演化计算实数空间变异算子
一起来学演化计算-实数空间变异算子
觉得有用的话,欢迎一起讨论相互学习~
参考文献
- [节选自] 文诗华. 多目标进化算法中变异算子的研究[D]. 湘潭大学. 这是来自郑金华教授的学生的硕士毕业论文。从入门演化计算时就读着郑老师的书走来的。在此对其表示最诚挚的敬意
实数搜索空间变异算子的实现

变异算子的设计原则

变异算子的研究概况



实数空间常用变异算子
均匀变异

非均匀变异

自适应变异

高斯变异

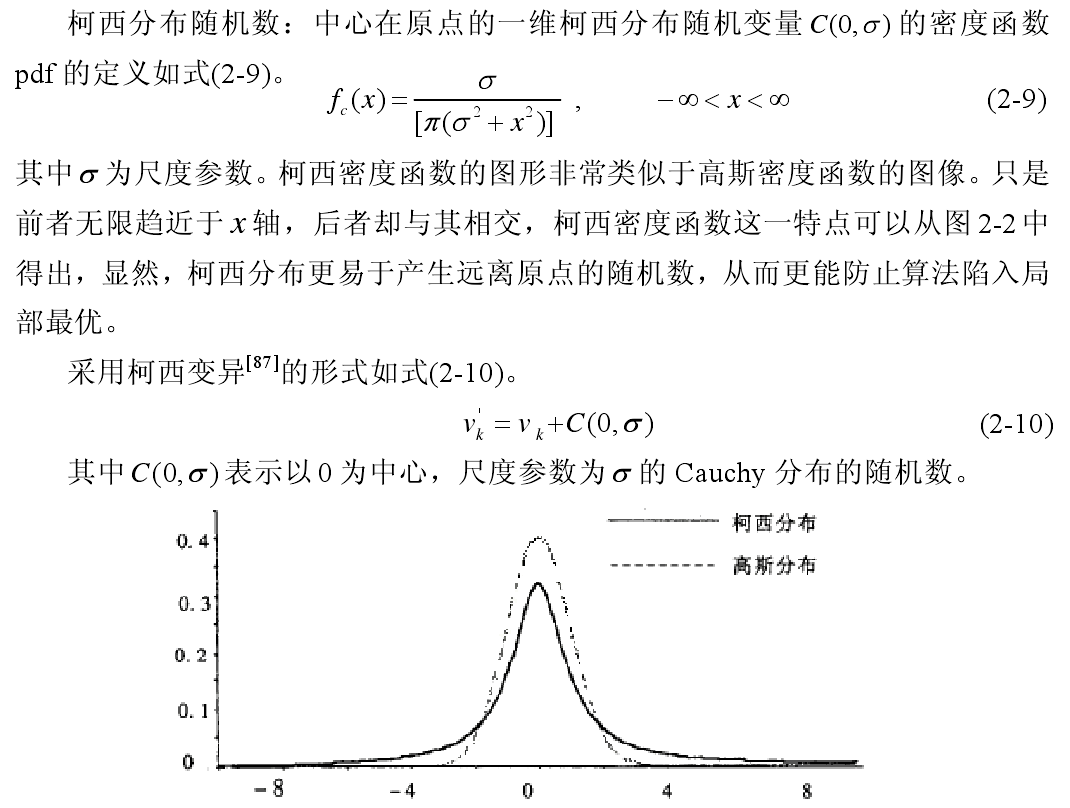
柯西变异
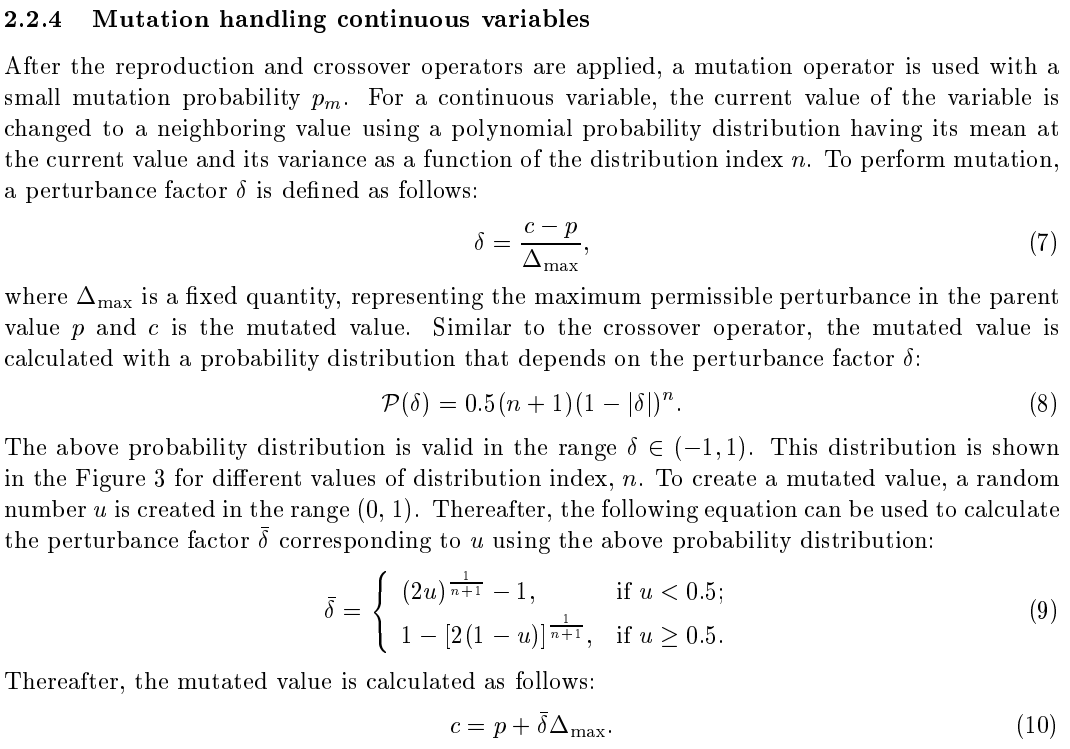
多项式变异

