AOP实现接口日志记录
需求
需要通过日志记录接口调用信息。便于后期调试排查。并且可能有很多接口都需要进行日志的记录。
接口被调用时日志打印格式如下:

思路分析
相当于是对原有的功能进行增强。并且是批量的增强,这个时候就非常适合用AOP来进行实现。
日志打印格式
log.info("=======Start=======");
// 打印请求 URL
log.info("URL : {}",);
// 打印描述信息
log.info("BusinessName : {}", );
// 打印 Http method
log.info("HTTP Method : {}", );
// 打印调用 controller 的全路径以及执行方法
log.info("Class Method : {}.{}", );
// 打印请求的 IP
log.info("IP : {}",);
// 打印请求入参
log.info("Request Args : {}",);
// 打印出参
log.info("Response : {}", );
// 结束后换行
log.info("=======End=======" + System.lineSeparator());
AOP
我们都知道使用AOP,要一个切面类,其中的切点是需要指定的,这里指定切点有两种方式:切面表达式和自定义注解,我们当然是用注解这种简单的方式辣。
1.创建自定义注解
自定义注解包括元注解和@Interface组成,也就是我们只要有元注解和@Interface修饰的接口那么我们的就是一个自定义的一个注解
详情请看:www.cnblogs.com/zpKang/p/15261318.html
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) //指定目标作用范围
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//注解保证在RUNTIME阶段
public @interface SystemLog {
String businessName();
}
这里@Target(ElementType.METHOD)为什么是作用到方法上呢,因为标注到Controller中的一个方法上,就代表它是收到我们的AOP切面所增强的
2.在要打印日志的接口上加上自定义注解
//更新个人信息
@PutMapping("/userInfo")
@SystemLog(businessName = "更新用户信息")
public ResponseResult updateUserInfo(@RequestBody User user){
return userService.updateUserInfo(user);
}
3.创建切面类
关于AOP的一些概念:
- JoinPoint(连接点):所谓连接点是指那些可以被增强到的点。在spring中,这些点指的是方法,因为spring只支持方法类型的连接点
- Pointcut(切入点):所谓切入点是指被增强的连接点(方法)
- Advice(通知/增强)︰所谓通知是指具体增强的代码
- Target(目标对象):被增强的对象就是目标对象
- Aspect(切面)︰是切入点和通知(引介)的结合
- Proxy(代理):一个类被AOP增强后,就产生一个结果代理类
1.切面加入到容器需要@Component标识
2.标注它是一个切面类@Aspect
3.切面类=切点(被增强的方法)+通知(增强的方法,怎么去增强)
4.用@PointCut指定切点,参数是自定义注解的全路径(只要加上自定义注解就标识要进行日志接口的打印)
5.定义通知方法 使用通知的注解(这里使用 @Around("pt()"))指定切点是哪一个(参数是方法名)
6.通知方法的参数 就是连接点JoinPoint(可以看成被增强方法的信息封装出来的对象)
7.通过ProceedingJointPoint对象调用proceed方法,(proceed方法的调用就相当于目标方法的调用 , )
8.proceed方法调用的返回值作为切面的返回值,proceed是需要异常处理(使用try catch是因为不经过统一异常处理的)的所以进行try finally(使用finally是因为输出最后的日志信息)操作并且给方法抛出异常
9.在执行目标方法(proceed)之前打印一些日志信息,封装成一个方法
10.在执行方法(proceed)之后打印一些日志细心你,封装成一个方法
11.通过RequestContextHolder对象的getRequestAttributes()方法返回一个接口实现类对象ServletRequestAttributes对象的getRequest()方法获取request
12.在相应的Controller的方法上加上自定义注解并注定属性信息
13.获取被增强方法上的注解对象
