UNIQUE VISION Programming Contest 2024 Christmas (AtCoder Beginner Contest 385) 题解记录A~F
开个新坑,感觉Atcoder的题目还是比较有意思的,有点启发意义吧。
A.Equally
题面:
您将获得三个整数 A,B,C 。确定是否可以将这三个整数分成两个或多个组,以使这些组的总和相等。
约束:
1≤A,B,C≤1000
输出:
如果可以 A,B,C 分成两个或多个总和相等的组,请打印 Yes;否则,打印 No。
思路:签到题啦,随便组合一下就好了
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<deque>
#include<cctype>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<random>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<functional>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
// #include <unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define endl "\n"// 交互题记得删除
using namespace std;
//using namespace __gnu_pbds;
mt19937 rnd(time(0));
// const ll p=13;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
ll ksm(ll x, ll y)
{
ll ans = 1;
while (y)
{
if (y & 1)
{
ans = ans % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
}
x = x % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
y >>= 1;
}
return ans % mod % mod;
}
ll gcd(ll x, ll y)
{
if (y == 0)
return x;
else
return gcd(y, x % y);
}
void fio()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
}
struct s
{
ll l, r;
bool operator<(const s& a)const
{
if (l != a.l)
return l < a.l;
else return r < a.r;
}
};
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(const s& a, const s& b)const
{
}
};
int main()
{
fio();
ll a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
if(a==b+c||b==a+c||c==a+b||(a==b&&b==c))cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
else
cout<<"No"<<endl;
return 0;
}
B.Santa Claus 1
题面:
有一个 \(H\) 行 \(W\) 列的网格。让 \((i, j)\) 表示从顶部数第 \(i\) 行,从左侧数第 \(j\) 列的单元格。
如果 \(S_{i, j}\) 是 #,那么单元格 \((i, j)\) 是不可通行的;如果它是 .,单元格是可通行的并且没有房子;如果它是 @,单元格是可通行的并且包含一个房子。
最初,圣诞老人在单元格 \((X, Y)\)。他将根据字符串 \(T\) 进行操作,如下所示:
让 \(|T|\) 表示字符串 \(T\) 的长度。对于 \(i=1,2,\ldots,|T|\),他按照以下方式移动。
让 \((x, y)\) 表示他当前所在的单元格。
如果 \(T_i\) 是 u 并且单元格 \((x-1, y)\) 是可通行的,移动到单元格 \((x-1, y)\)。
如果 \(T_i\) 是 d 并且单元格 \((x+1, y)\) 是可通行的,移动到单元格 \((x+1, y)\)。
如果 \(T_i\) 是 l 并且单元格 \((x, y-1)\) 是可通行的,移动到单元格 \((x, y-1)\)。
如果 \(T_i\) 是 r 并且单元格 \((x, y+1)\) 是可通行的,移动到单元格 \((x, y+1)\)。
否则,停留在单元格 \((x, y)\)。
找出他完成所有操作后所在的单元格,以及他在操作过程中经过或到达的不同房子的数量。如果同一个房子经过多次,只计算一次。
约束:
\(3 \leq H, W \leq 100\)
\(1 \leq X \leq H\)
\(1 \leq Y \leq W\)
所有给定的数字都是整数。
每个 \(S_{i, j}\) 可以是 #,. 或 @ 中的一个。
对于所有 \(1 \leq i \leq H\),\(S_{i, 1}\) 和 \(S_{i, W}\) 都是 #。
对于所有 \(1 \leq j \leq W\),\(S_{1, j}\) 和 \(S_{H, j}\) 都是 #。
$S_{X, Y} = .
