c++ STL标准库1.0
1、简介/C++1.0
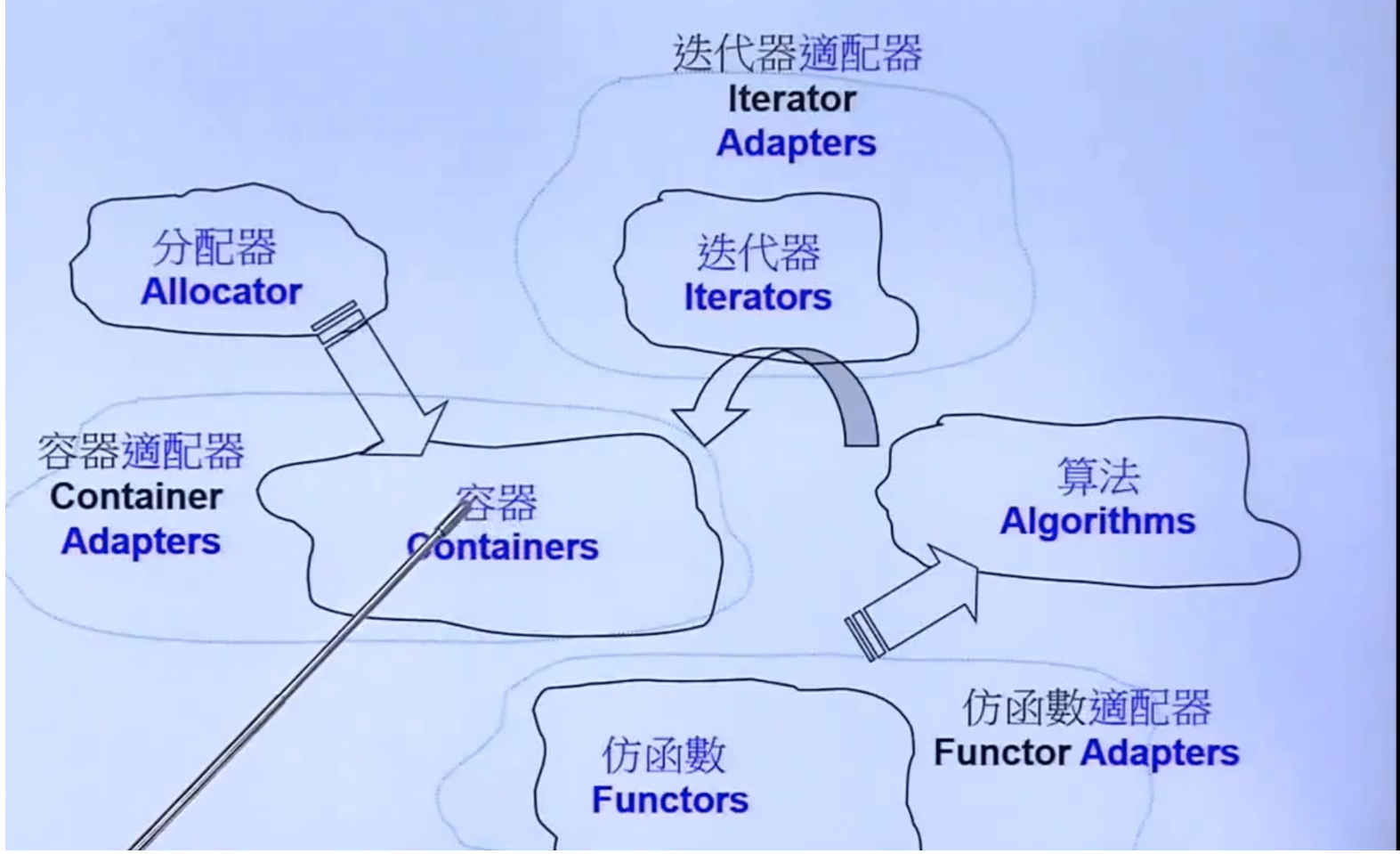
C++标准库 = STL(标准模板库)+ 其他
六大部件:
-
容器(Containers)
-
-
算法(Alogrithms)
-
迭代器(Iterators)
-
仿函式(Functors)
-
适配器(Adaptors)
2、allocator
allocator种类
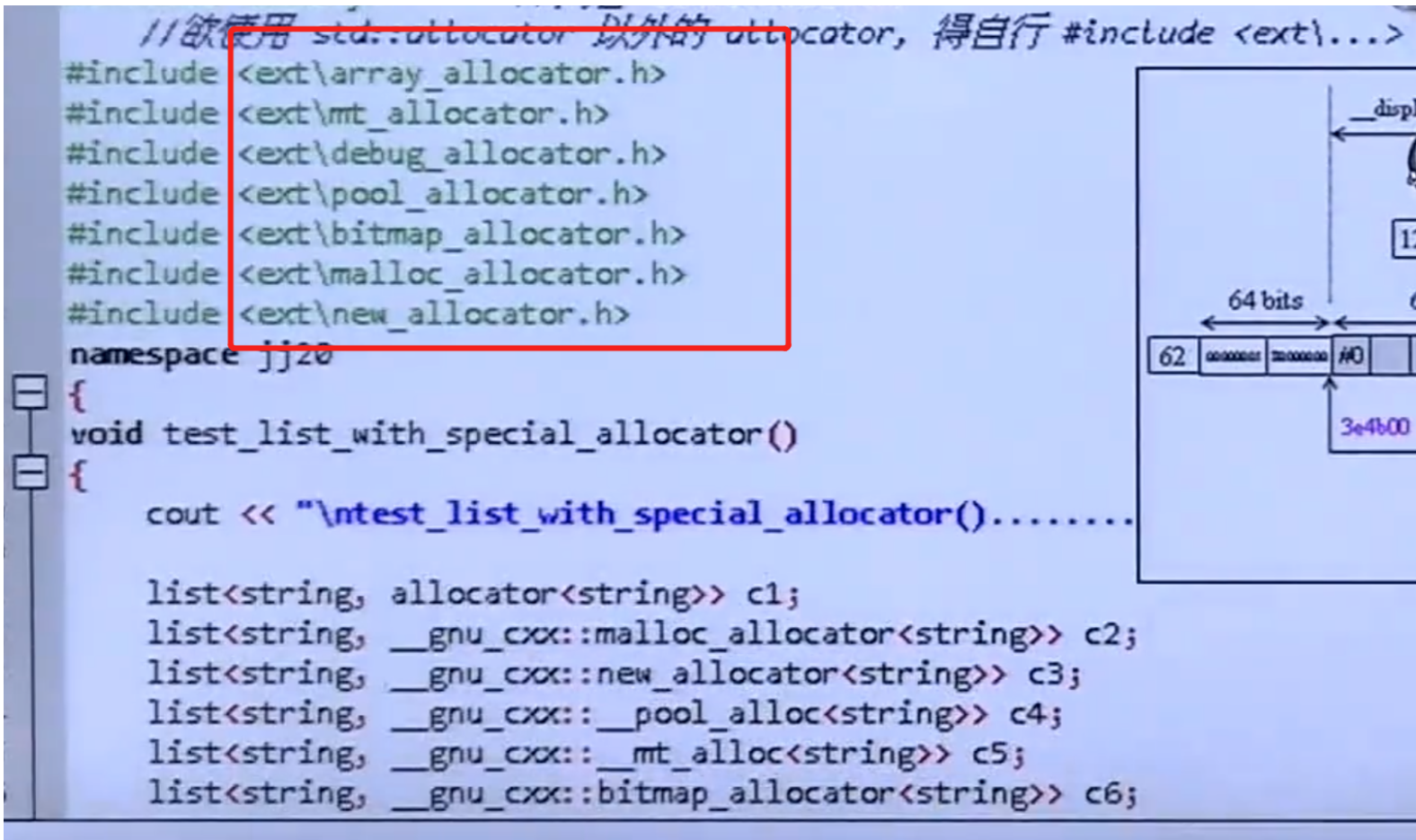
STL使用的内存:
https://www.cnblogs.com/sld666666/archive/2010/07/01/1769448.html
为何不直接使用alloc?
