]> list = new ArrayList(); for(Interval pair:intervals){ list.add(new int[]{pair.start,1}); list.add(new int[]{pair.end,-1}); } Collections.sort(list,(x,y)->{ if(x[0]!=y[0]) return x[0]-y[0]; return x[1]-y[1]; }); int result = 0; int count = 0; for(int[] pair:list) { count+=pair[1]; result=Math.max(result,count); } return result; } }
第二种解法:
/** * Definition of Interval: * public classs Interval { * int start, end; * Interval(int start, int end) { * this.start = start; * this.end = end; * } * } */ public class Solution { /** * @param intervals: an array of meeting time intervals * @return: the minimum number of conference rooms required */ public int minMeetingRooms(List<Interval> intervals) { Collections.sort(intervals,(x,y)->{ if(x.start==y.start) return x.end-y.end; return x.start-y.start; }); PriorityQueue<Interval> pq = new PriorityQueue<Interval>((x,y)->x.end-y.end); for(Interval interval:intervals){ if(pq.isEmpty()){ pq.offer(interval); } else{ Interval min = pq.poll(); if(min.end<interval.start) { min.end = interval.end; pq.offer(min); } else{ pq.offer(min); pq.offer(interval); } } } return pq.size(); } }
Given an array of intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi], merge all overlapping intervals, and return an array of the non-overlapping intervals that cover all the intervals in the input.
Example 1:
Input: intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]] Output: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]] Explanation: Since intervals [1,3] and [2,6] overlaps, merge them into [1,6].
Example 2:
Input: intervals = [[1,4],[4,5]] Output: [[1,5]] Explanation: Intervals [1,4] and [4,5] are considered overlapping.
Constraints:
1 <= intervals.length <= 104intervals[i].length == 20 <= starti <= endi <= 104
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
Arrays.sort(intervals,(x,y)->{
if(x[0]==y[0]) return x[1]-y[1];
return x[0]-y[0];
});
List<int[]> result = new ArrayList();
for(int[] interval:intervals){
if(result.isEmpty()) result.add(interval);
else{
int[] pre = result.get(result.size()-1);
if(interval[0]<=pre[1])
pre[1] = Math.max(pre[1],interval[1]);
else
result.add(interval);
}
}
int[][] arr = new int[result.size()][2];
for(int i=0;i<result.size();i++) arr[i]=result.get(i);
return arr;
}
}
LeetCode 1272. Remove Interval
Given a sorted list of disjoint intervals, each interval intervals[i] = [a, b] represents the set of real numbers x such that a <= x < b.
We remove the intersections between any interval in intervals and the interval toBeRemoved.
Return a sorted list of intervals after all such removals.
Example 1:
Input: intervals = [[0,2],[3,4],[5,7]], toBeRemoved = [1,6] Output: [[0,1],[6,7]]
Example 2:
Input: intervals = [[0,5]], toBeRemoved = [2,3] Output: [[0,2],[3,5]]
Constraints:
1 <= intervals.length <= 10^4-10^9 <= intervals[i][0] < intervals[i][1] <= 10^9
public List<List<Integer>> removeInterval( int[][] intervals, int[] removing ){ List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList(); for(int[] pair:intervals){ if(pair[0]>=removing[1] || pair[1]<=removing[0]) result.add(pair); else{ if(pair[0]<removing[0]){ result.add(pair[0],removing[0]); } if(pair[1]>removing[1]){ result.add(removing[1],pair[1]); } } } return result; }
You are given an array of non-overlapping intervals intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi] represent the start and the end of the ith interval and intervals is sorted in ascending order by starti. You are also given an interval newInterval = [start, end] that represents the start and end of another interval.
Insert newInterval into intervals such that intervals is still sorted in ascending order by starti and intervals still does not have any overlapping intervals (merge overlapping intervals if necessary).
Return intervals after the insertion.
