[5] [接口隔离] ( 3 ) 适配器 adapter
总结
-
GOF定义?
将一个类的接口转换成client希望的另一个接口.
Adapter模式使得原本由于接口不兼容,
而不能一起工作的那些class可以一起工作.
-
使用场景?
最常见的是, 遗留代码复用 , 代码迁移.
(它们常常有这样的潜规则: 你不更改旧模块,保持它们的编译/测试稳定性)
由于环境变化/迁移,
要将一些旧的对象在新环境中应用,
但是接口又不满足, 这时候就需要用适配器.
让两个接口不兼容的对象能够互相合作.
.
![image]()
-
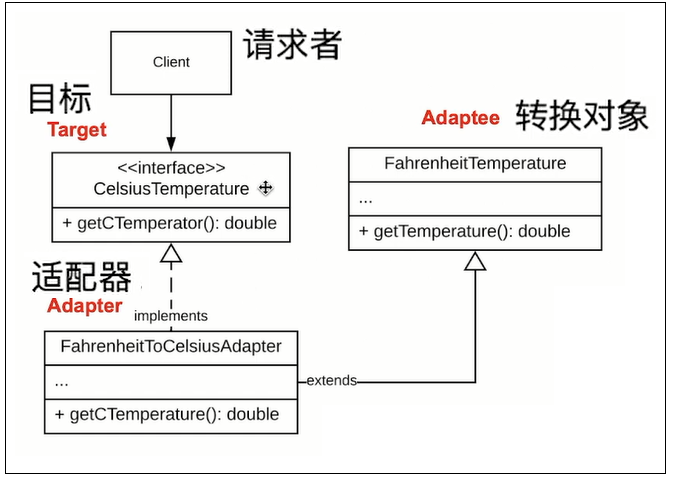
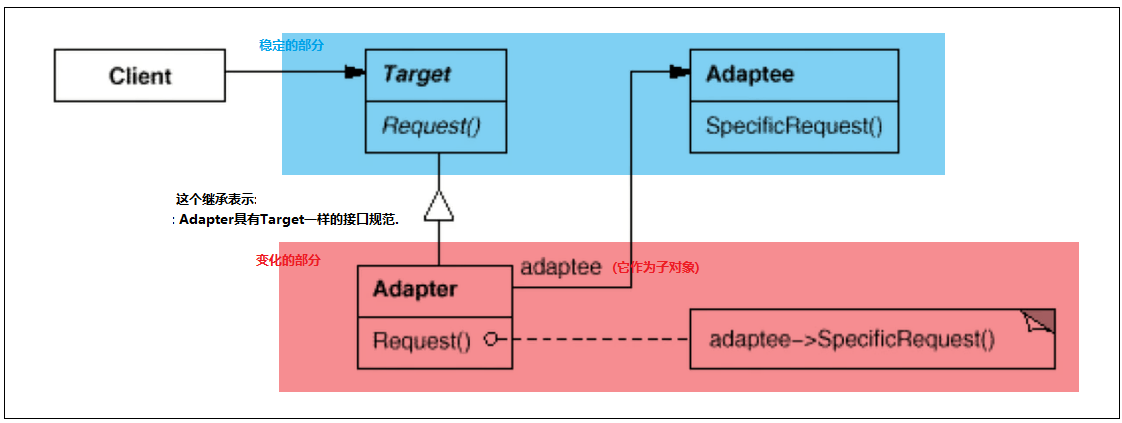
角色
![image]()
-
特点
![image]()
-
实际怎么做?
