【collection】使用jdk8的stream方法list转map踩坑
概述
最近工作中遇到一个特殊的情况,我们用list转map结构的时候,系统老是报错,然后花了好大的劲才发现,原来是我们用来转map的时候转换的value存在null值,但是我们知道hashmap的key和value是可以存放null对象的,那为啥会报错呢?
接下来我们一探究竟
遇到问题
先给现象,后台出现报错
java.lang.NullPointerException
at java.util.HashMap.merge(HashMap.java:1225)
at java.util.stream.Collectors.lambda$toMap$58(Collectors.java:1320)
at java.util.stream.ReduceOps$3ReducingSink.accept(ReduceOps.java:169)
at java.util.ArrayList$ArrayListSpliterator.forEachRemaining(ArrayList.java:1382)
at java.util.stream.AbstractPipeline.copyInto(AbstractPipeline.java:482)
at java.util.stream.AbstractPipeline.wrapAndCopyInto(AbstractPipeline.java:472)
at java.util.stream.ReduceOps$ReduceOp.evaluateSequential(ReduceOps.java:708)
at java.util.stream.AbstractPipeline.evaluate(AbstractPipeline.java:234)
at java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline.collect(ReferencePipeline.java:566)
at jdk.map.Code_list2map.test1(Code_list2map.java:31)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:59)
at org.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12)
at org.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:56)
at org.junit.internal.runners.statements.InvokeMethod.evaluate(InvokeMethod.java:17)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:306)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner$1.evaluate(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:100)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runLeaf(ParentRunner.java:366)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:103)
at org.junit.runners.BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.runChild(BlockJUnit4ClassRunner.java:63)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$4.run(ParentRunner.java:331)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$1.schedule(ParentRunner.java:79)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.runChildren(ParentRunner.java:329)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.access$100(ParentRunner.java:66)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$2.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:293)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner$3.evaluate(ParentRunner.java:306)
at org.junit.runners.ParentRunner.run(ParentRunner.java:413)
at org.junit.runner.JUnitCore.run(JUnitCore.java:137)
at com.intellij.junit4.JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.startRunnerWithArgs(JUnit4IdeaTestRunner.java:69)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.IdeaTestRunner$Repeater$1.execute(IdeaTestRunner.java:38)
at com.intellij.rt.execution.junit.TestsRepeater.repeat(TestsRepeater.java:11)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.IdeaTestRunner$Repeater.startRunnerWithArgs(IdeaTestRunner.java:35)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.JUnitStarter.prepareStreamsAndStart(JUnitStarter.java:232)
at com.intellij.rt.junit.JUnitStarter.main(JUnitStarter.java:55)
我们发现代码报错的位置代码是:
Map<String, String> collect1 = useList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(L2Map::getKey, L2Map::getValue));
