2023牛客寒假算法基础集训营1
新学到的小知识:
c++实现四舍五入的方法:round()函数:
https://www.nhooo.com/cpp/cpp-library-function-cmath-round.html
如:
《World Final? World Cup! (II)》

这道题我在写的时候开始是想到了用dp,回顾一下我思考dp的过程:
1.首先我习惯性地想如果是用dfs如何写:
ll ans=0;
dfs (int c,int x ,int y , int cnt ){
if (c==n){
if (x>y)cnt+=3
else if (x==y) cnt+=1
if (cnt>=m) ans++;
}
for i in x
for j in y
int f=if (i>j) 3
else if (i==j) 1
else 0
dfs (c+1 , x-i, y- j , cnt+f )
}
大概这样的感觉
2.将dfs的状态转化为dp的形式:
一般dfs是我用来找dp的维数和大致状态转移方法的
由于dfs和dp的状态转移的含义不同,一般不能将dfs和dp的状态转移相抄
这里 dp[n][x][y][cnt]:表示在前n局比赛中,一方(A方)一共进了x个球,另一方(B方)一共进了y个球,总共得了cnt分的方案数
if (i>j) dp[n][x][y][cnt]+=dp[n-1][x-i][y-j][cnt+3];
else if (i==j) dp[n][x][y][cnt]+=dp[n-1][x-i][y-j][cnt+1];
else if (i<j) dp[n][x][y][cnt]=dp[n-1][x-i][y-j][cnt];
完美!
但是 for n in N
for x in X
for y in Y
for cnt in m
for i in x
for j in y
时间复杂度为O(1e11)超时无疑
然后优化我实在不会,放弃。。。ORZ
《现在是,学术时间 (II)》

这道题没啥好说的:分类讨论
一定不能懒,光靠脑子想是想不出来的,一定要自己将每一种情况的面积用数学公式算出来
然后可以用求导,得出最大值的结论:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
void solve()
{
double x, y, xp, yp;
cin >> x >> y >> xp >> yp;
double bin, s;
if (xp <= x && yp <= y)
{
bin = x * y;
double s1 = xp * (y - yp), s2 = (x - xp) * (y - yp), s3 = (x - xp) * yp, s4 = xp * yp;
s = max(max(s1, s2), max(s3, s4));
}
else if (xp < x && yp > y)
{
if (xp >= x - xp)
// 选择源点:
bin = x * y + xp * (yp - y), s = y * xp;
else
bin = x * y + (x - xp) * (yp - y), s = y * (x - xp);
}
else if (xp > x && yp < y)
{
if (yp >= y - yp)
bin = x * y + (xp - x) * yp, s = yp * x;
else
bin = x * y + (y - yp) * (xp - x), s = (y - yp) * x;
}
else
bin = x * y + (xp - x) * (yp - y) + x * (yp - y) + y * (xp - x), s = x * y;
printf("%.9lf\n", s / bin);
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
《鸡算几何》

这道题的核心问题是:
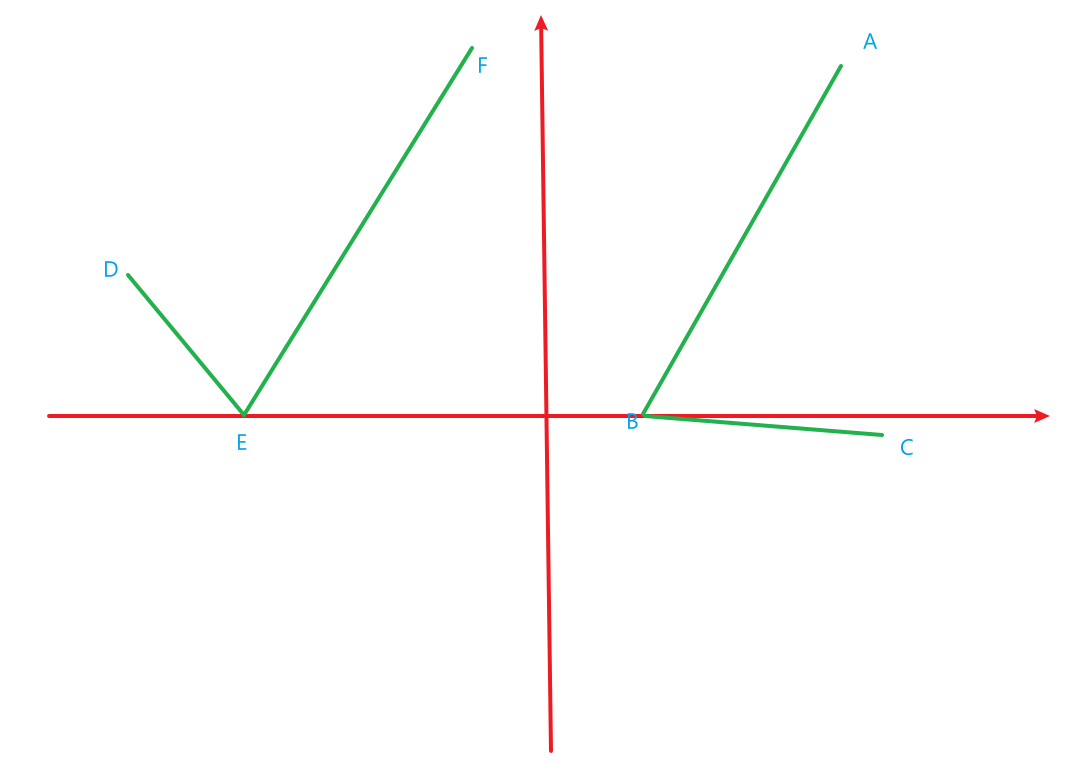
这张图上的ABC到DEF是否能够只通过在平面旋转和平移而得到?
答案是不能的,因为明显顺时针上看: BA到BC的角度 a 与 EF到ED的角度 b 关系为 a= π-b
那么我们在程序上是如何判断的?
通过叉乘:

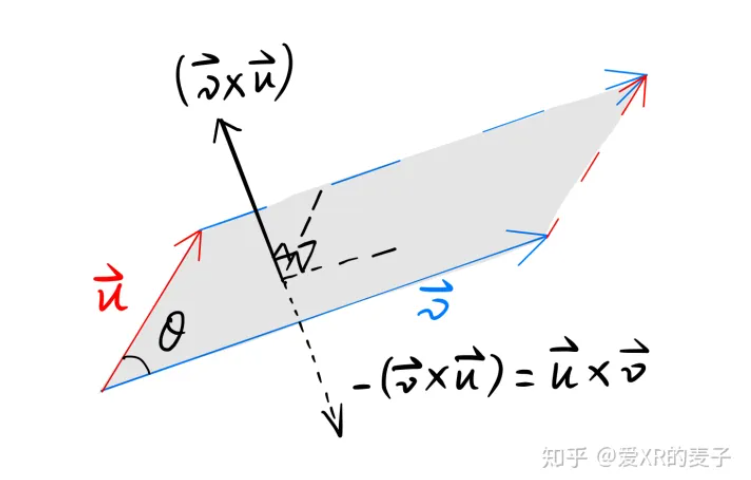
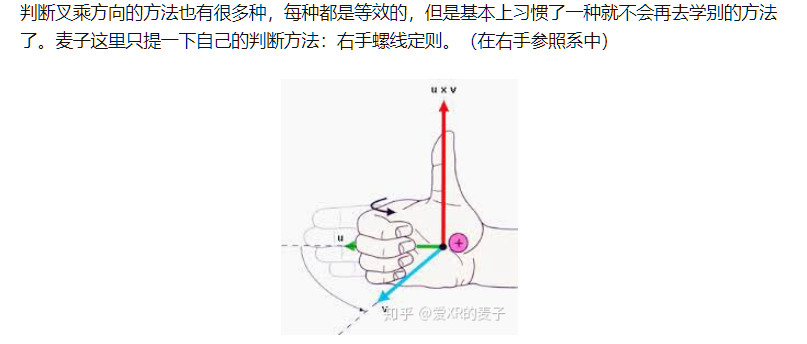

叉乘的角度为【0,180】
有了这些基础知识后:
上面向量BA(ax-bx,ay-by)与向量BC(cx-bx,cy-by)的叉乘为
BA*BC= (ax-bx)*(cy-by)-(ay-by)*(cx-bx);
根据右手法则,其方向,垂直屏幕向里
向量 EF与向量ED同理,但是方向是垂直屏幕向外
两者的值算出来最后是一正一负
可以分辨出来
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const double esp = 1e-5;
double get(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2)
{
return sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
}
double cross(double xz, double yz, double xl, double yl, double xs, double ys)
{
// 长的边的向量:
double ux = xl - xz, uy = yl - yz;
// 短的边的向量:
double vx = xs - xz, vy = ys - yz;
return ux * vy - uy * vx;
}
void solve()
{
double xa, ya, xb, yb, xc, yc, xd, yd, xe, ye, xf, yf;
cin >> xa >> ya >> xb >> yb >> xc >> yc;
cin >> xd >> yd >> xe >> ye >> xf >> yf;
double BA = get(xb, yb, xa, ya), BC = get(xb, yb, xc, yc);
double du1, du2;
if (abs(BA - BC) < esp)
{
cout << "NO" << endl;
return;
}
else if (BA > BC)
du1 = cross(xb, yb, xa, ya, xc, yc);
else
du1 = cross(xb, yb, xc, yc, xa, ya);
double ED = get(xe, ye, xd, yd), EF = get(xe, ye, xf, yf);
if (ED > EF)
du2 = cross(xe, ye, xd, yd, xf, yf);
else if (ED < EF)
du2 = cross(xe, ye, xf, yf, xd, yd);
if (du1 * du2 < 0)
cout << "YES" << endl;
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}
《鸡格线》

