博弈论之海盗分金
海盗分金
2025/3/7 hdu春季训练赛第一期,签到第三题出了一道经典博弈论之海盗分金,这题过了很多人可能大多数都是知道这个的,所以我觉得有必要补补博弈论的一些经典模型
先看看题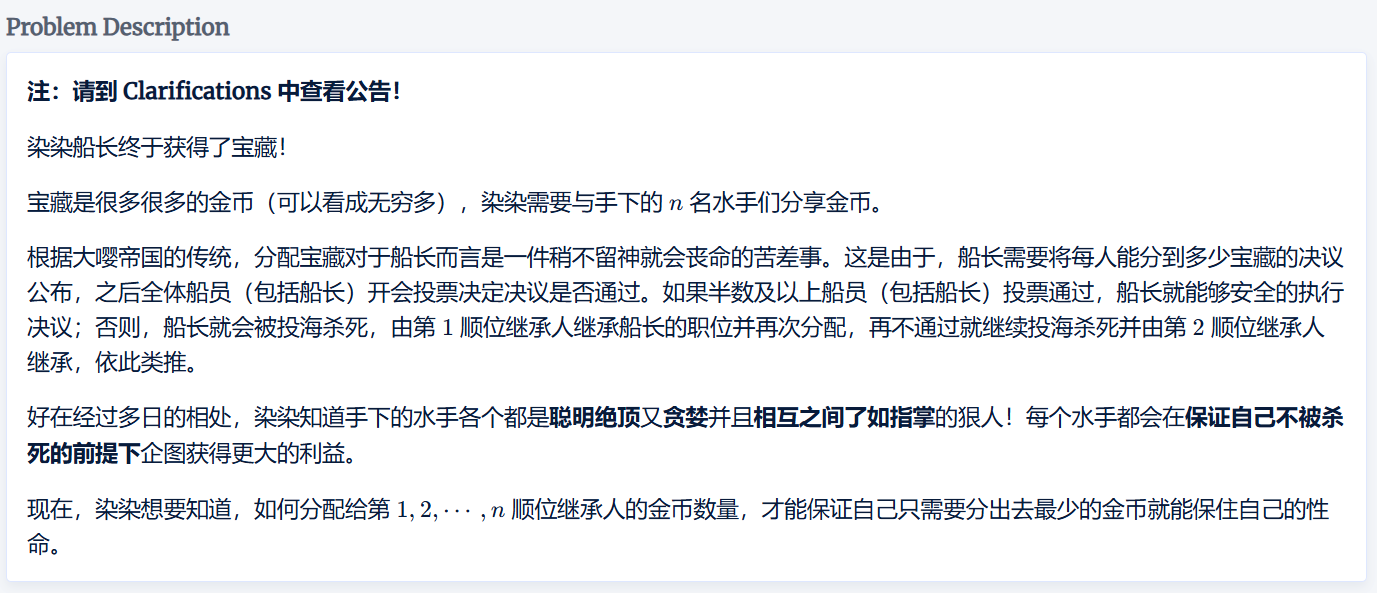
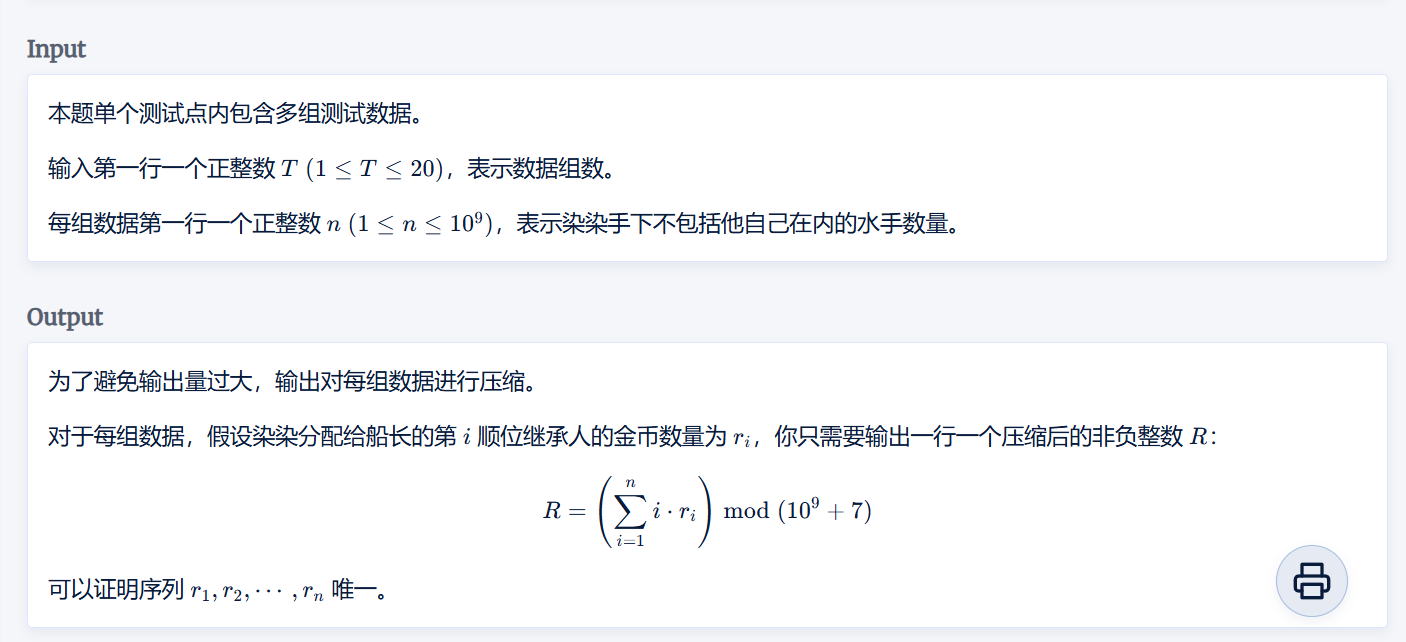
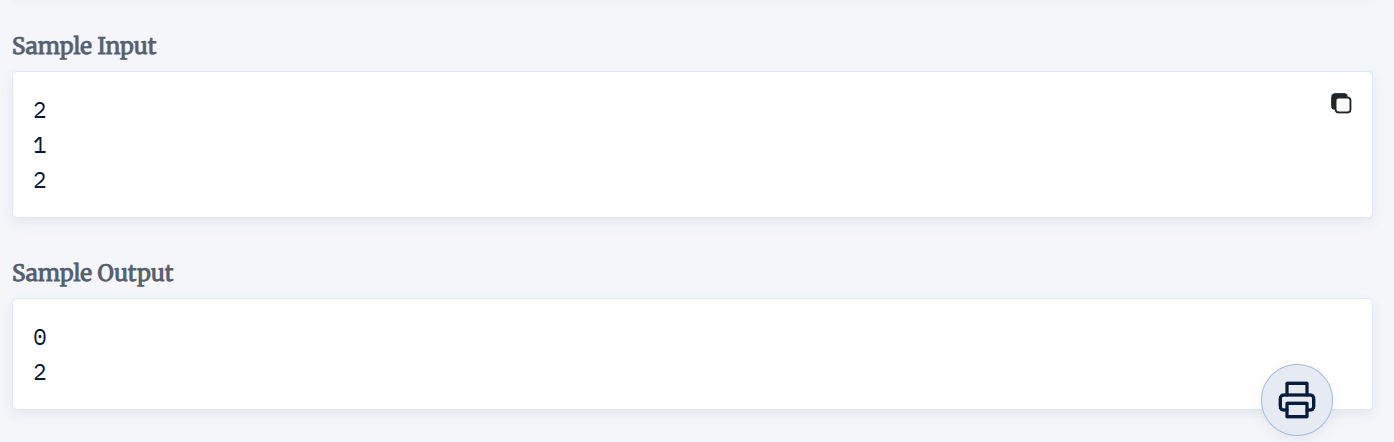
这题在比赛时出现了很多的疑问
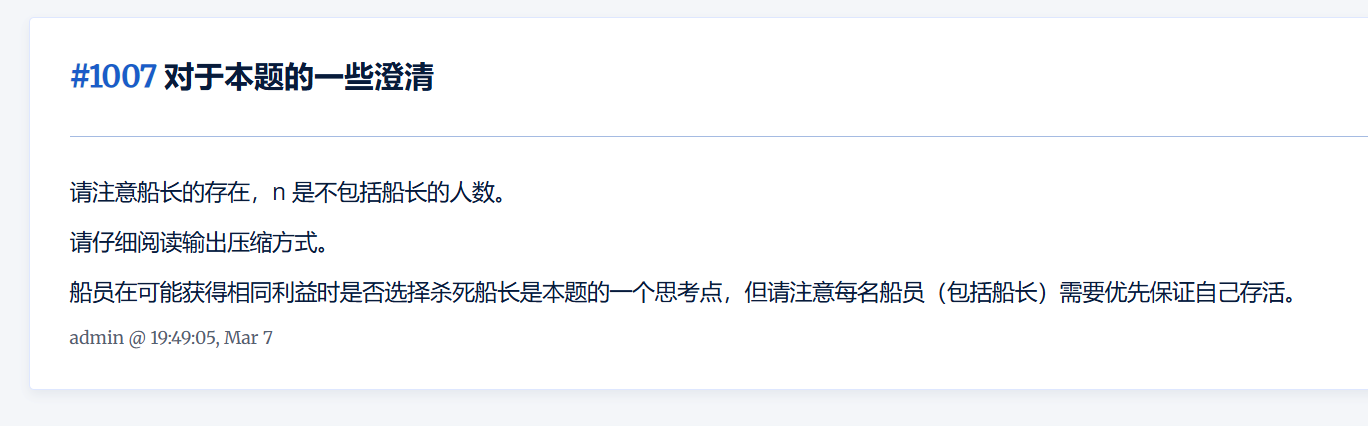
我一开始的想法觉的就应该只给最后一个人一个就行的,或者是都不给,因为如果大家都投了船长的话下一票估计还是找个结局,到最后大家都得go die了,这肯定不符合贪心博弈,但这个推算错估了很重要的一点就是理解错了一题目所说的无限财富,就是比如说这次船长只发了一枚金币,但是如果这任船长go die了以后,到了第二任船长继承的应该是无限财富。