适配器就是把A接口转换为B接口
(把旧的类塞到Adapter, 面向新接口使用)
java例子
华氏温度转换为摄氏温度
用继承实现
package v15_adapter.java;
// 摄氏度温度
interface CelsiusTemperature {
double getCTemperature();
}
// 华氏温度
class FahrenheitTemperature {
private double temperature;
public FahrenheitTemperature(double temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
}
// 获取温度
public double getTemperature() {
return temperature;
}
}
// 华氏度到摄氏度适配器
class FahrenheitToCelsiusAdapter extends FahrenheitTemperature implements CelsiusTemperature {
public FahrenheitToCelsiusAdapter(double temperature) {
super(temperature);
}
public double getCTemperature() {
return (super.getTemperature() - 32) * 5 / 9;
}
}
public class ClassAdapterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FahrenheitTemperature f = new FahrenheitTemperature(100);
CelsiusTemperature c = new FahrenheitToCelsiusAdapter(f.getTemperature());
System.out.println("The temperature is " + c.getCTemperature() + " degrees Celsius.");
}
}
用组合实现(主流方式)
package v15_adapter.java;
interface CelsiusTemperature {
public double getCTemperature();
}
class FahrenheitTemperature {
private double temperature;
public FahrenheitTemperature(double temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
}
public double getTemperature() {
return this.temperature;
}
}
class FahrenheitToCelsiusAdapter implements CelsiusTemperature {
private FahrenheitTemperature fahrenheit;
public FahrenheitToCelsiusAdapter(FahrenheitTemperature fahrenheit) {
this.fahrenheit = fahrenheit;
}
public double getCTemperature() {
return (this.fahrenheit.getTemperature() - 32) * 5 / 9;
}
}
public class ObjectAdapterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FahrenheitTemperature f = new FahrenheitTemperature(100);
FahrenheitToCelsiusAdapter c = new FahrenheitToCelsiusAdapter(f);
System.out.println("The temperature is " + c.getCTemperature() + " degrees Celsius.");
}
}
结构
双向适配器
package v15_adapter.java;
interface CelsiusTemperature {
public double getCelsiusTemperature();
}
interface FahrenheitTemperature {
public double getFahrenheitTemperature();
}
class Celsius implements CelsiusTemperature {
private double temperature;
public Celsius(double temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
}
public double getCelsiusTemperature() {
return this.temperature;
}
}
class Fahrenheit implements FahrenheitTemperature {
private double temperature;
public Fahrenheit(double temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
}
public double getFahrenheitTemperature() {
return this.temperature;
}
}
public class TwoWayAdapter implements CelsiusTemperature, FahrenheitTemperature {
private Celsius c;
private Fahrenheit f;
public TwoWayAdapter(Celsius c) {
this.c = c;
this.f = new Fahrenheit(c.getCelsiusTemperature() * 9 /5 +32);
}
public TwoWayAdapter(Fahrenheit f) {
this.f = f;
this.c = new Celsius((f.getFahrenheitTemperature() -32) *5 /9);
}
public double getCelsiusTemperature() {
return c.getCelsiusTemperature();
}
public double getFahrenheitTemperature() {
return f.getFahrenheitTemperature();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Celsius celsius = new Celsius(25);
TwoWayAdapter adapter = new TwoWayAdapter(celsius);
double fahrenheitTemperature = adapter.getFahrenheitTemperature();
System.out.println("Temperature in Fahrenheit: " + fahrenheitTemperature);
TwoWayAdapter adapter2 = new TwoWayAdapter(new Fahrenheit(100));
System.out.println("Temperature in Celsius: " + adapter2.getCelsiusTemperature());
}
}
c++例子
// 老接口
class IAdaptee{
public:
virtual void foo(int data)=0;
virtual int bar()=0;
};
// 老对象
class OldClass: public IAdaptee{
virtual void foo(int data){
// ...
}
virtual int bar(){
// ...
}
};
// 目标接口(新接口)
class ITarget{
public:
virtual void process()=0;
};
// 适配器
class Adapter: public ITarget{
protected:
// 老接口,老对象
IAdaptee* pAdaptee;
public:
Adapter(IAdaptee* pAdaptee){ this->pAdaptee=pAdaptee; }
// 实现新接口ITarget的方法
virtual void process(){
// 模拟转换过程, 实际可能相当的复杂
int data=pAdaptee->bar();
pAdaptee->foo(data);
// ...
}
};
int main(){
// 把旧的类塞到Adapter, 面向新接口使用.(适配器就是把A接口转换为B接口)
IAdaptee* pAdaptee=new OldClass();
ITarget* pTarget=new Adapter(pAdaptee);
pTarget->process();
}
// 另一种形式:类适配器(不如组合形式的对象适配器)
class Adapter: public ITarget, protected OldClass{ //多继承
// ...
}
结构





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号