Binary Search Tree 系列题目 98, 99, 96, 95, 450, 1008, 1373, 333,
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { //两步走:
//1.实现iterative方式的中序遍历
//2.添加一个pre变量存放前一个元素val,在中序遍历过程中逐个判定是否递增
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { if(root==null) return true; long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack(); while(root!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){ while(root!=null){ stack.push(root); root = root.left; } root = stack.pop(); if(root.val<=pre) return false; pre = root.val; root = root.right; } return true; } }
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution {
//recursive方式遍历,当前节点的左子树都应该小于该节点,右子树都应该大于该节点 public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) { return helper(root,Long.MIN_VALUE,Long.MAX_VALUE); } public boolean helper(TreeNode root,long min,long max){ if(root==null) return true; if(root.val<=min || root.val>=max) return false; return helper(root.left,min,root.val) && helper(root.right,root.val,max); } }
实现一颗二叉树的iterator,这个肯定不适合用recursive的方式了,应该用iterative方式,如果熟悉iterative方式的二叉树中序遍历,那么这个题只是把遍历的步骤拆散了而已
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class BSTIterator { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack(); TreeNode curr; public BSTIterator(TreeNode root) { curr = root; // 初始化的时候将左侧节点都放入stack addAllLeft(); } public int next() { // 去除栈顶 curr = stack.pop(); int val = curr.val; // 指向右子树 curr = curr.right; addAllLeft(); return val; } public boolean hasNext() { return !stack.isEmpty(); } public void addAllLeft(){ while(curr!=null){ stack.push(curr); curr = curr.left; } } } /** * Your BSTIterator object will be instantiated and called as such: * BSTIterator obj = new BSTIterator(root); * int param_1 = obj.next(); * boolean param_2 = obj.hasNext(); */
You are given the root of a binary search tree (BST), where the values of exactly two nodes of the tree were swapped by mistake. Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Example 1:
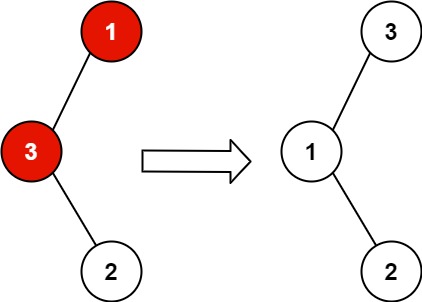
Input: root = [1,3,null,null,2] Output: [3,1,null,null,2] Explanation: 3 cannot be a left child of 1 because 3 > 1. Swapping 1 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Example 2:
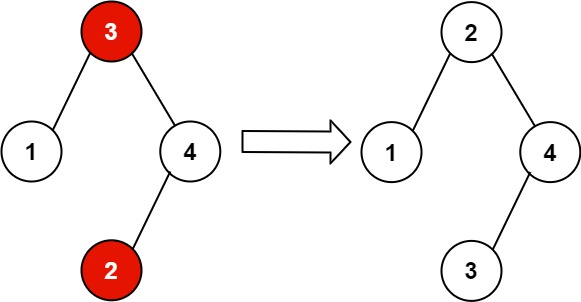
Input: root = [3,1,4,null,null,2] Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3] Explanation: 2 cannot be in the right subtree of 3 because 2 < 3. Swapping 2 and 3 makes the BST valid.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 1000]. -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
O(n) space is pretty straight-forward. Could you devise a constant O(1) space solution?
/**
1,2,3,4,5
第一种情况2个逆序对
1,5,3,4,2
x y
第二种情况1个逆序对
1,2,3,5,4
x y
*/
class Solution { public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) { TreeNode pre =null; TreeNode first = null; TreeNode second = null; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack();
//iteratively 遍历树,找到两个倒序的节点 while(root!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){ while(root!=null){ stack.push(root); root=root.left; } root = stack.pop(); if( pre!=null && pre.val>=root.val) { if(first==null) { first = pre; second = root; //tricky的地方 } else { second=root; break; } } pre=root; root = root.right; }
//交换这两个元素的位置 int temp = first.val; first.val = second.val; second.val = temp; } }
Given an integer n, return the number of structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) which has exactly n nodes of unique values from 1 to n.