Example 1:
Input: intervals = [[1,3],[6,9]], newInterval = [2,5] Output: [[1,5],[6,9]]
Example 2:
Input: intervals = [[1,2],[3,5],[6,7],[8,10],[12,16]], newInterval = [4,8] Output: [[1,2],[3,10],[12,16]] Explanation: Because the new interval[4,8]overlaps with[3,5],[6,7],[8,10].
Example 3:
Input: intervals = [], newInterval = [5,7] Output: [[5,7]]
Example 4:
Input: intervals = [[1,5]], newInterval = [2,3] Output: [[1,5]]
Example 5:
Input: intervals = [[1,5]], newInterval = [2,7] Output: [[1,7]]
Constraints:
0 <= intervals.length <= 104intervals[i].length == 20 <= starti <= endi <= 105intervalsis sorted bystartiin ascending order.newInterval.length == 20 <= start <= end <= 105
class Solution { public int[][] insert(int[][] intervals, int[] newI) { if(intervals.length==0) return new int[][]{newI}; List<int[]> list = new ArrayList(); for(int[] pair:intervals){ //还没插进去 if(newI!=null){//还没到 if(newI[0]>pair[1]) list.add(pair); else{ if(newI[1]<pair[0]) { //到了,但是跟当前的没有交叉 list.add(newI); } else{//到了并且有交叉,需要合并 pair[0] = Math.min(pair[0],newI[0]); pair[1] = Math.max(pair[1],newI[1]); } list.add(pair); newI = null; } } //已经插进去,后续的如果有overlap,直接merge else{ int[] pre = list.get(list.size()-1); if(pre[1]>=pair[0]) { pre[1] = Math.max(pre[1],pair[1]); } else list.add(pair); } } //如果遍历完所有的没找到机会插入 if(newI!=null) list.add(newI); return list.toArray(new int[list.size()][2]); } }
Given an array of intervals intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi], return the minimum number of intervals you need to remove to make the rest of the intervals non-overlapping.
Example 1:
Input: intervals = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[1,3]] Output: 1 Explanation: [1,3] can be removed and the rest of the intervals are non-overlapping.
Example 2:
Input: intervals = [[1,2],[1,2],[1,2]] Output: 2 Explanation: You need to remove two [1,2] to make the rest of the intervals non-overlapping.
Example 3:
Input: intervals = [[1,2],[2,3]] Output: 0 Explanation: You don't need to remove any of the intervals since they're already non-overlapping.
Constraints:
1 <= intervals.length <= 105intervals[i].length == 2-5 * 104 <= starti < endi <= 5 * 104
解法: greedy
class Solution { public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) { if(intervals.length<=1) return 0;
//先按照开始时间排序 Arrays.sort(intervals,(x,y)->x[0]-y[0]); int left = 0,right=1,count=0; while(right<intervals.length){ //没有overlap if(intervals[right][0]>=intervals[left][1]){ left=right; right++; } //有overlap,但是左边的没有包含右边的,总是去掉右边的 else if(intervals[right][1]>intervals[left][1]){ count++; right++; } //有overlap,并且左边的完全包含了右边的,这时去掉左边的,因为左边的还可能跟后续的其他元素交叉 else{ count++; left=right; right++; } } return count; } }
Given an array intervals where intervals[i] = [li, ri] represent the interval [li, ri), remove all intervals that are covered by another interval in the list.
The interval [a, b) is covered by the interval [c, d) if and only if c <= a and b <= d.
Return the number of remaining intervals.
Example 1:
Input: intervals = [[1,4],[3,6],[2,8]] Output: 2 Explanation: Interval [3,6] is covered by [2,8], therefore it is removed.
