pgsql替换mysql语法差异总结
普通字段数据类型映射
名称变量标记符号不同(表名,字段名,别名,函数名等等)
mysql是``
CREATE TABLE `test` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
)
pgsql是双引号"",不写默认是被认为是小写
-- 字段name是关键字必须要用""标记是字段
CREATE TABLE test1 (
id int8 NOT NULL,
"name" varchar NULL,
age int4 NULL,
CONSTRAINT newtable_pk PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
表名字段名大小写规则不同
mysql表名,字段严格区分大小写,和名称标记符号无关
# mysql的表名和字段名严格区分大写,名称变量标志符号``和大小写无关,只有在和系统定义的内置参数重名的时候才必须使用
CREATE TABLE `Test2` (
Id bigint NOT NULL,
`Name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
Age int DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
#表名也是 Test3,大写开头
CREATE TABLE Test3 (
Id bigint NOT NULL,
`Name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
Age int DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ;
show tables;
#结果 都是 Id,NameAge
desc Test2;
desc Test3;
pgsql表名和字段名区分大小写,但是默认都是使用小写,如果要区分大小写需要用双引号标注
-- 表名是小写的 test2,字段除了Name字段是首字母大写,别的都是小写
CREATE TABLE Test2 (
Id int8 NOT NULL,
"Name" varchar NULL,
Age int4 NULL,
constraint test2_pk primary key (id)
);
-- select * 就能看到字段名的大小写
select * from test2;
-- 表名是Test3
CREATE TABLE "Test3" (
Id int8 NOT NULL,
"Name" varchar NULL,
Age int4 NULL,
constraint test3_pk primary key (id)
);
select * from "Test3";
-- 查看有哪些表,可以看到表名
select * from pg_tables;
字符串的表示方式
mysql 可以使用 单引号和双引号
# 结果是 1 1 a a
select "1",'1',"a",'a';
pgsql只能使用单引号,双引号在pgsql里面特指名称变量(字段名表名别名等)。
-- 报错
select "1","a"
-- 结果 1 a
select '1','a'
数据类型
mysql的int和bigint可以指定长度,pgsql不能指定
需要注意mysql能指定长度,但是只有低版本才生效,mysql 8.0以后能指定,但是无效,只会当做int和bigint处理,指定的长度无效
mysql的varchar必须要指定长度,pgsql不能指定,就直接是变长
mysql
#mysql 高版本int(xxx) 都只会当做int处理,大的数值类型需要使用 bigint
#指定长度的建表sql
create table t1(id bigint(20) ,name varchar(255), age int(11));
# 8.0导出的sql是这样
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` bigint DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
# 5.7导出的sql是这样
CREATE TABLE `t1` (
`id` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- mysql高版本也可以不指定int bigint长度
# 如果是mysql至少要指定varchar的长度
create table t2(id bigint ,name varchar(256), age int);
pgsql
-- pgsql不能指定int bigint,varchar的长度
create table t1(id bigint ,name varchar, age int);
-- 实际生成的数据类型,bigint 对应int8 ,int对应int4
CREATE TABLE public.t1 (
id int8 NULL,
"name" varchar NULL,
age int4 NULL
);
常用数据类型对照表
| mysql | pgsql |
|---|---|
| bigint或者bigint(xx) | int8 |
| int或者int(xx) | int4 |
| varchar(xx) | varchar |
| char(xxx) | char(xxx) |
| json | json或者jsonb |
数据类型隐式装换
mysql数字类型和字符类型之间默认有类型装换,只是会让索引失效
pgsql查询的时候,如果字段类型是字符型,参数是数字类型会出现类型转换异常,如果字段类型是数字型,参数是字符型则不会。
# 在插入的时候字符串和数字类型可以自动转换
insert into test1(id,"name","age") values(1,'name1',11);
insert into test1(id,"name","age") values(2,'name1','12');
insert into test1(id,"name","age") values(3,'3',11);
insert into test1(id,"name","age") values(4,4,'12');
# 数字类型的字段上可以相互装换
select * from test1 where age = 11;
select * from test1 where age = '11';