一个很常规的操作,为啥会出现这个问题呢??
刚刚我们说了是因为在转map的时候value有null对象,那么key为null会有这个问题吗?
接下来对key有null,对value存在null分别进行讨论
正常常规操作
我们先构造一个正常的,没有任何null对象的数据
class L2Map {
String key;
String value;
public L2Map(String key, String value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(String key) {
this.key = key;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
@Test
public void test1() {
Random random = new Random();
List<L2Map> useList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
useList.add(new L2Map("key" + i, "value" + i));
}
Map<String, String> collect1 = useList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(L2Map::getKey, L2Map::getValue));
System.out.println(collect1.size());
}
我们发现没有任何问题,接下来我们基于这段代码进行改造
key为null
@Test
public void test1() {
Random random = new Random();
List<L2Map> useList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
useList.add(new L2Map("key" + i, "value" + i));
}
useList.add(new L2Map(null, "value-null"));
Map<String, String> collect1 = useList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(L2Map::getKey, L2Map::getValue));
System.out.println(collect1.size());
}
发现没有任何问题
value为null
@Test
public void test1() {
Random random = new Random();
List<L2Map> useList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
useList.add(new L2Map("key" + i, "value" + i));
}
useList.add(new L2Map("key-null", null));
Map<String, String> collect1 = useList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(L2Map::getKey, L2Map::getValue));
System.out.println(collect1.size());
}
问题复现

问题原因
接下来我们一点点debug找到报错的位置,然后看看为什么
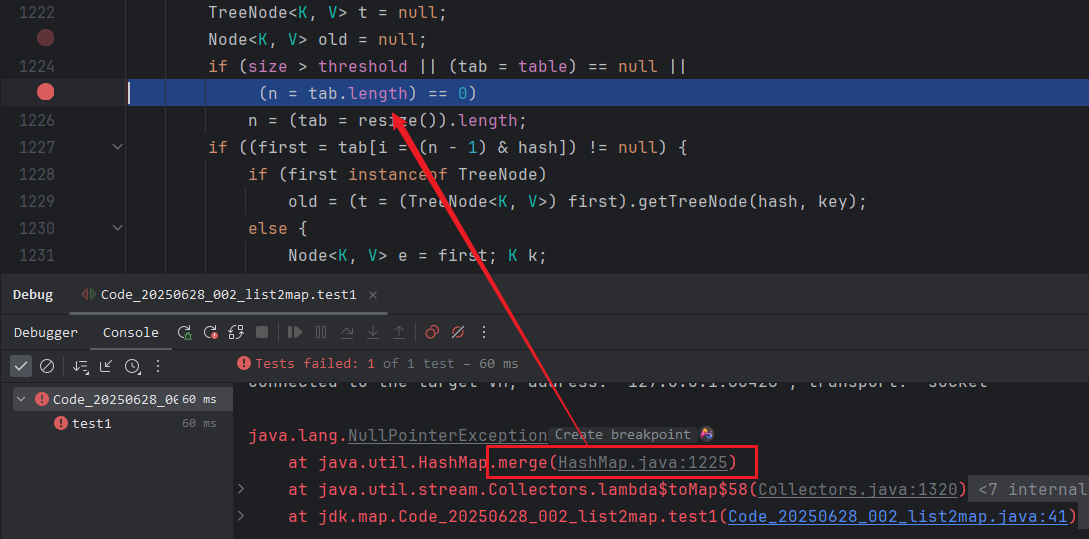
观察到这个位置报错,大概率就是tab对象是空的,再找一下tab对象从哪来的
if (size > threshold || (tab = table) == null ||
(n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
查看代码发现
(tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
说明tab对象是从table对象赋值来的,这里报空指针那么就说明table对象是null,但是前面判断了==null,按理说不会进入这一步的判断
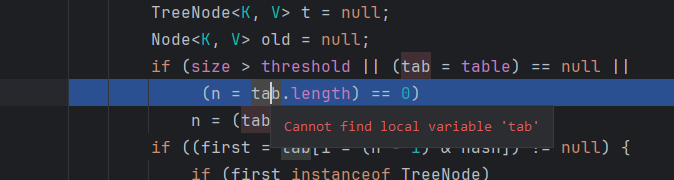
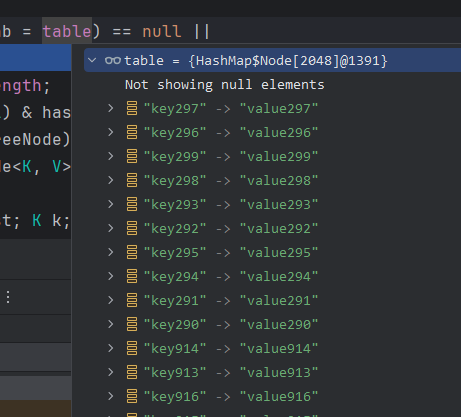
观察现象发现tab=table这一步似乎并没有生效?
为了简化定位问题的难度,我们缩小数据集
@Test
public void test1() {
Random random = new Random();
List<L2Map> useList = new ArrayList<>();
// for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
// useList.add(new L2Map("key" + i, "value" + i));
// }
// useList.add(new L2Map(null, "value-null"));
useList.add(new L2Map("key-null", null));
Map<String, String> collect1 = useList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(L2Map::getKey, L2Map::getValue));
System.out.println(collect1.size());
}
debug发现问题代码块
public static <T, K, U, M extends Map<K, U>>
Collector<T, ?, M> toMap(Function<? super T, ? extends K> keyMapper,
Function<? super T, ? extends U> valueMapper,
BinaryOperator<U> mergeFunction,
Supplier<M> mapSupplier) {
BiConsumer<M, T> accumulator
= (map, element) -> map.merge(keyMapper.apply(element),
valueMapper.apply(element), mergeFunction);
return new CollectorImpl<>(mapSupplier, accumulator, mapMerger(mergeFunction), CH_ID);
}
但是又发现第二个问题,前面一句对value=null进行了判断没啥没生效,反而在这一步出现报错???
