Two Sum -- Easy
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。
一、问题描述
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
意思是给定一个数组和目标数,以数组中任意两数之和为目标数的下标作为新数组元素,返回一个数组。
二、生词
indices n /'ɪndɪsiːz/ 索引(index的复数)
三、样例及说明

四、解题思路及代码
我首先想到的方法就是暴力破解。。。时间复杂度为O(n^2)
1 class Solution { 2 public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { 3 for(int i = 0; i < nums.length-1; i ++) { 4 for(int j = i+1; j < nums.length; j++) { 5 if(nums[i] + nums[j] == target) 6 return new int[] {i,j} ; 7 } 8 } 9 return null; 10 } 11 }
但是在跟答案的暴力破解相比的话,自己的代码有一个地方没有处理好,就是当没有找到相应的元素时,我返回的是一个null,显然这是不对的(虽然运行的时候没有错误)。
所以应该抛一个异常告诉调用者。
1 class Solution { 2 public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { 3 for(int i = 0; i < nums.length-1; i ++) { 4 for(int j = i+1; j < nums.length; j++) { 5 if(nums[i] + nums[j] == target) 6 return new int[] {i,j} ; 7 } 8 } 9 throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution"); 10 } 11 }
暴力破解法在运行时的复杂性提高的时候性能是非常劣势的,所以需要用一种更为有效的方法去检测目标数是否合法——哈希表!
1 class Solution { 2 public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { 3 Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>() ; 4 for(int i=0; i < nums.length; i++) { 5 map.put(nums[i],i); 6 } 7 for(int i=0; i < nums.length; i++) { 8 int complement = target - nums[i]; 9 if(map.containsKey(complement) && map.get(complement) != i) { 10 return new int[] {i,map.get(complement)} ; 11 } 12 } 13 throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution") ; 14 } 15 }
此时时间复杂度就降为了O(n)!上述代码第一个for循环先把数组中的key和value存放进容器中,由第二个for循环去判断目标数是否合法。但其实可以进一步优化代码-仅用一个for循环即可。
1 class Solution { 2 public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { 3 Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>() ; 4 for(int i=0; i < nums.length; i++) { 5 int complement = target - nums[i] ; 6 if(map.containsKey(complement)&&map.get(complement) != i) return new int[] {map.get(complement),i} ; 7 map.put(nums[i],i); 8 } 9 throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution") ; 10 } 11 }
和用暴力破解相比用哈希表的运行时间提了将近七倍!
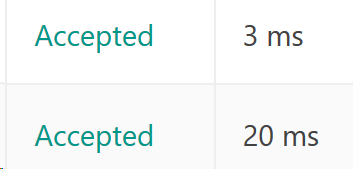
五、知识点补缺补漏
Map接口:public interface Map<K,V> 将键映射到值的对象。映射不能包含重复的键;每个键最多只能映射到一个值。
在Map接口下,有两个常用子类:HashMap、HashTable
常用方法:
- public V put(K key,V value) :向集合中保存数据
- public V get(Object key) :根据key查找对应的value数据
- public boolean containsKey(Object key) :如果该映射保护键值key就返回true,否则返回false



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号