# 在字符类型的字段上也能自动转换
select * from test1 where name = 1;
select * from test1 where name = '1';
-- 在修改的时候也能做到自动类型转换
update test1 set age = 11 where id = 1;
update test1 set age = '11' where id = 1;
update test1 set name = 11 where id = 1;
update test1 set name = '11' where id = 1;
pgsql数字类型和字符类型之间需要手动指定转换,否者类型异常会报错
-- 在插入的时候字符串和数字类型可以自动转换
insert into test1(id,`name`,`age`) values(1,'name1',11);
insert into test1(id,`name`,`age`) values(2,'name1','12');
insert into test1(id,`name`,`age`) values(3,'3',11);
insert into test1(id,`name`,`age`) values(4,4,'12');
-- 数字类型的字段上可以相互装换
select * from test1 where age = 11;
select * from test1 where age = '11';
-- 在字符类型的字段上的查询只能使用字符类型
-- 这一句报错(在字符类型上查询数字类型不会自动类型转换)
select * from test1 where name = 1;
-- 这一句正常执行
select * from test1 where name = '1';
-- 在修改的时候也能做到自动类型转换
update test1 set age = 11 where id = 1;
update test1 set age = '11' where id = 1;
update test1 set name = 11 where id = 1;
update test1 set name = '11' where id = 1;
关于数值类型和字符串类型比较的问题
比较的时候需要转化成一种类型然后比较,不同类似是不能比较的,字符比较首字母优先,数字高位优先同位相比。
字段类型是数值类型的时候(存的一定是纯数字,所以比较的一定是纯数字):
处理策略都是把参数转成数值类型,如果不能转mysql会得到0,pgsql会抛出异常。
字段类型是字符串类型的时候(可能数据库存的是纯数字,也可能是字母):
pgsql默认不处理,抛出需要类型转换异常,mysql处理方案是根据参数的类型来确定用什么类型对比,如果尝试是字符类型会按照字符类型对比,如果参数是数字类型,会按照数字类型对比,这时候需要把字段里面的数据向数字类型转换,如果装换失败结果是0。
备注:需要验证上诉过程需要再只需在字符类型的字段中查询存数字和部分字符串,然后查询的时候使用字符串的纯数字和数字类型去查询就能看到效果
比如有如下表格
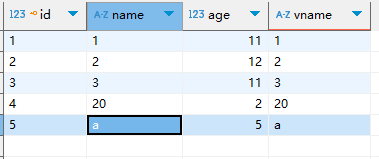
mysql
# 结果有1,2,3,20,a
select * from test1;
# 结果是3,20
select * from test1 where name > '2';
#结果是3,20
select * from test1 where name > 2;
pgsql
-- pgsql 字符串类型只能用字符串参数
select * from test1 where name > '2';
-- 如果使用数值类型参数需要强制类型转换,这种转换是稳定,因为数值类型参数一定可以转换成字符型
select * from test1 where name > 2::text;
-- 这个转换是不一定成功的,因为数据库的字段不一定可以转换成数值类型,比如有个a机会报错(这是一种显示的装换)
select * from test1 where name::bigint > 2;
pgsql中我们也可以隐式的装换
-- 定义两个隐式装换,我们这里需要其实只是第二条的varchar 到 numeric的装换
CREATE CAST (numeric AS varchar) WITH INOUT AS IMPLICIT;
CREATE CAST (varchar AS numeric) WITH INOUT AS IMPLICIT;
-- 删除隐式转换
-- DROP CAST (numeric as varchar);
-- DROP CAST (varchar as numeric);
-- 查询已经定义的隐式装换
select
c1.typname as "castsource",
c2.typname as "casttarget",
t.castcontext,
t.castmethod
from pg_cast as t
LEFT JOIN pg_type c1 on c1.oid=t.castsource
LEFT JOIN pg_type c2 on c2.oid=t.casttarget
#定义了varchar 到 numeric的隐式装换以后,就可以直接执行下面语句,但是如果字符安 name 中有不能转换的类型会报类型转换异常。
select * from test1 where name > 2;
#等价于显示装换的写法
#select * from test1 where name::bigint > 2;
mysql字符串转数字无法转换结果是0的验证
-- pgsql 会报错
select cast( 'a' as int4 )
# mysql 会得到0
select cast( 'a' as unsigned )
分组查询
pgsql和mysql高版本group by的查询都不能带group by 后面没指定的字段,排序字段也不能
mysql
# 除了第一条都不允许
# 分组字段只有 des,查询和 order by 不能带有别的字段,sql_mode=only_full_group_by异常
select des from goods group by des;
select des,id from goods group by des;
select des from goods group by des order by id;
#mysql低版本是允许带有分组以外字段的,高版本也可以通过修改sql_mode配置运行