package com.mrs.aspect;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.mrs.annotation.SystemLog;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
/**
* description: LogAspect
* date: 2022/8/11 21:10
* author: MR.孙
*/
@Component
@Aspect
@Slf4j
public class LogAspect {
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.mrs.annotation.SystemLog)")
public void pt(){
}
@Around("pt()")
public Object printLog(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
Object ret = null;
try {
handleBefore(joinPoint);
ret = joinPoint.proceed();
handleAfter(ret);
}finally {
//最终操作
//结束后换行
log.info("=======End=======" + System.lineSeparator());//System.lineSeparator系统的换行符
}
return ret;
}
private void handleAfter(Object ret) {
// 打印出参
log.info("Response : {}", JSON.toJSONString(ret));
}
private void handleBefore(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
ServletRequestAttributes servletRequestAttributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = servletRequestAttributes.getRequest();
//获取被增强方法上的注解对象
SystemLog systemLog = getSystemLog(joinPoint);
log.info("=======Start=======");
// 打印请求 URL
log.info("URL : {}",request.getRequestURI());
// 打印描述信息
log.info("BusinessName : {}", systemLog.businessName());
// 打印 Http method
log.info("HTTP Method : {}", request.getMethod());
// 打印调用 controller 的全路径以及执行方法
log.info("Class Method : {}.{}", joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName(),((MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()).getName());
// 打印请求的 IP
log.info("IP : {}",request.getRemoteHost());
// 打印请求入参
log.info("Request Args : {}", JSON.toJSONString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
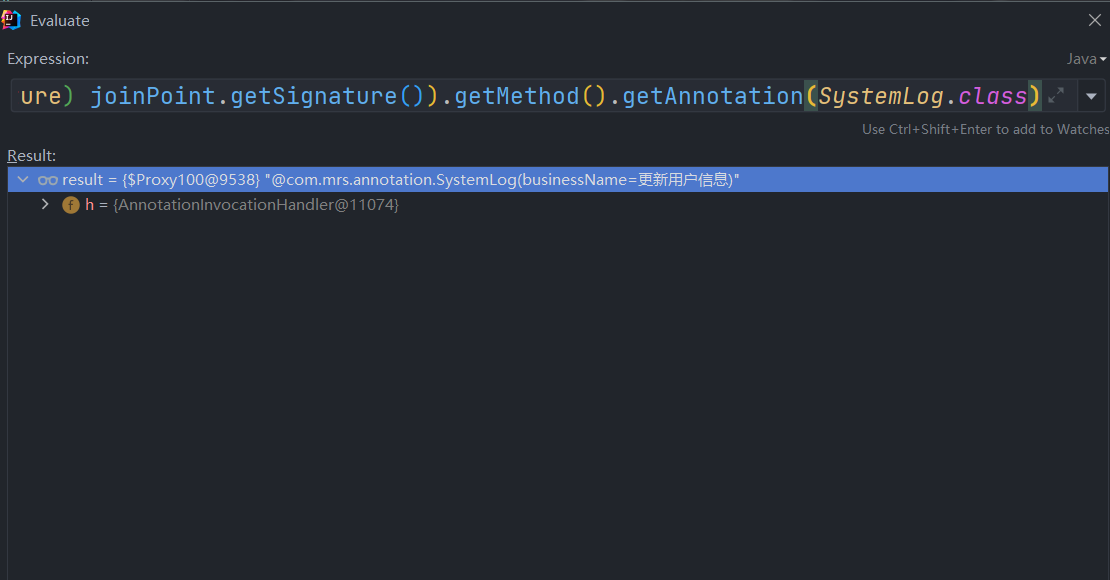
private SystemLog getSystemLog(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
SystemLog systemLog = methodSignature.getMethod().getAnnotation(SystemLog.class);
return systemLog;
}
}
注意:这里的joinPoint其实就是切点的信息被封装成了对象,所以我们可以看到下图中标注位置的对象信息,通过debug可以发现signature封装的就是被注解标注封装的对象,所以我们可以根据(MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()获取签名,然后通过前面获取注解作用的方法再去获取方法上的注解对象SystemLog systemLog = methodSignature.getMethod().getAnnotation(SystemLog.class)

测试




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号