Example 2:
Input: intervals = [[1,4],[2,3]] Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: intervals = [[0,10],[5,12]] Output: 2
Example 4:
Input: intervals = [[3,10],[4,10],[5,11]] Output: 2
Example 5:
Input: intervals = [[1,2],[1,4],[3,4]] Output: 1
Constraints:
1 <= intervals.length <= 1000intervals[i].length == 20 <= li <= ri <= 105- All the given intervals are unique.
class Solution { public int removeCoveredIntervals(int[][] intervals) { //先按照开始时间正序排序,再按照结束时间倒序排序 Arrays.sort(intervals,(x, y)->{ if(x[0]==y[0]) return y[1]-x[1]; return x[0]-y[0]; }); int left = 0, right=1, count=intervals.length; while(right<intervals.length){ //没有overlap, 或者 有overlap,但是左边的没有包含右边的,总是去掉右边的 if(intervals[right][0]>=intervals[left][1] || intervals[right][1]>intervals[left][1] ){ left=right; right++; } //有overlap,并且左边的完全包含了右边的,这时去掉右边的 else{ count--; right++; } } return count; } }
Given a data stream input of non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an, summarize the numbers seen so far as a list of disjoint intervals.
Implement the SummaryRanges class:
SummaryRanges()Initializes the object with an empty stream.void addNum(int val)Adds the integervalto the stream.int[][] getIntervals()Returns a summary of the integers in the stream currently as a list of disjoint intervals[starti, endi].
Example 1:
Input ["SummaryRanges", "addNum", "getIntervals", "addNum", "getIntervals", "addNum", "getIntervals", "addNum", "getIntervals", "addNum", "getIntervals"] [[], [1], [], [3], [], [7], [], [2], [], [6], []] Output [null, null, [[1, 1]], null, [[1, 1], [3, 3]], null, [[1, 1], [3, 3], [7, 7]], null, [[1, 3], [7, 7]], null, [[1, 3], [6, 7]]] Explanation SummaryRanges summaryRanges = new SummaryRanges(); summaryRanges.addNum(1); // arr = [1] summaryRanges.getIntervals(); // return [[1, 1]] summaryRanges.addNum(3); // arr = [1, 3] summaryRanges.getIntervals(); // return [[1, 1], [3, 3]] summaryRanges.addNum(7); // arr = [1, 3, 7] summaryRanges.getIntervals(); // return [[1, 1], [3, 3], [7, 7]] summaryRanges.addNum(2); // arr = [1, 2, 3, 7] summaryRanges.getIntervals(); // return [[1, 3], [7, 7]] summaryRanges.addNum(6); // arr = [1, 2, 3, 6, 7] summaryRanges.getIntervals(); // return [[1, 3], [6, 7]]
Constraints:
0 <= val <= 104- At most
3 * 104calls will be made toaddNumandgetIntervals.
Follow up: What if there are lots of merges and the number of disjoint intervals is small compared to the size of the data stream?
class SummaryRanges { private List<int[]> intervals=null; public SummaryRanges() { intervals = new ArrayList(); } public void addNum(int val) { int[] newI = new int[]{val,val}; insertInterval(newI); } public int[][] getIntervals() { return intervals.toArray(new int[intervals.size()][2]); } private void insertInterval(int[] newI){ int index = Collections.binarySearch(intervals,newI,(x,y)->x[0]-y[0]); if(index>=0) return; index = (index+1)*-1; int[] pre = index>0 ? intervals.get(index-1) : null; int[] post = index<intervals.size() ? intervals.get(index) : null; if(pre!=null && pre[1]==newI[0]-1 && post!=null && post[0]==newI[0]+1) {//刚好连接两侧的interval pre[1]=post[1]; intervals.remove(index); } else if(pre!=null && pre[1]>=newI[0]-1 ){//连接左侧的interval或者已经包含在了左侧interval中 pre[1]=Math.max(pre[1],newI[0]); } else if(post!=null && post[0]==newI[0]+1){//连接右侧的interval post[0]--; } else intervals.add(index,newI);//与左右都不相连 } } /** * Your SummaryRanges object will be instantiated and called as such: * SummaryRanges obj = new SummaryRanges(); * obj.addNum(val); * int[][] param_2 = obj.getIntervals(); */
[LeetCode] 1229. Meeting Scheduler
Given the availability time slots arrays slots1 and slots2 of two people and a meeting duration duration, return the earliest time slot that works for both of them and is of duration duration.
If there is no common time slot that satisfies the requirements, return an empty array.
The format of a time slot is an array of two elements [start, end] representing an inclusive time range from start to end.
