sendfile splice tee函数
今天在做吞吐性能优化时,涉及到了零拷贝的问题, 以前只是用sendfile 或者mmap。今天系统的看下总公有哪些零拷贝API以及使用场景。
常见的拷贝优化方案
memory mapping
shared buffers in kernel memory space
shared buffers between user and kernel space
different system calls, sendfile, splice, etc
sendfile with DMA Scatter/Gather copy
mmap 内存映射
内存映射(mmap)是指用户空间和内核空间的虚拟内存地址同时映射到同一块物理内存,用户态进程可以直接操作物理内存,避免用户空间和内核空间之间的数据拷贝。
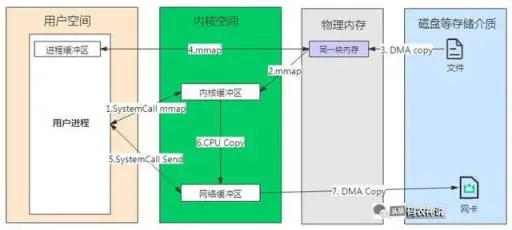
- 用户进程通过系统调用 mmap 函数进入内核态,发生第 1 次上下文切换,并建立内核缓冲区;
- 发生缺页中断,CPU 通知 DMA 读取数据;
- DMA 拷贝数据到物理内存,并建立内核缓冲区和物理内存的映射关系;
- 建立用户空间的进程缓冲区和同一块物理内存的映射关系,由内核态转变为用户态,发生第 2 次上下文切换;
- 用户进程进行逻辑处理后,通过系统调用 Socket send,用户态进入内核态,发生第 3 次上下文切换;
- 系统调用 Send 创建网络缓冲区,并拷贝内核读缓冲区数据;
- DMA 控制器将网络缓冲区的数据发送网卡,并返回,由内核态进入用户态,发生第 4 次上下文切换;
总结
-
避免了内核空间和用户空间的 2 次 CPU 拷贝,但增加了 1 次内核空间的 CPU 拷贝,整体上相当于只减少了 1 次 CPU 拷贝;
-
针对大文件比较适合 mmap,小文件则会造成较多的内存碎片,得不偿失;
-
当 mmap 一个文件时,如果文件被另一个进程截获可能会因为非法访问导致进程被 SIGBUS 信号终止;
sendfile api:
只需要 2 次上下文切换和 1 次内核 CPU 拷贝、2 次 DMA 拷贝
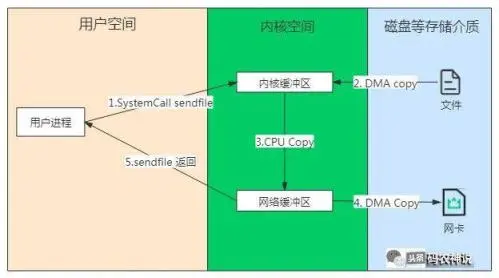
-
用户进程系统调用 senfile,由用户态进入内核态,发生第 1 次上下文切换;
-
CPU 通知 DMA 控制器把文件数据拷贝到内核缓冲区;
-
把内核缓冲区地址和 sendfile 的相关参数作为数据描述信息存在网络缓冲区中;
-
CPU 通知 DMA 控制器,DMA 根据网络缓冲区中的数据描述截取数据并发送;
-
sendfile 系统调用结束并返回,进程由内核态进入用户态,发生第 2 次上下文切换;
总结
-
需要硬件支持,如 DMA;
-
整个过程 2 次上下文切换,0 次 CPU 拷贝,2 次 DMA 拷贝,实现真正意义上的零拷贝;
-
依然不能修改数据;
注意:sendfile() copies data between one file descriptor and another.
Because
this copying is done within the kernel, sendfile() is more efficient
than the combination of read(2) and write(2), which would require
transferring data to and from user space.
in_fd should be a file descriptor opened for reading and out_fd should be a descriptor opened for writing.
If offset is not NULL,
then it points to a variable holding the file offset from which
sendfile() will start reading data from in_fd. When sendfile() returns,
this variable will be set to the offset of the byte following the
last byte that was read. If offset is not NULL, then sendfile() does
not modify the file offset of in_fd; otherwise the file offset is
adjusted to reflect the number of bytes read from in_fd.
If offset is NULL, then data will be read from in_fd starting at the file offset, and the file offset will be updated by the call.
count is the number of bytes to copy between the file descriptors.
