[LeetCode] 588. Design In-Memory File System
Design a data structure that simulates an in-memory file system.
Implement the FileSystem class:
FileSystem()Initializes the object of the system.List<String> ls(String path)- If
pathis a file path, returns a list that only contains this file's name. - If
pathis a directory path, returns the list of file and directory names in this directory.
- If
void mkdir(String path)Makes a new directory according to the givenpath. The given directory path does not exist. If the middle directories in the path do not exist, you should create them as well.void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content)- If
filePathdoes not exist, creates that file containing givencontent. - If
filePathalready exists, appends the givencontentto original content.
- If
String readContentFromFile(String filePath)Returns the content in the file atfilePath.
Example 1:
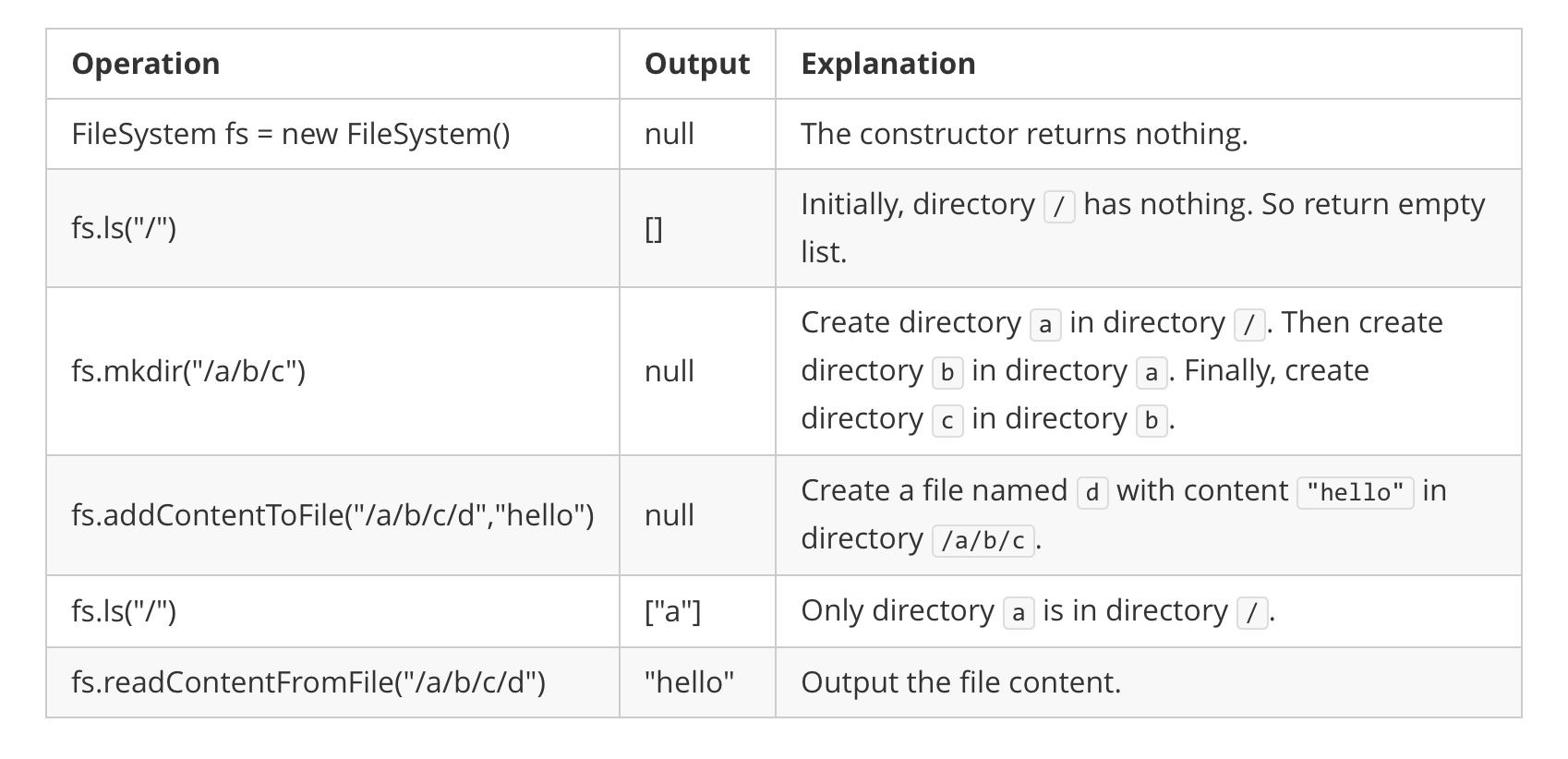
Input
["FileSystem", "ls", "mkdir", "addContentToFile", "ls", "readContentFromFile"]
[[], ["/"], ["/a/b/c"], ["/a/b/c/d", "hello"], ["/"], ["/a/b/c/d"]]
Output
[null, [], null, null, ["a"], "hello"]
Explanation
FileSystem fileSystem = new FileSystem();
fileSystem.ls("/"); // return []
fileSystem.mkdir("/a/b/c");
fileSystem.addContentToFile("/a/b/c/d", "hello");
fileSystem.ls("/"); // return ["a"]
fileSystem.readContentFromFile("/a/b/c/d"); // return "hello"
Constraints:
1 <= path.length, filePath.length <= 100pathandfilePathare absolute paths which begin with'/'and do not end with'/'except that the path is just"/".- You can assume that all directory names and file names only contain lowercase letters, and the same names will not exist in the same directory.
- You can assume that all operations will be passed valid parameters, and users will not attempt to retrieve file content or list a directory or file that does not exist.
1 <= content.length <= 50- At most
300calls will be made tols,mkdir,addContentToFile, andreadContentFromFile.
