Codeforsec 1234 记录
目录
- 综述
- A Equalize Prices Again
- B1 / B2 Social Network
- C Pipes
- D Distinct Characters Queries
- E Special Permutations
- F Yet Another Substring Reverse
综述
CF1234 是一场 Div.3,属于比较简单的比赛。
A Equalize Prices Again
题目描述
\(q\) 组数据。有 \(n\) 个商品,其中第 \(i\) 个商品的成本为 \(a_i\in\mathbb{N^*}\)。把所有的商品按同一个定价(整数)卖出去,问不亏本的定价最低是多少。
解题思路
不会的出门左转,去重修小学数学。
代码
while (q--) {
cin >> n;
sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i], sum += a[i];
cout << sum / n + ((sum % n) ? 1 : 0) << '\n';
}
B1 / B2 Social Network
题目描述
你将会收到 \(n\) 条短信,但你的手机上只能显示 \(k\) 名发信人信息。第 \(i\) 条短信的发送者是 \(\operatorname{id}_i\)。当你收到第 \(i\) 条短信时,手机将会按以下逻辑处理这条信息:
- 发信人正在被显示:不改变显示内容。
- 发信人没被显示,且当前显示的人数小于 \(k\):将发信人信息显示在最上方,其他人的信息下移。
- 发信人没被显示,且当前显示的人数等于 \(k\):删掉最下方的一条信息,然后按人数小于 \(k\) 的情况处理。
一开始手机上不显示信息。问:手机收到 \(n\) 条消息后会显示什么。
解题思路
直接模拟即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, k;
map<int, int> vis; // id <= 1e9
queue<int> q; stack<int> s;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int id;
cin >> id;
if (vis[id]) continue;
vis[id] = 1;
q.push(id);
if (q.size() > k) vis[q.front()] = 0, q.pop();
}
cout << q.size() << '\n';
while (q.size()) s.push(q.front()), q.pop();
while (s.size()) cout << s.top() << ' ', s.pop();
return 0;
}
C Pipes
题目描述
\(q\) 组数据。有一个 \(2\times n\) 的排水系统,坐标 \((i,j)\) 的水管类型是 \(a_{i,j}\)。下面是六种水管:
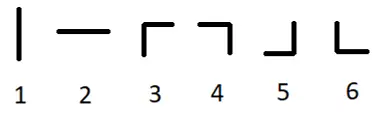
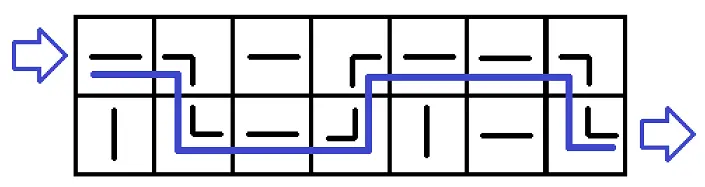
问:能否通过旋转一些水管,使得水能够从 \((1,1)\) 的左侧流入系统,并从 \((2,n)\) 的右侧流出。能就输出 \(\texttt{YES}\),不能就输出 \(\texttt{NO}\)。下面是一个 \(\texttt{YES}\) 的样例:
解题思路
注意到 \(2\) 号水管一定要旋转成 \(1\) 号,因为 \(2\) 号水管显然没有用。而且,\(3,4,5,6\) 四种水管可以看成是同一种:将水从第 \(1\) 行导向第 \(2\) 行或者从第 \(2\) 行导向第 \(1\) 行。所以如果答案是 \(\texttt{YES}\) 则水流的路径是唯一确定的。那么直接模拟水流即可。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
int n;
int a[3][N], dp[N];
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int _; cin >> _;
while (_--) {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= 2; i++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
a[i][j] = s[j - 1] - '0';
if (a[i][j] <= 2) a[i][j] = 1;
else a[i][j] = 3;
}
}
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (a[dp[i - 1]][i] == 1) dp[i] = dp[i - 1];
else if (a[1][i] != a[2][i]) {
dp[n] = 0;
break;
} else dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] == 1) ? 2 : 1;
}
if (dp[n] == 2) cout << "YES\n";
else cout << "NO\n";
}
return 0;
}
D Distinct Characters Queries
题目描述
维护一个长度为 \(n\) 的字符串,支持以下操作:
- 修改某个位置的字符
- 区间查询不同的字符个数
有 \(q\) 次操作。保证序列中的字符都是小写英文字符。\(n,q\le 10^5\)。
解题思路
这道题您可以使用自己喜欢的数据结构进行维护。这里提供 \(2\) 套方案:
- 莫队
- \(26\) 棵线段树或树状数组
莫队
因为这道题相当于《数颜色 / 维护队列》的弱化版,因此可以使用莫队进行解决。时间复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}(n^\frac{5}{3})\)。
\(26\) 棵线段树或树状数组
也可以维护 \(26\) 棵线段树或树状数组,每棵线段树或树状数组维护一种字母在区间内的出现次数。这样可以通过计算区间内每种字母的数量来计算答案。时间复杂度为 \(\mathcal{O}(kn\log n)\),\(k=26\)。
代码
莫队
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int block;
const int N = 1500010;
struct query {
int id, t, l, r;
bool operator < (const query &b) const {
if (l / block != b.l / block) {
return l / block > b.l / block;
} else if (r / block != b.r / block) {
return r / block > b.r / block;
} else {
return t > b.t;
}
}
} q[N];
struct cz {
int p, x;
} r[N];
int n, m, now, qcnt, rcnt, cnt[N], a[N], ans[N];
void add(int x) {
if (!cnt[x]) {
now += 1;
}
cnt[x] += 1;
}
void del(int x) {
cnt[x] -= 1;
if (!cnt[x]) {
now -= 1;
}
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
string s;
cin >> s;
n = s.size();
s = "#" + s;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i] = s[i];
cin >> m;
block = pow(n, 0.667);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int op, x, y;
char c;
cin >> op >> x;
if (op == 2) {
cin >> y;
qcnt++;
q[qcnt] = {qcnt, rcnt, x, y};