-
alloc除了分配的内存会大于申请的,主要多余的字节用来存储该次分配的内存大小,以便delete能正确删除(首尾都有,共计8字节)
3、list
-
结构:环状双向链表(最后一个元素是不属于list的,end指向的)
-
iterator:class __list_iterator
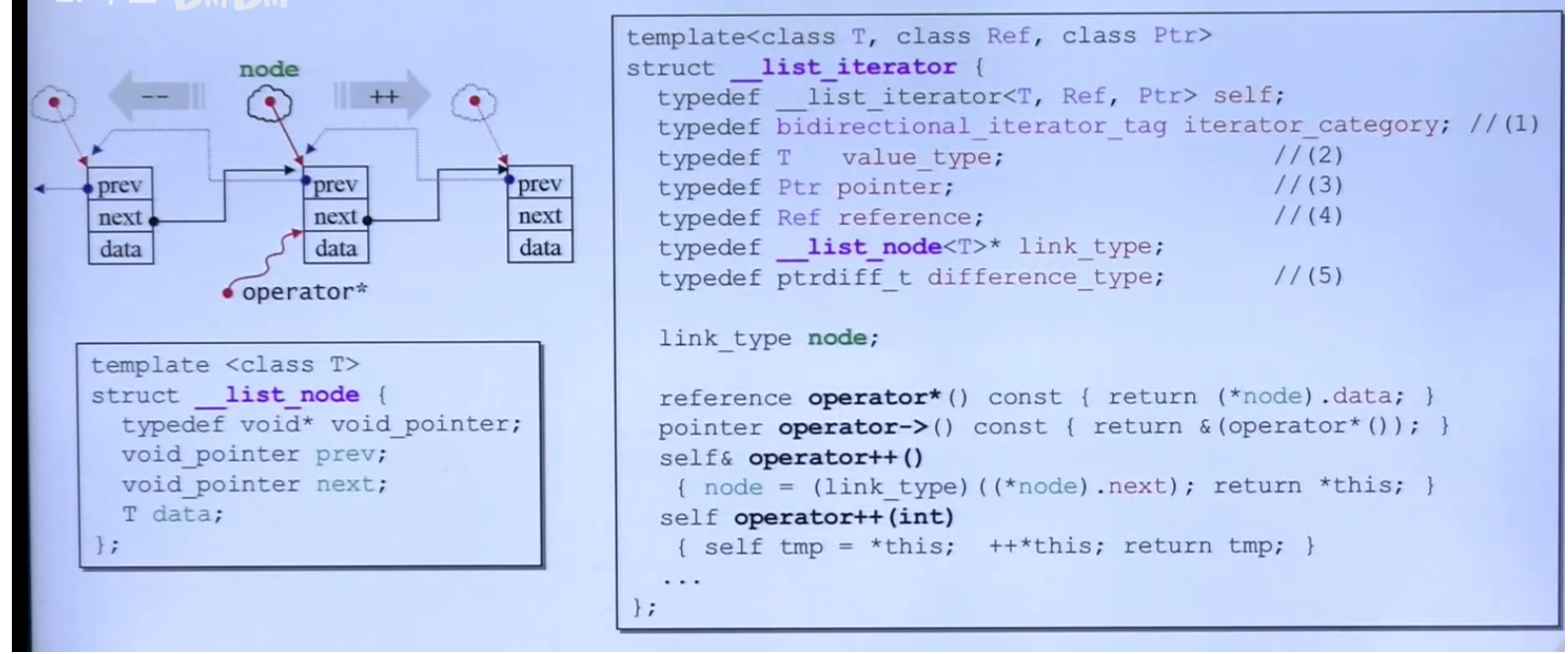
operator=优先级 > operator*
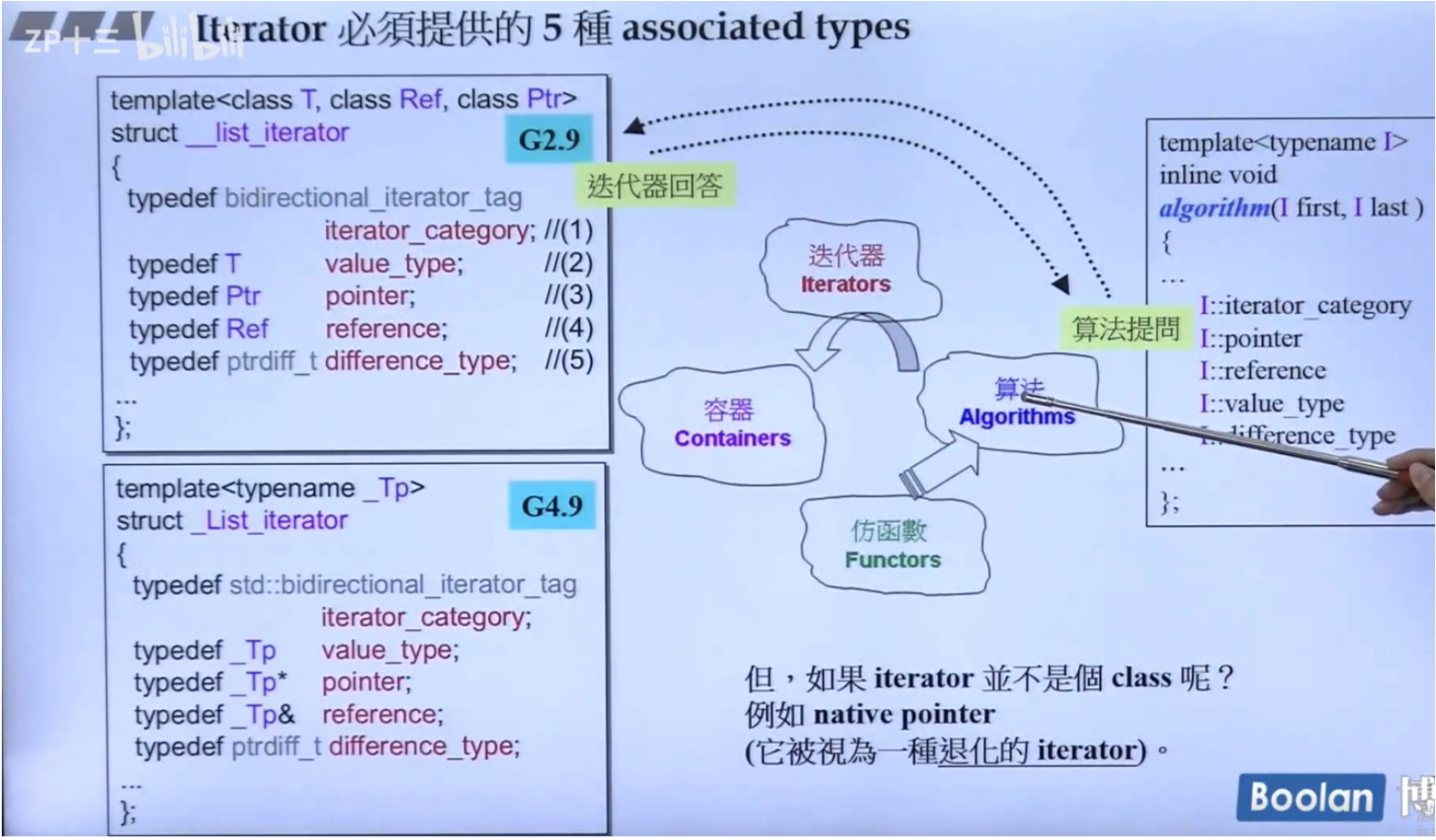
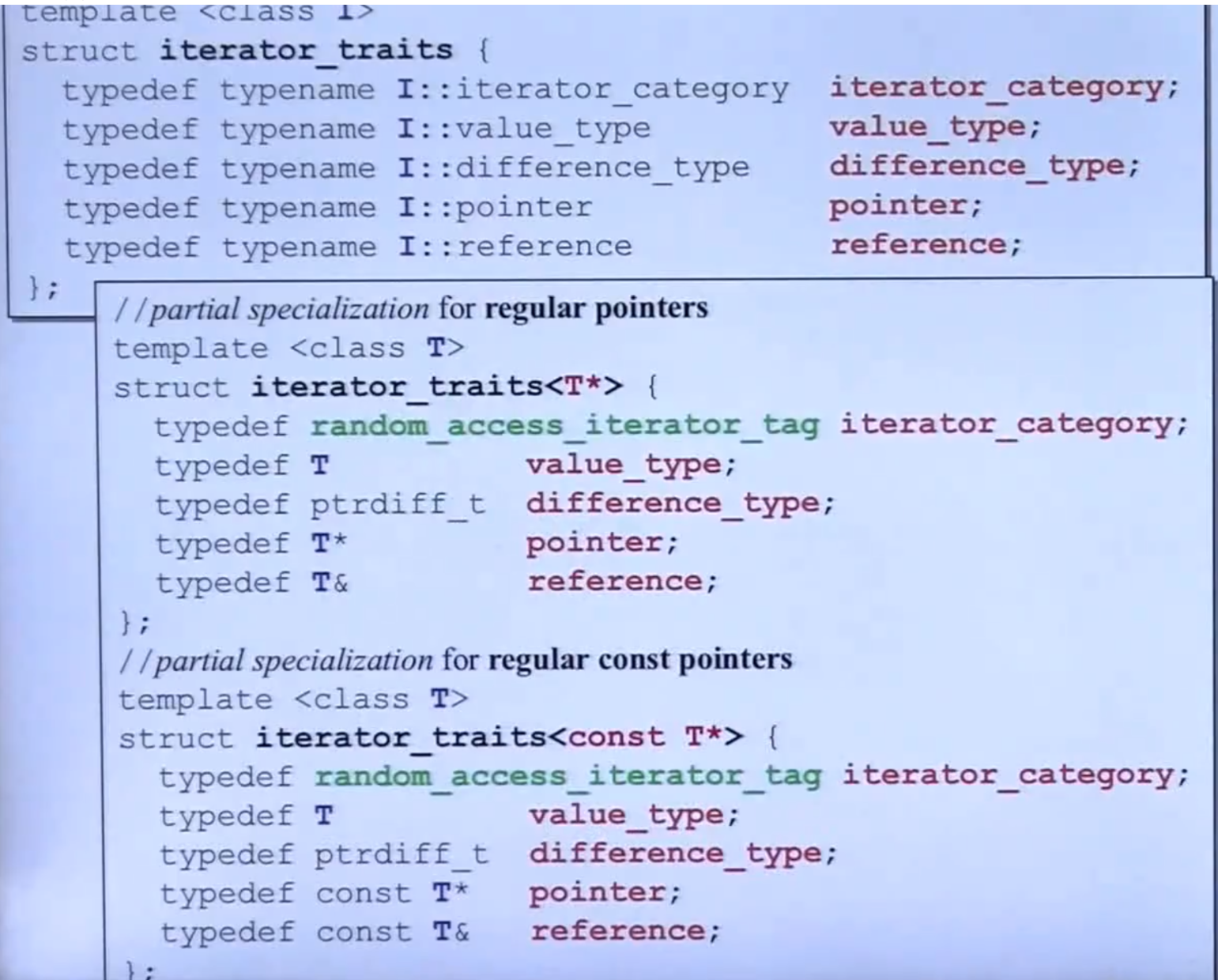
4、iterator traits
-
iterator 必须实现的五中tyoe
-
traints实现(特化、偏特化)
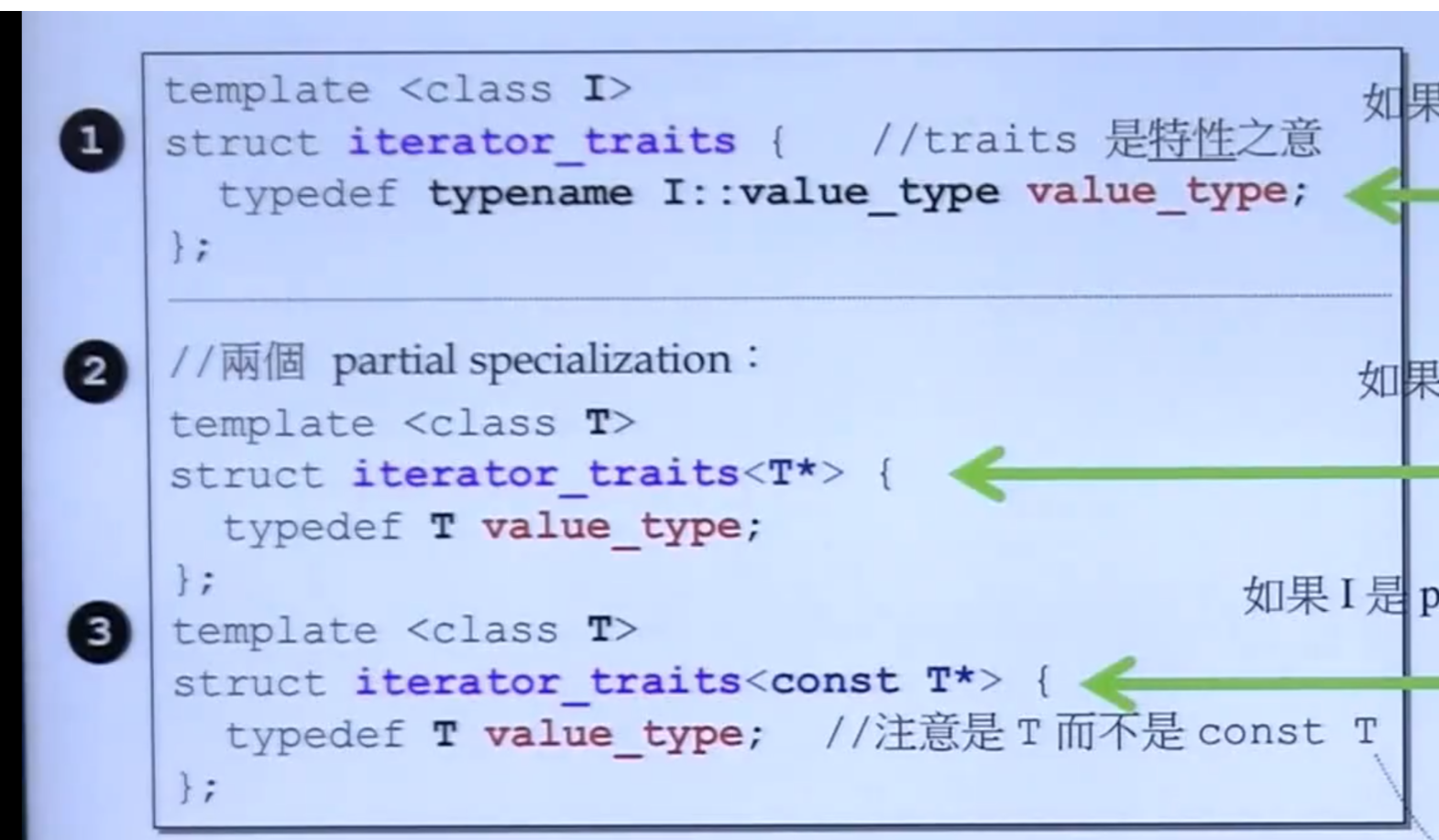
为何不是const?value_type用来声明变量的,如果无法被赋值,则没啥意义
-
完整的iterator traits
5、vector
三个iterator:start、finish、end_of_storage
size = finish - start
capacity = end_of_storage - start
空间成倍增长
迭代器类型
template<class T, class Alloc = alloc>
class vector {
public:
typedef T value_type;
typedef value_type* iterator; // T*
...
}
6、array
template < typename _Tp, std::size_t _Nm>
struct array {
typedef _Tp value_type;
typedef _Tp* pointer;
typedef value_type* iterator // 迭代器
...
_M_instance: _Tp[_Nm]; // 成员数组
...
iterator begin() {return &_M_instance[0];}
iterator end() {return &M_instance[_Nm];
}
7、deque
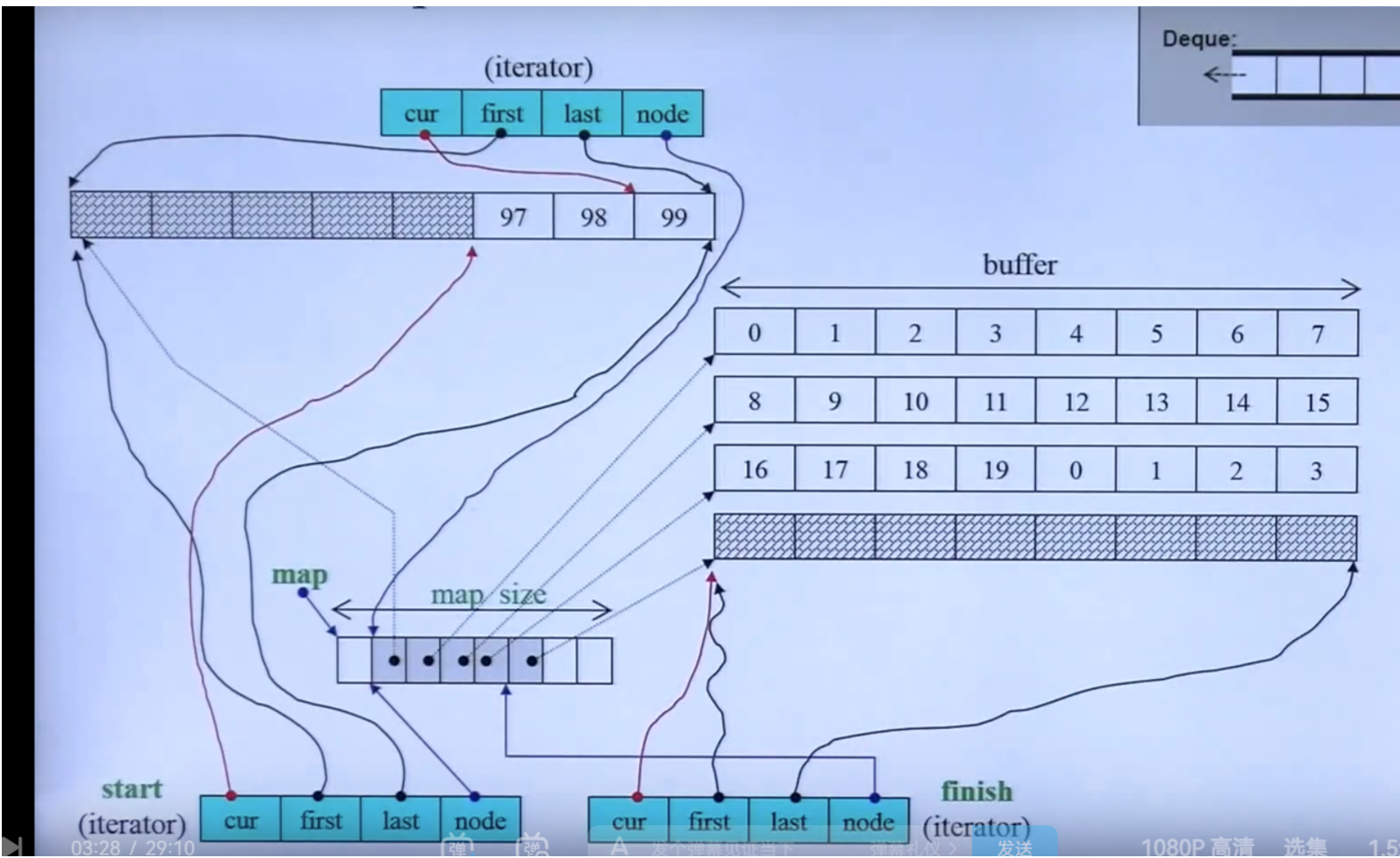
底层数据结构:分段数组,vector + 指针(指向缓冲区)
迭代器:
cur - 当前位置
first-当前这个段的初始位置
last-当前这个段的最后位置
node-这个段在vector中的下标(以便跳到下一个段)
