Pytorch-GAN
任务:使用8个高斯混合模型生成一系列数据,通过GAN学习它的分布,比较学习的分布和真实的分布是否一样。
GAN文字版算法:

GAN公式版算法:

在命令行执行如下语句(详细Visdom的使用见https://www.cnblogs.com/cxq1126/p/13285150.html)
python -m visidom.server
提前导包:
1 import torch 2 from torch import nn, optim, autograd 3 import numpy as np 4 import visdom 5 from torch.nn import functional as F 6 from matplotlib import pyplot as plt 7 import random 8 9 h_dim = 400 10 batchsz = 512 11 viz = visdom.Visdom()
1.实现Generator
输入点坐标,输出点坐标。
1 class Generator(nn.Module): 2 3 def __init__(self): 4 super(Generator, self).__init__() 5 6 self.net = nn.Sequential( 7 nn.Linear(2, h_dim), 8 nn.ReLU(True), 9 nn.Linear(h_dim, h_dim), 10 nn.ReLU(True), 11 nn.Linear(h_dim, h_dim), 12 nn.ReLU(True), 13 nn.Linear(h_dim, 2), 14 ) 15 16 def forward(self, z): 17 output = self.net(z) 18 return output
2.实现Discriminator
输入点坐标,输出数值(用来评判输入的坐标是否在真实数据附近)。
1 class Discriminator(nn.Module): 2 3 def __init__(self): 4 super(Discriminator, self).__init__() 5 6 self.net = nn.Sequential( 7 nn.Linear(2, h_dim), 8 nn.ReLU(True), 9 nn.Linear(h_dim, h_dim), 10 nn.ReLU(True), 11 nn.Linear(h_dim, h_dim), 12 nn.ReLU(True), 13 nn.Linear(h_dim, 1), 14 nn.Sigmoid() 15 ) 16 17 def forward(self, x): 18 output = self.net(x) 19 return output.view(-1)
3.权重初始化
1 def weights_init(m): 2 if isinstance(m, nn.Linear): 3 # m.weight.data.normal_(0.0, 0.02) 4 nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight) 5 m.bias.data.fill_(0)
4.生成数据集 8-gaussian mixture models
对于高斯混合模型的理解:

1 def data_generator(): 2 3 scale = 2. 4 centers = [ 5 (1, 0), 6 (-1, 0), 7 (0, 1), 8 (0, -1), 9 (1. / np.sqrt(2), 1. / np.sqrt(2)), 10 (1. / np.sqrt(2), -1. / np.sqrt(2)), 11 (-1. / np.sqrt(2), 1. / np.sqrt(2)), 12 (-1. / np.sqrt(2), -1. / np.sqrt(2)) 13 ] 14 centers = [(scale * x, scale * y) for x, y in centers] 15 while True: 16 dataset = [] 17 for i in range(batchsz): 18 point = np.random.randn(2) * .02 19 center = random.choice(centers) 20 21 #N(0,1)sample出来一个点 + center_x1/x2 22 point[0] += center[0] 23 point[1] += center[1] 24 dataset.append(point) 25 dataset = np.array(dataset, dtype='float32') 26 dataset /= 1.414 #stdev 27 yield dataset
5.可视化
1 def generate_image(D, G, xr, epoch): #xr表示真实的sample 2 """ 3 Generates and saves a plot of the true distribution, the generator, and the 4 critic. 5 """ 6 N_POINTS = 128 7 RANGE = 3 8 plt.clf() 9 10 points = np.zeros((N_POINTS, N_POINTS, 2), dtype='float32') 11 points[:, :, 0] = np.linspace(-RANGE, RANGE, N_POINTS)[:, None] 12 points[:, :, 1] = np.linspace(-RANGE, RANGE, N_POINTS)[None, :] 13 points = points.reshape((-1, 2)) # (16384, 2) 14 15 16 # draw contour 17 with torch.no_grad(): 18 points = torch.Tensor(points) # [16384, 2] 19 disc_map = D(points).cpu().numpy() # [16384] 20 x = y = np.linspace(-RANGE, RANGE, N_POINTS) 21 cs = plt.contour(x, y, disc_map.reshape((len(x), len(y))).transpose()) 22 plt.clabel(cs, inline=1, fontsize=10) 23 # plt.colorbar() 24 25 26 # draw samples 27 with torch.no_grad(): 28 z = torch.randn(batchsz, 2) # [b, 2] 29 samples = G(z).cpu().numpy() # [b, 2] 30 plt.scatter(xr[:, 0], xr[:, 1], c='orange', marker='.') 31 plt.scatter(samples[:, 0], samples[:, 1], c='green', marker='+') 32 33 viz.matplot(plt, win='contour', opts=dict(title='p(x):%d'%epoch))
6.训练
和上面图片中的梯度上升法不同,下面训练使用的梯度下降法,所以对于原本需要最大化的的数据添加负号,就能实现梯度下降。
optim.Adam()中的batas参数用于计算梯度的平均和平方的系数(默认: (0.9, 0.999))
1 def main(): 2 3 torch.manual_seed(23) 4 np.random.seed(23) 5 6 G = Generator() 7 D = Discriminator() 8 G.apply(weights_init) 9 D.apply(weights_init) 10 11 optim_G = optim.Adam(G.parameters(), lr=1e-3, betas=(0.5, 0.9)) 12 optim_D = optim.Adam(D.parameters(), lr=1e-3, betas=(0.5, 0.9)) 13 14 15 data_iter = data_generator() 16 print('batch:', next(data_iter).shape) #[b, 2] 17 18 viz.line([[0,0]], [0], win='loss', opts=dict(title='loss', legend=['D', 'G'])) 19 20 for epoch in range(1000): 21 22 # 1. train discriminator for k steps 23 for _ in range(5): 24 25 #1.1首先train on real data 26 x = next(data_iter) 27 xr = torch.from_numpy(x) #真实数据 28 predr = (D(xr)) # [b, 2] -> [b, 1] 29 # max log(lossr),即min (-lossr) 30 lossr = - (predr.mean()) 31 32 #1.2 train on fake data 33 z = torch.randn(batchsz, 2) # [b, 2]随机产生的伪数据 34 xf = G(z).detach() # [b, 2] 此处固定G,更新D,所以不更新G的参数 35 predf = (D(xf)) # [b] 36 # min predf 37 lossf = (predf.mean()) 38 39 loss_D = lossr + lossf 40 41 optim_D.zero_grad() 42 loss_D.backward() 43 optim_D.step() 44 45 46 # 2. train Generator 47 z = torch.randn(batchsz, 2) #[b, 2]随机产生的伪数据 48 xf = G(z) 49 predf = (D(xf)) 50 # max predf,即min(-predf) 51 loss_G = - (predf.mean()) 52 53 optim_G.zero_grad() #此处固定D,更新G,所以不更新D的参数 54 loss_G.backward() 55 optim_G.step() 56 57 58 if epoch % 100 == 0: 59 viz.line([[loss_D.item(), loss_G.item()]], [epoch], win='loss', update='append') 60 generate_image(D, G, xr, epoch) 61 print(loss_D.item(), loss_G.item()) 62 63 64 if __name__ == '__main__': 65 main()
下图显示Generator和Discriminator的训练结果,两者的loss都接近于0,sample出来的数据经过Generator后覆盖住了真实数据。
1 -0.6137181520462036 -0.0665668323636055 2 7.620922672430937e-23 -6.780519236493468e-22 3 2.8811570836759978e-37 -3.576674200342663e-41 4 2.7326036398933606e-12 -5.0371435361452164e-33 5 1.5811193901845998e-21 -1.796846778152569e-15 6 2.1587619070328268e-20 -0.0 7 2.0948376092776535e-32 -2.429269052203856e-16 8 6.822592214491066e-14 -0.0 9 9.122023851176224e-35 -2.9085079939065756e-34 10 0.0 -4.5381907731517276e-14