} else {
cin >> c;
while (c < 'a' || c > 'z') cin >> c;
rcnt++;
r[rcnt] = {x, c};
}
}
sort(q + 1, q + qcnt + 1);
int L = 1, R = 0, lst = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= qcnt; i++) {
while (R < q[i].r) {
add(a[++R]);
}
while (L > q[i].l) {
add(a[--L]);
}
while (R > q[i].r) {
del(a[R--]);
}
while (L < q[i].l) {
del(a[L++]);
}
while (lst < q[i].t) {
lst += 1;
if (r[lst].p >= L && r[lst].p <= R) {
add(r[lst].x);
del(a[r[lst].p]);
}
swap(a[r[lst].p], r[lst].x);
}
while (lst > q[i].t) {
if (r[lst].p >= L && r[lst].p <= R) {
add(r[lst].x);
del(a[r[lst].p]);
}
swap(a[r[lst].p], r[lst].x);
lst -= 1;
}
ans[q[i].id] = now;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= qcnt; i++) {
cout << ans[i] << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
\(26\) 棵树状数组
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 100010;
int n, m, a[N], bit[30][N];
int lowbit(int x) {return x & -x;}
void add(int x, int y, int z) {
while (y <= n) {
bit[x][y] += z;
y += lowbit(y);
}
}
int sum(int x, int y) {
int res = 0;
while (y) {
res += bit[x][y];
y -= lowbit(y);
}
return res;
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
string s;
cin >> s;
n = s.size();
s = "#" + s;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = s[i] - 'a' + 1;
add(a[i], i, 1);
}
cin >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int op, x, y;
char c;
cin >> op >> x;
if (op == 2) {
cin >> y;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) if (sum(i, y) - sum(i, x - 1) > 0) ans++;
cout << ans << '\n';
} else {
cin >> c;
while (c < 'a' || c > 'z') cin >> c;
y = c - 'a' + 1;
add(a[x], x, -1);
add(y, x, 1);
a[x] = y;
}
}
return 0;
}
E Special Permutations
题目描述
我们定义 \(p_i(n)\) 为如下排列:\([i, 1, 2, \dots, i - 1, i + 1, \dots, n]\)。也就是说,第 \(i\) 个排列几乎是一个恒等排列(即每个元素都映射到自身),但元素 \(i\) 被放在了第一个位置。例如:
- \(p_1(4) = [1, 2, 3, 4]\);
- \(p_2(4) = [2, 1, 3, 4]\);
- \(p_3(4) = [3, 1, 2, 4]\);
- \(p_4(4) = [4, 1, 2, 3]\)。
给定一个数组 \(x_1, x_2, \dots, x_m\)(\(1 \le x_i \le n\))。
记 \(pos(p, val)\) 表示元素 \(val\) 在排列 \(p\) 中的位置。例如,\(pos(p_1(4), 3) = 3\),\(pos(p_2(4), 2) = 1\),\(pos(p_4(4), 4) = 1\)。
定义函数 \(f(p) = \sum\limits_{i=1}^{m - 1} |pos(p, x_i) - pos(p, x_{i + 1})|\),其中 \(|val|\) 表示 \(val\) 的绝对值。该函数表示在排列 \(p\) 中,数组 \(x\) 的相邻元素之间的位置距离之和。
你的任务是计算 \(f(p_1(n)), f(p_2(n)), \dots, f(p_n(n))\)。
解题思路
注意到 \(p_{i-1}(n)\) 和 \(p_i(n)\) 的区别在于交换了两个数字的位置。因此求 \(f(p_i(n))\) 时可以在 \(f(p_{i-1}(n))\) 的基础上直接修改这两个数与相邻位置数字的差的绝对值。这样做每个数只被调用 \(\mathcal{O}(1)\) 次。
代码
F Yet Another Substring Reverse
题目描述
给你一个字符串 \(S\),你可以翻转一次 \(S\) 的任意一个子串。问翻转后 \(S\) 的子串中各个字符都不相同的最长子串长度。
\(∣S∣\le10^6\),\(S_i\in\{\texttt{a},\texttt{b},\texttt{c},\dots,\texttt{r},\texttt{s},\texttt{t}\}\)。
解题思路
注意到反转相当于把两个字串拼接到一起(忽略字符顺序)。
于是考虑设 \(f_i\) 表示字符集为 \(i\)(状压)且其中的每个字符仅出现一次时,最长的字串长度。此时 \(f_i\) 的取值是 \(0\)(不存在这种字串)或 \(\operatorname{popcount}(i)\)。又设 \(g_i=\max\limits_{j\in i} f_j\),此时答案为 \(\max (f_i+g_{\complement_Ui})\),其中 \(U\) 表示全集。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
int n, dp[1048580];
string s;
int main() {
cin >> s;
n = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i, k = 0; j - i < 20 && j < n; j++) {
int x = s[j] - 'a';
if (k & (1 << x)) break;
k |= (1 << x);
dp[k] = max(dp[k], j - i + 1);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 1048576; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 20; j++) {
if (i & (1 << j)) {
dp[i] = max(dp[i], dp[i ^ (1 << j)]);
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1048576; i++) ans = max(ans, dp[i] + dp[1048575 ^ i]);
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}
本文来自博客园,作者:cwkapn,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/cwkapn/p/19065508




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号