template <class T, ckass Alloc - alloc, size_t BufSiz=0> // BufSiz:每个段的大小
class deque {
typedef T value_type;
typedef __deque_iterator<T, t&, T*, BufSiz> iterator;
typedef point* map_pointer; // T*
iterator start; // 首部位置
iterator finish; // 尾部位置
map_pointer map; // 分段数组指针,map[i] 存储的是每一个段的指针/位置
size_type map_size; // vector的大小,非总的数据量
iterator begin() {return start;}
iterator end() {return finish;}
size_type size() const {return finish - strart}; // 迭代器操作符重载
}
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr, size_t BufSiz>
class __deque_iterator {
typedef random_access_iterator_tag iteratir_category;
typedef T value_type;
typedef Ptr pointer;
typedef Ref reference;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
typedef T** map_pointer;
typedef __deque_iterator self;
T* cur;
T* first;
T* last;
map_pointer node;
}
为何BufSiz=0?
inline size_t __deque_buf_size(size_t n, size_t sz) {
// sz 是sizeof(value_type) 也就是类型占用的空间
return n != 0 ? n : (sz < 512 ? size_t(512 / sz) : size_t(1));
}
queue 和 stack都是使用deque实现的、当然使用list也可以的,用法为 stack<string, list<string>>
8、RBTree
原则
1、RBTree不应该直接修改节点值、修改会导致变换操作,非常麻烦
2、允许重复 insert_equal() 、不允许重复 insert_unique()
源码
template< class Key, // 用来比较的key