The in_fd argument must correspond to a file which supports mmap(2)-like operations (i.e., it cannot be a socket).
In
Linux kernels before 2.6.33, out_fd must refer to a socket. Since
Linux 2.6.33 it can be any file. If it is a regular file, then
sendfile() changes the file offset appropriately.
sendfile+DMA gather
Linux2.4对sendfile进行了优化,为DMA控制器引入了gather功能,就是在不拷贝数据到网络缓冲区,而是将待发送数据的内存地址和偏移量等描述信息存在网络缓冲区,DMA根据描述信息从内核的读缓冲区截取数据并发送。它的流程是如下

- 用户进程系统调用senfile,由用户态进入内核态,发生第1次上下文切换;
- CPU通知DMA控制器把文件数据拷贝到内核缓冲区;
- 把内核缓冲区地址和sendfile的相关参数作为数据描述信息存在网络缓冲区中;
- CPU通知DMA控制器,DMA根据网络缓冲区中的数据描述截取数据并发送;
- sendfile系统调用结束并返回,进程由内核态进入用户态,发生第2次上下文切换;
总结
- 需要硬件支持,如DMA;
- 整个过程2次上下文切换,0次CPU拷贝,2次DMA拷贝,实现真正意义上的零拷贝;
- 依然不能修改数据;
splice api
鉴于 Sendfile 的缺点,在 Linux2.6.17 中引入了 Splice,它在读缓冲区和网络操作缓冲区之间建立管道避免 CPU 拷贝:先将文件读入到内核缓冲区,然后再与内核网络缓冲区建立管道
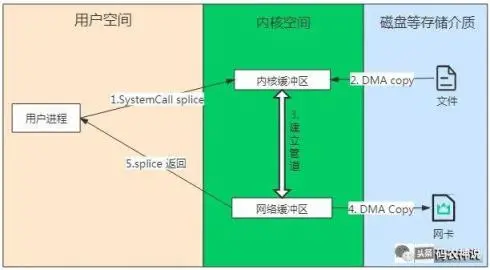
-
用户进程系统调用 splice,由用户态进入内核态,发生第 1 次上下文切换;
-
CPU 通知 DMA 控制器把文件数据拷贝到内核缓冲区;
-
建立内核缓冲区和网络缓冲区的管道;
-
CPU 通知 DMA 控制器,DMA 从管道读取数据并发送;
-
splice 系统调用结束并返回,进程由内核态进入用户态,发生第 2 次上下文切换;
总结
-
整个过程 2 次上下文切换,0 次 CPU 拷贝,2 次 DMA 拷贝,实现真正意义上的零拷贝;
-
依然不能修改数据;
-
fd_in 和 fd_out 必须有一个是管道;
splice() moves data between two file descriptors without copying between kernel address space and user address space. It transfers up to len bytes of data from the file descriptor fd_in to the file descriptor fd_out, where one of the file descriptors must refer to a pipe.
The following semantics apply for fd_in and off_in:
* If fd_in refers to a pipe, then off_in must be NULL.
* If fd_in does not refer to a pipe and off_in is NULL, then bytes are read from fd_in starting from the file offset, and the file offset is adjusted appropriately.
* If fd_in does not refer to a pipe and off_in is not NULL, then off_in must point to a buffer which specifies the starting offset from which bytes will be read from fd_in; in this case, the file offset of fd_in is not changed.
Analogous statements apply for fd_out and off_out.
The flags argument is a bit mask that is composed by ORing together zero or more of the following values:
SPLICE_F_MOVE
Attempt to move pages instead of copying. This is only a hint to the kernel: pages may still be copied if the kernel cannot move the pages from the pipe, or if the pipe buffers don't refer to full pages. The ini‐
tial implementation of this flag was buggy: therefore starting in Linux 2.6.21 it is a no-op (but is still permitted in a splice() call); in the future, a correct implementation may be restored.
SPLICE_F_NONBLOCK
Do not block on I/O. This makes the splice pipe operations nonblocking, but splice() may nevertheless block because the file descriptors that are spliced to/from may block (unless they have the O_NONBLOCK flag set).
SPLICE_F_MORE
More data will be coming in a subsequent splice. This is a helpful hint when the fd_out refers to a socket (see also the description of MSG_MORE in send(2), and the description of TCP_CORK in tcp(7)).
tee api
tee 与 splice 类同,但 fd_in 和 fd_out 都必须是管道。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号