Spring之配置数据源(2)
上一篇讲到无论是druid、c3p0等jar包都是第三方的,那么这种地方的bean能不能让spring配置呢?
-
答案是可以的,因为spring bean不会管你是不是第三方的还是自己定义的
-
那么怎么实现呢,最开始提到的是spring是通过无参构造创建对象的,如果想往里面设置点东西,就分为set注入和无参构造方法注入
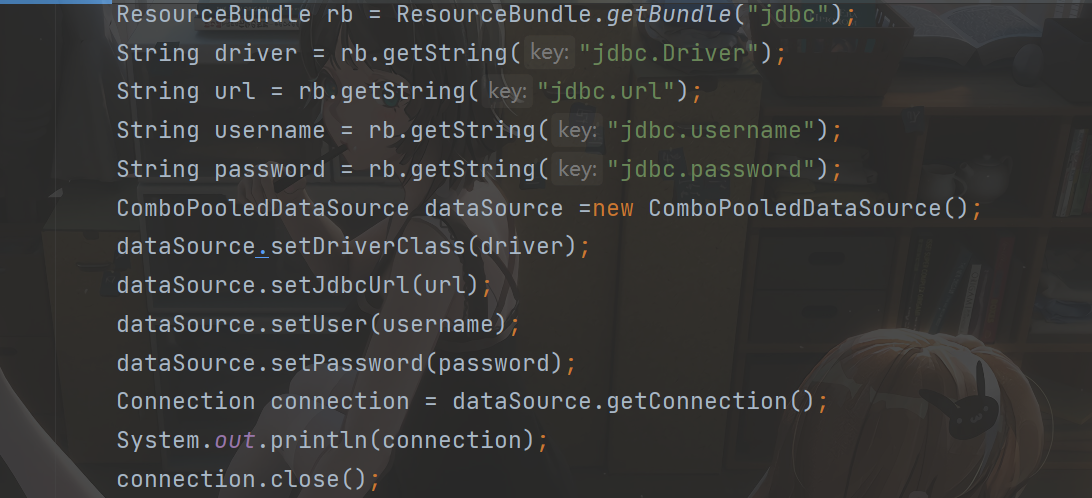
我们可以发现上面的代码基本上都是set或者是无参构造,所以我们可以用spring创建
Spring产生数据源
1.首先导入maven Spring的坐标
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.0.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
2.创建Spring的配置文件
- 首先spring通过无参构造来创建对象
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value=""></property>
</bean>
- 然后通过复制第三jar包的路径来让spring创建
当然仅仅创建一个bean它是没有属性的 - 所以这一步就是注入属性,因为他们都是set方法,所以我们可以用property标签来注入属性
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/study"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value=""></property>
</bean>
下面看一下测试的代码
//测试Spring容器产生数据源对象
@Test
public void test4() throws SQLException {
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
DataSource dataSource = app.getBean(DataSource.class);
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
- 这里回顾一下上次学到的知识,我们可以用字节码的类型来作为getBean方法的参数
下面讲一下spring抽取properties的属性

为什么要用spring抽取properties的属性,而不直接在spring的bean中配置呢?
- 这是因为常在开发中,把一些配置分别放在不同的配置文件中,比如数据库的就放在数据库的文件中,这样找问题时很方便,哪里出问题了找哪个配置文件。
下面具体讲一下spring怎么加载properties配置文件

-
引用context命令空间
* xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
* http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
* http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd" -
使用context标签加载properties文件
* <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/> -
使用spring表达式stl获得配置文件中的值(通过键)
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.Driver}"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号