并不是每次运行都是这种结果,Generator常常由于GAN训练的不稳定(真实数据和生成数据没有重叠),loss保持在非0的某个值,长期得不到更新。
解决方案:W-GAN(通过用Wasserstein距离代替JS散度来优化训练的生成对抗网络)
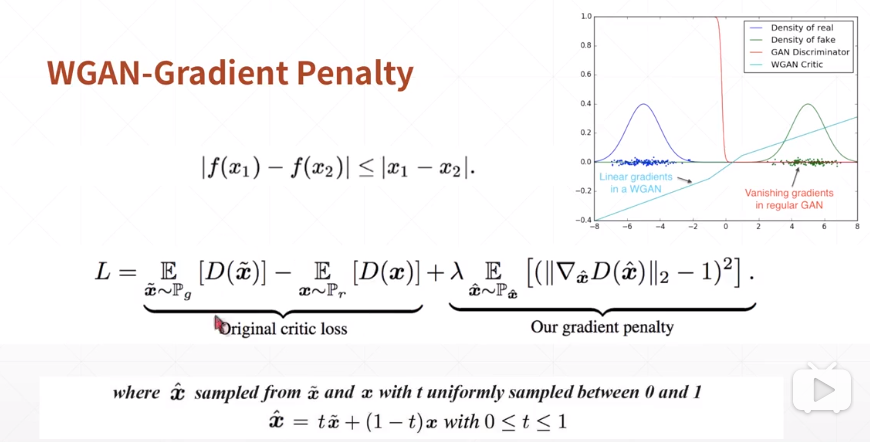
在代码中增加gradient penalty
1 def gradient_penalty(D, xr, xf): #xr和xf的shape=[b, 2] 2 3 t = torch.rand(batchsz, 1) #sample一个均值分布[b, 1] 4 t = t.expand_as(xr) #[b, 1] -> [b, 2] 5 6 mid = t *xr +(1-t) * xf #在真实数据和fake数据之间做线性差值,即图中的xhat 7 mid.requires_grad_() #设置导数信息 8 9 pred = D(mid) 10 grads = autograd.grad(outputs=pred, inputs=mid, 11 grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(pred), 12 create_graph=True, retain_graph=True, only_inputs=True)[0] #create_graph用来二次求导 13 14 gp = torch.pow(grads.norm(2, dim=1) - 1, 2).mean() 15 return gp
在主函数中计算Discriminator的loss时加上gp项。
1 #1.3 gradient penalty 2 gp = gradient_penalty(D, xr, xf.detach()) #因为不需要对D求导,所以detach 3 4 loss_D = lossr + lossf + 0.2 * gp
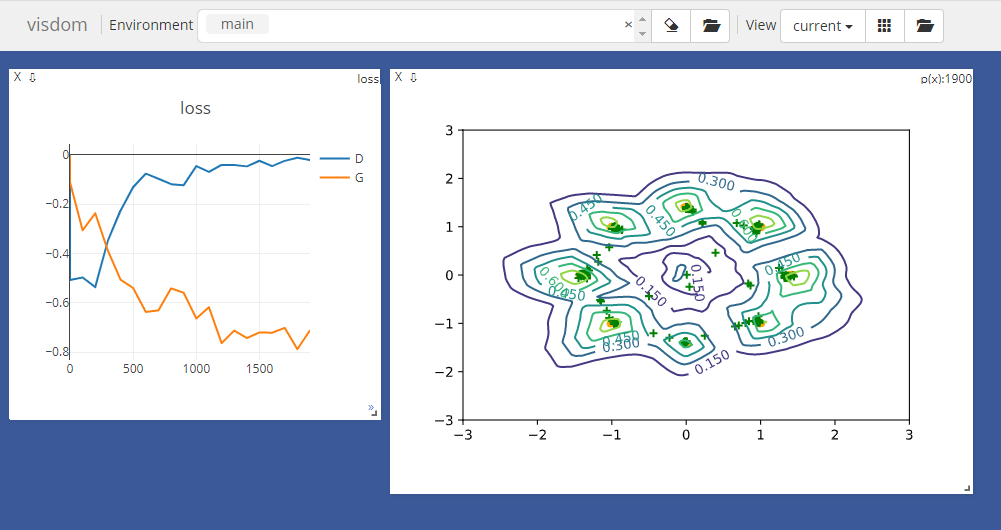
迭代2000次的结果如下:
1 -0.5074049830436707 -0.11114723235368729 2 -0.4972265362739563 -0.3060861825942993 3 -0.5360251665115356 -0.23698316514492035 4 -0.3480537533760071 -0.3882521390914917 5 -0.22527582943439484 -0.5057252645492554 6 -0.13060471415519714 -0.5396959185600281 7 -0.07626903057098389 -0.6366142630577087 8 -0.09713903069496155 -0.6304153203964233 9 -0.1190759465098381 -0.5412021279335022 10 -0.1230357214808464 -0.5588557124137878 11 -0.04560390114784241 -0.6632308959960938 12 -0.06906679272651672 -0.6173125505447388 13 -0.04104984924197197 -0.7628952860832214 14 -0.0408158078789711 -0.7121548652648926 15 -0.04687119275331497 -0.7424123287200928 16 -0.024066904559731483 -0.7196884751319885 17 -0.04576507583260536 -0.7208324670791626 18 -0.02462894842028618 -0.7012563943862915 19 -0.01230126153677702 -0.7875514030456543 20 -0.02122686244547367 -0.7108622193336487




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号