\(T\) 是一个长度至少为 1 且最多为 \(10^4\) 的字符串,由 U,D,L,R 组成。
输出:
让 \((X, Y)\) 表示他完成所有操作后所在的单元格,\(C\) 表示他在操作过程中经过或到达的不同房子的数量。按顺序打印 \(X, Y, C\),它们之间用空格分隔。
思路:数据范围很小,直接模拟一遍即可,对于走过的房子标记一下再考虑是否计数就好了
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<deque>
#include<cctype>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<random>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<functional>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
// #include <unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define endl "\n"// 交互题记得删除
using namespace std;
//using namespace __gnu_pbds;
mt19937 rnd(time(0));
// const ll p=13;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
ll ksm(ll x, ll y)
{
ll ans = 1;
while (y)
{
if (y & 1)
{
ans = ans % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
}
x = x % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
y >>= 1;
}
return ans % mod % mod;
}
ll gcd(ll x, ll y)
{
if (y == 0)
return x;
else
return gcd(y, x % y);
}
void fio()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
}
struct s
{
ll l, r;
bool operator<(const s& a)const
{
if (l != a.l)
return l < a.l;
else return r < a.r;
}
};
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(const s& a, const s& b)const
{
}
};
ll n,m,x,y;
string f[250];
ll ans=0;
bool vis[250][250];
void ck(char c)
{
if(c=='U'&&x-1>=1&&f[x-1][y]!='#')
{
x--;
if(f[x][y]=='@'&&vis[x][y]==0)ans++;
vis[x][y]=1;
}
else if(c=='D'&&x+1<=n&&f[x+1][y]!='#')
{
x++;
if(f[x][y]=='@'&&vis[x][y]==0)ans++;
vis[x][y]=1;
}
else if(c=='L'&&y-1>=1&&f[x][y-1]!='#')
{
y--;
if(f[x][y]=='@'&&vis[x][y]==0)ans++;
vis[x][y]=1;
}
else if(c=='R'&&y+1<=m&&f[x][y+1]!='#')
{
y++;
if(f[x][y]=='@'&&vis[x][y]==0)ans++;
vis[x][y]=1;
}
}
int main()
{
fio();
cin>>n>>m>>x>>y;
string k;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>f[i];
f[i]='0'+f[i];
}
cin>>k;
for(ll i=0;i<k.size();i++)
{
ck(k[i]);
}
cout<<x<<" "<<y<<" ";
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
C.Illuminate Buildings
题面:
有 \(N\) 座建筑物按相等的间隔排成一行。从前面数第 \(i\) 座建筑物的高度是 \(H_i\)。
你想用照明装饰其中一些建筑物,以便满足以下两个条件:
选择的建筑物都有相同的高度。
选择的建筑物按相等的间隔排列。
你最多可以选择多少座建筑物?如果你选择恰好一座建筑物,这被认为满足条件。
约束:
\(1 \leq N \leq 3000\)
\(1 \leq H_i \leq 3000\)
所有输入值都是整数。
输出:
输出答案
思路:由于N的最大值为3000,所以考虑了暴力,三重循环,最外面枚举长度,第二层枚举起点,第三层遍历等差点,由于第二层和第三层时间复杂度总和为调和级数级别左右,所以总时间复杂度大致为\(n^{2}logn\)左右,不会TLE
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<deque>
#include<cctype>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<random>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<functional>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
// #include <unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define endl "\n"// 交互题记得删除
using namespace std;
//using namespace __gnu_pbds;
mt19937 rnd(time(0));
// const ll p=13;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
ll ksm(ll x, ll y)
{
ll ans = 1;
while (y)
{
if (y & 1)
{
ans = ans % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
}
x = x % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
y >>= 1;
}
return ans % mod % mod;
}
ll gcd(ll x, ll y)
{
if (y == 0)
return x;
else
return gcd(y, x % y);
}
void fio()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
}
struct s
{
ll l, r;
bool operator<(const s& a)const