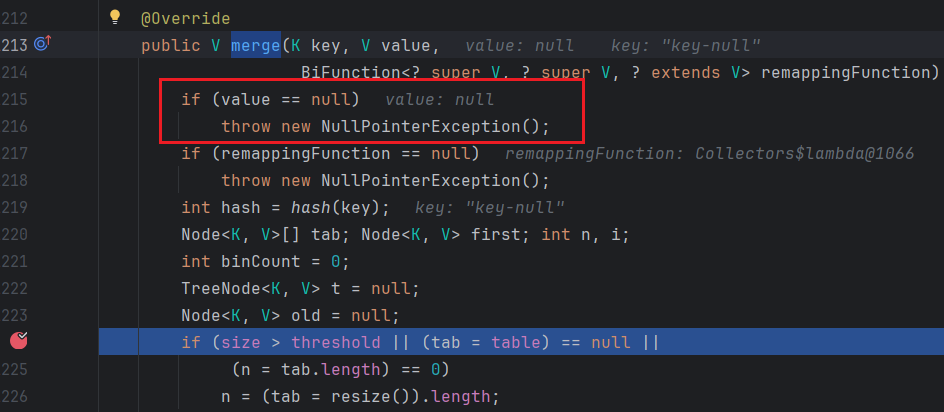
到这里我就换衣实际的class字节码编译之后是否是jvm做了优化,导致和jdk的源码对不上了呢??
那这里我们修改一下debug的方式,改成直接debug对应的class文件
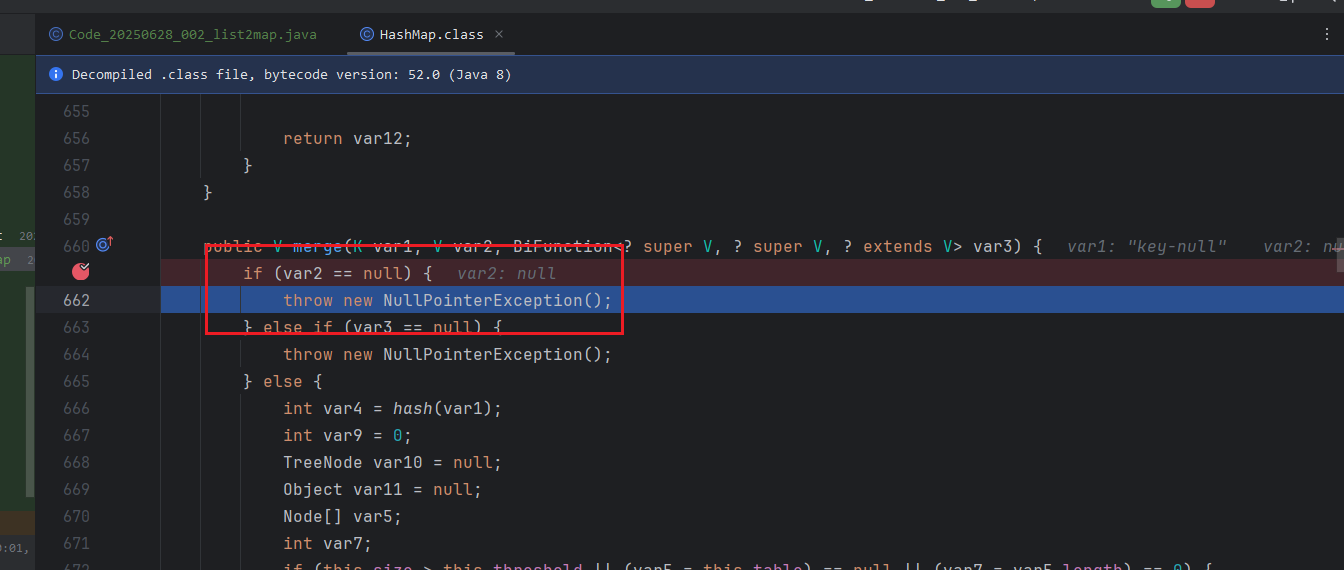
到这里就非常明显,就是这个merge方法有个判断:
if (var2 == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if (var3 == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
说明在merge方法中var2和var3都会进行校验,不允许为空
ok基于这个原因,我们再找一下为什么是merge方法呢,我们map进行数据添加的时候不应该是put么?