# 默认值是 ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION
select @@global.sql_mode;
#show variables 也能查看
show variables like '%sql_mode%';
# 修改成去掉ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY的值就行了
SET GLOBAL sql_mode='STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_ZERO_IN_DATE,NO_ZERO_DATE,ERROR_FOR_DIVISION_BY_ZERO,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION';
pgsql
-- 除了第一条都不允许
-- 分组字段只有 des,查询和 order by 不能带有别的字段
select des from goods group by des;
select des,id from goods group by des;
select des from goods group by des order by id;
字符串拼接
关于||符号 pgsql可以使用 ||做字符串拼接 ,mysql的||是或。
关于+,都只能做数字加和,mysql默认有隐式转换(数字和字符串),pgsql默认不对字段是字符类型,参数数字类型的查询做类转换。
关于concat函数,他们都能使用contact函数做字符串连接。
mysql
#mysql
#mysql的||是或,不是字符串连接符
#得到的结果是0
select 'a' || 'b';
#得到的结果是1
select '3' || '2';
#得到的结果是1
select 'a' || '2';
#得到的0
select false || false;
# +对数字类型相加,默认会隐式类型转换,不能转换成数字的当做0处理
#得到的结果是0
select 'a' + 'b';
#得到的结果是5
select '3' + '2';
#得到的结果是2
select 'a' + '2';
# 都能使用concat连接,并且如果不是字符类型都需要强制类型转换
select concat('a' ,'1' );
select concat('a' , cast( 1111 as char) );
-- 结果是 1,2,3
select concat_ws(',','1','2','3');
pgsql
-- pgsql
-- ||可以连接字符串
-- 得到的结果是ab
select 'a' || 'b';
-- 得到的结果是32
select '3' || '2';
-- 得到的结果是a2
select 'a' || '2';
-- +只能做数字的相加
-- 报错,
select '3' + '2';
--得到的结果是1
select 1 + 2;
-- 都能使用concat连接,并且如果不是字符类型都需要强制类型转换
select concat('a' ,'1' );
select concat('a' , cast( 1111 as char(4)) );
-- 结果是 1,2,3
select concat_ws(',','1','2','3');
分页处理的差异
mysql的分页语法是:limit startCount,pageSize
pgsql的分页语法是: limit pageSize offset startCount
mysql
#mysql的分页
select * from goods limit 1 ,5
pgsql
#pgsql分页
select * from test limit 5 offset 1
如果只查询前几条他们都是 limit pageSize ,这样看来感觉 pgsql的更加自然
自增主键
首先,尽量不要使用数据库主键自增,这东西对分布式环境的分库分表移库非常不友好
mysql的自增是 auto_increment关键字
pgSql的自增需要创建sequeues
mysql
# 创建自增键,只要在后面跟上auto_increment就行
CREATE TABLE `t1115` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`code` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `t1115_unique` (`code`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
# 查询指定表当前自增主键的值
select Auto_increment,Table_Schema,table_name FROM information_schema.TABLES where TABLE_SCHEMA ='hl' and table_name = 't1115';
pgsql
-- 使用特殊类型bigserial,等价于bigint + 名字为t333_id_seq的序列
CREATE TABLE public.t333 (
id bigserial NOT NULL,
"name" varchar NULL,
CONSTRAINT t333_pk PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
-- 自定义序列
-- 查看有哪些序列
-- --r =普通表, i =索引,S =序列,v =视图,m =物化视图, c =复合类型,t = TOAST表,f =外部表
select * from pg_class where relkind='S';
-- 查询指定序列的值,查一次会增加一次
select nextval('t333_id_seq');
-- 查询值,但是查询不会增加,可以通过它得到生成的自增序列
select currval('t333_id_seq');
-- 当前会话的最近序列值,不指定序列
select lastval();
-- 把指定序列的当前值设置为100,下一个值是101
select setval('t333_id_seq',100);
-- 把指定序列的下一个值设置为1000,当前值不变
select setval('t333_id_seq',1000,false);
-- 创建序列
create sequence seq1;
-- 在指定字段上使用序列
ALTER TABLE public.t333 ADD age bigint DEFAULT nextval('seq1') NULL;
