[C++17] 内存池资源(polymorphic memory resource, pmr)
例子1 hello world
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <memory_resource>
#include <unordered_map>
void foo1(){
unsigned char buff[1024]{};
// 用栈内存创建一个内存资源管理器
std::pmr::monotonic_buffer_resource pool(buff,1024,std::pmr::null_memory_resource());
// 使用内存池创建两个内存池string
std::pmr::string s1{"my string", &pool};
std::pmr::string s2{"my string", &pool};
// 创建一个内存池vec
std::pmr::vector<std::pmr::string> vec{&pool};
// 创建一个内存池map
std::pmr::unordered_map<int,std::pmr::string> map{&pool};
}
int main() {
foo1();
}
// null_memory_resource()的作用:
// 通过传递null_memory_resource()作为备选内存资源,
// 我们可以确保任何尝试分配 更多内存的行为都会抛出异常而不是在堆上分配内存。
// 就是说用了这个参数,可以保证不会发生堆分配.
例子2 从结果对比预期
从输出结果可以看到,
vec和map内部的元素是在池子中的,
但是vec和map本身不在.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <memory_resource>
#include <unordered_map>
//#define string std::pmr::string
//#define vector(T) std::pmr::vector<T>
//#define unordered_map(T1, T2) std::pmr::unordered_map<T1,T2>
//#define monotonic_buffer_resource std::pmr::monotonic_buffer_resource
//#define null_memory_resource std::pmr::null_memory_resource
bool isAddressInBuff(void *addr, void *start, std::size_t size);
void printResult(const std::pmr::string &name, void *addr, bool isInBuff);
void foo2();
int main() {
foo2();
}
void foo2() {
unsigned char buff[1024]{};
std::pmr::monotonic_buffer_resource pool(buff, 1024,
std::pmr::null_memory_resource());
std::pmr::string s1{"1111 ", &pool};
std::pmr::string s2{"2222 ", &pool};
std::pmr::string s3{"3333 ", &pool};
std::pmr::string &s4 = *new std::pmr::string{"4444 ", &pool};
std::pmr::string &s5 = *new std::pmr::string{"5555 ", &pool};
std::pmr::string &s6 = *new std::pmr::string{"6666 ", &pool};
std::pmr::vector<std::pmr::string> vec{&pool};
std::pmr::unordered_map<int, std::pmr::string> map{&pool};
vec.push_back(s1);
vec.push_back(s2);
vec.push_back(s3);
map.insert({1, s1});
map.insert({2, s2});
map.insert({3, s3});
printResult("string s1", &s1, isAddressInBuff(&s1, buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("string s2", &s2, isAddressInBuff(&s2, buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("string s3", &s3, isAddressInBuff(&s3, buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("string s4", &s4, isAddressInBuff(&s4, buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("string s5", &s5, isAddressInBuff(&s5, buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("string s6", &s6, isAddressInBuff(&s6, buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("s1.c_str()", (void *) s1.c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) s1.c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("s2.c_str()", (void *) s2.c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) s2.c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("s3.c_str()", (void *) s3.c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) s3.c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("s4.c_str()", (void *) s4.c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) s4.c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("s5.c_str()", (void *) s5.c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) s5.c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("s6.c_str()", (void *) s6.c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) s6.c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("vector vec", &vec, isAddressInBuff(&vec, buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("unordered_map map", &map, isAddressInBuff(&map, buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("vec[0]", (void *) vec[0].c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) vec[0].c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("vec[1]", (void *) vec[1].c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) vec[1].c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("vec[2]", (void *) vec[2].c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) vec[2].c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("map[0]", (void *) map[0].c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) map[0].c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("map[1]", (void *) map[1].c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) map[1].c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
printResult("map[2]", (void *) map[2].c_str(), isAddressInBuff((void *) map[2].c_str(), buff, sizeof(buff)));
}
bool isAddressInBuff(void *addr, void *start, std::size_t size) {
auto start_ptr = reinterpret_cast<const std::uint8_t *>(start);
auto addr_ptr = reinterpret_cast<const std::uint8_t *>(addr);
return (addr_ptr >= start_ptr) && (addr_ptr < (start_ptr + size));
}
void printResult(const std::pmr::string &name, void *addr, bool isInBuff) {
std::cout << name << ": " << ((isInBuff) ? "yes" : "no") << " - " << addr << std::endl;
}
输出:
string s1: no - 0x7ffdc4136540
string s2: no - 0x7ffdc4136570
string s3: no - 0x7ffdc41365a0
string s4: no - 0x55e8e9429eb0
string s5: no - 0x55e8e9429ee0
string s6: no - 0x55e8e9429f10
s1.c_str(): no - 0x7ffdc4136558
s2.c_str(): no - 0x7ffdc4136588
s3.c_str(): no - 0x7ffdc41365b8
s4.c_str(): no - 0x55e8e9429ec8
s5.c_str(): no - 0x55e8e9429ef8
s6.c_str(): no - 0x55e8e9429f28
vector vec: no - 0x7ffdc41364a0
unordered_map map: no - 0x7ffdc4136500
vec[0]: yes - 0x7ffdc4136690
vec[1]: yes - 0x7ffdc41366b8
vec[2]: yes - 0x7ffdc41366e0
map[0]: yes - 0x7ffdc4136850
map[1]: yes - 0x7ffdc4136740
map[2]: yes - 0x7ffdc41367e0
例子3 如何在内存池中分配一个,开发者自己写的class的实例?
