卡码java基础课 | 6.倒序输出数组与隔位输出
学习内容:
数组的概念和特点
数组的声明和定义、索引、数组元素的访问、以及数组的循环遍历
重点归纳:
数组的特点:
固定大小:数组一旦声明,其大小通常是固定的,不能在运行时动态更改。就好比开设了一个30人的班级,班级大小已经固定,不能再改变班级的规模。
相同数据类型: 数组中的所有元素必须具有相同的数据类型,假设这个班都是男生或者都是女生,只能有一种性别存在。
连续存储: 数组的元素在内存中是连续存储的,班级里的同学按照顺序就坐,中间没有留空位。
下标访问: 数组中的元素通过下标(索引)进行访问,每个人都有一个学号,学号就是自己的座位,这个学号被称为索引,但是数组里的索引是从0开始的,也就是说,第一个元素的索引是0,第二个元素的索引是1,依次类推。
java的编程习惯:如声明数组int[] nums;但该操作没有为数组分配存储空间,还需要进行初始化,一是静态初始化,如int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3},二是动态初始化,如int[] numbers = new int[3];
数组都有属性length,用法如int[] nums = {1, 2, 3};int length = nums.length。
进阶:ArrayList类
优势:在不确定数组大小时使用,可以动态添加和删除元素,只能存储对象而不是原始数据类型
创建:ArrayList
增强for循环:
如for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
例题:
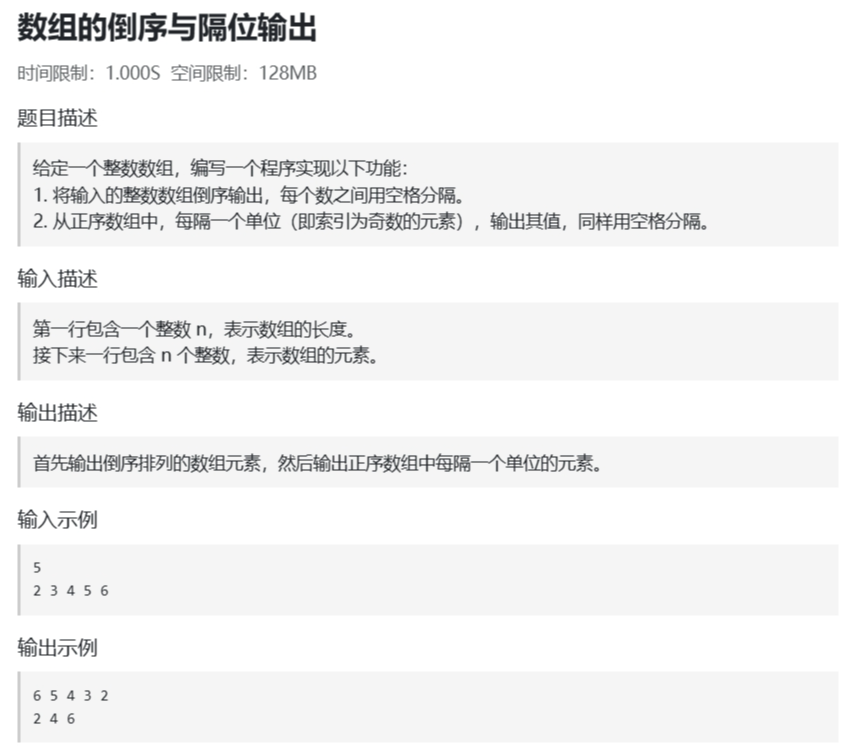
解:
两种数组的处理方法
// import java.util.Scanner;
// public class Main{
// public static void main (String[] args) {
// Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// int n = sc.nextInt();
// int[] array = new int[n];
// for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
// array[i] = sc.nextInt();
// }
// for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--){
// System.out.printf("%d ", array[i]);
// }
// System.out.println();
// for(int i = 0; i < (n + 1) / 2; i++){
// System.out.printf("%d ", array[i * 2]);
// }
// sc.close();
// }
// }
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
public static void main (String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
ArrayList<Integer> array = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
array.add(sc.nextInt());
}
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--){ // n = array.length
System.out.printf("%d ", array.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
for(int i = 0; i < (n + 1) / 2; i++){
System.out.printf("%d ", array.get(i * 2));
}
sc.close();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号