索引映射
主键
# mysql 的索引都是挂在表上的,名字不要求唯一,只要求表内唯一
CREATE TABLE `goods` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`stock` int DEFAULT NULL,
`des` varchar(255) CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`des2` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`data` text CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci,
`create_date` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
)
-- pgsql pgsql需要给每一个键去全局唯一的名字
CREATE TABLE public.t333 (
id bigserial NOT NULL,
"name" varchar NULL,
age int8 DEFAULT nextval('seq1'::regclass) NULL,
CONSTRAINT t333_pk PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
唯一键
可以建表语句里面写,也可以独立创建
# mysql mysql
CREATE TABLE `Test` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `Test_UK1` (`name`)
)
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX Test_UK2 USING BTREE ON hl.Test (name);
-- pgsql
CREATE TABLE public.t333 (
id bigserial NOT NULL,
"name" varchar NULL,
age int8 DEFAULT nextval('seq1'::regclass) NULL,
CONSTRAINT t333_pk PRIMARY KEY (id),
CONSTRAINT t335_uk1 UNIQUE (name)
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX t335_uk2 ON public.t333 USING btree (name);
普通索引
写法略有不同
mysql索引类型写在表名字段名前面
pgsql索引类型写在 表名和字段中间
# mysql
CREATE INDEX Test_name_IDX USING BTREE ON hl.Test (name);
-- pgsql
CREATE INDEX t333_name_idx2 ON public.t333 USING btree (name);
json和虚拟列映射
需要注意,mysql的虚拟列可以依赖虚拟列,pgsql不允许
虚拟列的定义方式
mysql
#GENERATED ALWAYS AS( 这里面是表达式 )
alter table test1 add `vname` varchar(100) generated always as (`name`) virtual null;
#定义json虚拟列
create table t33(
id bigint,
json_data json,
name varchar(255) generated always as( json_data->'$.name' ),
age int generated always as( json_data->'$.age' )
)
pgsql
-- GENERATED ALWAYS AS( 这里面是表达式 )
alter table test1 add "vname" varchar generated always as ("name") stored null;
-- 定义一个json虚拟列
create table t34(
id bigint,
json_data json,
name varchar generated always as( json_data->'{.name}' ) stored,
age int generated always as( (json_data->>'{age}')::int ) stored
)
json提取表达式的差异
mysql
# mysql表达式就是jsonpath语法,但是mysql的箭头符号好像只能用在字段上,不能用在json对象上
#得到的结果不会去掉"",如果数据是{"name":"张三"},结果是:"张三"
json字段名->'$.name'
# 得到结果会去掉"",如果数据是{"name":"张三"},结果是:张三
json字段名->>'$.name'
#这种语法只能在json字段上用,在json对象上不能用
select json_data->>'$.name' from t33;
#得到json对象
select cast( '{"name":"张三"}' as json );
#不能再json对象上用
select cast( '{"name":"张三"}' as json )->>'$.name';
pgsql的语法感觉就它一家在用
-- pgsql json值提取语法
->'顶层key'
#>'{顶层key,二层key}'
-- pgsql ->后面只能跟json对象的顶层key,和mysql一样->会去"",->>会去掉""
select '{"name":"张三"}'::jsonb->'name';
select '{"name":"张三"}'::jsonb->>'name';
-- 但是如果是多层json需要使用{第一层的key,第二层的key}
select '{"user1":{"name":"张三"}}'::jsonb#>'{user1,name}';
select '{"user1":{"name":"张三"}}'::jsonb#>>'{user1,name}';
-- 即便只是取顶层的值,也可以使用#>语法
select '{"name":"张三"}'::jsonb#>>'{name}';
-- #>后面跟的是数组,表示多层的key
select '{"user1":{"name":"张三"}}'::jsonb#>array['user1','name'];