在Deb K , Goyal M . A Combined Genetic Adaptive Search (GeneAS) for Engineering Design[C]// 1996.原文中,其是这样描述的。
matlab实现多项式变异
% polynomial mutation
% 多项式突变
function object=mutate(object,p,dim,mum)
rnvec_temp=p.rnvec;
for i=1:dim
% 因为问题的维度一般比较大,所以rand(1)<1/dim的概率很小
if rand(1)<1/dim
u=rand(1);
if u <= 0.5
del=(2*u)^(1/(1+mum)) - 1;
rnvec_temp(i)=p.rnvec(i) + del*(p.rnvec(i));
else
del= 1 - (2*(1-u))^(1/(1+mum));
rnvec_temp(i)=p.rnvec(i) + del*(1-p.rnvec(i));
end
end
end
object.rnvec = rnvec_temp;
end
jmetal实现多项式变异
public void doMutation(double probability, Solution solution) throws JMException {
double rnd, delta1, delta2, mut_pow, deltaq;
double y, yl, yu, val, xy;
XReal x = new XReal(solution);
for (int var = 0; var < solution.numberOfVariables(); var++) {
if (PseudoRandom.randDouble() <= probability) {//如果小于变异概率即可以进行变异操作
y = x.getValue(var);
yl = x.getLowerBound(var);
yu = x.getUpperBound(var);
delta1 = (y - yl) / (yu - yl);
delta2 = (yu - y) / (yu - yl);
rnd = PseudoRandom.randDouble();
mut_pow = 1.0 / (eta_m_ + 1.0);
if (rnd <= 0.5) {
xy = 1.0 - delta1;
val = 2.0 * rnd + (1.0 - 2.0 * rnd) * (Math.pow(xy, (distributionIndex_ + 1.0)));
deltaq = java.lang.Math.pow(val, mut_pow) - 1.0;
} else {
xy = 1.0 - delta2;
val = 2.0 * (1.0 - rnd) + 2.0 * (rnd - 0.5) * (java.lang.Math.pow(xy, (distributionIndex_ + 1.0)));
deltaq = 1.0 - (java.lang.Math.pow(val, mut_pow));
}
y = y + deltaq * (yu - yl);
if (y < yl)
y = yl;
if (y > yu)
y = yu;
x.setValue(var, y);
}
} // for
} // doMutation
[42] Andenbrandt C A. An Extension the Theory of Convergence and a Proof of the Time Complexity of Genetic Algorithms. In [343], 53~68,1993.
[43] C. A. Magele, K.Preis, W.Renhart, etc. Higher order evolution strategies for the global optimization of electromagnetic devices. IEEE Trans. On Magnetics,1993,29(2) :1775~1778.
[44] C. Kappler. "Are evolutionary algorithms improved by large mutation?", in Parallel Problem Solving from Nature( PPSN) IV (H.M Voigt, W Ebeling,I.Rochenberg, and H.P.Schwefeleds.Vo1.1141 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,(Berlin), Springer-Verlag,1996:346~355.
[45] Dai Xiaoming. Zou Runmin, Sun Rong etc. Convergence properties of non-crossover genetic algorithm. Proceedings of the 4th World Congress on Intelligent control and automation, Shanghai, China,2002:1882~1826.
[46] Dirk Büche, Sibylle Müller, and Petros Koumoutsakos. Self-Adaptation for Multi-objective Evolutionary Algorithms, in Carlos M. Fonseca, Peter J. Fleming,Eckart Zitzler, Kalyanmoy Deb and Lothar Thiele (editors), EvolutionaryMulti-Criterion Optimization. Second International Conference, EMO 2003, pp.267--281, Springer. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Volume 2632, Faro,Portugal, April 2003 .
[47] Fogarty T C. Varying the Probability of Mutation in the Genetic Algorithms. In[335],104~109,1989.
[48] Farhang-Mehr Ali and Shapour Azarm. An Information-Theoretic Metric forAssessing Multi-Objective Optimization Solution Set Quality. ASME,Transactions, Journal of Mechanical Design, 2003.
[49] G. Rudolph. An evolutionary algorithm for integer programming, Int'1 conf. 1994 in Parallel problem solving from nature,Y David, R. Männer and H.P.Schwefel eds.,Vo1.3:139~148.