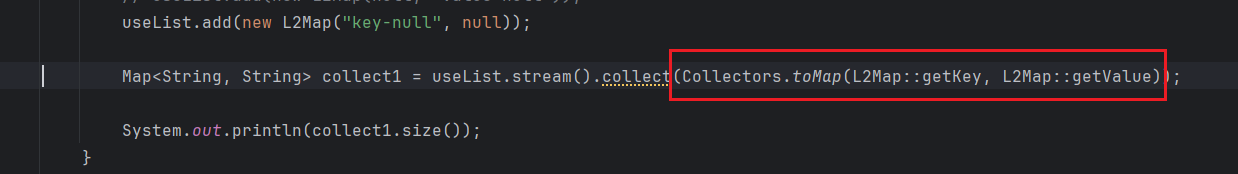
因为我们在进行合并的时候用的是Collectors.toMap(L2Map::getKey, L2Map::getValue)
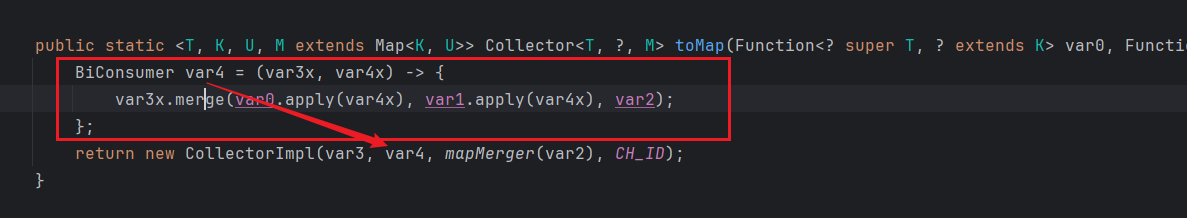
我们可以看到传入的函数对象var4对应的操作就是var3x.merge方法
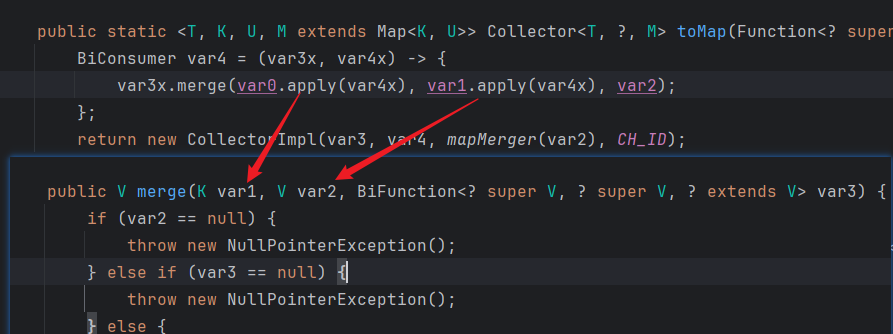
也就是如果采用merge方法,那么key和value都是不允许为空的,不然会被校验住,根本原因还是他没有采用put方法进行覆盖
解决方案
那么merge不行,我们换put不行么?
我们来试试,因为jdk底层源码中没有提供put操作的函数,我们自己封装一个
@Test
public void test1() {
Random random = new Random();
List<L2Map> useList = new ArrayList<>();
// for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
// useList.add(new L2Map("key" + i, "value" + i));
// }
// useList.add(new L2Map(null, "value-null"));
useList.add(new L2Map("key-null", null));
// Map<String, String> collect1 = useList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(L2Map::getKey, L2Map::getValue));
Map<String,
String> collect1 = useList.stream()
.collect(CustomCollectors.myToMap(L2Map::getKey, L2Map::getValue, CustomCollectors.throwingMerger(),
HashMap::new));
System.out.println(collect1.size());
}
先看效果:
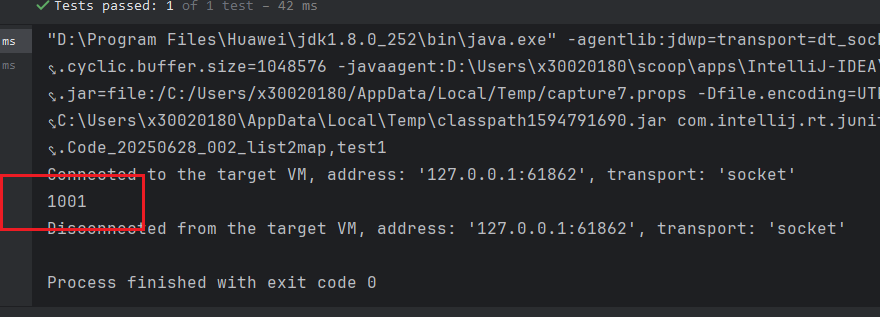
没有任何问题,成功解决
具体实现
那么我们是如何做到的呢?
