Guava包中的比较器(-)
Java中经常对集合排序,既然是排序那么肯定有比较字段,Guava中提供了一下比较器;
1. ComparisonChain
在我们写类实现Comparable接口覆写compareTo方法时候就避免写大量的if-else,guava包中的ComparisonChain就可以简化实现,并且有更清晰的逻辑;废话不说,直接展示代码:
package com.zl.guava.comparison; import com.google.common.collect.ComparisonChain; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; /** * 对象之间的比较 * * @author zhanglei * @ProjectName: MapDemo * @create 2019-07-24 18:27 * @Version: 1.0 * <p>Copyright: Copyright (zl) 2019</p> **/ @Getter @Setter public class Person implements Comparable<Person> { private String name; private Integer age; /** * @return int * @throws * @Description ComparisonChain执行一种懒比较:它执行比较操作直至发现非零的结果,在那之后的比较输入将被忽略。 * @Author zhanglei * @Date 18:42 2019/7/24 * @Param [that] **/ @Override public int compareTo(Person that) { return ComparisonChain.start() .compare(this.age, that.age) .compare(this.name, that.name).result(); } }
2.Ordering
它非常容易扩展,可以轻松构造复杂的comparator,然后用在容器的比较、排序等操作中;比如现在有学生的一个集合List,之前是通过age排序,现在想通过名称排序,通过Ordering可以更简便实现,代码如下:
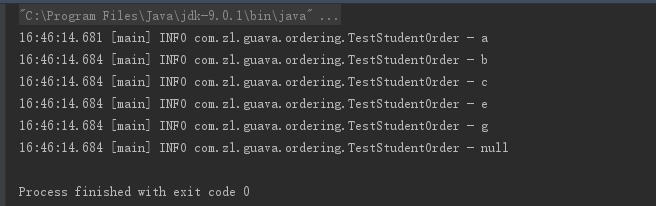
package com.zl.guava.ordering; import com.google.common.base.Function; import com.google.common.collect.Lists; import com.google.common.collect.Ordering; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import javax.annotation.Nullable; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; /** * @author zhanglei * @ProjectName: MapDemo * @create 2019-07-26 15:54 * @Version: 1.0 * <p>Copyright: Copyright (zl) 2019</p> **/ @Slf4j public class TestStudentOrder { public static void main(String[] args) { Ordering<Student> ordering = Ordering.natural().nullsLast().onResultOf(new Function<Student, Comparable>() { @Nullable @Override public Comparable apply(@Nullable Student student) { return student.getSortedBy(); } }); List<Student> studentList = Lists.newArrayList(new Student("a"), new Student("c"), new Student("b"), new Student("g"), new Student("e"), new Student(null)); Collections.sort(studentList, ordering); studentList.forEach(item -> log.info(item.getSortedBy())); } }
排序器的创建方法:
Ordering.natural(); || 自然排序,数字按照大小,日期按照时间...
Ordering.usingToString(); 按对象的字符串形式做字典排序
Ordering.from(); 把给定的Comparator转化为排序器
链式调用方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
| nullsLast() | 空值排到最后 |
| onResultOf(Function) | 对集合中元素调用Function,再按返回值用当前排序器排序 |
| compound(Comparator) | 合成另一个比较器,以处理当前排序器中的相等情况 |
即:
Ordering<Student> ordering = Ordering.natural().nullsLast().onResultOf(new Function<Student, Comparable>() {
@Nullable
@Override
public Comparable apply(@Nullable Student student) {
return student.getSortedBy();
}
});
代码可解释为:按照自然排序生成一个排序比较器,并且将空值放在排序的最后,排序比较的对象是Student的中的sortedBy字段;
排序结果: ![]()
我们曾如此渴望生命的波澜,到后来才发现,人生最曼妙的风景是内心的淡定与从容


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号