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <memory_resource>
void check(void *addr);
class MyClass {
public:
explicit MyClass(int value) : m_value(value) {
std::cout << "构造函数" << std::endl;
}
~MyClass() {
std::cout << "析构函数" << std::endl;
}
void printValue() const {
std::cout << "[value] " << m_value << std::endl;
}
private:
int m_value;
};
unsigned char buff[1024]{};
int main() {
// 1 创建池子
std::pmr::monotonic_buffer_resource pool(buff, 1024, std::pmr::null_memory_resource());
// 2 创建一个pmr分配器
std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<MyClass> alloc(&pool);
// 3 使用分配器的allocate()函数来分配内存
// 两步可以缩写成一步,MyClass *myClass = std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<MyClass>(&pool).allocate(1);
MyClass *myClass = alloc.allocate(1);
// 4 在内存池中构造MyClass对象
// allocate()执行之后,并没有自动调用构造函数,需要显式手动调用
std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<MyClass>(&pool).construct(myClass, 42);
// 5 调用对象的成员函数
myClass->printValue();
// 检查
check(myClass);
// 6 析构实例
std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<MyClass>(&pool).destroy(myClass);
// 7 在内存池中销毁MyClass实例,回收空间
std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<MyClass>(&pool).deallocate(myClass, 1);
return 0;
}
void check(void *addr) {
// 判断实例地址是否在buff内存空间中。
if (addr >= (void *) buff && addr < (void *) (buff + sizeof(buff))) {
std::cout << "实例在池子中:yes" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "实例在池子中:no" << std::endl;
}
}
输出:
构造函数
[value] 42
实例在池子中:yes
析构函数
例子4 在内存池中定义string/vector/map实例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <memory_resource>
#include <map>
void check(void *addr);
unsigned char buff[1024]{};
int main() {
// string
std::pmr::monotonic_buffer_resource pool(buff, 1024, std::pmr::null_memory_resource());
std::pmr::string *str = std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<std::pmr::string>(&pool).allocate(1);
std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<std::pmr::string>(&pool).construct(str, "hello_world");
check(str);
check((void *) (str->c_str()));
// vector<string>
using vec_t = std::pmr::vector<std::pmr::string>;
vec_t *vec = std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<vec_t>(&pool).allocate(1);
std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<vec_t>(&pool).construct(vec);
vec->emplace_back("aaaa");
vec->emplace_back("bbbb");
check(vec);
check((void *) vec);
check(&((*vec)[0])); // 第一个elem
check(&((*vec)[1])); // 第二个elem
check((void *) (*vec)[0].c_str()); // 第一个elem
check((void *) (*vec)[1].c_str()); // 第二个elem
// map<int,string>
using map_t = std::pmr::map<int, std::pmr::string>;
map_t *map = std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<map_t>(&pool).allocate(1);
std::pmr::polymorphic_allocator<map_t>(&pool).construct(map);
map->insert({1, std::pmr::string("cccc")});
map->insert({2, std::pmr::string("dddd")});
check(&(*map)[1]);
check((void *) (*map)[1].c_str());
return 0;
}
void check(void *addr) {
// 判断实例地址是否在buff内存空间中。
if (addr >= (void *) buff && addr < (void *) (buff + sizeof(buff))) {
std::cout << "实例在池子中:yes" << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << "实例在池子中:no" << std::endl;
}
}
输出:
实例在池子中:yes
实例在池子中:yes
实例在池子中:yes
实例在池子中:yes
实例在池子中:yes
实例在池子中:yes
实例在池子中:yes
实例在池子中:yes
实例在池子中:yes
实例在池子中:yes
例子5 嵌套内存资源管理器
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <memory_resource>
void check(void *addr);
unsigned char buff[128]{};
int main() {
std::pmr::monotonic_buffer_resource monotonic_pool(buff, sizeof(buff), std::pmr::null_memory_resource());
std::pmr::unsynchronized_pool_resource pool(&monotonic_pool);
std::pmr::vector<int> vec(&pool);
for (int k = 0; k < 10000; k++) {
vec.emplace_back(k);
}
return 0;
}
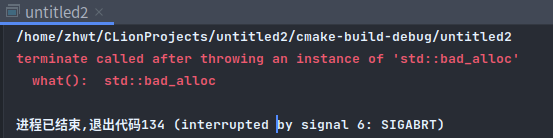
输出
可以看到, 超出空间后, 没有分配堆内存, 直接报错了, 这就是我想要的效果.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号