It is guaranteed that no two availability slots of the same person intersect with each other. That is, for any two time slots [start1, end1] and [start2, end2] of the same person, either start1 > end2 or start2 > end1.
Example 1:
Input: slots1 = [[10,50],[60,120],[140,210]], slots2 = [[0,15],[60,70]], duration = 8 Output: [60,68]Example 2:
Input: slots1 = [[10,50],[60,120],[140,210]], slots2 = [[0,15],[60,70]], duration = 12 Output: []
Constraints:
1 <= slots1.length, slots2.length <= 10^4slots1[i].length, slots2[i].length == 2slots1[i][0] < slots1[i][1]slots2[i][0] < slots2[i][1]0 <= slots1[i][j], slots2[i][j] <= 10^91 <= duration <= 10^6
解法一:数飞机
class Solution { public List<Integer> minAvailableDuration(int[][] slots1, int[][] slots2, int duration){ List<int[]> list = new ArrayList(); for(int[] pair:slots1){ list.add(new int[]{pair[0],1}); list.add(new int[]{pair[1],-1}); } for(int[] pair:slots2){ list.add(new int[]{pair[0],1}); list.add(new int[]{pair[1],-1}); } Collections.sort(list,(x,y)->{ if(x[0]==y[0]) return y[1]-x[1]; return x[0]-y[0]; }); int start=0; int count=0; for(int[] pair:list){ count+=pair[1]; if(count==2) start=pair[0]; else if(count==1 && pair[1]==-1){ if(pair[0]-start>=duration) return Arrays.asList(start,pair[0]); } } return Arrays.asList(); } }
解法二:
class Solution { public List<Integer> minAvailableDuration(int[][] slots1, int[][] slots2, int duration){ Arrays.sort(slots1,(x,y)->x[0]-y[0]); Arrays.sort(slots2,(x,y)->x[0]-y[0]); int ind1=0; int ind2=0; while( ind1<slots1.length && ind2<slots2.length ){ int start = Math.max(slots1[0],slots2[0]);
int start = Math.max(slots1[ind1][0],slots2[ind2][0]);
int end = Math.min(slots1[ind1][1],slots2[ind2][1]);
if(end-start>=duration) return Arrays.asList(start,end);//交叉部分满足长度要求,直接返回
else if(slots1[ind1][1]<slots2[ind2][1]) ind1++;//结束时间早的换下一个slot
else ind2++;
}
return Arrays.asList();
}
}
You are given two lists of closed intervals, firstList and secondList, where firstList[i] = [starti, endi] and secondList[j] = [startj, endj]. Each list of intervals is pairwise disjoint and in sorted order.
Return the intersection of these two interval lists.
A closed interval [a, b] (with a <= b) denotes the set of real numbers x with a <= x <= b.
The intersection of two closed intervals is a set of real numbers that are either empty or represented as a closed interval. For example, the intersection of [1, 3] and [2, 4] is [2, 3].
