NOIP2025模拟7
前言:
我菜菜菜菜菜菜,所以只改了两道题。

T2:原子(atom)
思路:
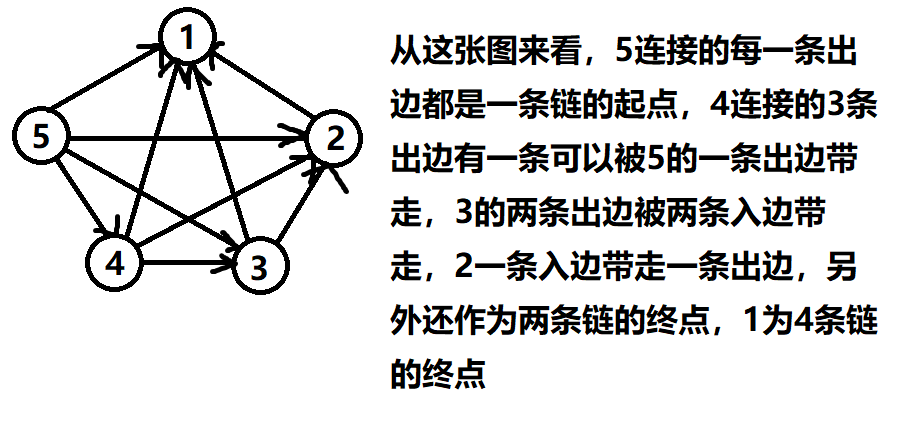
建图图图图图。
根据题意我们可以建出来一个完全图,然后求出图中最少有几条链就行。
我们发现,链的数量其实就是每个点的(出度减去入度)的加和。
然后再所有的把链跑出来就行。
提一嘴,队列是简单的,但是链式前向星是可写的。
代码:
$code$
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N=2005;
int n,ans,du[N];
queue<int> e[N],q;
int main(){
freopen("atom.in","r",stdin);
freopen("atom.out","w",stdout);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<=n;j++){
e[i].push(j);
du[i]++;du[j]--;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) if(du[i]>0) ans+=du[i];
cout<<ans<<'\n';
int i=1;
while(1){
while(e[i].empty()&&i<=n) i++;
if(i>n) break;
int x=i,cnt=0;
if(x>1){
q.push(x-1);
cnt++;
}
while(!e[x].empty()){
cnt++;
int y=e[x].front();e[x].pop();
q.push(y-x);
x=y;
}
cout<<cnt<<' ';
while(!q.empty()){
cout<<q.front()<<' ';
q.pop();
}
cout<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
T3:旅行计划(plan)
思路:
竟然是 \(3\) 个 \(dp\) 。
对于每一个点的状态,可以分为三种情况:出去一次,出去又回来,出去两趟。分别对它们进行状态转移。
先说出去又回来的。那先显然是它的子节点出去又回来的长度加和再加上这个点到子节点的重复路径数/2*2。
再说出去两趟的。显然是要求出出去一趟的最大值和次大值然后加和再加上从这个点出去又回来的路径长度,在和它的子节点的出去两趟的 \(dp\) 值加上该点到子节点的重复路径数/2*2取一下 \(max\) 就好了。
最后是出去一次的。就是这个点的所有子节点出去一次的最大值加上改点到子节点的(最长路径数 \(-1)/2*2\),再加上出去又回来的路径长度。
代码:
$code$
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+5;
int T,n,u,v,w,d1,d2,d3,cnt,head[N],f1[N],f2[N],f3[N];
struct flower{
int to,nxt,val;
}e[N<<1];
inline void add(int x,int y,int z){
e[++cnt].to=y;
e[cnt].val=z;
e[cnt].nxt=head[x];
head[x]=cnt;
}
inline void dfs(int x,int fa){
f1[x]=f2[x]=f3[x]=0;
int maxn=0,maxx=0;
for(int i=head[x];i;i=e[i].nxt){
int y=e[i].to,z=e[i].val;
if(y==fa) continue;
dfs(y,x);
if(z/2>=1){
d3=z/2*2+f3[y];
d2=z/2*2+f2[y]-d3;
}else d2=d3=0;
f2[x]=max(d2,f2[x]);
f3[x]+=d3;
d1=(z-1)/2*2+1+f1[y]-d3;
if(d1>maxn){
maxx=maxn;
maxn=d1;
}else if(d1>maxx) maxx=d1;
}
f1[x]=maxn+f3[x];
f2[x]=max(f2[x],maxn+maxx)+f3[x];
}
signed main(){
freopen("plan.in","r",stdin);
freopen("plan.out","w",stdout);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin>>T;
while(T--){
cnt=0;
memset(head,0,sizeof(head));
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
cin>>u>>v>>w;
add(u,v,w);add(v,u,w);
}
dfs(1,0);
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) ans=max(ans,max(f1[i],max(f2[i],f3[i])));
cout<<ans<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}


