一、Executor线程池工具类
Executor框架提供了各种类型的线程池,主要有以下工厂方法:
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() public static ScheduledExecutorService newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize)
以上工厂方法分别返回具有不同工作特性的线程池。这些线程池工厂方法的具体说明如下。
- newFixedThreadPool()方法:该方法返回一个固定线程数量的线程池。该线程池中的线程数量始终不变。当有一个新的任务提交时,线程池中若有空闲线程,则立即执行。若没有,则新的任务会被暂存在一个任务队列中,待有线程空闲时,便处理在任务队列中的任务。
- newSingleThreadExecutor()方法:该方法返回一个只有一个线程的线程池。若多余一个任务被提交到该线程池,任务会被保存在一个任务队列中,待线程空闲,按先入先出的顺序执行队列中的任务。
- newCachedThreadPool()方法:该方法返回一个可根据实际情况调整线程数量的线程池。线程池的线程数量不确定,但若有空闲线程可以复用,则会优先使用可复用的线程。若所有线程均在工作,又有新的任务提交,则会创建新的线程处理任务。所有线程在当前任务执行完毕后,将返回线程池进行复用。
- newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor()方法:该方法返回一个ScheduledExecutorService对象,线程池大小为1。ScheduledExecutorService接口在ExecutorService接口之上扩展了在给定时间执行某任务的功能,如在某个固定的延时之后执行,或者周期性执行某个任务。
- newScheduledThreadPool()方法:该方法也返回一个ScheduledExecutorService对象,但该线程池可以指定线程数量。
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MyThread my = new MyThread(); ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); // ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { executor.submit(my); } System.out.println("fire..."); executor.shutdown(); }
public class MyThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(5000L); System.out.println("current Thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()+ ",yoxi,timestamp:" + (System.currentTimeMillis()/1000) + "sec"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { } } }
控制台打印:
fire...
current Thread11,yoxi,timestamp:1563269559sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1563269559sec
current Thread12,yoxi,timestamp:1563269559sec
current Thread14,yoxi,timestamp:1563269559sec
current Thread10,yoxi,timestamp:1563269559sec
current Thread14,yoxi,timestamp:1563269564sec
current Thread11,yoxi,timestamp:1563269564sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1563269564sec
current Thread12,yoxi,timestamp:1563269564sec
换成newCachedThreadPool()则打印
current Thread10,yoxi,timestamp:1563269661sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1563269661sec
current Thread17,yoxi,timestamp:1563269661sec
current Thread16,yoxi,timestamp:1563269661sec
current Thread18,yoxi,timestamp:1563269661sec
current Thread15,yoxi,timestamp:1563269661sec
current Thread12,yoxi,timestamp:1563269661sec
current Thread11,yoxi,timestamp:1563269661sec
current Thread14,yoxi,timestamp:1563269661sec
二、计划任务
主要方法如下:
public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command,long delay, TimeUnit unit); public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long period, TimeUnit unit); public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, long initialDelay, long delay, TimeUnit unit);
方法schedule()会在给定时间,对任务进行一次调度。方法scheduleAtFixedRate()和scheduleWithFixedDelay()会对任务进行周期性的调度。但是两者有一点小小的区别,如图3.5所示。
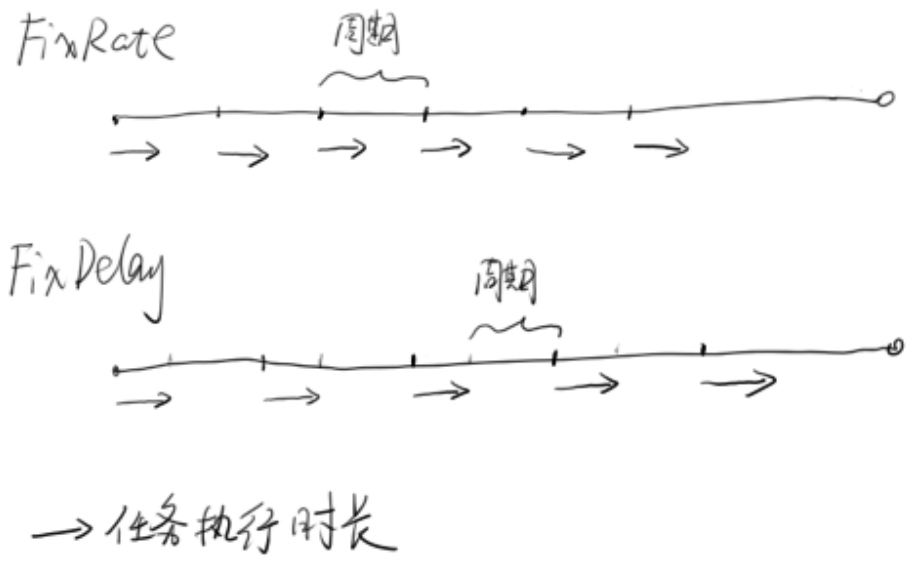
图3.5 FixedRate和FixDelay区别
对于FixedRate方式来说,任务调度的频率是一定的。它是以上一个任务开始执行时间为起点,之后的period时间,调度下一次任务。而FixDelay则是在上一个任务结束后,再经过delay时间进行任务调度。
下面的例子使用scheduleAtFixedRate()方法调度一个任务。这个任务会执行8秒钟时间,调度周期是2秒。也就是说每2秒钟,任务就会被执行一次。这个任务会执行8秒钟时间,任务的执行时间超过调度时间,任务不会堆叠出现,周期如果太短,那么任务就会在上一个任务结束后,立即被调用。
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); //Runnable executor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(10000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("current Thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()+ ",yoxi,timestamp:" + (System.currentTimeMillis()/1000) + "sec"); } }, 0, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
执行结果:
current Thread10,yoxi,timestamp:1596270553sec
current Thread10,yoxi,timestamp:1596270561sec
current Thread12,yoxi,timestamp:1596270569sec
current Thread10,yoxi,timestamp:1596270577sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1596270585sec
current Thread12,yoxi,timestamp:1596270593sec
current Thread14,yoxi,timestamp:1596270601sec
current Thread14,yoxi,timestamp:1596270609sec
current Thread14,yoxi,timestamp:1596270617sec
scheduleWithFixedDelay(),并且按照修改8秒,调度周期2秒计,那么任务的实际间隔将是10秒
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5); //Runnable executor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(8000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("current Thread" + Thread.currentThread().getId()+ ",yoxi,timestamp:" + (System.currentTimeMillis()/1000) + "sec"); } }, 0, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
执行结果:
current Thread10,yoxi,timestamp:1596270272sec
current Thread10,yoxi,timestamp:1596270282sec
current Thread12,yoxi,timestamp:1596270292sec
current Thread10,yoxi,timestamp:1596270302sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1596270312sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1596270322sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1596270332sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1596270342sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1596270352sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1596270362sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1596270372sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1596270382sec
current Thread13,yoxi,timestamp:1596270392sec