设计内存文件系统。
Java实现
1 class FileSystem { 2 private class FileNode { 3 private TreeMap<String, FileNode> children; 4 private StringBuilder file; 5 private String name; 6 7 public FileNode(String name) { 8 children = new TreeMap<>(); 9 file = new StringBuilder(); 10 this.name = name; 11 } 12 13 public String getContent() { 14 return file.toString(); 15 } 16 17 public String getName() { 18 return name; 19 } 20 21 public void addContent(String content) { 22 file.append(content); 23 } 24 25 public boolean isFile() { 26 return file.length() > 0; 27 } 28 29 public List<String> getList() { 30 List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 31 if (isFile()) { 32 list.add(getName()); 33 } else { 34 list.addAll(children.keySet()); 35 } 36 return list; 37 } 38 } 39 40 private FileNode root; 41 42 public FileSystem() { 43 root = new FileNode(""); 44 } 45 46 public List<String> ls(String path) { 47 return findNode(path).getList(); 48 } 49 50 public void mkdir(String path) { 51 findNode(path); 52 } 53 54 public void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content) { 55 findNode(filePath).addContent(content); 56 } 57 58 public String readContentFromFile(String filePath) { 59 return findNode(filePath).getContent(); 60 } 61 62 private FileNode findNode(String path) { 63 String[] files = path.split("/"); 64 FileNode cur = root; 65 for (String file : files) { 66 if (file.length() == 0) { 67 continue; 68 } 69 cur.children.putIfAbsent(file, new FileNode(file)); 70 cur = cur.children.get(file); 71 if (cur.isFile()) { 72 break; 73 } 74 } 75 return cur; 76 } 77 } 78 79 /** 80 * Your FileSystem object will be instantiated and called as such: 81 * FileSystem obj = new FileSystem(); 82 * List<String> param_1 = obj.ls(path); 83 * obj.mkdir(path); 84 * obj.addContentToFile(filePath,content); 85 * String param_4 = obj.readContentFromFile(filePath); 86 */



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号