Example 1:

Input: n = 3 Output: 5
Example 2:
Input: n = 1 Output: 1
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 19
class Solution { public int numTrees(int n) { return helper(n); } private int helper(int n) { // 个数为0或者1的时候,只有一种方式 if(n == 1 || n == 0) return 1; int result = 0; for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { // 第i个元素为root的总数: 左侧方式 * 右侧方式 result += helper(i - 1) * helper(n - i); } return result; } }
加memoization
class Solution { public int numTrees(int n){ int[] mem= new int[n+1]; return numTrees(n,mem); } public int numTrees(int n,int[] mem) { if(n<0) return 0; if(n==0 || n==1) return 1; if(mem[n]!=0) return mem[n]; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ mem[n] += numTrees(i-1,mem)*numTrees(n-i,mem); } return mem[n]; } }
Given an integer n, return all the structurally unique BST's (binary search trees), which has exactly n nodes of unique values from 1 to n. Return the answer in any order.
Example 1:

Input: n = 3 Output: [[1,null,2,null,3],[1,null,3,2],[2,1,3],[3,1,null,null,2],[3,2,null,1]]
Example 2:
Input: n = 1 Output: [[1]]
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 8
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public List<TreeNode> generateTrees(int n) { if(n==0) return new ArrayList(); return helper(1,n); } public List<TreeNode> helper(int start,int end){ List<TreeNode> list = new ArrayList(); if(start>end) { list.add(null); return list; } for(int i=start;i<=end;i++){ List<TreeNode> left = helper(start,i-1); List<TreeNode> right = helper(i+1,end); for(TreeNode lItem:left){ for(TreeNode rItem:right){ TreeNode root = new TreeNode(i); root.left = lItem; root.right = rItem; list.add(root); } } } return list; } }
Given a root node reference of a BST and a key, delete the node with the given key in the BST. Return the root node reference (possibly updated) of the BST.
Basically, the deletion can be divided into two stages:
- Search for a node to remove.
- If the node is found, delete the node.
Example 1:
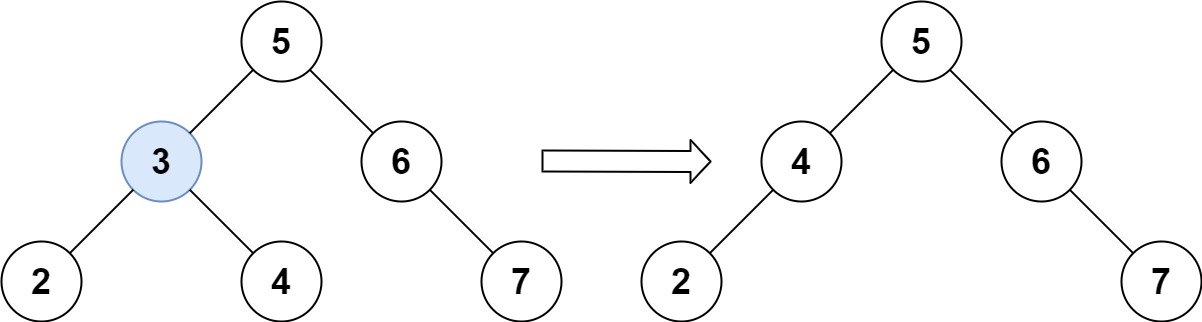
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 3 Output: [5,4,6,2,null,null,7] Explanation: Given key to delete is 3. So we find the node with value 3 and delete it. One valid answer is [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], shown in the above BST. Please notice that another valid answer is [5,2,6,null,4,null,7] and it's also accepted.
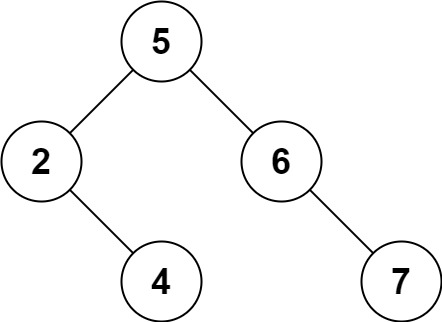
Example 2:
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], key = 0 Output: [5,3,6,2,4,null,7] Explanation: The tree does not contain a node with value = 0.