select '{"user1":{"name":"张三"}}'::jsonb#>>array['user1','name'];
-- pgsql数组表达式需要用{}括起来
array['user1','name'] 等价于 '{user1,name}'
json字段修改方式
mysql
# 结果是{"user1": {"name": "李四"}}
select json_set( '{"user1":{"name":"张三"}}', '$.user1.name','李四' );
pgsql
-- 结果是{"user1": {"name": "李四"}}
select jsonb_set( '{"user1":{"name":"张三"}}', '{user1,name}','"李四"' );
-- 结果是{"user1": "李四"}
select jsonb_set( '{"user1":{"name":"张三"}}', '{user1}','"李四"' );
-- 结果是{"user1": "李四"},上面的等价于下面的这种写法,中间的路径参数实际是array
select jsonb_set( '{"user1":{"name":"张三"}}', array['user1'],'"李四"' );
-- jsonb_se参数的说明,1,3参数是jsonb,2参数是array,如果第三个参数是字符串
jsonb_set( jsonb, array ,jsonb )
-- 注意第三个参数中的引号,如果没有json里面就没有引号
-- 结果是{"user1": "1"}
select jsonb_set( '{}', array['user1'],'"1"' );
-- 结果是{"user1": 1}
select jsonb_set( '{}', array['user1'],'1' );
-- 索引如果是字符串必须有引号
select jsonb_set( '{}', array['user1'],'"李四"' );
replace into,on duplicate key update 改成 on conflict do update
使用场景都是唯一键冲突的时候以覆盖的方式更新数据,达到类似upsert类似的效果,建议这种非标准的sql 少用,可以直接用程序编码里面判断。
mysql的 replace into 不能指定唯一键,所以是包含所有唯一键,也就是任意唯一键冲突都需要替换掉或者被删除掉,有多个唯一键的时候被删除或者替换的数据可能是多条。mysql默认替换全部字段。
pgsql的on conflict需要指定唯一键所在的列,并且指定列必须是一个唯一键(如果是两个唯一键就不行,多个列组成的唯一键也是可以的),所以它只会删除或者替换一条数据,并且pgsql替换哪些字段需要手动指定。
mysql
CREATE TABLE `t1115` (
`id` bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`code` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `t1115_unique` (`code`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
select * from t1115;
#插入5条数据
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(1,11,"name1","age1");
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(2,12,"name2","age2");
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(3,13,"name3","age3");
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(4,14,"name4","age4");
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(5,15,"name5","age5");
# 这句sql会替换掉id=1和code=12的两条记录
replace into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(1,12,"name6","age6");
mysql(on DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE )
# on DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE 有类似的upsert 效果,但是它是只要任意唯一键冲突就直接替换,不是类似删除老记录以后再插入,在多个唯一键,并且和不同记录冲突的时候,依旧不能替换成功,效类似pgsql的 on conflict (id) do update
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(111,13,"name16","age17")
on DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE id = values(id),code= values(code),name = values(name),age= values(age);
pgsql
select * from t1115;
-- 插入5条数据
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(1,11,'name1','age1');
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(2,12,'name2','age2');
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(3,13,'name3','age3');
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(4,14,'name4','age4');
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(5,15,'name5','age5');