[50] H.G Beyer. The theory of evolution strategies. Natural computing series. Springer,Heidelberg, 2001.
[51] Hashem, M.M.A.; Watanabe, M.; Izumi, K. Evolution strategy a new time-variant mutation for fine local tuning SICE '97. Proceedings of the 36th SICE Annual Conference. International Session Papers, 1997:1099~1104.
[52] Hesser J and Männer R. Investigation of the M-Heuristic for Optimal Mutation Probability. In [340], 115~125, 1992.
[53] I.D.Falco , A.D.Coippa , E.Tarantino. Mutation-based genetic algorithm: performance evaluation. Applied Soft Computing, (2002): 285~299.
[54] I. Rechenberg. Evolutionsstrategie: Optimierung texhnischer Systeme nach Prinzipien der biologischen Evolution. Stuttgart,Germany: Frogmann Holzboog, 1973.
[55] J.Smith. Self-adaptation in evolutionary algorithm. Ph .D. dissertation, Univ. of the West of England, Bristol, 1997.
[56] J.Smith. Operator and parameter adaptation in genetic algorithms. Soft computing.1997, 1(2):81~87.
[57] K.C.Tan, C.K. Goh, Y.J. Yang, T.H. Lee. Evolving better population distribution and exploration in evolutionary multi-objective optimization, European Journal of Operational Research , 2006, 171 (2) : 463~495.
[58] K. Deb and M. Goyal. A combined genetic adaptive search (GeneAS) for engineering design. Computer Science and Informatics, 1996, 26(4): 30-45.
[59] Kalyanmoy Deb. Multi-Objective Optimization using Evolutionary Algorithms. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, UK, 2001.
[60] K Deb, Mohan M, Mishra S. A fast multi-objective evolutionary algorithm for finding well-spread Pareto-optimal solutions [R]. KanGAL Report. No 2003002.
[61] L.Hildebrand; B.Reusch, Fathi, M.; Directed mutation—a new self-adaptation for evolution strategies. Evolutionary Computation, 1999. CEC99. Proceedings of the 1999 Congress on, Volume:2, 1999:1550~1557.
[62] Marco Laumanns, Günter Rudolph, Hans-Paul Schwefel. Mutation Control and Convergence in Evolutionary Multi-objective Optimization, In R. Matousek and P. Osmera (eds.), Proceedings of the 7th International Mendel Conference on Soft Computing (MENDEL 2001), Brno University of Technology, pp. 24--29, Brno, Czech Republic, June 2001.
[63] Matthieu Basseur, Franck Seynhaeve, El-ghazali Talbi. Design of Multi-objective evolutionary algorithms: Application to the flow-shop scheduling problem, in Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC'2002), Vol. 2, pp. 1151--1156, IEEE Service Center, Piscataway, New Jersey, May 2002.
[64] Matthieu Basseur, Franck Seynhaeve, El-ghazali Talbi. Adaptive mechanisms for multiobjective evolutionary algorithms, in IMACS multiconference, Computational Engineering in Systems Applications (CESA'03), paper S3-R-00-222, IEEE Service Center, Piscataway, New Jersey, July 2003 .
[65] Michalewicz Z. Genetic Algorithms + Data Structures= Programs. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.1992.
[66] Miqing Li and Jinhua Zheng. Spread Assessment for Evolutionary Multi-Objective Optimization, Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization, 5th International Conference (EMO 2009), Nantes, France 216-230, 2009.
[67] Miqing Li, Jinhua Zheng and Guixia Xiao. Uniformity Assessment for Evolutionary Multi-Objective Optimization, in Proceedings of IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC’2008), Hongkong, 625-632, 2008.