{
if (l != a.l)
return l < a.l;
else return r < a.r;
}
};
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(const s& a, const s& b)const
{
}
};
ll n,m,x,y;
string f[250];
ll ans=0;
bool vis[250][250];
void ck(char c)
{
if(c=='U'&&x-1>=1&&f[x-1][y]!='#')
{
x--;
if(f[x][y]=='@'&&vis[x][y]==0)ans++;
vis[x][y]=1;
}
else if(c=='D'&&x+1<=n&&f[x+1][y]!='#')
{
x++;
if(f[x][y]=='@'&&vis[x][y]==0)ans++;
vis[x][y]=1;
}
else if(c=='L'&&y-1>=1&&f[x][y-1]!='#')
{
y--;
if(f[x][y]=='@'&&vis[x][y]==0)ans++;
vis[x][y]=1;
}
else if(c=='R'&&y+1<=m&&f[x][y+1]!='#')
{
y++;
if(f[x][y]=='@'&&vis[x][y]==0)ans++;
vis[x][y]=1;
}
}
ll a[250000];
int main()
{
fio();
ll n;
cin>>n;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
ll ans=0;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(ll j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
ll cnt=0;
for(ll u=j;u<=n;u+=i)
{
if(a[u]==a[j])
{
cnt++;
}
else break;
}
ans=max(ans,cnt);
}
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
D.Santa Claus 2
题面:
在二维平面上有 \(N\) 个房子,位于点 \((X_1, Y_1), \ldots, (X_N, Y_N)\)。最初,圣诞老人位于点 \((S_x, S_y)\)。他将根据序列 \((D_1, C_1), \ldots, (D_M, C_M)\) 进行操作,如下所示:
按顺序对 \(i = 1, 2, \ldots, M\) 进行操作,他的移动方式如下:
让 \((x, y)\) 为他当前所在的点。
如果 \(D_i\) 是 u,从 \((x, y)\) 沿直线移动到 \((x, y + C_i)\)。
如果 \(D_i\) 是 d,从 \((x, y)\) 沿直线移动到 \((x, y - C_i)\)。
如果 \(D_i\) 是 l,从 \((x, y)\) 沿直线移动到 \((x - C_i, y)\)。
如果 \(D_i\) 是 r,从 \((x, y)\) 沿直线移动到 \((x + C_i, y)\)。
找出他完成所有操作后所在的点,以及他在操作过程中经过或到达的不同房子的数量。如果同一个房子经过多次,只计算一次。
约束:
\(1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5\)
\(1 \leq M \leq 2 \times 10^5\)
\(-10^9 \leq X_i, Y_i \leq 10^9\)
点对 \((X_i, Y_i)\) 是互不相同的。
\(-10^9 \leq S_x, S_y \leq 10^9\)
在 \((S_x, S_y)\) 处没有房子。
每个 \(D_i\) 可以是 u(上)、d(下)、l(左)、r(右)中的一个。
\(1 \leq C_i \leq 10^9\)
所有输入数字都是整数。
输出:
让 \((X, Y)\) 表示他完成所有操作后的点,\(C\) 表示经过或到达的不同房子的数量。按顺序打印 \(X, Y, C\),它们之间用空格分隔。
思路:其实就是优化暴力模拟,这里用set优化,分别存横坐标对应的纵坐标,纵坐标对应的横坐标。首先注意数据范围大必须得离散化,多维set的第一维就是离散化后的值,而存的数字必须为非离散化数字,其实每次移动,都是移动一段区间的,所以可以对x,y,中不变的数字所对应的set进行二分,然后while循环,直到没有点落在这个区间内就好了,记得删点时,把另一个set中的值删掉,其实时间复杂度也就\(n*logn*logn\)左右吧
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<deque>
#include<cctype>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<random>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<functional>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
// #include <unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define endl "\n"// 交互题记得删除
using namespace std;
//using namespace __gnu_pbds;
mt19937 rnd(time(0));
// const ll p=13;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
ll ksm(ll x, ll y)
{
ll ans = 1;
while (y)
{
if (y & 1)
{
ans = ans % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
}
x = x % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
y >>= 1;
}
return ans % mod % mod;
}
ll gcd(ll x, ll y)
{
if (y == 0)
return x;
else
return gcd(y, x % y);
}
void fio()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
}
struct s
{
ll l, r;
bool operator<(const s& a)const
{
if (l != a.l)
return l < a.l;
else return r < a.r;
}
};
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(const s& a, const s& b)const
{
}
};
ll a[250000];
set<ll>r[550000],l[550000];
int main()
{
fio();
ll n,m,x,y;
cin>>n>>m>>x>>y;