Example 3:
Input: root = [], key = 0 Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105- Each node has a unique value.
rootis a valid binary search tree.-105 <= key <= 105
解法:
0.目标位leaf node,直接return null
1.目标的左子树为空,直接返回右子树
2.目标的右子树为空,直接返回左子树
3.左右子树都不为空, 删除左子树最大值节点,然后将其值替换至目标节点
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key){ if(root==null) return null; //如果当前root为要删除的节点 if(root.val==key){ //如果是个叶子节点,直接返回null指向其父节点即可 if(root.left==null && root.right==null) return null; //如果left为null,直接返回right else if(root.left==null) return root.right; //如果right为null,直接返回left else if(root.right==null) return root.left; //如果left,right都不为null, 2. else{ //1.选择右子树最小值 int swap = find(root.right); //2.将该值放到当前节点 root.val=swap; //3.删除最小值所在节点 root.right=deleteNode(root.right,swap); } } //如果target小于当前val,只需去左子树 else if(key<root.val) root.left = deleteNode(root.left,key); //如果target大于当前val,只需去右子树 else root.right = deleteNode(root.right,key); return root; } private int find(TreeNode root){ while(root.left!=null) root=root.left; return root.val; } }
Given an array of integers preorder, which represents the preorder traversal of a BST (i.e., binary search tree), construct the tree and return its root.
It is guaranteed that there is always possible to find a binary search tree with the given requirements for the given test cases.
A binary search tree is a binary tree where for every node, any descendant of Node.left has a value strictly less than Node.val, and any descendant of Node.right has a value strictly greater than Node.val.
A preorder traversal of a binary tree displays the value of the node first, then traverses Node.left, then traverses Node.right.
Example 1:
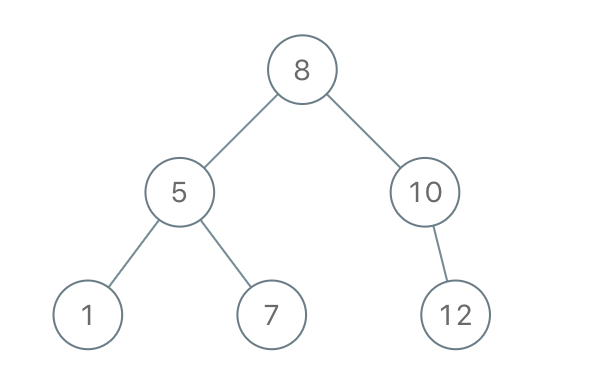
Input: preorder = [8,5,1,7,10,12] Output: [8,5,10,1,7,null,12]
Example 2:
Input: preorder = [1,3] Output: [1,null,3]
Constraints:
1 <= preorder.length <= 1001 <= preorder[i] <= 1000- All the values of
preorderare unique.
解法1:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode bstFromPreorder(int[] preorder) { return build(preorder,Long.MAX_VALUE,Long.MIN_VALUE); } private int index=0; private TreeNode build(int[] preorder,long max,long min){ if(index>=preorder.length) return null; if(preorder[index]<=min || preorder[index]>=max) return null; TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[index++]); root.left = build(preorder,root.val,min); root.right = build(preorder,max,root.val); return root; } }
解法2:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { public TreeNode bstFromPreorder(int[] preorder) { return build( preorder, 0, preorder.length-1 ); } private TreeNode build( int[] preorder, int left, int right ){ if(left>right) return null; TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[left]); if(left==right) return root; int rightind = right+1; for( rightind=left+1; rightind<=right; rightind++ ) if(preorder[rightind]>preorder[left]) break; root.left = build(preorder, left+1,Math.min(right,rightind-1)); root.right = build(preorder, rightind,right); return root; } }
1373. Maximum Sum BST in Binary Tree
Given a binary tree root, return the maximum sum of all keys of any sub-tree which is also a Binary Search Tree (BST).
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees
Example 1:
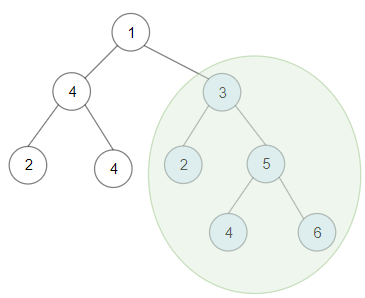
Input: root = [1,4,3,2,4,2,5,null,null,null,null,null,null,4,6] Output: 20 Explanation: Maximum sum in a valid Binary search tree is obtained in root node with key equal to 3.