答案是,我们模仿Collectors.toMap(L2Map::getKey, L2Map::getValue),手写了一个函数方法,但是把之前merge操作改成了put操作
原先:
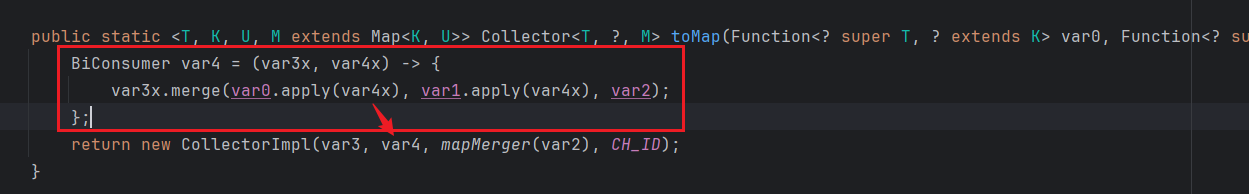
现在:
我们修改var3和var4的取值
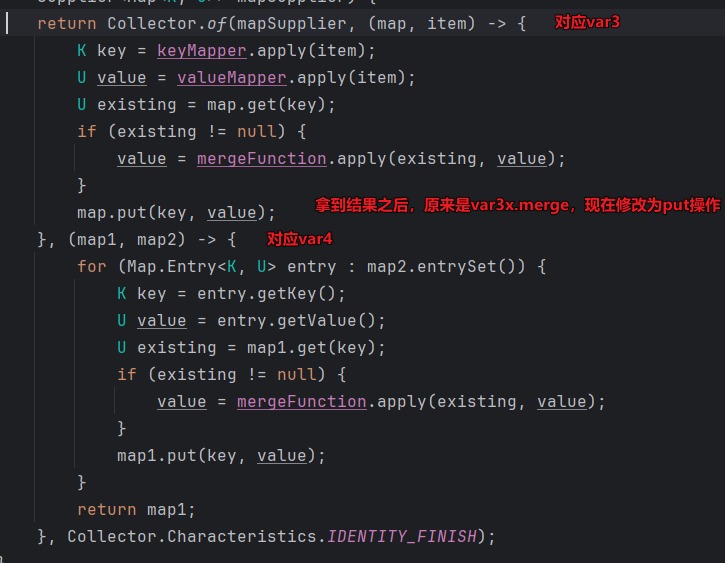
第二种解决方案

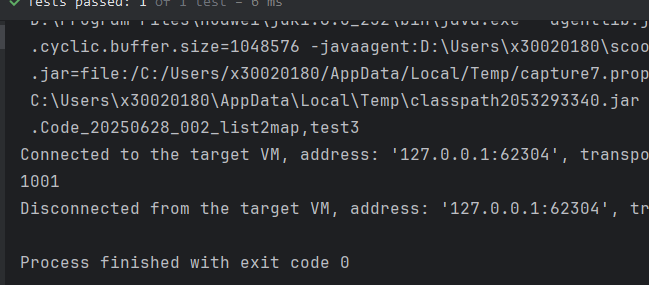
总结
使用流式list转map的核心原因其实就是因为底层用的是merge操作,而不是put操作
那为什么要用merge而不是put呢
功能对比:
| 特性 | put(K key, V value) |
merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<V, V, V> remappingFunction) |
|---|---|---|
| 基本功能 | 直接插入键值对,覆盖已存在的键 | 插入键值对,若键已存在,则通过 remappingFunction 合并新旧值 |
| 键不存在时行为 | 直接插入新键值对 | 直接插入新键值对 |
| 键存在时行为 | 覆盖旧值 | 调用 remappingFunction 合并新旧值 |
| 是否允许 null 值 | 允许(但可能引发后续空指针异常) | 不允许(若 value 为 null,HashMap 会抛出异常) |
场景对比:
| 场景 | 推荐方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 无需处理键冲突 | put |
直接覆盖旧值,简单高效 |
| 需要合并值或处理冲突 | merge |
通过合并函数动态处理冲突,避免数据丢失 |
| 并发写入 | merge |
ConcurrentHashMap.merge 是线程安全的,无需额外同步 |
| 函数式编程风格 | merge |
与 Collectors.toMap 等 API 天然契合,代码更简洁 |
| 性能敏感且无冲突 | put |
避免调用合并函数的开销 |


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号