[6] [状态变化] ( 1 ) 备忘录模式 memento
总结
-
有什么用?
在不破坏对象封装性的前提下,
保存或恢复对象的内部状态.
(在对象之外进行保存)
-
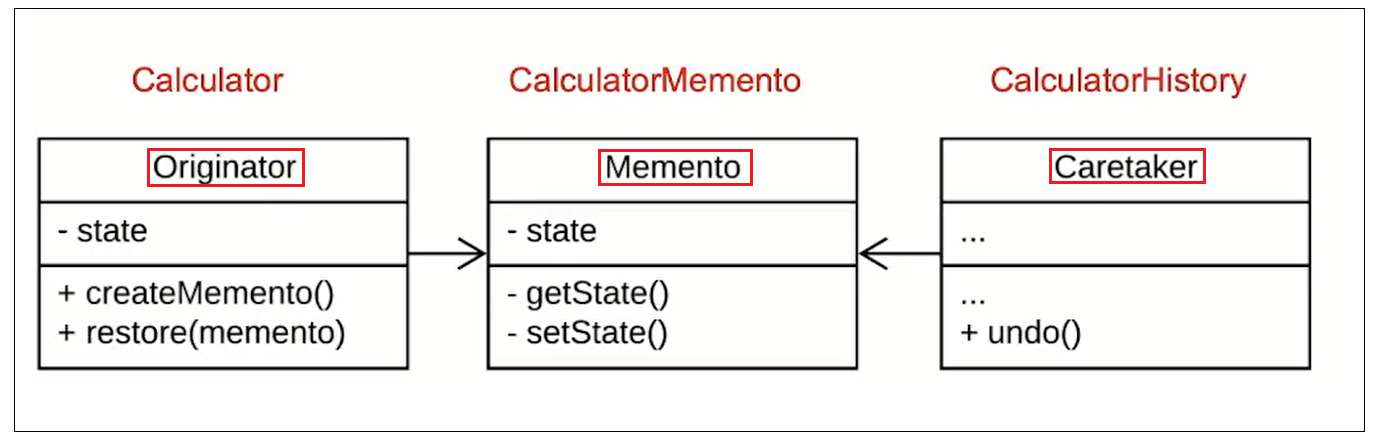
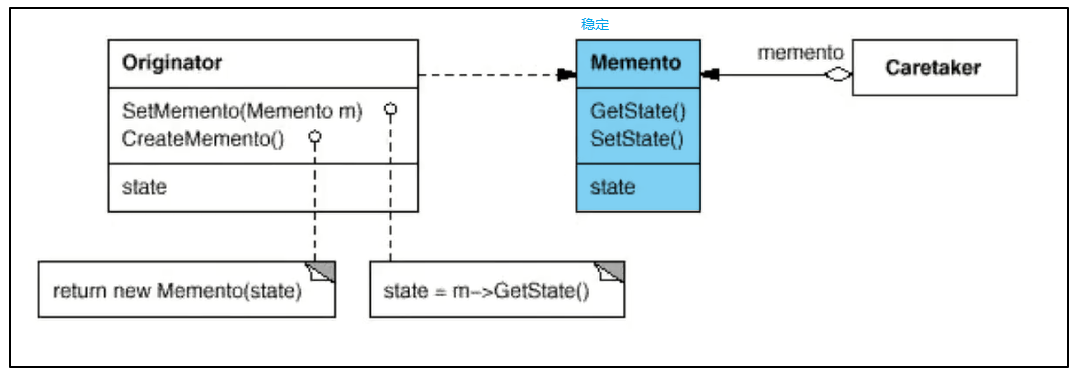
核心
Memento模式的核心是信息隐藏,
即Originator需要向外接隐藏息, 保持其封装性.
