jmu-Java-PTA题解 (6.5 - 倒排索引) 网安2312陈卓
问题要求
对若干行文字建立倒排索引(根据单词找到所在行号)。然后根据关键字,在倒排索引查找进行查找,找到包含所有该关键字所在的行数并输出。
输入格式:
- 若干行英文,以!!!!!为结束。
- 输入一行查询关键字,以1个空格为分隔
输出格式:
- 输出构建好的倒排索引。索引的键(单词)按照字母升序排列,值(行号)按照行号升序排列。
- 输出查询结果。若找到符合条件的行,输出包含所查询关键字的行集(即行集中每一行的内容);若未找到,输出 found 0 results。
输入样例:
where are you from are you ok
this is a test
that is an apple
there are lots of apples you eat it
who are you
!!!!!
you are
eat
you test
abc
输出样例:
a=[2]
an=[3]
apple=[3]
apples=[4]
are=[1, 4, 5]
eat=[4]
from=[1]
is=[2, 3]
it=[4]
lots=[4]
of=[4]
ok=[1]
test=[2]
that=[3]
there=[4]
this=[2]
where=[1]
who=[5]
you=[1, 4, 5]
[1, 4, 5]
line 1:where are you from are you ok
line 4:there are lots of apples you eat it
line 5:who are you
[4]
line 4:there are lots of apples you eat it
found 0 results
found 0 results
关键点
- 倒排索引构建:要把每一个单词映射到它所在的行号集合。
- 查询处理:依据输入的关键字,在倒排索引里找出包含所有关键字的行号。
- 输出格式:倒排索引的键要按字母升序排列,值按行号升序排列;查询结果要按行号升序输出。
解题步骤
第一步:初始化数据结构
运用 TreeMap 来存储倒排索引,因为 TreeMap 能自动按键的字母升序排列。同时,使用 ArrayList 来存储每一行的文本:
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Map<String, ArrayList<Integer>> map = new TreeMap<>();
ArrayList<String> arr = new ArrayList<String>();
第二步:构建倒排索引
逐行读取输入的文本,直至遇到 !!!!! 结束。针对每一行,把它拆分成单词,再将每个单词添加到倒排索引中:
String s = in.nextLine();
arr.add(s);
int number = 1;
while(!s.equals("!!!!!")){
ArrayList numbers;
String[] words = s.split("\\s+");
for(String e:words){
if(e.isEmpty()){
continue;
}
if(!map.containsKey(e)){
numbers = new ArrayList<String>();
map.put(e,numbers);
}else{
numbers = map.get(e);
}
if(!numbers.contains(number)){
numbers.add(number);
}
}
s = in.nextLine();
arr.add(s);
number += 1;
}
第三步:输出倒排索引
遍历 TreeMap,按字母升序输出每个单词及其对应的行号集合:
for(String e : map.keySet()){
System.out.print(e + "=");
System.out.println(map.get(e));
}
第四步:处理剩余顾客
持续读取查询关键字,直到没有更多输入为止。对于每个查询,找出包含所有关键字的行号集合,若找到则输出这些行的内容,若未找到则输出 found 0 results:
while(in.hasNextLine()){
s = in.nextLine();
String[] words = s.split("\\s+");
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<>();
int flag = 1;
for(String word : words){
if(!map.containsKey(word)){
break;
}else{
if(flag == 1){
set1 = new HashSet<>(map.get(word));
flag = 2;
}else{
Set<Integer> set2 = new HashSet<>(map.get(word));
set1.retainAll(set2);
}
}
}
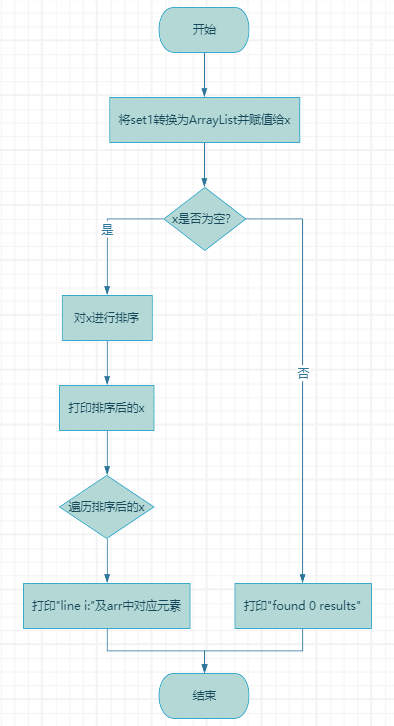
List<Integer> x = new ArrayList<>(set1);
Collections.sort(x);
if(!x.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(x);
for(Integer i : x){
System.out.print("line " + i + ":");
System.out.println(arr.get(i-1));
}
}else{
System.out.println("found 0 results");
}
}
整体流程图:
整体代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Map<String, ArrayList<Integer>> map = new TreeMap<>();
ArrayList<String> arr = new ArrayList<String>();
String s = in.nextLine();
arr.add(s);
int number = 1;
while(!s.equals("!!!!!")){
ArrayList numbers;
String[] words = s.split("\\s+");
for(String e:words){
if(e.isEmpty()){
continue;
}
if(!map.containsKey(e)){
numbers = new ArrayList<String>();
map.put(e,numbers);
}else{
numbers = map.get(e);
}
if(!numbers.contains(number)){
numbers.add(number);
}
}
s = in.nextLine();
arr.add(s);
number += 1;
}
for(String e : map.keySet()){
System.out.print(e + "=");
System.out.println(map.get(e));
}
while(in.hasNextLine()){
s = in.nextLine();
String[] words = s.split("\\s+");
Set<Integer> set1 = new HashSet<>();
int flag = 1;
for(String word : words){
if(!map.containsKey(word)){
break;
}else{
if(flag == 1){
set1 = new HashSet<>(map.get(word));
flag = 2;
}else{
Set<Integer> set2 = new HashSet<>(map.get(word));
set1.retainAll(set2);
}
}
}
List<Integer> x = new ArrayList<>(set1);
Collections.sort(x);
if(!x.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(x);
for(Integer i : x){
System.out.print("line " + i + ":");
System.out.println(arr.get(i-1));
}
}else{
System.out.println("found 0 results");
}
}
}
}
思考:在解决倒排索引的构建与查询问题时,选用 TreeMap 来存储倒排索引是因为它能自动按键的字母升序排列,这在输出倒排索引时非常方便。而 ArrayList 用于存储每一行的文本,方便后续根据行号输出具体内容。在查询处理时,使用 HashSet 来存储行号集合,能高效地进行集合的交集操作。在实际应用中,若处理大规模文本数据,可考虑使用更高效的数据结构和算法,例如使用 ConcurrentHashMap 来实现并发处理,提升性能。同时,还可以对文本进行预处理,如去除停用词、词干提取等,以提高索引的质量和查询的准确性。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号