Example 1:
Input: firstList = [[0,2],[5,10],[13,23],[24,25]], secondList = [[1,5],[8,12],[15,24],[25,26]] Output: [[1,2],[5,5],[8,10],[15,23],[24,24],[25,25]]
Example 2:
Input: firstList = [[1,3],[5,9]], secondList = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: firstList = [], secondList = [[4,8],[10,12]] Output: []
Example 4:
Input: firstList = [[1,7]], secondList = [[3,10]] Output: [[3,7]]
Constraints:
0 <= firstList.length, secondList.length <= 1000firstList.length + secondList.length >= 10 <= starti < endi <= 109endi < starti+10 <= startj < endj <= 109endj < startj+1
这个题实际就是上一道题稍微改变了一下
解法一:数飞机
class Solution { public int[][] intervalIntersection(int[][] slots1, int[][] slots2) { List<int[]> list = new ArrayList(); for(int[] pair:slots1){ list.add(new int[]{pair[0],1}); list.add(new int[]{pair[1],-1}); } for(int[] pair:slots2){ list.add(new int[]{pair[0],1}); list.add(new int[]{pair[1],-1}); } Collections.sort(list,(x,y)->{ if(x[0]==y[0]) return y[1]-x[1]; return x[0]-y[0]; }); int start=0; int count=0; List<int[]> result = new ArrayList(); for(int[] pair:list){ count+=pair[1]; if(count==2) start=pair[0]; else if(count==1 && pair[1]==-1){ result.add(new int[]{start,pair[0]}); } } return result.toArray(new int[result.size()][2]); } }
解法二:
class Solution { public int[][] intervalIntersection(int[][] slots1, int[][] slots2) { Arrays.sort(slots1,(x,y)->x[0]-y[0]); Arrays.sort(slots2,(x,y)->x[0]-y[0]); int ind1=0; int ind2=0; List<int[]> result = new ArrayList(); while( ind1<slots1.length && ind2<slots2.length ){ int start = Math.max(slots1[ind1][0],slots2[ind2][0]); int end = Math.min(slots1[ind1][1],slots2[ind2][1]); if(end>=start) {//有交叉,加入list result.add(new int[]{start,end}); } if(slots1[ind1][1]<slots2[ind2][1]) ind1++;//没交叉结束时间早的换下一个slot else ind2++; } return result.toArray( new int[result.size()][2] ); } }
我们得到一个员工的schedule列表,代表每个员工工作时间。
每个员工有一个不重合时段的列表 Intervals,这些时段按序排列。
返回一个所有员工共有的空闲时段的列表,并按序排列。
我们的Intervals是一个一维数组,其中每两个数表示一个区间,即[1,2,8,10]表示这个员工的工作时间是[1,2]和[8,10]。
并且,我们的答案不会包括像[5,5]这样的,因为它们的长度是0。
schedule和schedule[i]为长度范围在[1, 100]的列表。0 <= schedule[i].start < schedule[i].end <= 10^8。
样例 1:
输入:schedule = [[1,2,5,6],[1,3],[4,10]]
输出:[[3,4]]
解释:共有三个员工,并且所有员工共有的空闲时段是[-inf, 1], [3, 4], [10, inf]。去除掉包含inf的答案。样例 2:
输入:schedule = [[1,3,6,7],[2,4],[2,5,9,12]]
输出:[(5,6),(7,9)]
解释:共有三个员工,并且所有员工共有的空闲时段是[-inf, 1], [5, 6], [7, 9],[12,inf]。去除掉包含inf的答案。/** * Definition of Interval: * public class Interval { * int start, end; * Interval(int start, int end) { * this.start = start; * this.end = end; * } * } */ public class Solution { /** * @param schedule: a list schedule of employees * @return: Return a list of finite intervals */ public List<Interval> employeeFreeTime(int[][] schedule) { // Write your code here List<int[]> list = new ArrayList(); for(int[] temp:schedule){ for(int i=0;i<temp.length;i++){ list.add(new int[]{temp[i],i%2==0 ? 1 : -1}); } } Collections.sort(list,(x,y)->{ if(x[0]!=y[0]) return x[0]-y[0]; return y[1]-x[1]; //这个地方一定要确保,先起飞,后降落 }); int max = 0; int start = Integer.MIN_VALUE; List<Interval> result = new ArrayList(); for(int[] pair:list){ max += pair[1]; if(max==1 && pair[1]==1 && start!=Integer.MIN_VALUE) {//天上的飞机从0->1的时候,说明空闲时段结束 result.add(new Interval(start,pair[0])); } else if(max==0){//天上飞机1->0的时候,说明空闲时段开始 start = pair[0]; } } return result; } }
A city's skyline is the outer contour of the silhouette formed by all the buildings in that city when viewed from a distance. Given the locations and heights of all the buildings, return the skyline formed by these buildings collectively.
The geometric information of each building is given in the array buildings where buildings[i] = [lefti, righti, heighti]:
leftiis the x coordinate of the left edge of theithbuilding.rightiis the x coordinate of the right edge of theithbuilding.heightiis the height of theithbuilding.
You may assume all buildings are perfect rectangles grounded on an absolutely flat surface at height 0.