class Value, // value = key + data
class KeyOfValue, // 如何用value中获取key
class Compare, // 比较key的函数
class Alloc = alloc>
class rb_tree {
typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node;
typedef rb_tree_node* link_type;
size_type node_count; // rb tree 大小
link_type header; // 为了实现方便,不是真正的元素
Compare key_compare; // key 大小比较准则,function object(由于是空clas 所以大小为1 加上对齐,所以32为系统大小为12) 新版本24字节: 3指针 + 1color
...
}
使用方法
rb_tree<int, int, identity<int>, less<int>, alloc> myTree;
template<class T> struct identity {
const operator()(const T& x) const {return x;}
}
template<class T> struct less : public binary_function<T, T, bool> {
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y) const {
return x < y;
}
}
9、set map
set multiset
1、底层结构:红黑树
2、元素的value和key合一,value就是key
3、key不可修改
template <class Key, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class set {
typedef Key key_type;
typedef Key value_type;
typedef Compare key_compare;
typedef Compare value_compare;
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type, identity<value_type>, key_compare<key_type>, alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t;
...
typedef typename rep_type::const_iterator iterator; // const类型保证不可修改
}
map multimap
1、底层结构:红黑树
2、key不可修改,value可修改,key用来构建红黑树
template <class Key,
class T,
class Compare = less<Key>,
class Alloc = alloc>
class map {
tyoedef Key key_type;
typedef T data_type;
typedef T mapped_type;
typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type; // 禁止修改key
typedef Compare key_compare;
typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type, select1st<value_type>, key_compare, alloc> rep_type;
rep_type t;
typedef typename rep_type::iterator iterator;
}
10、hashtable
template <class Value, // value = key + data
class Key,
class HashFcn,
class ExtractKey, // 从value中获取key
class EqualKey,
class Alloc=alloc>
class hashtable {
typedef HashFcn hasher;
typedef EqualKey key_equal; //sizeof总数19->20
typedef size_t size_type;
hasher hash; // 哈希函数
key_equal equals; // key相等的判断
ExtractKey get_key; // 从value中获取key的方法
typpedef __hashtable_node<Value> node;
vector<node*, alloc> buckets; // 桶个数 sizeof=12
size_type num_elements; // 元素个数 sizeof=4
}
template <class Value>
struct __hashtable_node {
Value val;
__hashtable_node* next;
}
struct __hashtable_iterator {
...