map<ll,ll>q;
ll cnt=0;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
ll x1,y1;
cin>>x1>>y1;
if(q[x1]==0)q[x1]=++cnt;
if(q[y1]==0)q[y1]=++cnt;
l[q[y1]].insert(x1);
r[q[x1]].insert(y1);
}
ll ans=0;
while(m--)
{
char f;
cin>>f;ll op;
cin>>op;
if(f=='L')
{
if(l[q[y]].size()>0)//x~x-op
{
while(1)
{
auto j=l[q[y]].lower_bound(x-op);
if(j==l[q[y]].end())break;
else
{
if(*j>x)break;
r[q[*j]].erase(y);
l[q[y]].erase(*j);
ans++;
}
}
}
x-=op;
}
else if(f=='R')//x~x+op
{
if(l[q[y]].size()>0)
{
while(1)
{
auto j=l[q[y]].lower_bound(x);
if(j==l[q[y]].end()||*j>x+op)break;
r[q[*j]].erase(y);
l[q[y]].erase(*j);
ans++;
}
}
x+=op;
}
else if(f=='D')//y-op~y
{
if(r[q[x]].size()>0)
{
while(1)
{
auto j=r[q[x]].lower_bound(y-op);
if(j==r[q[x]].end()||*j>y)break;
l[q[*j]].erase(x);
r[q[x]].erase(*j);ans++;
}
}
y-=op;
}
else
{
if(r[q[x]].size()>0)//y~y+op
{
while(1)
{
auto j=r[q[x]].lower_bound(y);
if(j==r[q[x]].end()||*j>y+op)break;
l[q[*j]].erase(x);
r[q[x]].erase(*j);ans++;
}
}
y+=op;
}
}
cout<<x<<" "<<y<<" ";
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
E.Snowflake Tree
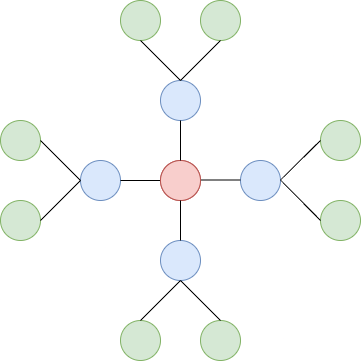
“雪花树”定义为可以通过以下步骤生成的树:
选择正整数 \(x, y\)。
准备一个顶点。
准备 \(x\) 个更多的顶点,并将它们每一个都连接到步骤 2 中准备的顶点上。
对于步骤 3 中准备的每一个 \(x\) 个顶点,附上 \(y\) 个叶子。
下图展示了一个 \(x=4, y=2\) 的雪花树。步骤 2、3、4 中准备的顶点分别用红色、蓝色和绿色表示。
给定一个有 \(N\) 个顶点的树 \(T\)。顶点编号从 1 到 \(N\),第 \(i\) 条边(\(i = 1, 2, \ldots, N - 1\))连接顶点 \(u_i\) 和 \(v_i\)。
考虑删除 \(T\) 中的一个或多个顶点及其相邻的边,使得剩余的图成为一个单一的雪花树。找到必须删除的最小顶点数。在这个问题的约束条件下,总是可以将 \(T\) 转换为一个雪花树。
约束:
\(3 \leq N \leq 3 \times 10^5\)
\(1 \leq u_i < v_i \leq N\)
给定的图是一个树。
所有输入值都是整数。
输出:
输出答案
思路:如何找中心点呢?试着遍历所有点作为中心点!首先先dfs一遍进行sz记录,然后第二遍dfs得考虑两个事:1.统计答案,2.实现根的变化,根的变化好解决,无非就是sz的变换。统计答案呢?思考这是一棵树,所以我可以先遍历一遍把必须要删除的点进行统计(中心点往外面扩大3层及以后的点都不要了),然后对于可能的答案点进行去重统计,随后排个序,一个答案被选定后,比他小的答案的所有点都得被删除,比他大的点必须减少到刚好为这个答案,所以前缀和预处理一遍,在倒序一遍就可以得出答案。ans取个min就可以了
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<deque>
#include<cctype>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<random>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<functional>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
// #include <unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define endl "\n"// 交互题记得删除
using namespace std;
//using namespace __gnu_pbds;
mt19937 rnd(time(0));
// const ll p=13;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
ll ksm(ll x, ll y)
{
ll ans = 1;
while (y)
{
if (y & 1)
{
ans = ans % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
}
x = x % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
y >>= 1;
}
return ans % mod % mod;
}
ll gcd(ll x, ll y)
{
if (y == 0)
return x;
else
return gcd(y, x % y);
}
void fio()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
}
struct s
{
ll l, r;
bool operator<(const s& a)const
{
if (l != a.l)
return l < a.l;
else return r < a.r;
}
};
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(const s& a, const s& b)const
{
}
};
vector<ll>g[450000];
ll sz[450000];
ll a[450000];
ll pre[450000];
int main()
{
fio();
ll n;
cin>>n;
for(ll i=1;i<n;i++)
{
ll l,r;
cin>>l>>r;
g[l].push_back(r);
g[r].push_back(l);
}
function<void(ll,ll)>df=[&](ll x,ll f)
{
sz[x]=1;
for(auto j:g[x])
{
if(j==f)continue;
else df(j,x);
sz[x]+=sz[j];
}
};
df(1,0);