The skyline should be represented as a list of "key points" sorted by their x-coordinate in the form [[x1,y1],[x2,y2],...]. Each key point is the left endpoint of some horizontal segment in the skyline except the last point in the list, which always has a y-coordinate 0 and is used to mark the skyline's termination where the rightmost building ends. Any ground between the leftmost and rightmost buildings should be part of the skyline's contour.
Note: There must be no consecutive horizontal lines of equal height in the output skyline. For instance, [...,[2 3],[4 5],[7 5],[11 5],[12 7],...] is not acceptable; the three lines of height 5 should be merged into one in the final output as such: [...,[2 3],[4 5],[12 7],...]
Example 1:
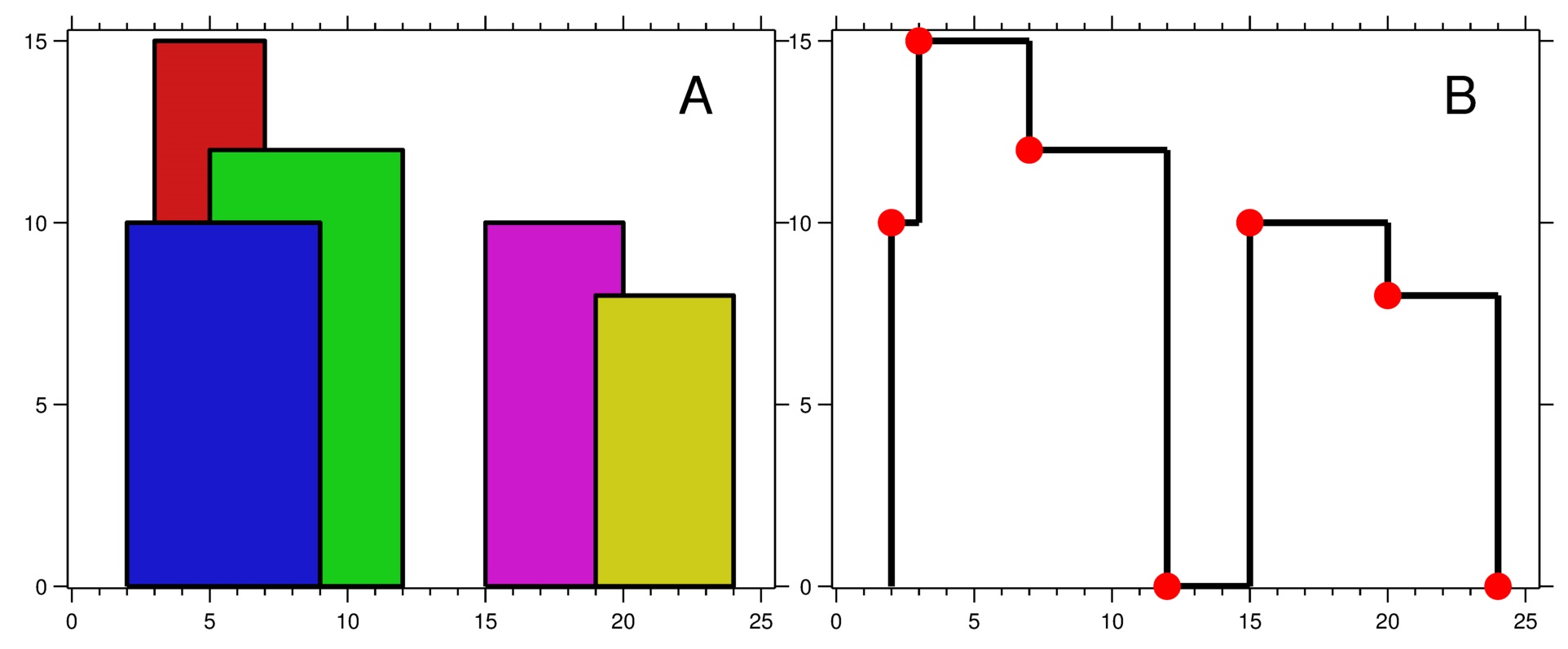
Input: buildings = [[2,9,10],[3,7,15],[5,12,12],[15,20,10],[19,24,8]] Output: [[2,10],[3,15],[7,12],[12,0],[15,10],[20,8],[24,0]] Explanation: Figure A shows the buildings of the input. Figure B shows the skyline formed by those buildings. The red points in figure B represent the key points in the output list.