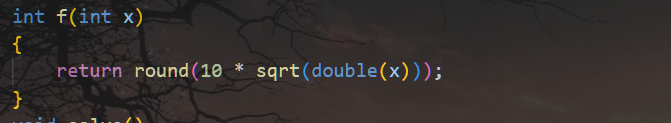
这道题有多种做法,但是不管哪种做法,最终都需要看出这个式子的含义:f(x)=round(10*sqrt(x))
我开始拿到这道题的时候,我很快就发现了:
对于任何一个数,一定是经过一定次数的f(x)操作后,这个数的数值应该不会再变化了,
而且这个次数一定不会很大
但是遗憾的是,我显然第地认为任何数最终都会变成0
但是通过打表我们可以发现
num>=100,最后都会变成100
0<num<100,最后都会变成99
num==0,一直都是0
而且进行的操作不超过20次
解决这个问题的关键就变成了,给定一个区间我们如何快速知道这个区间哪些数要改
从而避免遍历整个区间导致超时
方法一:线段树
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 2;
// 基本思想是:
// 线段树直接将单点修改,最多只要单点修改20*n次,所以不会超时
// 重点还是要看出f(x)=round(10 sqrt(x))这个式子的奥妙
// 这个式子的数,最终只会有3个结果:0,100,99
int f(int x)
{
/* cout << "pre:" << x << endl;
cout << "after:" << round(10 * sqrt(double(x))) << endl; */
return round(10 * sqrt(double(x)));
}
int n, m, a[N];
struct tree
{
int l, r, maxn, minn;
long long sum;
} tr[N * 4];
void pushup(int u)
{
tr[u].maxn = max(tr[u << 1].maxn, tr[u << 1 | 1].maxn);
tr[u].minn = min(tr[u << 1].minn, tr[u << 1 | 1].minn);
tr[u].sum = tr[u << 1].sum + tr[u << 1 | 1].sum;
}
void build(int u, int l, int r)
{
tr[u].l = l, tr[u].r = r;
if (l == r)
{
tr[u].maxn = tr[u].minn = tr[u].sum = a[l];
if (a[l] == 0)
tr[u].maxn = tr[u].minn = 100;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(u << 1, l, mid), build(u << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r);
pushup(u);
}
void modify(int u, int l, int r, int k)
{
if (tr[u].maxn <= 100 && tr[u].minn >= 99)
// 说明这个区间的数只有100和99了,已经不用修改了
// 什么,你问我0呢,0在build中已经被我设置成100了
return;
if (tr[u].l == tr[u].r)
{
int num = tr[u].sum;
/* cout << num << " "; */
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
/* cout << "!!" << num << endl; */
if (num == f(num))
break;
else
num = f(num);
}
tr[u].maxn = tr[u].minn = tr[u].sum = num;
/* cout << tr[u].l << " " << tr[u].r << " " << tr[u].sum << endl; */
return;
}
int mid = (tr[u].l + tr[u].r) >> 1;
/* cout << mid << endl */;
if (l <= mid)
modify(u << 1, l, r, k);
if (r > mid)
modify(u << 1 | 1, l, r, k);
pushup(u);
}
int main()
{
// 这是线段树的做法:
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
build(1, 1, n);
while (m--)
{
int op;
cin >> op;
if (op == 2)
cout << tr[1].sum << endl;
else
{
int l, r, k;
cin >> l >> r >> k;
modify(1, l, r, k);
}
}
return 0;
}
方法二:
通过map,将数值还不是0,99,100的数保存下来
map的key是其下标,为了匹配区间有用
map的value是数值
map中有内置lower_bound(i)方法,可以二分找到最小的key值>=i的迭代器指针
找不到则返回 map.end()