ll ans=1e18;
map<ll,ll>k;
function<void(ll,ll)>dfs=[&](ll x,ll f)
{
ll l=0;
ll z=1e18;
ll cnt=0;
k.clear();
for(auto j:g[x])
{
cnt+=sz[j]-1-(g[j].size()-1);//基本费用
if(k[g[j].size()-1]==0)
{
l++;
a[l]=g[j].size()-1;
}
k[g[j].size()-1]++;
}
sort(a+1,a+1+l);
for(ll i=1;i<=l;i++)
{
pre[i]=pre[i-1]+k[a[i]]*(a[i]+1);
}
ll op=0;
ll uo=0;
for(ll i=l;i>=1;i--)
{
ans=min(ans,pre[i-1]+op+cnt);
uo+=k[a[i]];//个数,
op+=uo*a[i]-uo*a[i-1];
}
//if(x==2)cout<<sz[3]<<endl;
for(auto j:g[x])
{
if(j==f)continue;
sz[x]-=sz[j];
sz[j]+=sz[x];
dfs(j,x);
sz[j]-=sz[x];
sz[x]+=sz[j];
}
};
dfs(1,0);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
F.Visible Buildings
题面:
在数轴上有 \(N\) 座编号为 1 到 \(N\) 的建筑物。第 \(i\) 座建筑物位于坐标 \(X_i\),高度为 \(H_i\)。除了高度以外,其他方向的尺寸可以忽略不计。
从坐标为 \(x\)、高度为 \(h\) 的点 \(P\) 出发,如果存在建筑物 \(i\) 上的点 \(Q\),使得线段 \(PQ\) 不与任何其他建筑物相交,则认为建筑物 \(i\) 是可见的。
找出在坐标 0 处无法看到所有建筑物的最大高度。高度必须是非负的;如果在坐标 0 的高度 0 处可以看到所有建筑物,则报告 -1。
约束:
\(1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5\)
\(1 \leq X_1 < X_2 < \cdots < X_N \leq 10^9\)
\(1 \leq H_i \leq 10^9\)
所有输入值均为整数。
输出:
思路:其实就是两个相邻点的最大斜率就是了,在循环过程中加个数字判断下斜率是否是递增的,如果是的话就得输出-1,否则输出斜率最大值.
给出证明,如果一个点和前面非相邻点斜率比这个点和前面的点斜率更大,那么前面非相邻的点和前面的点的斜率将会更大
反之越小也是同理。所以答案即为极限值,因为可以有误差,所以输出这个点的值就可。默认多了个无穷小。
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<deque>
#include<cctype>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<random>
#include<stack>
#include<string>
#include<functional>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
//#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
// #include <unordered_map>
#define ll long long
#define lowbit(x) (x & -x)
#define endl "\n"// 交互题记得删除
using namespace std;
//using namespace __gnu_pbds;
mt19937 rnd(time(0));
// const ll p=13;
const ll mod = 1e9+7;
ll ksm(ll x, ll y)
{
ll ans = 1;
while (y)
{
if (y & 1)
{
ans = ans % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
}
x = x % mod * (x % mod) % mod;
y >>= 1;
}
return ans % mod % mod;
}
ll gcd(ll x, ll y)
{
if (y == 0)
return x;
else
return gcd(y, x % y);
}
void fio()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
}
struct s
{
ll x,h;
bool operator<(const s& a)const
{
if (x != a.x)
return x < a.x;
else return h < a.h;
}
}p[250000];
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(const s& a, const s& b)const
{
}
};
int main()
{
fio();
ll n;
cin>>n;
ll uo=0;
ll cn1,cn2;
cn1=1,cn2=0;
ll pd=0;
// ll pd=0;
// for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)
// {
// cin>>p[i].x>>p[i].h;
// ll u=p[i].x,z=p[i].h;
// ll k=gcd(u,z);
// u/=k,z/=k;
// ll d=gcd(u,cn1);
// cn1=u/d*cn1,cn2=u/d*cn2;
// u=cn1,z=cn1/u*z;
// if(z<=cn2)
// pd=1;
// cn1=u,cn2=z;
// k=gcd(cn1,cn2);
// cn1/=k,cn2/=k;
// }
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>p[i].x>>p[i].h;
long double ans=0;
p[0].x=p[0].h=0;
long double co=-1;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++)//y=k(x-p[i].x)+p[i].h
{
long double k=(long double)(p[i].h-p[i-1].h)/(long double)(p[i].x-p[i-1].x);
if(co>=(long double)p[i].h/(long double)p[i].x)
pd=1;
co=(long double)p[i].h/(long double)p[i].x;
//printf("%.8Lf\n",co);
ans=max(ans,p[i].h-k*p[i].x);
}
if(pd==0)
cout<<-1<<endl;
else
printf("%.18Lf\n",ans);
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号