Example 2:
Input: buildings = [[0,2,3],[2,5,3]] Output: [[0,3],[5,0]]
Constraints:
1 <= buildings.length <= 1040 <= lefti < righti <= 231 - 11 <= heighti <= 231 - 1buildingsis sorted byleftiin non-decreasing order.
数飞机:
class Solution { /** 关键点:扫描线 1.什么时候记录? 最高点进入时需要记录 最高点出去时需要记录下一个高度 2.扫描线如何排序? a.优先比坐标 b.坐标相同先退出再进入 c.出入相同,进入高->低,退出低->高 */ public List<List<Integer>> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) { // build scan line List<int[]> scanLine = new ArrayList(); for(int[] building : buildings) { int start = building[0], end = building[1], height = building[2]; scanLine.add(new int[]{start, height, 1}); scanLine.add(new int[]{end, height, -1}); } // sort scan line Collections.sort(scanLine, (x, y) -> { if(x[0] != y[0]) return x[0] - y[0];// 优先比较坐标 if(x[2] != y[2]) return y[2] - x[2];// 再比较出入 return x[2]>0 ? y[1]-x[1] : x[1]-y[1]; //如果是进入,先考虑高的,如果是退出,先考虑低的 }); // create max heap to store height PriorityQueue<Integer> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((x, y) -> { return y - x; }); // traversal scanline List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); for(int[] line : scanLine) { int pos = line[0], height = line[1], flag = line[2]; // start if(flag > 0) { if(heap.isEmpty() || heap.peek() < height) { result.add(Arrays.asList(pos, height)); } heap.offer(height); } //end else { heap.remove(height); int nextH = heap.isEmpty() ? 0 : heap.peek(); if(height > nextH) { // there's a drop, need to draw result.add(Arrays.asList(pos, nextH)); } } } return result; } }
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) { //1.create list and sort by [0](asc) [2](des) List<int[]> list = new ArrayList(); for(int[] buil:buildings){ list.add(new int[]{buil[0],buil[2],1}); list.add(new int[]{buil[1],buil[2],-1}); } Collections.sort(list,(x,y)->{
// 关键点1 if(x[0]!=y[0]) return x[0]-y[0]; if(y[2]!=x[2]) return y[2]-x[2];
// 关键点2: return x[2]>0 ? y[1]-x[1] : x[1]-y[1]; }); //2.create PQ PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((x,y)->y-x); List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList(); //3.foreach int height = 0; for(int[] buil:list){
// 如果是start if(buil[2]==1){
// 如果当前加入是最高,那么需要draw if(pq.isEmpty() || buil[1]>pq.peek()){ result.add(Arrays.asList(buil[0],buil[1])); } pq.offer(buil[1]); }
// 如果是end else{ pq.remove(buil[1]); int newH = pq.isEmpty() ? 0 : pq.peek();
// 如果下一个高度比刚remove的低,那么需要draw if(buil[1]>newH) result.add(Arrays.asList(buil[0],newH)); } } return result; // } }
更简化的写法:
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) { //1.create list and sort by [0](asc) [2](des) List<int[]> list = new ArrayList(); for(int[] buil:buildings){ list.add(new int[]{buil[0],-buil[2]}); list.add(new int[]{buil[1],buil[2]}); } Collections.sort(list,(x,y)->{ if(x[0]!=y[0]) return x[0]-y[0]; return x[1]-y[1]; }); //2.create PQ PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((x,y)->y-x); List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList(); //3.foreach pq.offer(0); for(int[] buil:list){ int pre = pq.peek(); if(buil[1]<0) pq.offer(-buil[1]); else pq.remove(buil[1]); if(pre!=pq.peek()){ result.add(Arrays.asList(buil[0],pq.peek())); } } return result; } }
1882. Process Tasks Using Servers
You are given two 0-indexed integer arrays servers and tasks of lengths n and m respectively. servers[i] is the weight of the ith server, and tasks[j] is the time needed to process the jth task in seconds.