[68] T.Bäck and H.P. Schwefel. Evolutionary computation: an overview. In Proc. of the 1996 IEEE Int'1 Conf. on Evolutionary Computation (ICEC1996) Nagoya Japan, IEEE Press, New York, NY, 1996:20~29.
[69] Sang Hwan Lee, Hyo Byung Jun, Kwee Bo Sim. Performance improvement of evolution strategies using reinforcement learning. Fuzzy Systems Conference Proceedings, 1999.IEEE' 99.1999 IEEE International, V olume:2 ,2 2~25.
[70] S.D.Müller, N.N.Schraudlph, P.D.Koumoutsakos. Step size adaptation in evolutions trategies using reinforcement learning. Evolutionary Computation, 2002 .CEC'02. Proceedings of the 2002 Congress, Volume:l ,2002:151~156.
[71] Q .Zhou and Yanda Li. Directed variation in evolution strategies. IEEE trans. On Evolutionary computation, 2003,7 (4):356~366.
[72] Yu Yongquan; Huang Ying; Zeng Bi; Chen Xianchu; Learning fuzzy model for nonlinear system using evolution strategies with adaptive direction mutation. Fuzzy Systems, 2003. FUZZ '03. The 12th IEEE International Conference, Volume: 1, 2003:237~241.
[73] X.Yao and Y.Liu. "Fast evolution strategies", Proc.4th, IEEE conf in Evolutionary Programming VI, P.J Angeline, R.Reynolds,J.McDonnell, and R.Eberthart, eds. Berlin, Germany Springer~Verlag, 1997:151~161.
[74] 林丹, 李敏强, 寇纪淞. 进化规划和进化策略中变异算子的若干研究[J]. 天 津大学学报, 2000,33(5):627~630.
[75] 王云诚, 唐焕文. 单峰函数最优化问题的一个快速收敛进化策略[J]. 小型微 型计算机系统, 2002, 23 (11):1390~1392.
[76] 刘若辰, 杜海峰, 焦李成. 基于柯西变异的免疫单克隆策略[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2004, 31 (4):551~556.
[77] 王战权 , 赵 朝 义 . 进 化 策 略 中 变 异 算 子 的 改 进 研 究 [J]. 计算机仿真,1999,16(3):8 ~11.
[78] 王战权, 赵朝义, 夏云庆. 进化策略中基于柯西分布的变异算子改进探讨[J]. 系统工程, 1999,17 (4): 49~54.
[79] Yong Liang, Kwong Sak Leung. Two-way mutation evolution strategies. CEC'02 .Proceedings of the 2002 Congress on Evolutionary Computation, Volume: 1,2002: 789~794.
[80] R.Hinterding , Z.Michalewicz and A.E.Eiben. Adaptation in evolutionary computation. In Proc. 2nd IEEE Conf. Evolutionary computation. Piscataway, N J: IEEE Press, 1997:65~69.
[81] 潘正君. 基于演化计算的并行问题求解[D]. 武汉:武汉大学博士学位论文,1996.
[82] Varun Aggarwal, Una-May O'Reilly. COSMO: A Correlation SensitiveMutation Operator for Multi-Objective Optimization, Proceedings of the 9th annual conference on Genetic and evolutionary computation, New York: ACM , 2007: 741~748.
[83] 潘正君, 康立山, 陈毓屏. 演化计算[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 1998.5.
[84] P.J.Angeline. Adaptive and self-adaptive evolutionary computation. In Computation intelligence: a dynamic system perspective. M. Palaniswami, YAttikiouzel etc. eds. New York: IEEE Press, 1995:152~161.
[85] Pan Z J, Kang L S, Nie S X. Evolving Both the Topology and weights of Neural Networks. Parallel Algorithms and Applications, Vol.9, 299~307, 1996.
[86] Zbigniew Michalewicz, David B.Fogel. How to Solve It: Modern Heuristics. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.2000.
[87] X. Yao and Y. Liu. "Fast evolution strategies", Proc.4th, IEEE conf in Evolutionary Programming VI, P.J Angeline, R.Reynolds, J.McDonnell, and R.Eberthart, eds. Berlin, Germany Springer-Verlag, 1997:151-163.






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号