但同时又需要将状态保持到外界(Memento)
-
memento模式的进化
由于现代语言运行时 (如C#、Java等) 都具有相当的对象序列化支持,
因此往往采用效率较高、
又较容易正确实现的序列化方案来实现Memento模式。
-
案例
![image]()
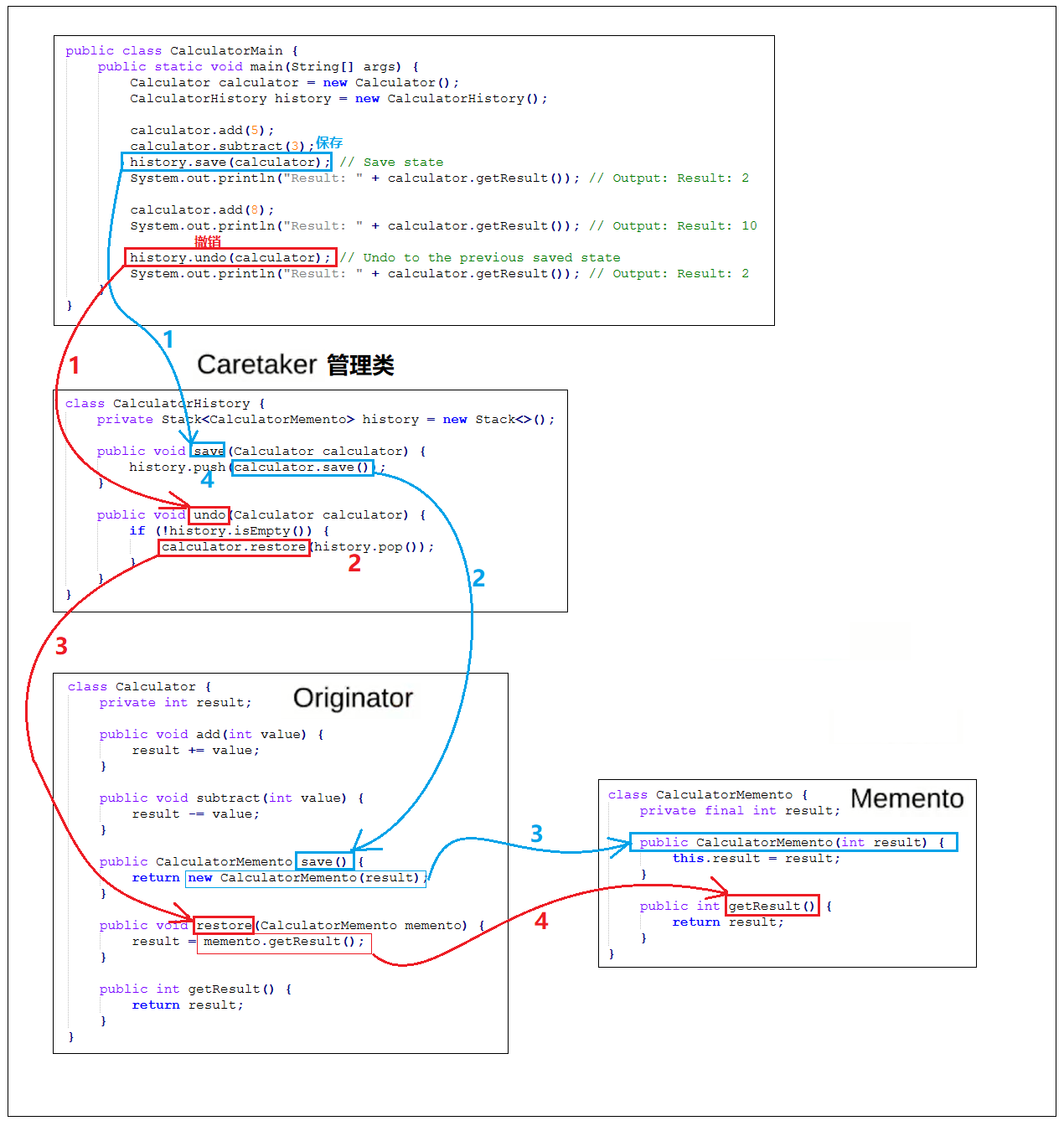
java例子1
package v27_memento.java;
import java.util.Stack;
// Originator class
class Calculator {
private int result;
public void add(int value) {
result += value;
}
public void subtract(int value) {
result -= value;
}
public CalculatorMemento save() {
return new CalculatorMemento(result);
}
public void restore(CalculatorMemento memento) {
result = memento.getResult();
}
public int getResult() {
return result;
}
}
// Memento class
class CalculatorMemento {
private final int result;
public CalculatorMemento(int result) {
this.result = result;
}
public int getResult() {
return result;
}
}
// Caretaker class
class CalculatorHistory {
private Stack<CalculatorMemento> history = new Stack<>();
public void save(Calculator calculator) {
history.push(calculator.save());
}
public void undo(Calculator calculator) {
if (!history.isEmpty()) {
calculator.restore(history.pop());
}
}
}
public class CalculatorMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
CalculatorHistory history = new CalculatorHistory();
calculator.add(5);
calculator.subtract(3);
history.save(calculator); // Save state
System.out.println("Result: " + calculator.getResult()); // Output: Result: 2
calculator.add(8);
System.out.println("Result: " + calculator.getResult()); // Output: Result: 10
history.undo(calculator); // Undo to the previous saved state
System.out.println("Result: " + calculator.getResult()); // Output: Result: 2
}
}
c++例子
class Memento{
string state;
//..
public:
Memento(const string & s) : state(s) {}
string getState() const { return state; }
void setState(const string & s) { state = s; }
};
class Originator{
string state;
//....
public:
Originator() {}
Memento createMomento() {
Memento m(state);
return m;
}
void setMomento(const Memento & m) {
state = m.getState();
}
};
int main(){
Originator orginator;
//捕获对象状态,存储到备忘录
Memento mem = orginator.createMomento();
//... 改变orginator状态
//从备忘录中恢复
orginator.setMomento(memento);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号