SkipList 跳表 + Memory pool 内存池

基础跳表原理
- 【编程】动画解析 Redis zset 的底层结构:跳表:原理讲解+代码实现
- 层峦叠嶂:跳表结构讲解和 C++ 实现: 数据原理讲解+代码实现
跳表是一种类似于链表的数据结构。更加准确地说,跳表是对有序链表的改进。
为方便讨论,后续所有有序链表默认为 升序 排序。
一个有序链表的查找操作,就是从头部开始逐个比较,直到当前节点的值大于或者等于目标节点的值。很明显这个操作的复杂度是 \(O(n)\)。
跳表在有序链表的基础上,引入了 分层 的概念。首先,跳表的每一层都是一个有序链表,特别地,最底层是初始的有序链表。
"通过概率性生长的层级结构,跳表在保持链表动态优势的同时,创造出类似二分查找的快速通道。每一层都是下层链表的"快照缩影""
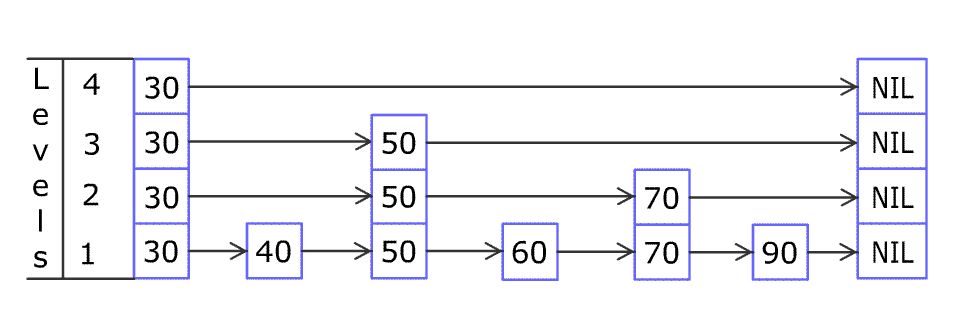
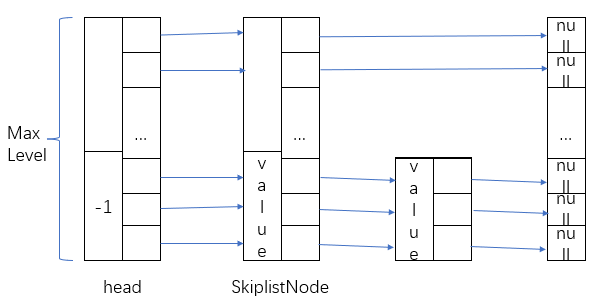
每个SkiplistNode结构如下:
struct SkiplistNode {
int value;
vector<SkiplistNode*> forward;
SkiplistNode(int value, int level): value(value), forward(level, nullptr) {}
};
forward作为向量,注意其中元素类型为SkiplistNode *
基础跳表实现
class Skiplist {
private:
static constexpr int maxLevel = 32;
static constexpr double p = 0.4;
struct SkiplistNode {
int value;
vector<SkiplistNode*> forward;
SkiplistNode(int value, int level): value(value), forward(level, nullptr) {}
};
SkiplistNode *head;
int level; // 当前Skiplist的层数
// 注意需要保证返回时level > 0
int randomLevel() {
int level = 1;
const int threshold = p * RAND_MAX;
while (rand() < threshold && level < maxLevel) level++;
return level;
}
public:
Skiplist(): head(new SkiplistNode(-1, maxLevel)), level(0) {}
bool search(int target) {
SkiplistNode *x = head;
// 从Skiplist的最高层开始
// 外循环用于循环层数
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 内循环用于循环相同层的链表元素
while (x->forward[i] != nullptr && x->forward[i]->value < target) {
x = x->forward[i];
}
}
return x->forward[0] != nullptr && x->forward[0]->value == target;
}
// 运行插入多个值相同的元素
void add(int num) {
SkiplistNode *x = head;
// 因为即将插入一个新的SkiplistNode,需要记录下每层其前一个SkiplistNode是什么
// update向量即是记录各个SkiplistNode
vector<SkiplistNode*> update(maxLevel, nullptr);
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->forward[i] != nullptr && x->forward[i]->value < num) {
x = x->forward[i];
}
update[i] = x;
}
int currentLevel = randomLevel();
if (currentLevel > level) {
for (int i = level; i < currentLevel; i++) update[i] = head;
level = currentLevel;
}
SkiplistNode *current = new SkiplistNode(num, currentLevel);
for (int i = 0; i < currentLevel; i++) {
current->forward[i] = update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i] = current;
}
}
bool erase(int num) {
SkiplistNode *update[maxLevel];
SkiplistNode *x = head;
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->forward[i] != nullptr && x->forward[i]->value < num) {
x = x->forward[i];
}
update[i] = x;
}
// update[0]->forward[0]是最底层的SkiplistNode,如果其都为null或者value不为num
// 那么说明num在跳表中不存在
x = update[0]->forward[0];
if (x == nullptr || x->value != num) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < x->forward.size(); i++) {
update[i]->forward[i] = x->forward[i];
}
delete x;
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (level > 0 && head->forward[i] == nullptr) level--;
}
return true;
}
};
内存池
"现代编译器的 malloc 管理内存的方式本质就是内存池,malloc 从操作系统申请堆内存,然后将内存划分给应用程序,并进行内存的释放,合并等等管理。大多数情况下,可能你自己设计的内存池还不如 malloc 管理的好,毕竟这些库都是很多人测试很多次了。因此,请谨慎判断是否需要内存池以及如何设计内存池。"
template <typename T>
class MemoryPool {
private:
struct MemoryBlock {
MemoryBlock *next;
};
static const size_t EXPANSION_SIZE = 32;
MemoryBlock* freeList = nullptr;
void expandFreeList(size_t size = EXPANSION_SIZE) {
size_t nodeSize = sizeof(T);
MemoryBlock *node = (MemoryBlock *)new char[nodeSize];
// 注意这里需要给node->next进行初始化为nullptr,否则会有野指针问题
node->next = nullptr;
freeList = node;
for (size_t i = 0; i < size - 1; i++) {
node->next = (MemoryBlock *)new char[nodeSize];
node = node->next;