node* cur;
hashtable* ht;
}
// 实际使用方式
hashtable<const char*,
const char*,
hash<const char*>,
identity<const char*>,
eqstr,
alloc>
ht;
struct eqstr {
bool operator()(const char* s1, const char* s2) {
return strcmp(s1, s2) == 0;
}
}
一个万用的hash Function
struct Customer {
std::string fname;
std::string lname;
int no;
}
// 万用的哈希函数
class CustomerHash {
std::size_t operator(const Customer& c) {
return hash_val(c.fname, c.lname, c.no);
}
}
// 哈希函数的实现
// 泛化、特化实现变参函数
template<typename... Types>
inline size_t hash_val(const Types&... args) {
size_t seed = 0;
hash_val(seed, args...);
return seed;
}
template<typename T, typename... Types>
inline void hash_val(size_t& seed, const T& val, const Types&... args) {
hash_combine(seed, val);
hash_val(seed, args...);
}
template<typename T>
inline void hash_val(size_t& seed, const T& val) {
hash_combine(seed, val);
}
// hash_combine实现
template<typename T>
inline void hash_combination(size_t& seed, const T& val) {
seed ^= std::hash<T>()(val) + 0x9e3779b9 + // 0x9e3779b9/ 0x7fffffff = 黄金比例
(seed <<6) + (seed >> 2);
}
实现hash的三种方式
-
写一个hash函数传入容器
-
写一个hash仿函数传入容器
-
实现namespace std内 特化版本的hash<T>仿函数(注意要写namespace std)
11、unordered容器
底层实现:hashtable
12、算法、迭代器
算法的普遍形式
template <typename iterator>
algorithm(iterator i1, iterator i2) {}
template<typename iterator, typename Cmp>
algorithm(iterator i1, iterator i2, Cmp _cmp) {}
// 通过迭代器进行操作
// iterator traits
12.1、迭代器分类
struct input_iterator_tag{}; // istream_iterator
struct output_iterator_tag{}; // ostream_iterator
struct forward_iterator_tag: public input_iterator_tag{};
struct bidirectional_iterator_tag: public forward_iterator_tag{};
struct random_access_iterator_tag: public bidirectional_iterator_tag{};
根据迭代器类型、对算法实现不同的版本
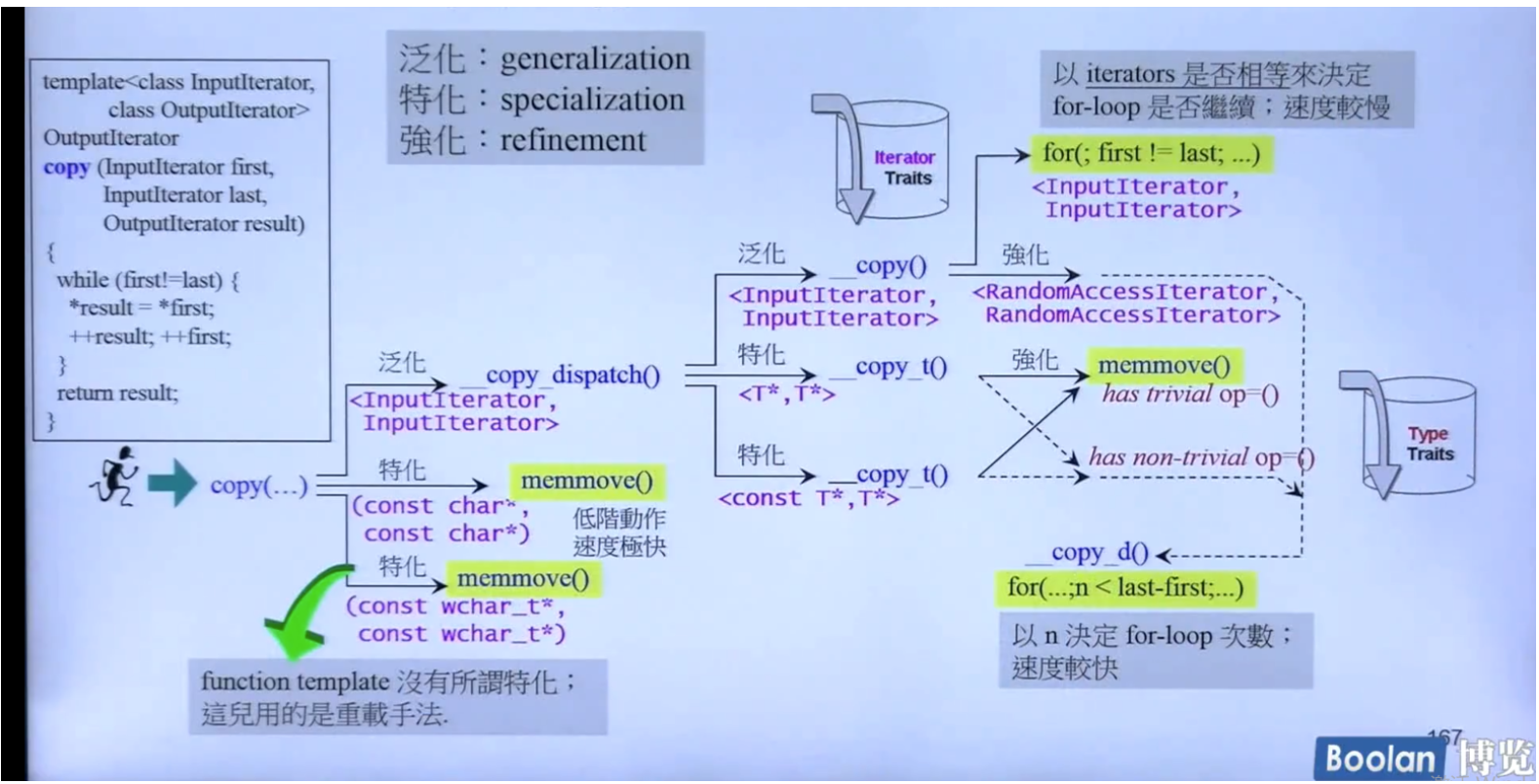
算法对支持的iterator category有"暗示"
12.1 、type traits
G2.9
// 泛化, GCC2.9版本
template <typename type>
stuct __type_traits { // type traits要回答的问题
typedef __true_type this_dummy_member_must_be_first;
typedef __false_type has_trivial_default_constructor;
typedef __false_type has_trivial_copy_constructor;
typedef __false_type has_trivial_assignment_operator;
typedef __false_type has_trivial_destructor;
typedef __false_type is_POD_type; // 是否为基础类型
}
// 偏特化
template<> struct __type_traits<int> {
typedef __true_type has_trivial_default_constructor;
typedef __true_type has_trivial_copy_constructor;
typedef __true_type has_trivial_assignment_operator;
typedef __true_type has_trivial_destructor;
typedef __true_type is_POD_type;
}
template<> struct __type_traits<double> {
typedef __true_type has_trivial_default_constructor;
typedef __true_type has_trivial_copy_constructor;
typedef __true_type has_trivial_assignment_operator;
typedef __true_type has_trivial_destructor;
typedef __true_type is_POD_type;
}
// 用法
type_traits<Foo>::has_trivial_copy_constructor;
// 所以可以给自己的自定义类 设计特化版本
G4.9
