import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
# 模拟数据
x = np.array(
[137.97, 104.50, 100, 126.32, 79.20, 99.00, 124.0, 114.0, 106.69, 140.05, 53.75, 46.91, 68.0, 63.02, 81.26, 86.21])
x = x - np.mean(x) # x全为正,需要减去平均数让均值为0
y = np.array([1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
# 设置超参
iter = 20000
learn_rate = 0.000001
loss_list = []
acc_list = []
# 初始化训练参数
w = tf.Variable(0.0001*np.random.randn())
b = tf.Variable(0.0001*np.random.randn())
print('初始w:{},b:{}'.format(w,b))
# 设计损失函数
for i in range(iter):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
y_p = 1 / (1 + tf.exp(-(w * x + b)))
loss = tf.reduce_mean(-(y * tf.math.log(y_p) + (1 - y) * tf.math.log(1 - y_p)))
dloss_dw, dloss_db = tape.gradient(loss, [w, b]) # 获得参数的偏导
accuary = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(tf.equal(tf.round(y_p), y), tf.float32))
loss_list.append(loss)
acc_list.append(accuary)
# 迭代更新参数
w.assign_sub(learn_rate * dloss_dw)
b.assign_sub(learn_rate * dloss_db)
if i % 100 == 0:
print('y:',y)
print('y_p:',y_p)
print('tf.equal(tf.round(y_p),y):\n',tf.equal(tf.round(y_p),y))
print('第{}次迭代,loss:{},w:{},b:{},accuary:{}'.format(i,loss,w,b,accuary))
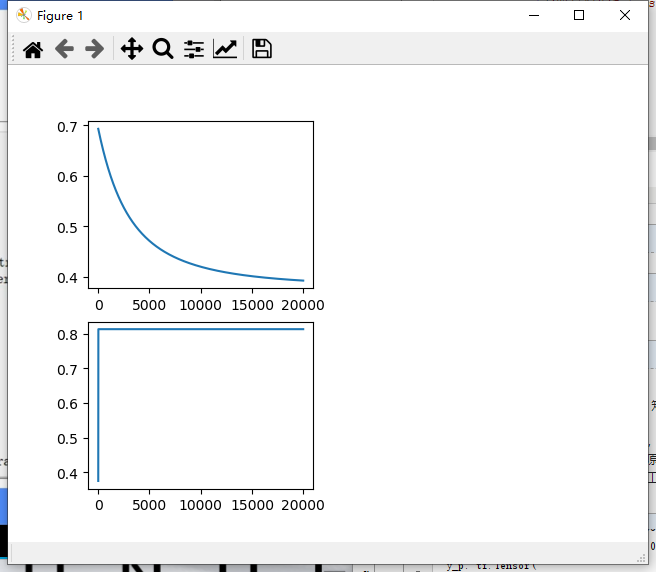
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(loss_list)
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot(acc_list)
plt.show()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号