越推到后面我越是想不明白这题是什么思路有种左脑攻击右脑的错觉。
那么正确的思路是什么呢,后面我也发现了这个问题,但是在赛后听到群u在讨论海盗分金这个词,我才反应过来这应该是个博弈论模型,不然不可能过这么多人,但凡当时上网搜搜()。
好了言归正传这题的正确思路是什么,这题的原型是5个海盗分赃100枚金币,就是著名的博弈论原型海盗分金问题。
我们从少往多列举:
如果有两个人的情况下,那么船长肯定私吞所有金币,那么第二个人就算投了反对票依旧无效
如果有三个人的情况下,那么船长就应该给第三个人一个金币,让第三个人投出赞成票,因为如果处死了船长让第二个人拿到船长的决定权肯定会出现上一种情况,第三个人什么也得不到,尽管他知道船长侵占了绝大多数的金币,但也只能忍气吞声。而在第二个人的视角,如果处死船长他就能拿到金币的决定权,所以不管在什么情况下他都会投反对票,所以船长的视角下这票是不可能争取得到的,在往后的所有情况中都不会分给第二个人任何一枚金币。
那么如果有四个人的情况下,肯定不会给第二个人任何一枚金币,那么就要再争取到一个人的同意,而这个人就是第三个人,因为如果轮到第二个人掌管金币就不会给他任何一枚金币,那么最后的情况就是 99 0 1 0
那么如果有五个人的情况下呢,还是不会给第二个人任何一枚金币,那么就得争取到两个人的同意,其中的一个人应该是第三个人,逻辑和上面的相同,那么还有个人应该是最后一个人,因为如果让在四个人的情况下他是拿不到金币的,那么最后的情况就是 98 0 1 0 1
那么如果往外推的话就是在给在人数-1的情况下没拿到金币的人一枚金币就是他的最优解
接下来的情况应该就是:
6 : 98 0 1 0 1 0
7: 97 0 1 0 1 0 1
8 : 97 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
.......