// is_void实现
template<typename _Tp>
struct is_void : public __is_void_helper<typename remove_cv<_Tp>::type>::type
{};
template<typename _Tp> is_void_helper : public false_type {};
template<> is_void_helper<void> : public true_type {};
13、仿函数
template<class T> // 类型1
struct plus: public binary_function<T, T, T> {
T operator()(const T& x, const T& y) const {
return x + y;
}
}
template<class T> // 类型2 注意public继承的函数
struct equal_to: public binary_function<T,T, bool> {
bool operator(const T& x, const T& y) const {
return x == y;
}
}
// STL要求仿函数必须继承才能融入STL、
// 不继承当然也可以使用,只是无法融入,不可适配(不能用adaptor)
template<class Arg, class Result>
struct unary_function {
typedef Arg arguement_type;
typedef result_type;
};
template<clas Arg1, class Arg2, class Result>
struct binary_function {
typedef Arg1 first_arguement_type;
typedef Arg2 second+arguement_type;
typedef Result result_type;
}
// 这几个typedef可能会被adaptor用到,这就是必须继承的原因
14、adaptor
换肤工程:包装STL其他的部件(容器、函数、迭代器)
实现方式:内含、非继承
14.1 容器适配器:
stack queue
14.2 函数适配器
binder2and -> bind、not1
std::bind可以绑定:
-
functions
-
function objects
-
member functions, _1必须是object地址
-
data members, _1必须是某个object地址
_1表示占位符,namespace std::placeholders;
using namespace std::placeholders;
double my_divide(double x, double y) {
return x/y;
}
auto fn = bind(my_divide, _1, 2);
cout <<fn(10) << endl; // 5
fn = bind<int>(my_divide, _1, _2);
cout <<fn(10, 3) << endl; // bind<int> 表明返回值为整数
struct MyPair {
double a, b;
double multiply() {return a * b};
}
MyPair p(10, 2)
auto menfn = bind(&MyPair::multiply, _1);
cout <<menfn(p) <<endl;
auto mendata = bind(&MyPair::b, p);
cout <<mendata() <<endl; // 2
count_if(v,begin(), v,end(), bind(less<int>(), _1, 50)); // < 50元素个数
14.3、迭代器适配器
reverse_iterator
reverse_iterator
rbegin() {return reverse_iterator(end());}
reverse_iteraror
rend() {return reverse_iterator(begin());}
template<class Iterator>
class reverse_iterator {
Iterator current; // 对应的正向迭代器
// 逆向迭代器的五中associated types,和正向的一致
typedef typename iterator_traits<Iterator>::iterator_category iterator_category;
typedef typename iterator_traits<Iterator>::value_type value_type;
...;
// 关键
// 逆向迭代器取值 = 正向迭代器 - 1的值
reference operator*() const { Iterator tmp = current; return *--tmp;}
self& operator++() {--current; return *this;}
self& operator--() {++current; return *this;}
}
inserter
template<class Container>
class insert_iterator {
Container* container; // 底层容器
typename Cintainer::iterator iter;
typedef output_iterator_tag iterator_category;
insert_itertor(Container& x, typename Container::iterator i):
container(&x), iter(i) {}
// 关键 重载赋值操作符
insert_iterator<Container>&
operator=(const typename Container::value_type& value) {
iter = container->insert(iter, value);
++iter;
return *this
}
}
使用方式:
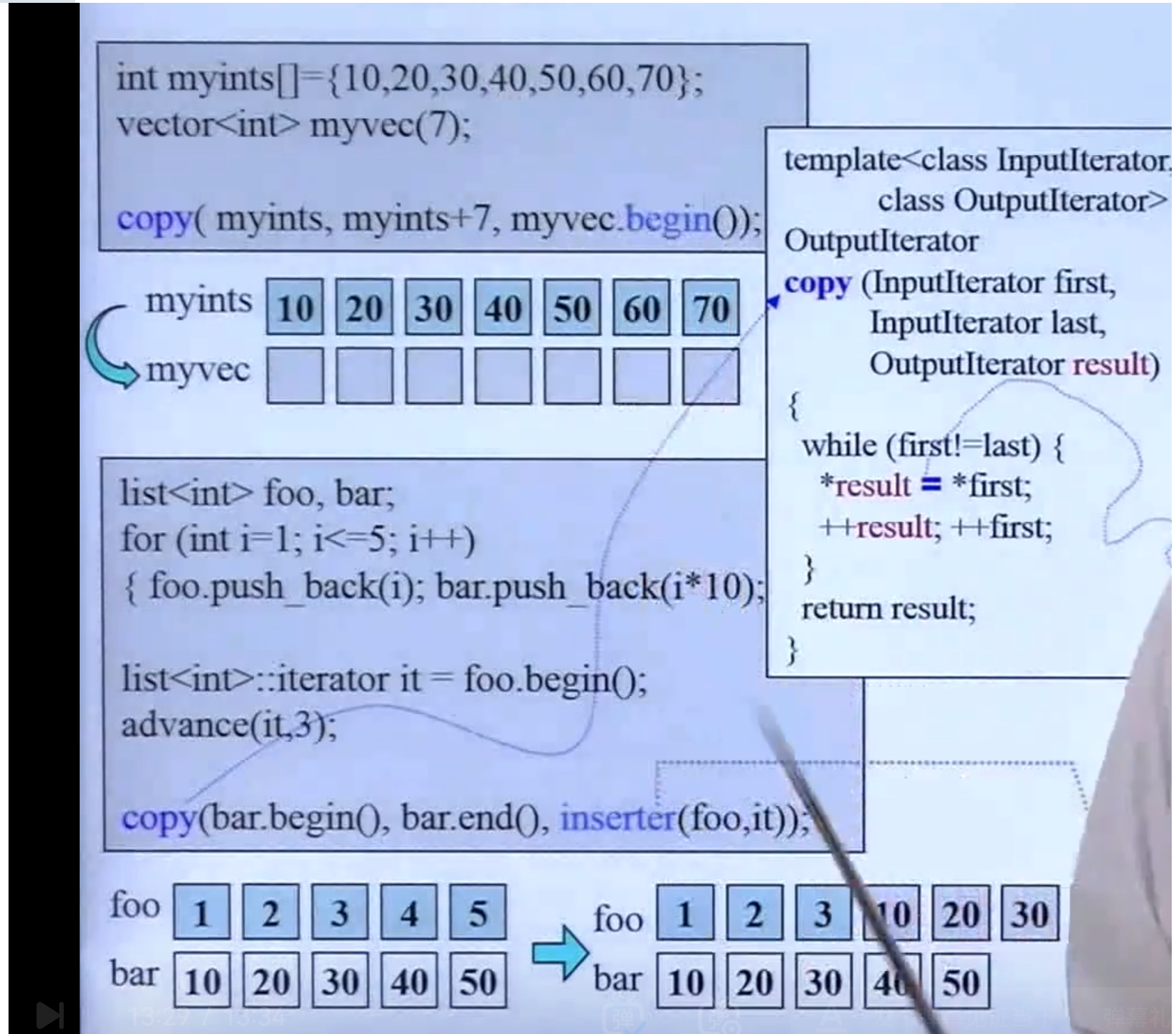
x 适配器:ostream_iterator
使用方式:

实现
template<class T, class charT=char, class traits=char_traits<charT>>