Tasks are assigned to the servers using a task queue. Initially, all servers are free, and the queue is empty.
At second j, the jth task is inserted into the queue (starting with the 0th task being inserted at second 0). As long as there are free servers and the queue is not empty, the task in the front of the queue will be assigned to a free server with the smallest weight, and in case of a tie, it is assigned to a free server with the smallest index.
If there are no free servers and the queue is not empty, we wait until a server becomes free and immediately assign the next task. If multiple servers become free at the same time, then multiple tasks from the queue will be assigned in order of insertion following the weight and index priorities above.
A server that is assigned task j at second t will be free again at second t + tasks[j].
Build an array ans of length m, where ans[j] is the index of the server the jth task will be assigned to.
Return the array ans.
Example 1:
Input: servers = [3,3,2], tasks = [1,2,3,2,1,2] Output: [2,2,0,2,1,2] Explanation: Events in chronological order go as follows: - At second 0, task 0 is added and processed using server 2 until second 1. - At second 1, server 2 becomes free. Task 1 is added and processed using server 2 until second 3. - At second 2, task 2 is added and processed using server 0 until second 5. - At second 3, server 2 becomes free. Task 3 is added and processed using server 2 until second 5. - At second 4, task 4 is added and processed using server 1 until second 5. - At second 5, all servers become free. Task 5 is added and processed using server 2 until second 7.
Example 2:
Input: servers = [5,1,4,3,2], tasks = [2,1,2,4,5,2,1] Output: [1,4,1,4,1,3,2] Explanation: Events in chronological order go as follows: - At second 0, task 0 is added and processed using server 1 until second 2. - At second 1, task 1 is added and processed using server 4 until second 2. - At second 2, servers 1 and 4 become free. Task 2 is added and processed using server 1 until second 4. - At second 3, task 3 is added and processed using server 4 until second 7. - At second 4, server 1 becomes free. Task 4 is added and processed using server 1 until second 9. - At second 5, task 5 is added and processed using server 3 until second 7. - At second 6, task 6 is added and processed using server 2 until second 7.
Constraints:
servers.length == ntasks.length == m1 <= n, m <= 2 * 1051 <= servers[i], tasks[j] <= 2 * 105
class Solution { class Server{ int pos; int weight; int end; Server(int pos,int weight,int end){ this.pos = pos; this.weight = weight; this.end = end; } public String toString(){ return this.pos+"-"+this.weight+"-"+this.end; } } public int[] assignTasks(int[] servers, int[] tasks) { int[] result = new int[tasks.length]; //按照weight,pos进行排序 PriorityQueue<Server> idle = new PriorityQueue<>((x,y)->{ if(x.weight==y.weight) return x.pos-y.pos; return x.weight-y.weight; }); //按照结束时间,weight,pos进行排序 PriorityQueue<Server> busy = new PriorityQueue<>((x,y)->{ if(x.end==y.end) { if(x.weight==y.weight) return x.pos-y.pos; return x.weight-y.weight; } return x.end-y.end; }); //将所有的task都放到空闲列表 for(int i=0;i<servers.length;i++){ idle.offer(new Server(i,servers[i],0)); } for(int i=0;i<tasks.length;i++){ //每次先检查工作列表中是否有机器闲下来了,如果闲下来了就移回空闲列表 while(!busy.isEmpty()&&busy.peek().end<=i){ idle.offer(busy.poll()); } Server curr = null; //优先使用空闲列表机器 if(!idle.isEmpty()){ curr = idle.poll(); curr.end = i+tasks[i]; } //如果没有空闲机器,就从忙机器中选择结束时间最早的进行安排 else{ curr = busy.poll(); curr.end = curr.end+tasks[i]; } busy.offer(curr); result[i]=curr.pos; } return result; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号