那么再来看回来这道题就会变得异常简单,给出去的金币数量就是(n - 2) / 2(n是没算上船长的情况下,也是原题的n)
原题要求输出的是每个船员的下标然后除余,那么就是从2开始加到n,那么设置k = n / 2,ans = 2 * k + k* (k - 1) = k * (k + 1)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const char nl = '\n';
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
using i64 = unsigned long long;
using i32 = unsigned;
using i128 = unsigned __int128;
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
template<class T>
constexpr T power(T a, i64 b) {
T res = 1;
for (; b; b /= 2, a *= a) {
if (b % 2) {
res *= a;
}
}
return res;
}
constexpr i64 mul(i64 a, i64 b, i64 p) {
i64 res = a * b - i64(1.L * a * b / p) * p;
res %= p;
if (res < 0) {
res += p;
}
return res;
}
template<i64 P>
struct MLong {
i64 x;
constexpr MLong() : x{} {}
constexpr MLong(i64 x) : x{norm(x % getMod())} {}
static i64 Mod;
constexpr static i64 getMod() {
if (P > 0) {
return P;
} else {
return Mod;
}
}
constexpr static void setMod(i64 Mod_) {
Mod = Mod_;
}
constexpr i64 norm(i64 x) const {
if (x < 0) {
x += getMod();
}
if (x >= getMod()) {
x -= getMod();
}
return x;
}
constexpr i64 val() const {
return x;
}
explicit constexpr operator i64() const {
return x;
}
constexpr MLong operator-() const {
MLong res;
res.x = norm(getMod() - x);
return res;
}
constexpr MLong inv() const {
assert(x != 0);
return power(*this, getMod() - 2);
}
constexpr MLong &operator*=(MLong rhs) & {
x = mul(x, rhs.x, getMod());
return *this;
}
constexpr MLong &operator+=(MLong rhs) & {
x = norm(x + rhs.x);
return *this;
}
constexpr MLong &operator-=(MLong rhs) & {
x = norm(x - rhs.x);
return *this;
}
constexpr MLong &operator/=(MLong rhs) & {
return *this *= rhs.inv();
}
friend constexpr MLong operator*(MLong lhs, MLong rhs) {
MLong res = lhs;
res *= rhs;
return res;
}
friend constexpr MLong operator+(MLong lhs, MLong rhs) {
MLong res = lhs;
res += rhs;
return res;
}
friend constexpr MLong operator-(MLong lhs, MLong rhs) {
MLong res = lhs;
res -= rhs;
return res;
}
friend constexpr MLong operator/(MLong lhs, MLong rhs) {
MLong res = lhs;
res /= rhs;
return res;
}
friend constexpr istream &operator>>(istream &is, MLong &a) {
i64 v;
is >> v;
a = MLong(v);
return is;
}
friend constexpr ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const MLong &a) {
return os << a.val();
}
friend constexpr bool operator==(MLong lhs, MLong rhs) {
return lhs.val() == rhs.val();
}
friend constexpr bool operator!=(MLong lhs, MLong rhs) {
return lhs.val() != rhs.val();
}
};
template<>
i64 MLong<0LL>::Mod = i64(1E18) + 9;
template<int P>
struct MInt {
int x;
constexpr MInt() : x{} {}
constexpr MInt(i64 x) : x{norm(x % getMod())} {}
static int Mod;
constexpr static int getMod() {
if (P > 0) {
return P;
} else {
return Mod;
}
}
constexpr static void setMod(int Mod_) {
Mod = Mod_;
}
constexpr int norm(int x) const {
if (x < 0) {
x += getMod();
}
if (x >= getMod()) {
x -= getMod();
}
return x;
}
constexpr int val() const {
return x;
}
explicit constexpr operator int() const {
return x;
}
constexpr MInt operator-() const {
MInt res;
res.x = norm(getMod() - x);
return res;
}
constexpr MInt inv() const {
assert(x != 0);
return power(*this, getMod() - 2);
}
constexpr MInt &operator*=(MInt rhs) & {
x = 1LL * x * rhs.x % getMod();
return *this;
}
constexpr MInt &operator+=(MInt rhs) & {
x = norm(x + rhs.x);
return *this;
}
constexpr MInt &operator-=(MInt rhs) & {
x = norm(x - rhs.x);
return *this;
}
constexpr MInt &operator/=(MInt rhs) & {
return *this *= rhs.inv();
}
friend constexpr MInt operator*(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) {
MInt res = lhs;
res *= rhs;
return res;
}
friend constexpr MInt operator+(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) {
MInt res = lhs;
res += rhs;
return res;
}
friend constexpr MInt operator-(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) {
MInt res = lhs;
res -= rhs;
return res;
}
friend constexpr MInt operator/(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) {
MInt res = lhs;
res /= rhs;
return res;
}
friend constexpr istream &operator>>(istream &is, MInt &a) {
i64 v;
is >> v;
a = MInt(v);
return is;
}
friend constexpr ostream &operator<<(ostream &os, const MInt &a) {
return os << a.val();
}
friend constexpr bool operator==(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) {
return lhs.val() == rhs.val();
}
friend constexpr bool operator!=(MInt lhs, MInt rhs) {
return lhs.val() != rhs.val();
}
};
template<>
int MInt<0>::Mod = 998244353;
template<int V, int P>
constexpr MInt<P> CInv = MInt<P>(V).inv();
constexpr int P = 1000000007;
using Z = MInt <P>;
void solve(){
ll n;
cin >> n;
if(n == 1){
cout << 0 << nl;
return;
}
Z ans = 0;//当然你可以直接取余
ll k = n / 2;
ans = k * (k + 1);
cout << ans << nl;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号