Spring集成web环境(1)
因为这里是web集成环境(这里用servlet),所以我们先导入maven坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
@WebServlet("/userServlet")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService user = app.getBean(UserService.class);
user.save();
}
}
我们在web层在这个内部我们用spring容器调用service对象的save方法,
然后测试运行。
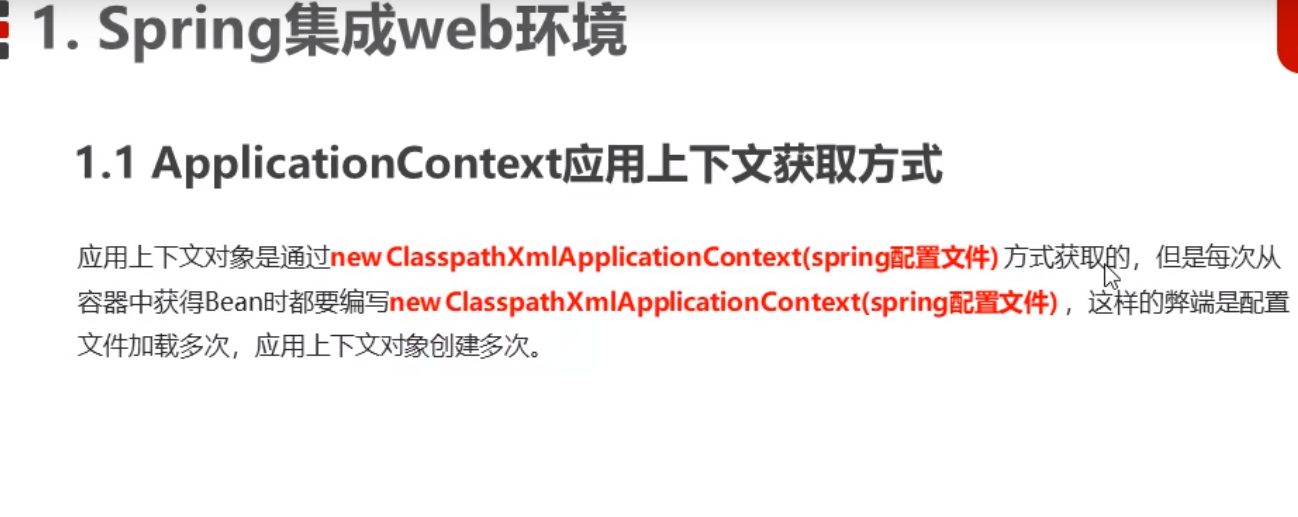
这张图片的意思就是,在web层中,将来有很多的东西每个doget、dopost都得重新创建上下文非常浪费,所以我们只要创建一次上下文就行了。
那么怎么做呢?

1、ServletContext 对象是一个为整个 web 应用提供共享的内存,任何请求都可以访问里面的内容
在 Servlet API 中有一个 ServletContextListener 接口,它能够监听 ServletContext 对象的生命周期,实际上就是监听 Web 应用的生命周期。
1.我们新建一个listen包在其中创建一个监听器类
的servlet
public class ContextLoaderListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
}
}
2.在监听器中读取spring配置文件得到上下文对象
ServletContext servletContext = servletContextEvent.getServletContext();
3. 通过获得servletContext对象域把ApplicationContext存储
然后在web.xml中配置监听器
//将Spring的上下文对象存储到ServletContext域中
ServletContext servletContext = servletContextEvent.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("app",app);
System.out.println("Spring容器创建完毕...");
这个输出是为了测试服务器刚启动时,它就输出了,也就是服务器一启动时,ApplicationContext就被创建好了。
监听器完整代码如下:
public class ContextLoaderListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//将Spring的上下文对象存储到ServletContext域中
ServletContext servletContext = servletContextEvent.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("app",app);
System.out.println("Spring容器创建完毕...");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
}
}
4.接下来就是取了
通过获取ServletContext域中的spring容器,来调用对象的方法
@WebServlet("/userServlet")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
ApplicationContext app = (ApplicationContext)servletContext.getAttribute("app");
UserService user = app.getBean(UserService.class);
user.save();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号