// 避免野指针问题
node->next = nullptr;
}
}
public:
MemoryPool(size_t size = EXPANSION_SIZE) {
expandFreeList(size);
}
~MemoryPool() {
char *ptr = (char *)freeList;
while (ptr != nullptr) {
// 注意这里delete[]是因为我们在创建节点时是new char[]进行创建的
freeList = freeList->next;
delete[] ptr;
ptr = (char *)freeList;
}
}
void *alloc() {
if (freeList == nullptr) expandFreeList();
MemoryBlock *node = freeList;
freeList = freeList->next;
return (void *)node;
}
void free(void *node) {
MemoryBlock *head = (MemoryBlock *)node;
head->next = freeList;
freeList = head;
}
};
class Skiplist {
private:
static constexpr int maxLevel = 32;
static constexpr double p = 0.4;
struct SkiplistNode {
int value;
vector<SkiplistNode*> forward;
SkiplistNode(int value, int level): value(value), forward(level, nullptr) {}
~SkiplistNode() {forward.clear();}
};
SkiplistNode *head;
int level; // 当前Skiplist的层数
MemoryPool<SkiplistNode> mempool;
// 注意需要保证返回时level > 0
int randomLevel() {
int level = 1;
const int threshold = p * RAND_MAX;
while (rand() < threshold && level < maxLevel) level++;
return level;
}
public:
Skiplist(): head(new SkiplistNode(-1, maxLevel)), level(0){}
SkiplistNode *createSkiplistNode(int value, int level) {
void *ptr = mempool.alloc();
return new (ptr) SkiplistNode(value, level);
}
void freeSkiplistNode(SkiplistNode *node) {
// 因为这里的node是不直接delete的,而是回收利用的,所以需要先将原来SkiplistNode中的值删除
node->~SkiplistNode();
mempool.free(node);
}
bool search(int target) {
SkiplistNode *x = head;
// 从Skiplist的最高层开始
// 外循环用于循环层数
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// 内循环用于循环相同层的链表元素
while (x->forward[i] != nullptr && x->forward[i]->value < target) {
x = x->forward[i];
}
}
return x->forward[0] != nullptr && x->forward[0]->value == target;
}
// 运行插入多个值相同的元素
void add(int num) {
SkiplistNode *x = head;
// 因为即将插入一个新的SkiplistNode,需要记录下每层其前一个SkiplistNode是什么
// update向量即是记录各个SkiplistNode
vector<SkiplistNode*> update(maxLevel, nullptr);
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->forward[i] != nullptr && x->forward[i]->value < num) {
x = x->forward[i];
}
update[i] = x;
}
int currentLevel = randomLevel();
if (currentLevel > level) {
for (int i = level; i < currentLevel; i++) update[i] = head;
level = currentLevel;
}
SkiplistNode *current = createSkiplistNode(num, currentLevel);
for (int i = 0; i < currentLevel; i++) {
current->forward[i] = update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i] = current;
}
}
bool erase(int num) {
SkiplistNode *update[maxLevel];
SkiplistNode *x = head;
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (x->forward[i] != nullptr && x->forward[i]->value < num) {
x = x->forward[i];
}
update[i] = x;
}
// update[0]->forward[0]是最底层的SkiplistNode,如果其都为null或者value不为num
// 那么说明num在跳表中不存在
x = update[0]->forward[0];
if (x == nullptr || x->value != num) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < x->forward.size(); i++) {
update[i]->forward[i] = x->forward[i];
}
freeSkiplistNode(x);
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (level > 0 && head->forward[i] == nullptr) level--;
}
return true;
}
};
代码需要注意如下几点:
- 野指针问题:leetcode常见错误:runtime error: member access within misaligned address 0xbebebebebebebebe for type
我们在访问某个变量时,因为这个变量中含有未赋值的指针。定义但是不赋值的指针叫做野指针。野指针指向不明,对程序有不可知的后果,引用了更是出大问题,所以,c语言严格反对野指针。
MemoryBlock
MemoryBlock这个结构体设计的比较巧妙,想象一下普通的链表结构体为:
struct Node{
int value;
Node *next;
}
现在MemoryBlock *ptr能直接指向一片内存空间,同时还可以用next指向下一个MemoryBlock


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号