map中还有 map.erase(idx),通过迭代器指针删除的方法
每次我们暴力更改区间内数值还不是100,99,0的数值
如果他们是了,则从map中删除
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e5 + 2;
int a[N];
map<int, int> mapp;
int f(int x)
{
return round(10 * sqrt(double(x)));
}
void solve()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int num;
scanf("%d", &num);
if (num != f(num))
mapp[i] = num;
ans += num;
}
while (m--)
{
int op;
scanf("%d", &op);
if (op == 1)
{
int l, r, k;
cin >> l >> r >> k;
int p = l;
while (true)
{
auto idx = mapp.lower_bound(p);
if (idx == mapp.end() || idx->first > r)
break;
int num = idx->second;
bool flag = false;
ans -= num;
/* cout << "Pre: " << num << endl; */
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
if (num == f(num))
{
flag = true;
break;
}
else
num = f(num);
}
/* cout << "After: " << num << endl; */
ans += num;
mapp[idx->first] = num;
if (flag)
mapp.erase(idx);
p = (idx->first);
p++;
}
}
else
cout << ans << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
/* double ans = 1e5;
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++)
{
ans = 10 * sqrt(ans);
if (ans - int(ans) > 0.5)
ans = int(ans) + 1;
else
ans = int(ans);
cout << ans << endl;
} */
// 这道题的重难点为:如何快速找到区间[l,r]中要修改的地方,
// 而避免了整个区间[l,r]扫一遍的超时风险
// 方法1:用map和其中内置二分查找的low_bound()函数
// 我觉得题解上这里用set有问题吧,这里并没说数组a没元素相同
solve();
return 0;
}
《本题也主要考察了DFS》
这道题的关键是能够看出:在n*n的方阵中,最多有1个牛牛点
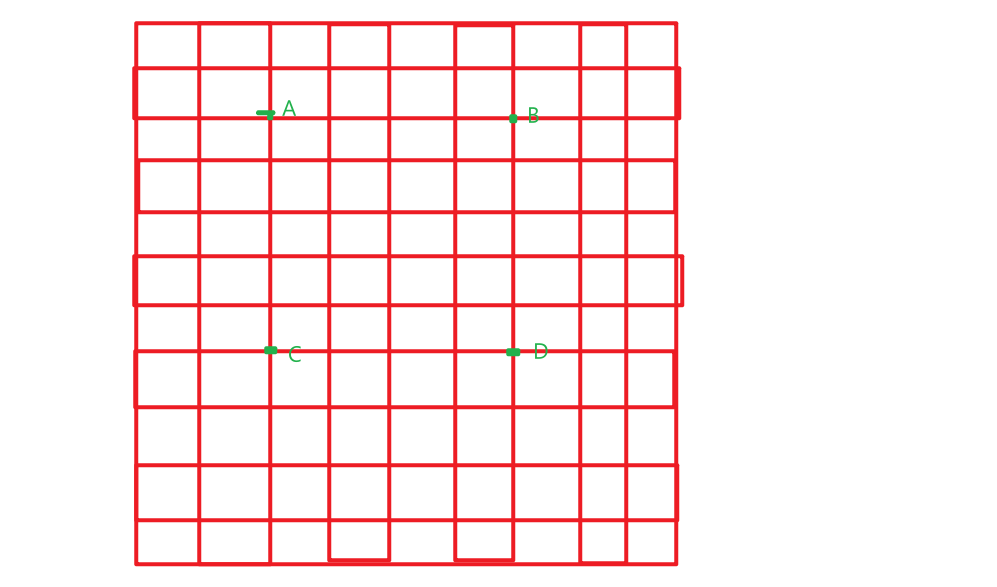
如图:假设点B与点C是牛牛点
则可以有 C->D(表示点C的数>点D的数)
C->D->B->A->C
最后是C->C,矛盾
我们也发现这道题有明显的拓扑序关系:
如图假设A是牛牛点:
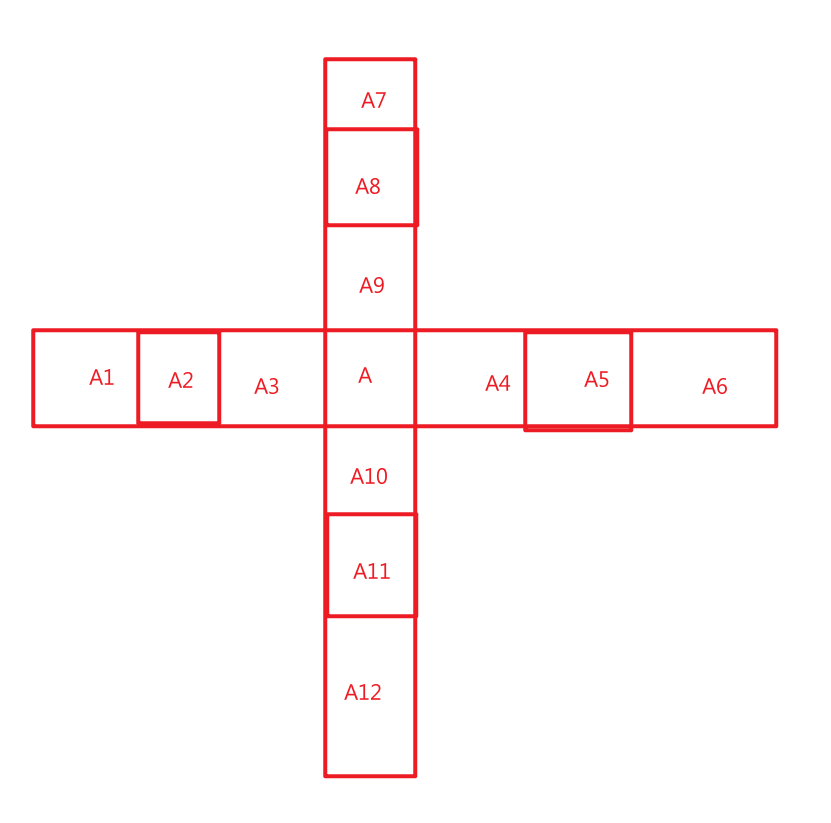
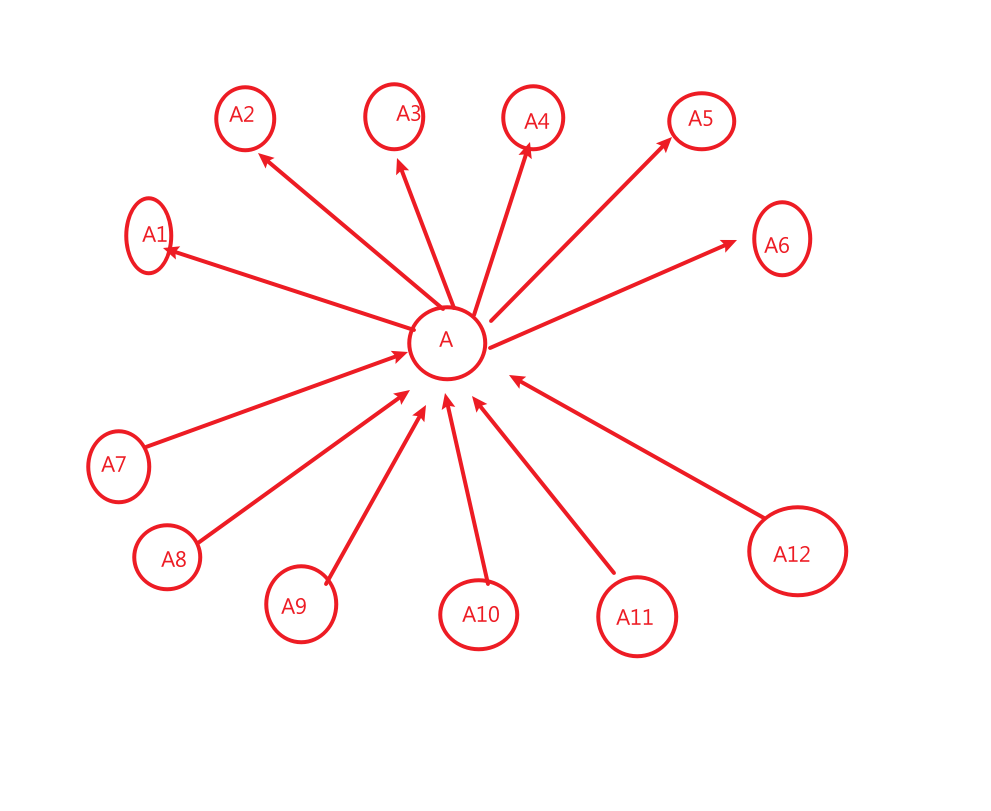
我们用A7->A:表示A7上的数要>A
可以用拓扑排序的方法写出(但是我写了3个小时,debug1小时,最后还是错了)放弃
《本题主要考察了运气》

概率期望问题:
首先我们先猜团体:
一次猜中的概率p1=1/5
两次猜中的概率p2=4/5*1/4=1/5 (首先是第一次没猜中4/5,再4个中猜中1/4)
后面同理p3=1/5
第四次一定猜中,因为如果第四次错了,其为第5个团体,否则猜中
p4=4/5*3/4*2/3=2/5
猜团体的期望次数为E=p1*1+p2*2+p3*3+p4*4
然后猜个人:
同理
最后算出来的期望为5.05,再通过下面的公式算一下,得到32



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号