-- replace into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(1,12,'name6','age6');
-- 替换掉id是1的记录,并且只修改了 name和age
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(1,11,'name6','age16') on conflict (id) do update set name = excluded.name,age= excluded.age;
-- 替换掉code是11的记录,并且只修改了 name和age
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(1,11,'name7','age17') on conflict (code) do update set name = excluded.name,age= excluded.age;
-- 注意这里本应该是替换掉id=1,但是code的唯一键和之前的数据冲突了,所以会报错,会包所有重复的都删除然后插入。
-- 明显如果我们的需求和mysql一样,这时候只能程序里面处理,或者成了联合唯一键
insert into t1115(id,code,name,age) values(1,12,'name7','age17') on conflict (id) do update set name = excluded.name,age= excluded.age,code=excluded.code;
函数映射
-
获取当前日期
mysql-- 结果2025-01-20 select current_date;pgsql
# 2025-01-20 select curdate(); -
查询字符串位
mysqlselect locate('b','ayyvkhlbm')pgsql
select position('b' in 'ayyvkhlbm'); -
获取当前时间
mysql
select unix_timestamp(now())pgsql
select EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM current_timestamp)::bigint -
json_set换成jsonb_set
-- 需要注意pgsqljsonb_set一次只能改一个值,如果改多个值需要使用||这种json连接函数 update xxx set json_data = json_data || jsonb_set('{}',xx,xx)|| jsonb_set('{}',xx,xx); -- 如果json_data不止一层数据,要考虑覆盖问题,可能用嵌套语法比较好 update xxx set json_data = jsonb_set(jsonb_set(json_data,xx,xx),xx,xx); -- 如果是mysql换pgsql,并且代码中使用了大量jsonpath语法修改虚拟字段,那么建议直接在程序里面使用jsonPath得到结果燃弧更新json字段,而不是使用jsonb_set函数 -- 比如直接在代码里面使用 fastJson的jsonPath支持得到修改的的最终数据,然后更新 在这之前查询出json_data和id的对应关系,然后全量更新 update xxx set json_data = json_data(全量)比如代码里面这么干,indexDataIncre里面传入是修改的json字段,key是jsonPath表达式,value是值,query是查询参数的封装
public List<Map<String, Object>> updateIndexData(Map<String, Object> indexDataIncre, RuleQueryDto query) { List<Map<String, Object>> updateResult = new ArrayList(); Map<String, Object> hashMap = new HashMap(); updateResult.add(hashMap); List<Map<String, Object>> sourceIndexDataMap = adminRuleMapper.search(query,RuleQueryDto.getIndexDataSearchColumnMap()); if (sourceIndexDataMap.isEmpty()) { hashMap.put("updated", 0); return updateResult; } for (Map<String, Object> sourceIndexData : sourceIndexDataMap) { String id = sourceIndexData.get("id").toString(); String source = sourceIndexData.get("indexData").toString(); JSONObject newIndexData = JSONObject.parseObject(source); for (Map.Entry<String, Object> next : indexDataIncre.entrySet()) { String key = next.getKey(); Object value = next.getValue(); JSONPath.compile(key).set(newIndexData, value); } sourceIndexData.put("json_data", JSONObject.toJSONString(newIndexData)); } int updateCount = adminRuleMapper.updateIndexData(sourceIndexDataMap); hashMap.put("updated", updateCount); return updateResult; } -
空值函数
mysql# 结果是1 select ifnull( null,1 )pgsql
-- 结果是2 select coalesce(null ,2)
能耍的时候就一定要耍,不能耍的时候一定要学。
--天道酬勤,贵在坚持posted on 2025-01-24 09:29 zhangyukun 阅读(368) 评论(0) 收藏 举报




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号