class ostream_iterator: public iterator<output_iterator_tag, void, void, void, void> {
basic_ostream<charT, traits>* out_stream;
const charT* delim;
// 类型定义
typedef charT char_type;
typedef traits traits_type;
typedef basic_ostream<charT, traits> ostream_type;
//构造
ostream_iterator(ostream_type& s):out_stream(&s), delim(0) {}
ostream_iterator(ostream_type&s, const charT* d): out_stream(&s), delim(d) {}
ostream_iterator(const ostream_iter<T, charT, traits>& x): out_stream(x.out_stream), delim(x.delim) {}
//核心重载函数
ostream_iterator<T, charT, traits>& operator=(const T& value) {
*out_stream << value;
if (delim != 0) *cout << delim;
return *this;
}
ostream_iterator<T, charT, traits>& operator*() {return *this};
ostream_iterator<T, charT, traits>& operator++() {return *this};
ostream_iterator<T, charT, traits>& operator++(int) {return *this};
}
x适配器:istream_iterator
使用方法


实现:
template<class T, class charT=char, class traits=char_traits<charT>, class Disrance-ptrdiff_t>
class istream_iterator: public iterator<iutput_iterator_tag, T, Distance, const T*, const T&> {
basic_istream<charT, traits>* in_stream;
T value;
// 类型定义
typedef charT char_type;
typedef traits traits_type;
typedef basic_ostream<charT, traits> istream_type;
//构造
istream_iterator(): in_stream(0) {}
istream_iterator(istream_type& s):in_stream(&s) {++*this}
istream_iterator(const istream_iter<T, charT, traits, Distance>& x): out_stream(x.out_stream), value(x.value) {}
//核心重载函数
istream_iterator<T, charT, traits, Distance>& operator++(const T& value) {
if (in_stream && !(*in_stream >> value)) in_stream = 0;
return *this;
}
const T& operator*() {return value};
const T* operator->() {return &value};
ostream_iterator<T, charT, traits>& operator++(int) {
istream_iterator<T, charT, traits, Distance> tmp = *this;
++*this;
return tmp;
}
}
15、其他
15.1、 tuple
实现方法
// 特化
template<>
class tuple<> {};
// 泛化
template<typename Head, typename... Tail>
class tuple<Head, Tail...> : private tuple<Tail...>
{
typedef tuple<Tail...> inherited;
// 构造
tuple(){}
tuple(Head v, Tail... vtail) : m_head(v), inherited(vtail...) {};
typename Head::type head() {return m_head;}
inherited& tail() {return *this;} // 自己指向自己,改变类型即可
Head m_head;
}
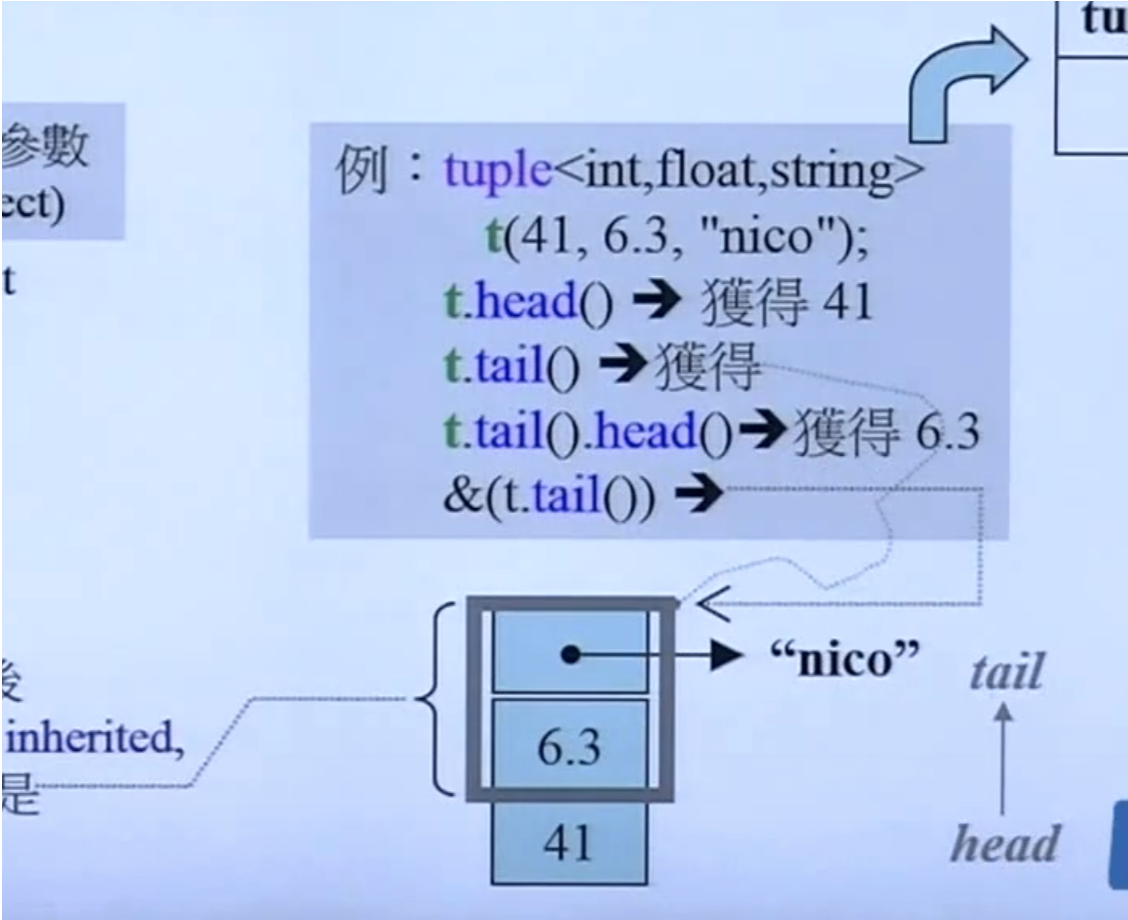
15.2、cout
实现
extern __IO_ostream_withassign cout;
class __IO_ostream_withassgin : public ostream {
public:
__IO_ostream+withassign& operator=(ostream&);
__IO_ostream+withassign& operator=(__IO_ostream_withassgin& rhs) {
rteturn operator=(static_cast<ostream&>(rhs));
}
}
// ostream支持的打印类型
class ostream: virtual public ios {
public:
ostream& operator<<(char c);
ostream& operator<<(int c);
...
}
// 如何让自定义类支持?
// 重载操作符 <<
template<T>
operator<<(basic_ostream&, os, T) {
...
}
15.3、写一个movable的class
-
移动构造函数
-



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号