Example 2:
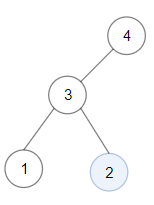
Input: root = [4,3,null,1,2] Output: 2 Explanation: Maximum sum in a valid Binary search tree is obtained in a single root node with key equal to 2.
Example 3:
Input: root = [-4,-2,-5] Output: 0 Explanation: All values are negatives. Return an empty BST.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 4 * 104]. -4 * 104 <= Node.val <= 4 * 104
这个题关键点:
1.top-down很难判定下面的子树是否合法,因为如果上层已经不合法,因此我们要用bottomup
2.关键点就是 bottomup 如何判定整个子树是否合法bst
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode() {} * TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { * this.val = val; * this.left = left; * this.right = right; * } * } */ class Solution { class Result{ boolean isValid;//是否为合法bst int min,max,sum;//当前子树最大值,最小值,sum Result(boolean isValid,int min,int max,int sum){ this.isValid = isValid; this.min = min; this.max = max; this.sum = sum; } } private int max = 0; public int maxSumBST(TreeNode root) { dfs(root); return max; } private Result dfs( TreeNode root ){ //空节点认为是一个合法的bst,但是注意最大最小值的设置,这么设置MAX和MIN是避免叶子节点对该值的检查 if(root==null) return new Result(true,Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MIN_VALUE,0);//这个MAX_VALUE/MIN_VALUE使用非常巧妙 //处理左右子树 Result left = dfs(root.left); Result right = dfs(root.right); //如果左子树或右子树不满足,或者当前节点不满足,返回false if( !left.isValid || !right.isValid || root.val<=left.max || root.val>=right.min ) return new Result(false,0,0,0); //如果是valid bst int sum = root.val + left.sum + right.sum; //计算最大值 max = Math.max( max, sum); return new Result(true,Math.min(root.val,left.min),Math.max(root.val,right.max),sum); } }
333. Largest BST Subtree
Given the root of a binary tree, find the largest subtree, which is also a Binary Search Tree (BST), where the largest means subtree has the largest number of nodes.
A Binary Search Tree (BST) is a tree in which all the nodes follow the below-mentioned properties:
- The left subtree values are less than the value of their parent (root) node's value.
- The right subtree values are greater than the value of their parent (root) node's value.
Note: A subtree must include all of its descendants.
Example 1:
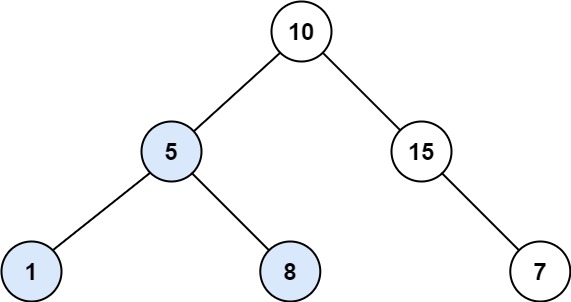
Input: root = [10,5,15,1,8,null,7] Output: 3 Explanation: The Largest BST Subtree in this case is the highlighted one. The return value is the subtree's size, which is 3.
Example 2:
Input: root = [4,2,7,2,3,5,null,2,null,null,null,null,null,1] Output: 2
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 104]. -104 <= Node.val <= 104
解法:这个题就是上一题的套娃题
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
class Result{
int max,min;
boolean isValid;
int count;
Result(boolean isValid,int min,int max,int count){
this.isValid = isValid;
this.min = min;
this.max = max;
this.count = count;
}
}
private int maxCount = 0;
public int largestBSTSubtree(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return maxCount;
}
private Result dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return new Result(true,Integer.MAX_VALUE,Integer.MIN_VALUE,0);
Result left = dfs(root.left);
Result right = dfs(root.right);
if(!left.isValid || !right.isValid || root.val<=left.max || root.val>=right.min){
return new Result(false,0,0,0);
}
int currCount = left.count+right.count+1;
maxCount = Math.max(currCount,maxCount);
Result curr = new Result(true,Math.min(root.val,left.min),Math.max(root.val,right.max),currCount);
return curr;
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号